- Olanzapine-fluoxetine. Olanzapine-fluoxetine combination (OFC) was approved for the treatment of bipolar I depression in 2003.
- Quetiapine. Quetiapine was approved as monotherapy for the treatment of bipolar depressive episodes by the FDA in October 2006.
- Lurasidone. Lurasidone was approved for the treatment of adults with bipolar I depression as a monotherapy or an adjunct to lithium or divalproex.
- Lamotrigine. The anticonvulsant lamotrigine was approved for maintenance treatment of bipolar I disorder. ...
- Ketamine. Glutamate receptor dysfunction is implicated in the pathophysiological course of bipolar depression.
- Modafinil Armodafinil. Modafinil is not an FDA-approved treatment for bipolar depression; however, it is approved for the treatment of excessive sleepiness, which is often a characteristic of bipolar depression.
What is the most recent treatment for bipolar depression?
Lurasidone is the most recently approved agent for bipolar depression. Olanzapine-fluoxetine combination and quetiapine are approved as single modality therapies while lurasidone is approved as a monotherapy and as an adjunct to lithium or divalproex.
How many FDA-approved medications for bipolar disorder have been approved?
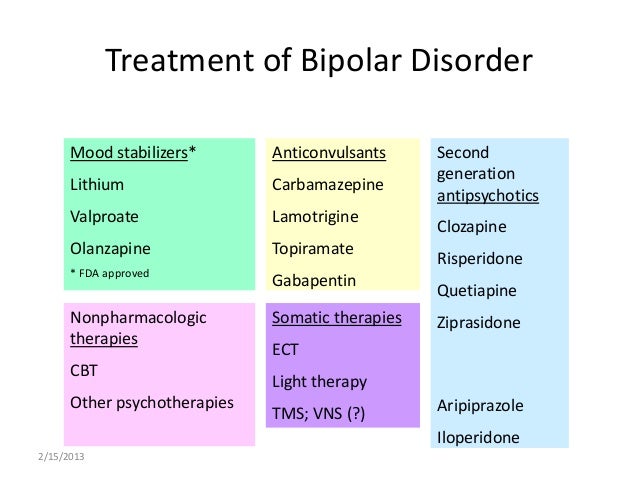
This discrepancy is also seen in the FDA-approved medications for acute treatment in bipolar disorder, 10 of which are approved for mania, and three for depressive episodes. Table: FDA-Approved Medications for Bipolar Disorder
What are the pharmacotherapeutic approaches for acute bipolar depression?
The following group of pharmacotherapeutic approaches applies to patients presenting with acute bipolar depression – signifying that they have a high/urgent risk of suicide and/or homicidal ideation. Emerging data points to the recommendation of electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) to manage urgent, acute bipolar depressive episodes.
What are the FDA’s indications for bipolar disorder?
Pharmacologically, the FDA has split its indications for bipolar disorder into three categories: acute manic episodes, acute depressive episodes, and maintenance treatment.

What drugs are FDA-approved for bipolar depression?
Three drugs are FDA-approved for the treatment of bipolar depression: quetiapine (Seroquel) by itself, olanzapine (Zyprexa) when used with fluoxetine (Prozac) (which also comes as a combination pill called Symbyax), and lurasidone (Latuda) used alone or with lithium or valproate (Depakote).
Which mood stabilizers are FDA-approved for bipolar maintenance?
Aripiprazole (Abilify), lamotrigine (Lamictal), lithium, olanzapine (Zyprexa), olanzapine + sandorphan (Lybalvi), risperidon consta (Consta), and quetiapine (Seroquel) or ziprasidone (Geodon), are medications that have been approved by the FDA specifically for maintenance therapy for bipolar disorder.
Is Lamictal FDA-approved for bipolar depression?
1.2 Bipolar Disorder LAMICTAL is indicated for the maintenance treatment of Bipolar I Disorder to delay the time to occurrence of mood episodes (depression, mania, hypomania, mixed episodes) in adults (≥18 years of age) treated for acute mood episodes with standard therapy.
What is the best medicine for bipolar depression?
Lithium and quetiapine top the lists for all three phases of the illness: mania, depression, and the maintenance phase. Lurasidone and lamotrigine are either untested (lurasidone) or ineffective (lamotrigine) in mania, but they are essential tools for bipolar depression.
Is Wellbutrin good for bipolar depression?
Wellbutrin may work to reduce depressive symptoms by inhibiting the reuptake of the neurotransmitters serotonin, dopamine and norepinephrine, and prolonging their action, which prevents depression.
Is Topamax FDA-approved for bipolar disorder?
Some people use Topamax to treat other conditions, like anxiety, depression, bipolar disorder, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), but Topamax is not approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for these purposes.
Is Latuda FDA-approved for mania?
It's FDA-approved to treat the following mental health conditions: Major depressive episodes related to bipolar I disorder. Bipolar I disorder is a type of mood disorder that involves phases of mania and depression. Latuda treats major depressive episodes.
What is the newest drug for bipolar disorder?
Caplyta is now FDA-approved for depressive episodes from bipolar I and II. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Caplyta (lumateperone) for the treatment of bipolar depression in adults.
Is Depakote FDA-approved?
Approval Date: 12/20/2002.
What is the most common drug used for bipolar patients?
Lithium. In the UK, lithium is the main medicine used to treat bipolar disorder. Lithium is a long-term treatment for episodes of mania and depression. It's usually prescribed for at least 6 months.
What is the most common treatment for bipolar disorder?
Typically, treatment entails a combination of at least one mood-stabilizing drug and/or atypical antipsychotic, plus psychotherapy. The most widely used drugs for the treatment of bipolar disorder include lithium carbonate and valproic acid (also known as Depakote or generically as divalproex).
What is the best mood stabilizer for bipolar ll?
A review of 32 trials shows that lithium is the only mood stabilizer that has lowered the suicide rate in patients with bipolar disorder. Lithium has also been shown to mitigate relapse of bipolar disorder from 61% to 40%, and it prevents more manic episodes when compared with depressive episodes.
Is bipolar depression FDA approved?
Relatively few agents are FDA -approved for bipolar depression. The selection and sequencing of agents in bipolar depression should give primacy to those agents that are FDA-approved.
Is lurasidone a monotherapy?
Olanzapine-fluoxetine combination and quetiapine are approved as single modality therapies while lurasidone is approved as a monotherapy and as an adjunct to lithium or divalproex.
What is the drug NMDA?
N-methyl D-aspartate (NMDA) Antagonist. Neuroactive Steroid Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA)-A Receptor Positive Modulator. Read the following information to find out some general facts about the different kinds of medicine for depression. Like all drugs, depression medicine may cause side effects.
How to take care of a baby when you are depressed?
Depression can make it hard for a woman to take care of herself and her baby. It is important to talk to your healthcare provider about your feelings. Also, try to get some help from your family, friends, or a support group. Ask a relative to watch your baby for a few hours. Join a group for new mothers.
How long does it take to feel sad after depression?
These feelings can get in the way of everyday life. Talk to your healthcare provider about your feelings if you have noticed these signs for at least 2 weeks or immediately if you have any dangerous thoughts or behaviors.
Do antidepressants kill themselves?
Some children and teens who take antidepressants may be more likely to think about hurting or killing themselves when starting treatment or when dose is changed. Call a healthcare provider or 911 if the person: Tries to hurt or kill himself/herself. Talks about specific ways they plan to hurt or kill himself/herself.
Can you take monoamine oxidase inhibitors while pregnant?
Do not take with these medicines: Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs), and in some cases thioridazine or Orap (pimozide). Women should talk to their healthcare providers about the risks of taking these medicines during pregnancy. Use with caution if you have narrow-angle glaucoma.
Does the FDA run pregnancy studies?
Pregnancy registries can help women and their doctors learn more about how depression medicines affect women during pregnancy. The FDA does not run pregnancy studies, but it keeps a list of registries. Check to see if there is a registry for your depression medicine or other medicines at: www.fda.gov/pregnancyregistries.
First-line and alternative medications for treating depression associated with bipolar disorder, including clinical considerations for prescribing and potential adverse effects
First-line and alternative medications for treating depression associated with bipolar disorder, including clinical considerations for prescribing and potential adverse effects.
Bipolar Depression Treatments: Urgent and First-Line Approaches
The following group of pharmacotherapeutic approaches applies to patients presenting with acute bipolar depression – signifying that they have a high/urgent risk of suicide and/or homicidal ideation.
Alternative Treatment for Treatment-Resistant Bipolar Depression
As an alternative treatment, the use of olanzapine and fluoxetine combination (OFC) is also approved for acute bipolar depression. However, due to significant metabolic effects resulting in long-term risk for morbidity and mortality, OFC is not recommended early on in treatment.
Additional Medications for Bipolar Depression: Second- and Third-Line Agents
Other options for use in bipolar depression – whether acute or chronic – are limited. Valproate was studied in four small trials (total n=142) as a maintenance treatment to prevent bipolar depression and concluded that valproate may be effective. 17 On the contrary, a 2014 meta-analysis found valproate to not be effective.
Prescribing for Bipolar Disorder
Discrepancies remain with recommendations made by the PAPHSS and other guidelines for bipolar depression. The differences are largely due to the PAPHSS emphasis on long-term adverse effects associated with potential treatments. When providing recommendations, other guidelines do not weigh adverse effects heavily in making their recommendations.
Is quetiapine a monotherapy?
Quetiapine was approved as monotherapy for the treatment of bipolar depressive episodes by the FDA in October 2006. The efficacy of quetiapine in acute bipolar depression is supported by results from 5 studies with quetiapine immediate release (IR) and 1 study with quetiapine extended release (XR). The design of all 6 clinical trials was similar insofar as the principal aim was to compare the efficacy of quetiapine monotherapy to placebo in adults with bipolar I/II depression (the registration trial that compared quetiapine XR to placebo was limited to depression in bipolar I disorder).
Is modafinil good for bipolar?
Modafinil is not an FDA-approved treatment for bipolar depression; however, it is approved for the treatment of excessive sleepiness, which is often a characteristic of bipolar depression. The antidepressant effect of modafinil in bipolar depression has been studied. In 1 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, 85 eligible subjects diagnosed with bipolar I or II depression as outlined by DSM-IV-TR criteria, unresponsive to mood stabilizers, were treated with modafinil (n = 41) or placebo (n = 44) for 6 weeks. All subjects received 100 mg/day at week 1, which was increased to 200 mg/day at week 2 and every week thereafter.#N#Reference Frye, Grunze and Suppes#N#16
What is the FDA approved medication for bipolar disorder?
The medications approved at this time for acute bipolar depressive episodes are quetiapine (Seroquel), the combination of fluoxetine and olanzapine ...
When was quetiapine approved?
The immediate-release formulation of quetiapine was approved by the FDA for bipolar depression in 2006, and approval of the XR formulation followed two years later.
When was Symbyax first approved?
Symbyax —one of the first drugs in a trend of packaging two drugs together in one pill to create a new patented medication—was first approved in 2003 as treatment for bipolar depression. It is a combination of fluoxetine and olanzapine.
Is lamotrigine good for bipolar?
Lamotrigine ( Lamictal) is a popular choice, primarily because of its lack of side effects relative to other treatments for bipolar disorder, and because, in my experience, it seems to keep people on the “happy” side of the mood spectrum, which is appreciated by patients who feel dulled on traditional mood stabilizers.
Is a positive family history of mania a sign of bipolarity?
In general, instead of simply exploring current symptoms when seeing a depressed patient for the first time, it’s useful to get a very careful personal and family history of potential mania, as most experts propose that a positive family history is suggestive of bipolarity.
Is lurasidone a good antipsychotic?
Lurasidone has little affinity for the H1 receptor (higher affinity is most often the culprit for weight gain in this category) and appears to have fewer weight-gain and metabolic concerns than other atypical antipsychotics, so it is one of the better choices among atypicals.
