Symptoms
Your doctor may also prescribe one or more of these types of drugs:
- Anticoagulants. These thin your blood to prevent clots, a life-threatening lupus symptom.
- Monoclonal antibodies. Belimumab ( Benlysta) is the first drug created just to treat lupus. Given intravenously (in a vein) or subcutaneously (under your skin), it targets specific immune cells. ...
- Repository corticotropin injection. A medicine called H.P. ...
Causes
There is not enough evidence to recommend most natural remedies for treating lupus. If you want to incorporate natural therapies into your care, be sure to talk about it with your healthcare provider first. They can help you determine which therapies might complement your treatment plan best and how to choose the right products.
Complications
Saphnelo approved in the EU for the treatment of moderate to severe systemic lupus erythematosus
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). ...
- American College of Rheumatology. Guidelines for referral and management of systemic lupus erythematosus in adults. ...
- Touma Z, et al. ...
- Cornet A, et al. ...
- Morand EF, et al. ...
- Furie R, et al. ...
- Furie R, et al. ...
- Al Sawah S, et al. ...
- Kabadi S, et al. ...
- ClinicalTrials.gov. ...
What are the best treatments for lupus?
- Office hours and how the office responds to patient calls after hours.
- Which hospital (s) the doctor is affiliated with.
- The type of insurance accepted.
- The payment policy for services.
- The doctor’s experience in treating people with lupus. Provide pertinent information about your loved one’s health care needs to determine if the doctor is able to help
Is there a natural cure for lupus?
What medications are used to treat lupus?
Who is the best lupus Doctor?
What is the course of treatment for lupus?
Corticosteroids. Prednisone and other types of corticosteroids can counter the inflammation of lupus. High doses of steroids such as methylprednisolone (Medrol) are often used to control serious disease that involves the kidneys and brain.
What is the first treatment for lupus?
Early Progress With Lupus Treatment Involves Antimalarials and Corticosteroids. The first medication used for lupus, quinine (an antimalarial), was described by Payne in 1894 (Payne, 1894).
What is the most effective treatment for lupus?
Most lupus patients are treated with hydroxychloroquine [Plaquenil], which is a fairly benign drug. It's not a super potent drug but it does a pretty good job of controlling disease activity in many patients,” she says.
Can be used to treat lupus erythematosus?
Prednisone is the most common steroid that doctors use to treat lupus. If you have liver problems, your doctor may recommend different steroids called prednisolone or methylprednisolone (Medrol®). There are a few different ways to take steroids: Most people take steroids as pills.
How long do you take methotrexate for lupus?
People taking methotrexate usually feel improvements in 3-6 weeks, but it can take up to 3 months to feel the full benefit of the drug. Be sure to take this medication as directed. If you miss a dose, you can usually take the medication up to 4 or 5 days after.
Do you take chemo for lupus?
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy body cells and tissues. Doctors may use chemotherapy drugs to treat lupus. These medications suppress overactive immune reactions, helping ease inflammation, limit organ damage, and improve quality of life.
What is lupus?
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), commonly known as lupus, is an autoimmune illness that affects all parts of the body. The term "lupus" is also...
What causes lupus?
The exact cause of lupus is unknown, but most scientists believe that genetics, combined with outside triggers – such as infections, medications or...
What are the different types of lupus?
There are five recognized forms of lupus: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is the disease most commonly mentioned, and the most serious since it...
What are the risk factors for lupus?
Gender, race and ethnicity, and age are all key factors. Younger women, and especially younger women of color, are most at risk.
If I have lupus, do I have a greater risk of getting the COVID-19 coronavirus?
People with rheumatic diseases and suppressed immune systems, such as lupus patients, may be more vulnerable to the disease known as COVID-19, whic...
What are the symptoms of lupus?
Symptoms vary from person to person, but the typical lupus patient is a young woman who develops arthritis of the fingers, wrists or other small jo...
How is lupus diagnosed?
A diagnosis for lupus is generally based on laboratory tests that exclude other diseases which may have similar symptoms (such as Lyme disease), an...
What is the treatment for lupus?
Depending on the symptoms, blood test results and the particular organs involved, a person with lupus may receive one or more of the following: non...
What are the health complications of lupus?
The severity of lupus varies from mild to life-threatening. After many years of having lupus, patients may develop: osteoporosis (especially in tho...
Are people with lupus at a higher risk for blood clots?
Lupus patients who are positive for antiphospholipid antibody (aPL) can develop blood clots and heart valve disease and may require additional medi...
What is the best treatment for lupus?
Corticosteroids. Prednisone and other types of corticosteroids can counter the inflammation of lupus. High doses of steroids such as methylprednisolone (Medrol) are often used to control serious disease that involves the kidneys and brain.
How to help someone with Lupus?
Connect with others who have lupus. Talk to other people who have lupus. You can connect through support groups in your community or through online message boards. Other people with lupus can offer unique support because they're facing many of the same obstacles and frustrations that you're facing.
What does a low platelet count mean in a lupus test?
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate. This blood test determines the rate at which red blood cells settle to the bottom of a tube in an hour.
What are the challenges of living with Lupus?
The challenges of living with lupus increase your risk of depression and related mental health problems, such as anxiety, stress and low self-esteem. To help you cope, try to:
What are the side effects of lupus?
Side effects include weight gain, easy bruising, thinning bones, high blood pressure, diabetes and increased risk of infection. The risk of side effects increases with higher doses and longer term therapy. Immunosuppressants. Drugs that suppress the immune system may be helpful in serious cases of lupus.
What are the tests for Lupus?
Laboratory tests. Blood and urine tests may include: Complete blood count. This test measures the number of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets as well as the amount of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells. Results may indicate you have anemia, which commonly occurs in lupus. A low white blood cell or platelet count may occur in ...
Can you take care of Lupus at Mayo Clinic?
If you receive care for lupus at Mayo Clinic, consider registering for this online class: Living Well with Lupus. Diagnosis and treatment. Take steps to care for your body if you have lupus. Simple measures can help you prevent lupus flares and, should they occur, better cope with the signs and symptoms you experience.
What are the criteria for SLE?
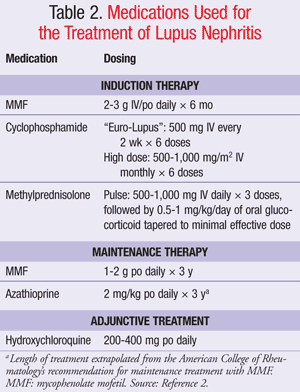
For classification as SLE, four criteria (at least one of them clinical and at least one immunological) have to be fulfilled or lupus nephritis has to be diagnosed histologically in the presence of ANA or anti-dsDNA antibodies. The SLICC criteria are not diagnostic criteria. SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus.
What are the non-specific symptoms of SLE?
Fever, fatigue, and arthralgia are the most frequently occurring non-specific symptoms at disease onset; additional joint swelling or a "butterfly rash"”particularly in women of childbearing age”should prompt consideration of SLE (2).
Is chloroquine good for SLE?
Hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine are licensed for the treatment of SLE. Apart from their good efficacy against arthritis and LE-specific skin lesions (8), antimalarials maintain SLE in remission, are associated with fewer disease flares, and reduce damage in the course of the disease (23, e18).
Is hydroxychloroquine good for Lupus?
In particular, hydroxychloroquine is associated with a higher rate of remission, fewer relapses, and reduced damage in the course of the disease, even in lupus nephritis.
What is lupus erythematosus?
What is lupus? Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), commonly known as lupus, is an autoimmune illness that affects many organs and systems in the body. Lupus is a chronic condition, but symptoms tend to cycle in alternate periods of "flares" (or "flares-ups") and remissions.
What to do if your primary care doctor suspects you have lupus?
If your primary care doctor suspects you may have lupus, contact a rheumatologist to confirm the diagnosis and get appropriate treatment. HSS is top-ranked for rheumatology by U.S. News & World Report and offers a dedicated team of specialists and resources at the Lupus and APS Center of Excellence.
How many times does lupus occur in Caucasian women?
The incidences of lupus in women of African descent is three times that of incidences in Caucasian women. The incidences of lupus in women of Asian descent are twice that of incidences in Caucasian women. The incidences of lupus in women of Latin descent are twice that of incidences in Caucasian women. Age: Symptoms that lead to a lupus diagnosis ...
What tests are used to diagnose lupus?
A diagnosis for lupus is generally based on laboratory tests that exclude other diseases which may have similar symptoms (such as Lyme disease), and specific serologic tests – blood tests that determine the presence of certain antibodies.
What are the symptoms of Lupus?
Symptoms vary from person to person, but the typical lupus patient is a young woman who develops arthritis of the fingers, wrists or other small joints, hair loss, a rash (often on the face, in butterfly pattern over the nose and cheeks).
What are the factors that affect the risk of lupus?
Gender, race and ethnicity, and age are all key factors. Younger women, and especially younger women of color, are most at risk. Gender: Most lupus patients are female. The ratio of women to men who have lupus is about 9 to 1.
How old do you have to be to get Lupus?
Age: Symptoms that lead to a lupus diagnosis most commonly appear in people between 15 and 44 years of age.
What is the treatment for SLE?
Patients suffering from SLE are typically treated with corticosteroids and immunosuppressive agents (1). An eminent direct or indirect target of novel therapeutic approaches has been the lupus B cell (2–4).
What is RC18 in Lupus?
B cells are being targeted directly or indirectly in patients with lupus. RC18 is a recombinant human BLyS receptor antibody fusion protein and it is used in a phase III placebo-controlled study plus standard treatment with primary outcome an SRI response rate at week 52 (59).
What is Daratumumab used for?
Daratumumab, a mAb approved for the treatment of multiple myeloma, is an IgG1k mAb directed against CD38 causing depletion of plasma cells. Long-lived plasma cells are residents in niches in the bone marrow or (perhaps more importantly) in inflamed tissue and they do not respond to immunosuppressants, including B-cell-targeting treatments. Two patients with severe manifestations of SLE received daratumumab at a dose of 16 mg/kg of body weight once a week for 4 weeks followed by maintenance treatment with I.V. belimumab ( 18 ). Daratumumab treatment resulted in remarkable clinical outcomes not only of severe manifestations such as lupus nephritis, autoimmune hemolytic anemia and autoimmune thrombocytopenia but also on less severe manifestations such as arthritis, skin rashes, pericarditis, cutaneous vasculitis, alopecia, and mucosal ulcers. Daratumumab treatment was also associated with favorable serologic responses. Importantly, previous therapeutic interventions with a variety of agents such as bortezomib, mycophenolate mofetil, and cyclophosphamide were ineffective. Despite the extremely small number of patients, data are encouraging supporting further evaluation of daratumumab in meaningfully larger numbers of patients with SLE. It is of interest however that the authors did not ascribe their anti-CD38 mAb-mediated clinical effect (s) exclusively to reductions of plasma cell numbers. Other circulating cells also express CD38 and their numbers decreased following daratumumab treatment. Among them are subsets of B cells, plasmacytoid dendritic cells, and a greatly expanded CD38 + T cell subpopulation. Only recently it was shown by Katsuyama et al. that this expanded CD38 + CD8 + T cell subset is responsible for the significantly compromised cytotoxicity encountered in patients with lupus ( 19 ).
What are the B cells in Lupus?
The B cell, as a major component of the adaptive immune system, may mediate autoimmune disease. B cells are not only capable of producing autoantibodies after their differentiation into plasma cells, but they also present autoantigens to T cells and they secrete cytokines. Therefore, B cells represent an established and clear target of treatment approaches; lupus B cells have been targeted either directly via regimens that cause B cell depletion or indirectly via regimens affecting B cell survival, or via inhibiting their antigen-receptor-initiated function.
Can Rituximab be used for Lupus?
Rituximab (RTX) causing B cell depletion can also be administered according to the ACR and EULAR guidelines in refractory lupus nephritis despite failed clinical trials, and is often used off-label for other manifestations as well, based on the encouraging results of diverse studies.
Is lupus erythematosus a multisystem disease?
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune multisystem disease with a variable presentation and manifestations ranging from mild to severe or even life-threatening. There is an ongoing and unmet need for novel, disease-specific, effective and safe treatment modalities.
Is IL-2 good for lupus?
It has been suggested that low levels of IL-2 may result in disruption of immune tolerance. Lupus is a “low IL-2” disease and this is thought to play a role in the pathogenesis of the disease. According to the results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial, low-doses of IL-2 might be a beneficial and safe choice in the treatment of patients with SLE ( 40 ). More specifically, 60 SLE patients (including patients with lupus nephritis) received either IL-2 ( n = 30) or placebo ( n = 30) for 12 months. The SRI-4 response rates were 55.17% in the IL-2 group and 30% in the placebo group, at week 12. At week 24, the SRI-4 response rate was 65.2% in the IL-2 group and 36.67% in the placebo group. Treatment with low doses of IL-2 was associated with a predicted expansion of peripheral Treg cells, improving perhaps immune tolerance. Addition of low-doses of IL-2 in combination with rapamycin in 50 patients with SLE resulted in a reduction of the SLEDAI score after 6, 12, and 24 weeks of treatment ( 41 ). Median prednisone dosages were decreased. The same regimen resulted in an expansion of Treg cells and a restoration of the Th17/Treg ratio declaring that Treg cells may participate in the pathogenesis of SLE. There is an ongoing trial of treatment with IL-2 at different doses in patients with SLE and its primary outcome is the SRI-4 response at week 12 ( 42 ). Studies targeting cytokines are depicted in Table 2.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Alternative Medicine
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.