Common Microorganisms Used in Wastewater Treatment
- Aerobic Bacteria. Aerobic bacteria are mostly used in new treatment plants in what is known as an aerated environment.
- Anaerobic Bacteria. Anaerobic bacteria are used in wastewater treatment on a normal basis. The main role of these...
- Facultative. Facultative microorganisms in sewage treatment are bacteria that can...
What is microbes sewage treatment?
The treatment of wastewater is done by the heterotrophic microbes, naturally present in the sewage. Thus, Microbes Sewage treatment, also known as wastewater treatment, is the removal of impurities from sewage before it enters natural water bodies. What is Microbes Treatment Method? Residential and industrial establishments generate sewage.
What type of bacteria are used in secondary sewage treatment?
Most secondary treatment systems use aerobic bacteria that consume the organic components of the sewage, like sugar, fat, etc. Anaerobic bacterias in sewage treatment also reduce sludge volume and create methane gas from it which is used as an alternative energy source. Q.4. Explain the types of microbes used in sewage treatment?
How many microorganisms are present in sewage?
Per ml, about 100,000 to 1,000,000 microorganisms are present in typical domestic wastewater before entering the processing plant. Mostly these microbes perform the wastewater process, but some other microorganisms are also used according to the organic materials present. But how could we know what was present in the sewage?
Are there any alternative microbes used in waste material treatment?
While there are many alternative microbes utilized in waste material treatment, 3of them are well-known microbes that play an important role to keep water and sewage clean. Every one of those kinds of bacteria facilitates the treatment method during cleaning.
Which microbes are present in sewage naturally?
The two categories of naturally occurring microbes present in sewage are bacteria and fungi. The bacteria along with the fungal filaments form flocs which are utilized during the secondary treatment of sewage. The primary effluent after separation of the grit and debris is taken to the secondary treatment.
How are microbes useful in sewage treatment?
Microorganisms are the workhorses of wastewater treatment systems and anaerobic digesters, where they are responsible for removal of pollutants and pathogens, recovery of nutrients and energy, and producing clean water.
What types of microorganisms participate in wastewater treatment?
Microorganisms that are natural to the wastewater environment play a vital role in the wastewater treatment process. Beneficial bacteria, protozoa, metazoa, algae, and fungi feed on organic material in wastewater, breaking it down.
How microbes are used in sewage treatment class 12?
Aerobic microorganisms are inoculated into the sewage treatment plant. These microbes utilize the organic components of the sewage and reduce the toxicity. This can be measured by BOD (Biological oxygen demand). After the biological treatment, the sludge is pumped from the treatment plant into a large tank.
Which of these microbes are commonly used in sewage treatment bacteria virus fungi or algae?
So, the correct answer is 'Aerobic bacteria and fungus'
Which anaerobic bacteria is used in sewage treatment?
They are responsible for methane fermentation of sewage sludge, facilitating decomposition of macromolecular organic matter into simpler compounds. Among the bacterial genera involved in the anaerobic methane fermentation process are Methanosarcina, Methanosaeta (Van Lier et al.
What is sewage microbiology?
Sewage is the used and wastewater consisting of human excreta, wash waters, and industrial and agricultural wastes (e.g. wastes from live stock i.e. chicken, cattle, horse, etc.) that enter the sewage system. In general sewage contains about 95.5% water and 0.1 to 0.5% organic and inorganic materials.
What is sewage treatment class 7?
Sewage Treatment: The process of removing impurities from waste water before it can be reused or sent to the water bodies is called sewage treatment or cleaning of water. Sewage: The liquid waste which has water as its largest component (along with various types of impurities) is called sewage.
What is sewage treatment class 8?
Answer: Sewage treatment involves three processes, namely physical, chemical and biological. They remove physical, chemical and biological contaminants present in the wastewater.
Why are bacteria used in sewage treatment plants Class 7?
The bacteria decompose the suspended waste that include domestic wastes and other undesirable organic substances present in the clarified water. The activity of bacteria produces decomposed organic material from which solid waste is separated. This solid waste s used as manure.
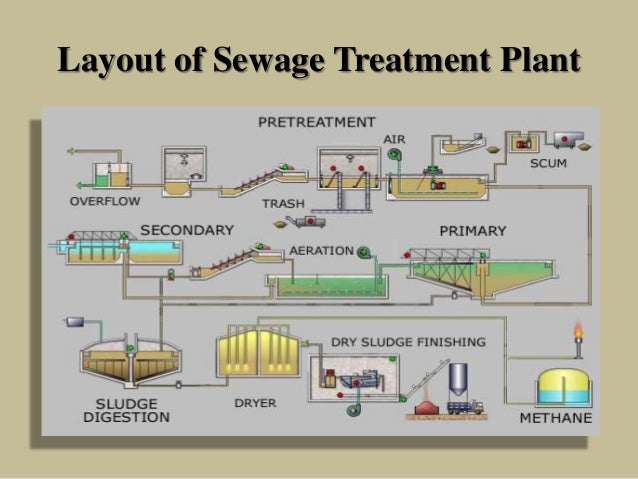
What is a sewage treatment plant and how does it work?
A semi-solid waste or slurry byproduct of sewage treatment is called sewage sludge. Different processes like physical, chemical and biological meth...
What are the main steps in sewage treatment?
a. Primary treatment or Physical process b. Secondary treatment or Biological process
What is the major function of Microbes in Sewage Treatment?
Sewage is treated in sewage treatment plants (STPs) by the heterotrophic microbes present in the sewage before being disposed of in water bodies. M...
Explain types of microbes used in sewage treatment?
Aerobic Bacteria: These bacteria degrade the contaminants in the wastewater using free oxygen in the water, then turn into the energy that can be u...
Why is sewage treatment important?
Sewage treatment helps in reducing the rate of harmful contaminants that cause pollution of water and soil. Wastewater that is treated in these STP...
Why are microbes important in sewage treatment?
In today’s world, microbes became essential for any kind of industrial process, and thus, various techniques are discovered where microorganisms are utilized for solving multiple problems. In that way, the role of microbes in sewage treatment is critical.
What is the most exciting part of sewage treatment?
However, the most exciting part of sewage treatment is that those microbes we need to eradicate ...
What is the objective of wastewater treatment?
Thus, we can say the principal objective of wastewater treatment is to decrease biological oxygen demand (BOD), Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) and also eutrophication, and much more , so that it won’t spread toxicity in the environment . Moreover, microbes have an essential role in fulfilling the purpose of sewage treatment.
How many steps are there in sewage treatment?
And the large-scale treatment involves lots of other physical, chemical, and biological processes. Besides these two parts, the entire sewage treatment process comprises four significant steps and various sub-steps. These four steps are: Also Check: Ways to prevent ocean acidification.
What is the purpose of sewage treatment?
Purpose of Sewage Treatment 1 To remove pollutants 2 Destruction of the deadly pathogens 3 To counterbalance coarse particles. 4 Elimination of poisonous substances
What is the product of sewage after sedimentation?
The sewage water after sedimentation or settling is now called effluent, and the settled down product is known as sludge.
How could we know what was present in the sewage?
But how could we know what was present in the sewage? For that reason, the analysis of wastewater is first performed to identify the types of components present with their quantity. Then required microbes are added from the outside. Generally, three types of microbes, bacteria, fungi, and protozoa, are utilized for different functions.
Why are aerobic bacteria used in sewage treatment?
The main role of these bacteria in sewage treatment is to reduce the volume of sludge and produce methane gas from it. The great thing about this type of bacteria and why it’s used more frequently than aerobic bacteria is that the methane gas, if cleaned and handled properly, can be used as an alternative energy source.
Why are microorganisms important in wastewater treatment?
That’s because waste from humans and pets are a source of several types of waterborne diseases and bacterial contamination. Thanks in part to microorganisms, treating wastewater and sewage is possible.
What is aerobic bacteria?
Aerobic Bacteria. Aerobic bacteria are mostly used in new treatment plants in what is known as an aerated environment. This bacterium uses the free oxygen within the water to degrade the pollutants in the wastewater and then converts it into energy that it can use to grow and reproduce.
What are the roles of microorganisms in wastewater treatment?
The role of microorganisms in wastewater treatment helps to treat and purify wastewater and make it less harmful to the environment. While there are many different microbes used in sewage treatment, there are three well-known microbes that play an instrumental role in keeping sewage clean. Each of these types of bacteria help ...
What is the purpose of wastewater treatment?
Many industrial and municipal wastewater treatment plants use bacteria and other microorganisms to help with the process of cleaning sewage. Picking the right bacteria can be tricky since your selection depends on the condition of your area for effective use. Wastewater treatment can also provide a great source for alternative energy if the anaerobic bacteria are handled correctly.
Do aerobic bacteria need oxygen?
Unlike aerobic bacteria, this type of bacteria is able to get more than enough oxygen from its food source and will not require adding oxygen to help do its job. Phosphorus removal from wastewater is another benefit of anaerobic microbes used in sewage treatment.
Is wastewater treatment an alternative source of energy?
Wastewater treatment can also provide a great source for alternative energy if the anaerobic bacteria are handled correctly. Learning the names of microbes used in sewage treatment and the role bacteria in sewage treatment plays doesn’t have to be a solo job.
Why are bacteria used in sewage treatment plants?
It’s for this reason that anaerobic bacteria are the most used microorganisms in sewage treatment plants, as the methane gas can then be collected and used as a valuable and alternative energy source across a host of industries. But most importantly, this biogas (as it’s most commonly known) can be recycled back within the plant to fuel the continuing wastewater treatment process.
Why are microorganisms important in wastewater treatment?
Although you may not know it, microorganisms in sewage treatment plants play a hugely important role in how our wastewater gets recycled. Every day, the vast majority of us run water down our drains, take showers and flush our loos all without wondering where all this water goes and what happens to it.
Why is pH important in sewage treatment?
PH levels are just as critical as microorganisms in sewage treatment plants. Wastewater itself often contains high levels of both heavy and toxic metals that are dissolved within the water. Treatment processes can artificially adjust the pH level to induce these metals to bond chemically, becoming more insoluble and easier to remove.
Why are facultative bacteria important?
This makes them highly important in improving the efficacy of sewage treatment plants.
How do microorganisms help the environment?
Instead of introducing toxic chemicals that can negatively hurt our environment, naturally occurring microorganisms are actually used to help break down organic material in our sewage systems, thereby reducing odour levels, sludge, and grease in treatment plants, lagoons, and ponds.
What temperature should sewage be treated?
Bacteria in general prefer aquatic environments with warmer temperatures in which to thrive and grow. Between 12°C to 38°C are considered most optimal.
What are the elements in wastewater?
Microorganisms in sewage treatment plants are a complex petri dish of elements, such as protozoa, rotifers, and fungi. But 95% of what can be found in wastewater are naturally forming bacteria.
Why is sewage treatment important?
Wastewater treatment is as essential to human health as it is to environmental protection. Indeed, the use of these bacteria accelerates the treatment of pollution on a small surface: the purification plant. It’s better than letting the river handle it, because even though it’s the same purification process that occurs in nature, the quantities of pollution discharged today are too high to keep the natural cycle intact. Thus, sewage treatment plants can prevent eutrophication of rivers, for example, but also prevent the diffusion of diseases.
What is biological wastewater treatment?
Biological wastewater treatment is the most common sanitation method in the world. This technology uses different types of bacteria and other microorganisms for the treatment and purification of polluted water. Wastewater treatment is as essential to human health as it is to the protection of the environment.
How long does it take for bacteria to colonize a medium?
The colonization of a medium by the necessary bacteria and microorganisms required for depollution generally takes between 4 and 8 weeks. Once again, it is the temperature that has the greatest impact on this growth time.
How much COD can bacteria degrade?
Some bacteria are so specialized in fat degradation that they are able to degrade high loads, up to 300,000 mg/L of COD.
How is the use of bacteria different from current treatment techniques?
The use of bacteria is different from current treatment techniques because it uses simple and natural means whose final result allows the elimination of pollution without generating new pollution. Most of the time, their installation requires the use of a dedicated bioreactor, as well as the nutrients necessary for their multiplication in large numbers. Dosing is easy and requires little operating time.
How to restore water to a healthy environment?
First, by changing the operating settings, and waiting for the right species to colonize the environment again. Second, by completely removing the microorganisms in place when the first solution did not work. Be careful, this method is not recommended because the biomass will take several days to develop, so the water will not be properly treated during this period. The third solution consists in injecting specially selected, cultured and multiplied bacteria in order to recover the advantage over the undesirable bacteria present in the environment.
What is the name of the mass of bacteria that agglutinates?
Usually, these organisms swarm and agglutinate into a flake-like mass in free cultures, called the floc. These flocs, visible to the naked eye, contain living and dead cells of bacteria, fungi, protozoa and metabolic products. They agglomerate around the suspended organic matter on which they feed. This is the case for example with activated sludge. In addition, in fixed cultures, similar biofilms develop on contact surfaces. For example, biofilters and biological disks are fixed cultures.
What is Midas project?
The MiDAS project is a collaborative scheme that has taken place since 2006 between more than 50 wastewater treatment plants, consultants and the Center for Microbial Communities, Aalborg University. It includes regular DNA and FISH analyses of the microbial community composition, in-depth studies of focus topics, and workshops and reports for plant operators. It also includes development and maintenance of the MiDAS field guide, and various MiDAS-curated taxonomies to promote a common language between researchers in the field. The newest is MiDAS 3.6, which is a comprehensive 16S RNA gene reference database based on high-quality sequences derived from activated sludge and anaerobic digester systems, and an improved taxonomy.
What is the work of Denmark?
Work in Denmark has laid the foundations for identifying all the microbes in wastewater treatment systems and anaerobic digesters around the world with the aid of genetic fingerprinting. By Per Halkjær Nielsen.
Why are some microbes only present in wastewater treatment plants?
Many species are only present because they are added with the feed, such as primary sludge or surplus activated sludge, and are thus not active.
What is Midas 3 database?
The MiDAS 3 database was the framework for an update of the MiDAS field guide – an online resource linking the identity of microorganisms in wastewater treatment systems to the available data on their functional importance. The new guide contains a complete list of genera (>1800) and species (>4000) found in activated sludge and anaerobic digesters. The identity of the microbes is linked to information on their function, where available. The website also enables classification of sequences using MiDAS 3 taxonomy directly online. Complex microbial communities define the function of biological wastewater treatment systems and understanding the role of individual microbes requires knowledge of their identity, to which known and putative functions can be assigned.
Why is surveillance important in wastewater treatment?
Surveillance of microbial communities can be used as a standard way to control and optimise wastewater treatment processes – it will be possible, if the identity and function of the most microorganisms is known, to determine whether the correct processes are in place, whereas today this is hard to resolve.
What are the workhorses of wastewater treatment systems?
Microorganisms are the workhorses of wastewater treatment systems and anaerobic digesters, where they are responsible for removal of pollutants and pathogens, recovery of nutrients and energy, and producing clean water. Numerous different microbes exist in these systems; however, just how many is unknown, with information about their identity ...
How many wastewater treatment plants are part of MiDAS?
With all the work described here, we are gaining a lot of experience. More than 50 wastewater treatment plants have been part of the MiDAS project since 2006. From this, we have collected extensive and comprehensive datasets providing community composition information for different full-scale plants, primarily with nutrient removal, including variations over the years. Most bacterial species are present in all plants but in varying abundances. We do not always understand why, but the new reference database and online identification will speed up deciphering factors driving the communities.
What do microbes use in rivers?
If this is not done, then microbes naturally present in the river use the organic compounds as a source of energy and reproduce in huge numbers. Since they respire aerobically, they use up much of the oxygen dissolved in the water, leaving little for other organisms such as invertebrates or fish, many of which will die.
Why is sewage treated?
Sewage must therefore be treated to reduce the amount of organic matter, and thus reduce the Biological Oxygen Demand or BOD, defined as the amount of oxygen required by the aerobic microbes to decompose the organic compounds in a sample of water. The process of sewage treatment can be thought of as a complex form of composting.
What is the difference between sewage treatment and compost?
Apart from the raw material, the other big difference between a sewage treatment works and a compost heap is that inside a compost heap, temperatures become high – well above 60 °C – which is detrimental to most species of microbes, but in which some can flourish.
Why is it important to grow anaerobic microbes?
Growing anaerobic microbes on a large scale is essential for the industrial processes of brewing beer, making wine and carrying out other types of fermentation and for producing large quantities of microbes, for example yeast for bakeries.
Why is photosynthesis not used in sewage treatment?
Photosynthesis is generally not used in the sewage works because it is a process that builds organic compounds from carbon dioxide, whereas the objective of sewage works is to break down organic compounds.
How are anaerobic microbes stored?
When anaerobic microbes are cultured on Petri dishes, the dishes are also stored in airtight containers that are constantly flushed with nitrogen or carbon dioxide to keep them anaerobic. Many anaerobic organisms also need some unusual elements to grow, and these are added to the culture media.
What is the material that is formed in a tank?
During this process, a fairly solid material known as activated sludge is formed. This contains a mix of microbes and undigested material.
