Can Botox be used to treat abductor spasmodic dysphonia ABSD?
Jul 19, 2004 · Botulinum toxin is administered either unilaterally (injected into the left or right vocal fold muscle) or bilaterally (injected into the vocal fold muscles on both sides), with smaller dosage levels reported for effective bilateral injections ( Adams 1995; Bielamowicz 2000; …
What is the treatment for adductor spasmodic dysphonia?
The main muscle that causes AB SD is the PCA (Posterior Cricoarytenoid Muscle), purple in this photo. It is located on the back of the voice box. It is the muscle that opens the vocal folds widely for breathing. It is at its most active during sniffing. It should be basically at rest during speaking.
Can Botox be injected into the posterior cricoarytenoid PCA muscle?
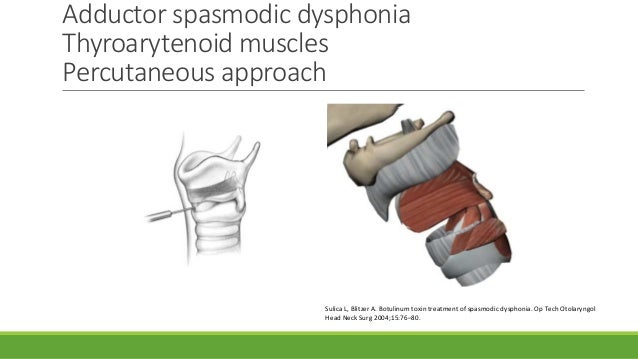
For the more common adductor spasmodic dysphonia, the injection is done into the thyroarytenoid muscle. One should not eat or drink anything for 45 -60 minutes after the …
Can botulinum toxin treat spasmodic dysphonia?
3 rows · Injection for Ab-SD. The muscle to be injected is localized by LEMG. The needle is then passed ...

Who does Botox injections for spasmodic dysphonia?
Which muscles are injected with Botox?
- Forehead Lines: Frontalis Muscle. ...
- Glabella/Frown Lines: Corrugator Supercilii and Procerus muscles. ...
- Crow's Feet (Lateral Orbital Lines): Orbicularis Oculi and Procerus Muscles. ...
- Bunny Lines (Transverse nasal): Injections of 5 to 25u will usually be adequate.
Where is Botox injected for cervical dystonia?
How is abductor spasmodic dysphonia treated?
- Speech and Voice Therapy. By working with a clinician experienced in the behaviors needed to produce healthy voice, the person with SD may learn how to adapt to the spasms with less interruption in their speech. ...
- Oral Medications. ...
- Botulinum Toxin Type A Injections (Botox®) ...
- Surgery.
What happens when Botox is injected into muscle?
Does Botox get injected into muscle?
What muscles are involved in cervical dystonia?
What type of muscle does dystonia affect?
What are the side effects of Botox injections in the neck?
How does Botox help spasmodic dysphonia?
What is the difference between muscle tension dysphonia and spasmodic dysphonia?
What kind of doctor treats spasmodic dysphonia?
What is spasmodic dysphonia?
Spasmodic dysphonia is a voice disorder that causes involuntary contraction of the laryngeal muscles during phonation. It is a neurological condition of unknown cause [1]. The pathophysiology is due to irregular release of acetyl choline at the neuromuscular junction in the intrinsic muscles of the larynx. This is usually regulated centrally ...
Is spasmodic dysphonia a neurological disorder?
Spasmodic dysphonia is a rare neurological voice disorder, which is often missed by the inexperienced ear. There is no laboratory test or investigation to diagnose this condition therefore, it is best diagnosed by listening to the patient’s voice. Laryngeal endoscopy is necessary to support the diagnosis and to exclude other laryngeal disorders.
What is botulinum toxin A?
There are several serotypes of botulinum toxin. Type A is the one commonly used in spasmodic dysphonia and other forms of dystonia. There are potential complications of injecting botulinum toxin A especially if the wrong muscles are injected or from overdose of injection. The most common side-effect after botulinum toxin injection in ...
What are the side effects of botulinum toxin A?
The most common side-effect after botulinum toxin injection in the larynx is a breathy and weak voice and rarely dysphagia. This effect is temporary and is somewhat expected.
Why does my voice sound strained?
The voice will sound strained and strangled if the adductor muscles are affected, whereas the voice will be weak and breathy if the abductors are affected. Rarely, there may be mixed type. The most common type is the adductor spasmodic dysphonia constituting 90% of cases.
How is Botox injected?
The Botox is injected through a very small needle which is connected by a wire to an electromyography (EMG) machine that records the activity of the muscle. The placement of the needle into the muscle is verified by the electrical signals shown on the EMG machine.
Does Botox help with dystonia?
Therefore it is important to remember that Botox does not treat the cause of dystonia, but only provides temporary symptomatic relief.
What is spasmodic dysphonia?
Spasmodic dysphonia (SD) is a type of neurologic disorder called a dystonia. It affects the muscles of the larynx. This page describes SD and its treatment using a medication called botulinum toxin (Botox).
What is the cause of SD?
The cause of SD is believed to originate in a part of the brain called the basal ganglia. The are several different types of SD.
What causes a strained voice?
In the most common variant the muscles that close ("adduct") the folds contract too tightly. This condition, called adductor spasmodic dysphonia, produces a strained or strangled sound to the voice.
How long does it take to get Botox injections?
There generally is minimal discomfort associated with the injection. The entire procedure takes about fifteen minutes. This image shows a side view of the manner in which the botox is injected.
How long does Botox last?
In most cases, the effect of Botox lasts 2-4 months. It is important to remember that, although Botox is derived from the botulinum organism, the organism itself is never injected. The material that is injected is the muscle relaxant produced by the botulinum bacteria.
Where is botulinum toxin injected?
Injections Through the Skin. Botulinum toxin is usually injected through the skin of the neck into the appropriate spots with the aid of electromyography (EMG). The procedure is performed in a physician’s office. Afterwards, the patient may usually go on with the normal activities of the day.
How many types of botulinum toxin are there?
Different Types of Botulinum Toxin. Of the eight types of botulinum toxin that exist, two are available for use in humans – botulinum toxin, type A and botulinum toxin, type B. Botulinum toxin, type A: Has been used to improve voice symptoms of patients with SD in the United States since 1984.
How long does botulinum toxin last?
Acetylcholine is a substance that triggers muscle contraction. Effects Are Temporary. The effects of botulinum toxin are temporary, lasting about three months, and dose-dependent, so that the muscle weakness is proportional to the amount of toxin used.
Does Botox help with spasmodic dysphonia?
According to the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA), there is no current cure for spasmodic dysphonia. ASHA does say that injections of Botox, is recommended and performed by doctors. The shot of Botox is injected into one or both vocal cords in small doses. This makes the laryngeal muscles weaker, this smoothing of the adduction and abduction of the vocal folds and leading to a less effortful voice. The job of the SLP comes after the Botox treatment when temporary difficulty with swallowing or breathiness is experienced by some. The SLP’s job is to help the client use their voice in the healthiest way.#N#In addition, the SLP should refer the client to a competent psychiatrist or psychologist since the client will need to learn to accept the disorder and learn to cope with its limitations. This is especially important if voice plays a big role in the client’s life (like if the client is a teacher.)
Where is the needle in Adductor SD?
In adductor SD, the needle is passed through the skin that lies over the superior edge of the cricoid, just lateral to midline. The needle is then advanced through the CT ememberan and superiorly and and laterally directed into the right or left vocal fold to reach the TA muscle as seen in the image on the left.

Diagnosis
Treatment
- The standard first line treatment is botulinum toxin A injection . There are different manufacturers of the botulinum toxin A but the chemical nature is the same. The commonly used ones are Botox, dysport and Xeomin.
Essential Materials
- Botulinum toxin A injection Botox or Xeomin 100 iu bottle (see Figure 1)
- Electromyography (see Figure 2)
- Teflon coated disposable hypodermic needle electrode 37 x 40mm (27G)
- ChloroPrep (Chlorhexidine skin prep)
Procedure
- Technique of Botox injection in adductor spasmodic dysphonia- ADSD One hundred units of Botox diluted with 4cc of normal saline and 0.06cc is drawn in a 1mm syringe. This is equivalent to 1.5 units of Botox. This is usually the recommended starting dose. Some patients may require a higher or lower dose at a subsequent visit or may even need only a unilateral injection. Xeomin d…
Discussion
- There are several serotypes of botulinum toxin. Type A is the one commonly used in spasmodic dysphonia and other forms of dystonia. There are potential complications of injecting botulinum toxin A especially if the wrong muscles are injected or from overdose of injection. The most common side-effect after botulinum toxin injection in the larynx is ...
Conclusion
- Botulinum toxin injection remains the first treatment option in spasmodic dysphonia and is best performed under EMG guide via percutaneous approach. This eliminates the need for a general anaesthesia as in the suspension microlaryngoscopic approach. The percutaneous injection may also be performed with video flexible nasal endoscopic guide. The main disadvantage of botulin…