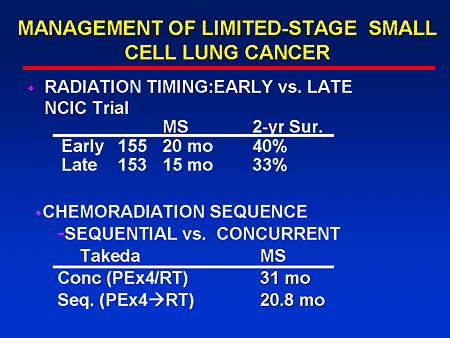
Chemotherapy is often used along with radiation therapy to treat lung cancer. Together, chemo drugs and radiation may work better to destroy your cancer cells. In some people with lung cancer, chemo can keep your tumor small so that the radiation can work better to destroy it.
How effective is Chemo and radiation therapy for lung cancer?
In some people with lung cancer, chemo can keep your tumor small so that the radiation can work better to destroy it. It may also keep your cancer cells from growing back after radiation therapy. While chemo and radiation therapy used together can be a powerful weapon against lung cancer, this combination can have strong side effects.
What is radiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer?
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays or particles to kill cancer cells. Depending on the stage of the non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and other factors, radiation therapy might be used:
Can chemo be used after surgery for lung cancer?
When Chemotherapy Is Used Chemotherapy is the main treatment for small-cell lung cancer (SCLC), but doctors may also use it before or after surgery, or instead of surgery, in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Adjuvant therapy is chemo given after lung cancer surgery to treat any remaining cancer.
What is the treatment for lung cancer?
As the main treatment (sometimes along with chemotherapy ), especially if the lung tumor can’t be removed because of its size or location, if a person isn’t healthy enough for surgery, or if a person doesn’t want surgery. After surgery (alone or along with chemotherapy) to try to kill any small areas of cancer that surgery might have missed.

Is chemotherapy or radiation better for lung cancer?
Together, chemo drugs and radiation may work better to destroy your cancer cells. In some people with lung cancer, chemo can keep your tumor small so that the radiation can work better to destroy it. It may also keep your cancer cells from growing back after radiation therapy.
What is the best cancer treatment for lung cancer?
If you have a larger lung cancer, your doctor may recommend chemotherapy or radiation therapy before surgery in order to shrink the cancer. If there's a risk that cancer cells were left behind after surgery or that your cancer may recur, your doctor may recommend chemotherapy or radiation therapy after surgery.
What is the most successful treatment for lung cancer?
People with non-small cell lung cancer can be treated with surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, or a combination of these treatments. People with small cell lung cancer are usually treated with radiation therapy and chemotherapy. Surgery. An operation where doctors cut out cancer tissue.
What is the success rate of radiation for lung cancer?
The overall five-year survival rate for all stages is 25%. By the three groupings, five-year survival is: Local: 63% Regional: 35%
What is the newest treatment for lung cancer?
Atezolizumab is approved to treat some people with non-small cell lung cancer after surgery. An immune checkpoint inhibitor is a drug that blocks proteins on immune system cells which then allows them to fight cancer.
Which is better surgery or radiation for lung cancer?
While surgery is still the gold standard for lung cancer treatment, radiation therapy can offer a less invasive approach with quicker recovery times.
How many radiation sessions are needed for lung cancer?
Most often, radiation treatments to the lungs are given 5 days a week for 5 to 7 weeks, but this can vary based on the type of EBRT and the reason it's being given. Newer EBRT techniques have been shown to help doctors treat lung cancers more accurately while lowering the radiation exposure to nearby healthy tissues.
Is lung cancer always terminal?
Life expectancy Doctors classify lung cancer as a terminal illness. Approximately 16% of people with this type of cancer survive more than 5 years after their initial diagnosis. Various factors influence a person's life expectancy estimate following a diagnosis of lung cancer.
What are the odds of beating lung cancer?
5-year relative survival rates for non-small cell lung cancerSEER stage5-year relative survival rateLocalized64%Regional37%Distant8%All SEER stages combined26%Mar 2, 2022
Is radiation therapy worse than chemotherapy?
The radiation beams change the DNA makeup of the tumor, causing it to shrink or die. This type of cancer treatment has fewer side effects than chemotherapy since it only targets one area of the body.
What are the disadvantages of radiation therapy?
What are the disadvantages? Radiotherapy can cause side effects, including tiredness, sickness and runny poo (diarrhoea). If you have chemoradiotherapy, you may get side effects from the chemotherapy.
Can lung cancer be treated with only radiation?
Radiation can be used before lung cancer surgery to shrink the tumor or after surgery to kill any cancer cells left in the lungs. Sometimes external radiation is used as the main type of lung cancer treatment.
Types of Radiation Therapy
To understand success rates when treating lung cancer with radiation therapy, it's important to look at the different methods/types of radiation and the goals of treatment. Radiation therapy has changed considerably in recent years and has become much more effective and precise (fewer side effects) than in the past.
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) Success Rate
Small cell lung cancer accounts for roughly 13% of lung cancers and tends to spread early (often to the brain) and aggressively. 10 Roughly one-third of these cancers are diagnosed when they are considered "limited stage" tumors, and two-thirds are already extensive at the time of diagnosis. 11
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Success Rate
The effects of treatments for non-small cell lung cancer are reported in different ways. In some cases, these are divided by the four stages of the disease. In others, they are roughly broken down into three stages: local tumors (stage 1 and some stage 2 tumors), regional (some stage 2 and some stage 3 tumors), and distant (stage 4 lung cancer).
Influencing Factors
There are a number of factors that can influence the success rate of radiation therapy, and it's important to keep these in mind when looking at general statistics that compare people as a whole.
Side Effects
As with any cancer treatment, radiation therapy can have side effects and adverse reactions at times. Some of these include:
Talk to Your Healthcare Provider
There is a lot of information to digest simply looking at the role of radiation therapy in the different types and stages of lung cancer, but individual differences are crucial as well. Every person is unique, and every lung cancer is different in some way.
Summary
Radiation therapy may be used for nearly any type or stage of lung cancer, but treatment goals differ. In early-stage lung cancer, radiation may be used in an attempt to cure the cancer. In this case, specialized radiation called stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) may be as effective as surgery in some settings.
Why is HDR brachytherapy important?
High-dose rate brachytherapy (HDR): Because the lungs support breathing and are located near the heart and other essential structures, it is important for radiation treatment to be tightly focused on tumors to avoid serious side effects. That is why HDR brachytherapy may be a beneficial treatment option for lung cancer patients.
Why do we use respiratory gating?
Respiratory gating: We also use respiratory gating to accurately target tumors by adjusting for tumor motion during IMRT. Tumors, such as those near the lungs, often move as a result of breathing and other involuntary movements in the body. Respiratory gating enables us to “paint” concentrated doses of radiation onto tumors with greater accuracy.
What is IMRT radiation?
Radiation exposure to healthy lung tissue and nearby organs is limited or eliminated, reducing side effects like difficulty breathing. Intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT): Three-dimensional planning with IMRT allows the radiation oncologist to simultaneously treat lung cancer tumors with different doses of radiation, ...
What are the benefits of HDR brachytherapy?
Some other potential benefits of HDR brachytherapy include: Radiation beams are precisely targeted inside the tumors, controlling the location and intensity, and offering more precision and concentrated dosing. Radiation exposure to healthy lung tissue and nearby organs is limited or eliminated, reducing side effects like difficulty breathing. ...
What is EBRT treatment?
External beam radiation therapy (EBRT): EBRT helps to lower the risk of side effects typically associated with radiation treatment for lung cancer, such as difficulty breathing or heart damage. Some additional advantages of EBRT may include:
What is SBRt in lung cancer?
Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT): Preserving healthy tissue is important for many lung cancer patients, who may be struggling with other conditions like emphysema. With stereotactic body radiation, the procedure: Delivers higher radiation doses to tumors, which would not be possible with other radiation therapies.
What is the best way to treat lung cancer?
Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT): Preserving healthy tissue is important for many lung cancer patients, who may be struggling with other conditions like emphysema. With stereotactic body radiation, the procedure: 1 Delivers higher radiation doses to tumors, which would not be possible with other radiation therapies 2 Causes less damage to healthy lung tissue 3 Requires fewer number of treatments than conventional radiation therapy
What is neoadjuvant therapy?
Neoadjuvant therapy is chemo given to shrink the tumor before surgery. Even elderly people with lung cancer can have this treatment. If you’re unable to have surgery for some reason, you may have chemotherapy along with radiation therapy to shrink your tumor.
What is the treatment for small cell lung cancer?
Chemotherapy is the main treatment for small-cell lung cancer (SCLC), but doctors may also use it before or after surgery, or instead of surgery, in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Adjuvant therapy is chemo given after lung cancer surgery to treat any remaining cancer. Neoadjuvant therapy is chemo given to shrink the tumor before surgery.
How long does it take to recover from chemo?
You get chemo in cycles of 3 to 4 weeks. Between cycles, you can rest and recover. You may take your drug only once a week or over a few days of each cycle. If your cancer is advanced, you may need four to six cycles of treatment. Chemo Side Effects. Chemotherapy drugs can have many side effects.
How does chemotherapy work for lung cancer?
You may get a quick shot into your vein or an infusion of the drug through a tube, which can take longer. You’ll get it either in your doctor’s office, clinic, or hospital. You rest while the drugs drip into your vein.
What is the treatment for lung cancer called?
Chemotherapy is a lung cancer treatment that uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It’s also called chemo. Your chemotherapy plan depends on the type and stage of lung cancer you have, your overall health, and your personal treatment goals and preferences.
What is checkpoint inhibitor?
Checkpoint inhibitors are a new type of immunotherapy that uses your own immune system to fight lung cancer and even wipe it out. Immunotherapy now may be the first lung cancer treatment for some people instead of chemo. Pagination. 1.
Does chemo work for SCLC?
That’s because radiation is beamed directly to your tumor. It doesn’t work if your cancer is widespread. SCLC chemo usually includes etoposide ( Toposar, Vepesid) along with a platinum agent like cisplatin ( Platinol) or carboplatin ( Paraplatin ). This is called the EP regimen.
What is EBRT in cancer?
External beam radiation therapy (EBRT) focuses radiation from outside the body onto the cancer. This is the type of radiation therapy most often used to treat NSCLC or its spread to other organs. Treatment is much like getting an x-ray, but the radiation dose is stronger.
How long does radiation treatment last in the lungs?
Most often, radiation treatments to the lungs are given 5 days a week for 5 to 7 weeks, but this can vary based on the type of EBRT and the reason it’s being given. Newer EBRT techniques have been shown to help doctors treat lung cancers more accurately while lowering the radiation exposure to nearby healthy tissues.
What is the treatment for non-small cell lung cancer?
Radiation Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays or particles to kill cancer cells. Depending on the stage of the non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and other factors, radiation therapy might be used: As the main treatment (sometimes along with chemotherapy ), especially if the lung tumor can’t be removed ...
What is the purpose of a nsclc?
To treat cancer spread to other areas such as the brain or bone. To relieve (palliate) symptoms of advanced NSCLC such as pain, bleeding, trouble swallowing, cough, or problems caused by spread to other organs such as the brain.
How does 3D CRT work?
Three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy (3D-CRT) uses special computers to precisely map the tumor’s location. Radiation beams are then shaped and aimed at the tumor (s) from several directions, which makes it less likely to damage normal tissues.
What is the purpose of chemo after surgery?
After surgery (alone or along with chemotherapy) to try to kill any small areas of cancer that surgery might have missed. Before surgery (usually along with chemotherapy) to try to shrink a lung tumor to make it easier to operate on. To treat cancer spread to other areas such as the brain or bone. To relieve (palliate) symptoms ...
How long does radiation last?
Less often, small radioactive “seeds” are left in place permanently, and the radiation gets weaker over several weeks.