Proteins produced in bacteria are an important source of medicines. These include insulin (for treating diabetes), erythropoietin (for treating anaemia), growth hormone (for treating growth disorders) and others. Today, bacteria (and other organisms) are used routinely as biological ‘factories’ to produce protein medicines in large amounts.
What role do gut bacteria play in the relationship between diabetes?
Recently, scientists set out to identify which specific gut bacteria species might play a role in this association between diet and diabetes. The gut microbiome includes hundreds of species of bacteria. Scientists have shown that an imbalance in the microbiome, or dysbiosis, has associations with adverse health outcomes.
Can bacteria produce insulin?
For the insulin-producing bacteria, scientists at Cornell University created a strain of benign E. coli that would produce a protein called GLP-1. GLP-1 then triggers the production of insulin in the stomach cells of the diabetic mice.
How do scientists produce high-quality protein from bacteria?
To produce large amounts of high-quality protein, the appropriate promoter should be chosen – which one is best depends on the introduced gene and on the bacterium that is hosting it. Often, scientists use strong promoters that can be switched on and off.
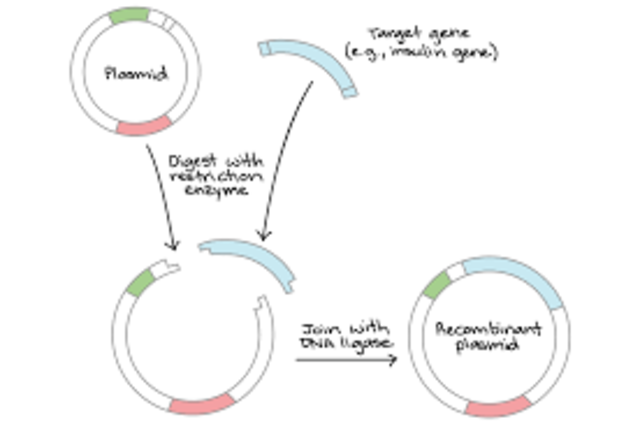
How is insulin made from human DNA and bacterial plasmid?
Using the same restriction enzyme to cut both the human DNA and bacterial plasmid results in complementary sticky ends that join by base pairing. A different enzyme is used to join the insulin gene and the bacterial plasmid. The bacterial plasmid containing the insulin gene is placed into a bacterial cell.

Which human protein used in the treatment of diabetes can be produced in bacteria?
The development in the field of genetic engineering allowed the production of insulin in E. coli and yeast, which have been approved for therapeutic applications in human by FDA [14,15]. Nowadays, recombinant human insulin is mainly produced either in E. coli or Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
What is the name for the human insulin produced by the bacteria?
Insulin Aspart is another fast-acting insulin analogue, which was produced in S. cerevisiae, developed by Novo Nordisk and approved by US FDA in 2001 for therapeutic use in human.
Why can bacteria produce human proteins such as insulin?
Right option. That is the answer for this question. The bacteria are So basically all organisms share a common genetic code. That's why human proteins such as insulin can be produced by bacterial cells.
Is Humulin a protein?
In October 1982, Humulin® won FDA approval as the first marketed human healthcare product derived from recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology. “Humulin was the first therapeutic recombinant protein which established the feasibility of recombinant proteins,” J.
What is human insulin made of?
Human insulin is synthetically made in a lab using E. coli bacteria. It replicates the insulin naturally found in your body. Until the commercial availability of human insulin in the late 1900s, animal-derived insulin was used to help people manage diabetes.
How is insulin made for diabetes?
Scientists make insulin by inserting a gene that codes for the insulin protein into either yeast or bacteria. These organisms become mini bio-factories and start to spit out the protein, which can then be harvested and purified.
What proteins are produced by bacteria?
Proteins produced in bacteria are an important source of medicines. Many medicines and drugs – particularly hormones – are proteins. These include insulin (for treating diabetes), erythropoietin (for treating anaemia), growth hormone (for treating growth disorders) and others.
Can bacteria produce human proteins?
Recombinant DNA is a technology scientists developed that made it possible to insert a human gene into the genetic material of a common bacterium. This “recombinant” micro-organism could now produce the protein encoded by the human gene.
Does bacteria produce insulin?
Synthetic human insulin was the first golden molecule of the biotech industry and the direct result of recombinant DNA technology. Currently, millions of diabetics worldwide use synthetic insulin to regulate their blood sugar levels. Synthetic insulin is made in both bacteria and yeast.
What produces Humulin?
The new insulin, called Humulin, is manufactured by a technique known as recombinant DNA, which involves inserting human genetic instructions into a bacterium that then produces the drug.
Is Humulin human insulin?
Humulin N, NPH, human insulin (recombinant DNA origin) isophane suspension. Humulin is human insulin used for treating diabetes.
How is Humulin or insulin produced?
Humulin was the first drug produced by genetic engineering techniques to gain the FDA approval for human use. It was made by inserting human genes responsible for insulin production into E. Coli bacteria, thus stimulating the bacteria to synthesize insulin.
How Is Human Insulin produced?
Human insulin is laboratory created by growing insulin proteins within E-coli bacteria (Escherichia coli).
What Types of Human Insulin Are available?
Human insulin is available in two forms, a short acting (regular) form and an intermediate acting (NPH) form. NPH (Neutral Protamine Hagedorn) insu...
What Are Premixed Human Insulins?
Premixed insulins consist of a mix of regular and NPH insulin. The premixed insulins are available in a number of different ratios of mixing. For e...
How Quickly Do Human Insulins Act?
Short acting (regular) insulin starts to act from about 30 minutes after injecting, with their peak action occurring between 2 and 3 hours after in...
Benefits and Disadvantages of Human Insulin
Human insulin was welcomed in the 1980s as it meant insulin could be created in large amounts at a relatively low cost. It has been reported that h...
The History of Human Insulin
Human insulin is more recent than animal insulin - coming almost 50 years after animal insulin was first used.
Which bacteria are responsible for reducing the effects of Western diet?
They managed to narrow down the list to four bacteria that appeared to play a key role in reducing or intensifying the harmful effects of a Western diet: Lactobacillus johnsonii, Lactobacillus gasseri, Romboutsia ilealis, and Ruminococcus gnavus.
What did the researchers give mice to study their metabolism?
Impacting metabolism. The researchers combined experiments on mice with the analysis of large quantities of data from previous research in mice and humans. The scientists gave mice either a regular diet or food equivalent to a Western diet.
Why is reducing fat in the liver important?
Scientists have previously shown that reducing fat in the liver is important for recovery from type 2 diabetes. Trusted Source. . The authors of the recent study found that genes that controlled liver cell mitochondrial function, which have links with lipid metabolism and overall glucose control, were upregulated.
What happens if you have type 2 diabetes?
Individuals with type 2 diabetes do not produce enough insulin, or their cells do not respond to it appropriately . As a result, cells do not absorb sugar efficiently, and blood sugar level rises. Over time, this can cause damage to internal organs.
Can gut bacteria help with diabetes?
The authors of a recent study believe that the medical application of specific gut bacteria might, in the future, help treat type 2 diabetes. people who have diabetes in the United States have type 2 diabetes. Individuals with type 2 diabetes do not produce enough insulin, or their cells do not respond to it appropriately.
Does the Western diet increase the risk of diabetes?
The Western diet, which is high in saturated fats and refined sugars, increases the risk. Trusted Source. of developing type 2 diabetes. Recently, scientists set out to identify which specific gut bacteria species might play a role in this association between diet and diabetes.
Do mice have higher BMI?
An analysis of data from human research showed that the four bacteria identified in mice also correlates with the body mass index (BMI) of people on a Western diet. People who had higher levels of the two “improvers” had a lower BMI; people with more “worseners” were more likely to have higher BMI.
What is the function of insulin?
Insulin is a hormone central regulating carbohydrate and fat metabolism in the body. Insulin is secreted by the Islets of Langerhans of pancreas which catabolizes glucose in blood. Insulin causes liver cells, muscle cells and fat tissue to take up glucose from the blood and store it as glycogen in the liver and muscle. Insulin consists of two polypeptide chains, Chain A ( 21 amino acid long) and B ( 30 amino acid long). Its precursor is proinsulin which also contains two polypeptide chains, A and B, and is connected with a third peptide chain –C (35 amino acid long). In the Islets of Langerhans, insulin accumulates in secretary vesicles as a single polypeptide chain called proinsulin. Before secretion into the bloodstream the third C chain of the proinsulin molecule is excised, leaving the A and B chains joined by disulphide bridges as the active insulin. E. coli is not capable of removing the C chain. There are several strategies for producing insulin from bacteria, but the most successful is to synthesize the A and B separately and then join them together. The gene sequence of determining the A chain has been fused to the ß-galactosidase gene (lac Z) of E.coli. The whole lac-Z-A chain fusion is cloned into pBR322. Bacteria with this plasmid synthesize ß-galactosidase with the insulin A chain. The B chain is produced in an identical manner. After purification of the two chains they are mixed , oxidized and then reduced which allows the disulphide bridges to form and active insulin to be produced. The recombinant plasmid is inserted into the bacteria by the process of transformation. The recombinant bacteria are sorted by growing them in the presence of an antibiotic. The bacteria which survive are the ones which have taken up the plasmid. They are said to Continue reading >>
Who funded the development of insulin?
The separate chains were then joined to construct complete insulin molecules. The development of genetically engineered human insulin was funded by Genentech. However, the work was a cooperative effort between Genentech and City of Hope.
What is GMO insulin?
GMO insulin is also known as synthetic insulin, or human insulin. It is produced with genetically modified bacteria, instead of the traditional method that produces what is known as pork insulin. In this method, sometimes called natural insulin, the pancreas of a cow or pig is used to produce insulin.
What were the first organisms to be genetically modified?
Genetically modified bacteria were the first organisms to be modified in the laboratory, due to their simple genetics. [1] These organisms are now used for several purposes, and are particularly important in producing large amounts of pure human proteins for use in medicine. [2] History The first example of this occurred in 1978 when Herbert Boyer, working at a University of California laboratory, took a version of the human insulin gene and inserted into the bacterium Escherichia coli to produce synthetic "human" insulin. Four years later, it was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Pharmaceutical production The drug industry has made use of this discovery to produce medication for diabetes. [3] Similar bacteria have been used to produce clotting factors to treat haemophilia although in the paper referenced, hamster cell lines are used to produce the clotting factors rather than bacteria, [4] and human growth hormone to treat various forms of dwarfism. [5] [6] These recombinant proteins are safer than the products they replaced. Prior to recombinant protein products, several treatments were derived from cadavers or other donated body fluids and could transmit diseases. [7] Indeed, transfusion of blood products had previously led to unintentional infection of haemophiliacs with HIV or hepatitis C; similarly, treatment with human growth hormone derived from cadaver pituitary glands may have led to outbreaks of Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease. [7] [8] Other uses Genetically modified bacteria can serve various purposes beyond producing medicinal compounds. For instance, bacteria which generally cause tooth decay have been engineered to no longer produce tooth-corroding lactic acid. [9] These transgenic bacteria, if allowed to colonize a person's mouth, co Continue reading >>
How many amino acids are in insulin?
Insulin consists of two polypeptide chains, Chain A ( 21 amino acid long) and B ( 30 amino acid long). Its precursor is proinsulin which also contains two polypeptide chains, A and B, and is connected with a third peptide chain –C (35 amino acid long). In the Islets of Langerhans, insulin accumulates in secretary vesicles as a single polypeptide ...
What is the most common source of insulin?
Insulin produced from this newer method is known as GMO insulin, and genetically modified bacteria have become the most common source of pharmaceutical insulin. In addition to bacteria, baker’s yeast is also a common template onto which the human insulin-producing gene can be attached.
What is recombinant DNA?
Recombinant DNA, or rDNA, is DNA which specifically encodes a protein. This is cut from genomic DNA by a restriction enzyme which cuts DNA at specific sequences along the chain. These pieces are then analyzed and the DNA needed to make the protein is extracted and purified.
What is the function of DNA in bacteria?
The implanted DNA stimulates the cell to produce insulin. Human insulin is the only animal protein to have been made in bacteria in such a way that its structure is absolutely identical to that of the natural molecule, thus reducing the possibility of complications resulting from antibody production.
How do proteins develop?
Protein development in a cell begins with DNA transcribing into RNA, and RNA translating into proteins. Proteins are made up of amino acids that are arranged in different combinations and lengths. The differences in arrangements and lengths of amino acids determine the function of the protein.
What is the function of HGH in children?
Produced by the pituitary gland, human growth hormone (HGH) is essential for proper growth in children. Some children, however, have disorders that cause reduced HGH levels. If children go without treatment, they mature as unusually short adults. This condition is treated by administering HGH, which today is produced by using recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology. Recombinant DNA Scientists use rDNA technology, a group of techniques that isolate genes (specific pieces of DNA), attach them to other pieces of DNA and transfer the newly combined genetic material to another species such as bacteria. Sometimes called genetic engineering, rDNA technology is a relatively recent invention that dates to the 1970s. Insulin was the first protein produced using rDNA methods. Pituitary Glands HGH is a protein, and like all proteins, it's made from a chain of amino acid subunits. (In the case of HGH, the protein is roughly 190 amino acids long.) Before the invention of rDNA technology, HGH could only be produced laboriously by isolating it from pituitary gland tissue taken from human cadavers. This process was inefficient, expensive and sometimes unsafe. For example, the resulting HGH product occasionally contained contaminants from cadaver tissues. Rarely, patients injected with HGH from cadavers developed Creutzfeld-Jakob disease, a very serious human version of mad cow disease. Infection is caused by proteins called prions. By eliminating the need for human tissue, rDNA technology avoids these and other potential contamination problems. Isolation Genes like the one for HGH contain coded instructions for protein production. Inside cells, this information is first re-coded from DNA, which provides long-term information storage, to a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule, which provides specific Continue reading >>
How is insulin produced?
This mRNA is used to synthesise DNA which codes for insulin production The mRNA is then combined with free nucleotides and reverse transcriptase to make DNA mRNA is easier to isolate than DNA A DNA plasmid is removed from an E.coli bacterium The plasmid is cut open using the same restriction enzymes as were used to cut out the gene of interest to give complementary sticky ends. The isolated gene then binds to the restriction site on the plasmid. This creates a recombinant vector carrying the gene of interest. Production and Collection of insulin The bacteria are then grown on an industrial scale in huge fermenters to produce large amounts of insulin The insulin made is extracted from the fermenters and purified so that it can be sold and used. Why Bacteria? Insulin was originally extracted from pig and cow pancreases. This insulin is slightly different to human insulin (by a few amino acids) so it is far more effective to use bacteria to make actual human insulin • It is easier to create high quantities of insulin • It can be produced more rapidly • It is produced at lower a lower cost than animal insulin • It is less likely to cause an adverse reaction as it’s identical to human insulin • It overcomes ethical concerns from vegetarians and others • This form of insulin is absorbed more rapidly Advantages of using bacteria Continue reading >>
What is the process of transferring DNA to a new organism?
The transfer of a DNA fragment from one organism to a self-replicating genetic element is known as recombinant DNA technology. This process is also referred to as DNA cloning, molecular cloning and gene cloning. This process has been around since the 1970s, and today is practiced frequently in molecular biology labs. One use for this technology is to create insulin, which is used by diabetics who cannot produce enough on their own. Insulin is produced and secreted by the beta cells of the pancreas' islets of Langerhans and functions to regulate the use and storage of food. The old method of creating insulin was to extract and purify abattoir by-product. This method had side effects of immune bodies producing antibodies against it, which in turn made the insulin inaffective. Researchers eventually came upon the idea of synthesizing Humalin, and recombinant technology was just the method to use. In the first step, a plasmid is removed from and E. Coli cell. A special enzyme then opens up this plasmid. The DNA coding for human insulin is inserted into the opened plasmid, which is then closed by another special enzyme (recombination). The recombined plasmid is introduced back into the E. Coli host cell where it divides into new identical cells. The implanted DNA stimulates the cell to produce insulin. Human insulin is the only animal protein to have been made in bacteria in such a way that its structure is absolutely identical to that of the natural molecule, thus reducing the possibility of complications resulting from antibody production. Today, the majority of insulin dependent patients are now treated with genetically engineered recombinant human insulin. However, doctors and patients have become concerned about the increase in the number of hypoglycemic episodes experi Continue reading >>
What enzyme is used to stick insulin in place?
The insulin gene is then inserted into the gap in the vector, and stuck in place by an enzyme called DNA ligase.
Where is insulin inserted in the cell?
The DNA coding for human insulin is inserted into the opened plasmid, which is then closed by another special enzyme (recombination). The recombined plasmid is introduced back into the E. Coli host cell where it divides into new identical cells. The implanted DNA stimulates the cell to produce insulin.
When was human insulin invented?
Human insulin was developed through the 1960s and 1970s and approved for pharmaceutical use in 1982. Before human insulin was developed animal insulin, usually a purified form of porcine (pork) insulin, was used.
What is a premixed insulin?
Premixed insulins consist of a mix of regular and NPH insulin. The premixed insulins are available in a number of different ratios of mixing. For example Humulin M3 is a mix of 30% short acting to 70% intermediate whereas Humulin M5 is made up of 50% of both short and intermediate acting.
What was the newer insulin called in the 1990s?
1990s. In the 1990s a newer form of human insulins, called analogue insulin , were produced. Analogue insulins allowed for short acting insulins to act more rapidly and longer acting insulin to have, what is termed as, a flatter profile.
How long does it take for insulin to work?
The duration is up to 10 hours . Intermediate acting (NPH) insulin takes about 2 to 4 hours to start acting, has its peak activity between 4 and 10 hours and has duration of up to 18 hours. Read further on the actions of insulin.
How do bacteria produce proteins?
Bacteria can produce foreign proteins from introduced genes, using their own gene expression machinery. Producing proteins in bacteria has greatly simplified the study of how proteins work. It has also made it possible to make large amounts of medically important proteins, such as insulin, within bacteria. How to make a foreign protein in bacteria To produce a foreign protein in bacteria, you first need to clone the gene that encodes it, then introduce the vector containing your gene into bacteria. For further information, see article: How to add foreign DNA to bacteria. It’s important that the vector you clone it into is an ‘expression vector’ – that is, a vector that includes a bacterial promoter sequence in front of your gene of interest. By including a bacterial promoter, you are giving the bacterium instructions to make a protein from your gene of interest – essentially, you are ‘tricking’ bacteria into producing a foreign protein. For further information, see article: Proteins – what they are and how they’re made. Which promoter? To produce large amounts of high-quality protein, the appropriate promoter should be chosen – which one is best depends on the introduced gene and on the bacterium that is hosting it. Often, scientists use strong promoters that can be switched on and off. This means that bacteria won’t begin to make the foreign protein until their environment is changed in some way (for instance, a chemical is added to the bacterial culture or the temperature is changed). Producing proteins in bacteria aids scientific research Before foreign proteins were first produced in bacteria, scientists had to collect their protein of interest from its natural source. This process was long, and it was difficult to collect large amounts of prot Continue reading >>
Why do diabetics need insulin?
Some diabetes patients need insulin injections in order to survive. Human insulin is produced through the use of bacteria. It’s Cold in This Library Bacteria contain small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. Plasmids have regions that can be cut such that a human gene can be inserted into the plasmid.
What do diabetics use today?
What diabetics use today is a purified mixture of insulin from the pancreas glands of cows and pigs slaughtered for food. But the worldwide demand for insulin is believed to be putting some strain on these supplies. And some diabetics develop allergic reactions to the animal insulin or its chemical precursors.
What is GMO insulin?
GMO insulin is also known as synthetic insulin, or human insulin. It is produced with genetically modified bacteria, instead of the traditional method that produces what is known as pork insulin. In this method, sometimes called natural insulin, the pancreas of a cow or pig is used to produce insulin.
How does DNA cloning work?
The plasmid is introduced into bacteria via process called transformation, and bacteria carrying the plasmid are selected using antibiotics. Bacteria with the correct plasmid are used to make more plasmid DNA or, in some cases, induced to express the gene and make protein. When you hear the word “cloning,” you may think of the cloning of whole organisms, such as Dolly the sheep. However, all it means to clone something is to make a genetically exact copy of it. In a molecular biology lab, what’s most often cloned is a gene or other small piece of DNA. If your friend the molecular biologist say that her “cloning” isn’t working, she's almost certainly talking about copying bits of DNA, not making the next Dolly! DNA cloning is the process of making multiple, identical copies of a particular piece of DNA. In a typical DNA cloning procedure, the gene or other DNA fragment of interest (perhaps a gene for a medically important human protein) is first inserted into a circular piece of DNA called a plasmid. The insertion is done using enzymes that “cut and paste” DNA, and it produces a molecule of recombinant DNA, or DNA assembled out of fragments from multiple sources. Diagram showing the construction of a recombinant DNA molecule. A circular piece of plasmid DNA has overhangs on its ends that match those of a gene fragment. The plasmid and gene fragment are joined together to produce a gene-containing plasmid. This gene-containing plasmid is an example of recombinant DNA, or a DNA molecule assembled from DNA from multiple sources. Next, the reco Continue reading >>
How is insulin made?
How Insulin Is Made Using Bacteria. Website Search Description: Synthetic human insulin was the first golden molecule of the biotech industry and the direct result of recombinant DNA technology. Currently, millions of diabetics worldwide use synthetic insulin to regulate their blood sugar levels.
What is DNA research?
DNA research, controversial realm of genetic experimentation known popularly as gene splicing. What the scientists at the University of California at San Francisco did was to transplant into bacteria the genes from rat cells that carry the genetic instructions for making insulin.
What is the DNA sequence of insulin?
To start, the DNA sequence for human insulin is inserted into the bacteria E. coli, which creates an organism that now has DNA from two very different species in it. This new E. coli is a genetically modified organism (GMO) and serves as a cheap factory for mass-producing the human insulin protein.
When was insulin discovered?
Since Banting and Best discovered the hormone, insulin in 1921. (1) diabetic patients, whose elevated sugar levels (see fig. 1) are due to impaired insulin production, have been treated with insulin derived from the pancreas glands of abattoir animals.
How is insulin made?
The insulin protein produced via genetic engineering is chemically identical to the insulin protein made in a healthy human body. Genetically engineered plants are made through a very similar process. A gene of particular interest is inserted into a plant.
What is the name of the plant that produces insulin?
To create the cheap "prairie insulin," scientists at the University of Calgary genetically engineered the human gene for insulin into the common plant safflower. Once the gene activates, the flower begins producing insulin faster than traditional methods that utilize pigs, cows, yeast, or bacteria.
What is the technique used to insert genes into loops of DNA called?
The technique illustrated in this animation produced by WGBH and Digizyme, Inc., shows how scientists use natural processes and technological innovations to insert genes into loops of DNA called plasmids . Plasmids can then be introduced into bacterial or other cells, which will proceed to replicate the inserted genes or induce the cells to produce such valuable proteins as human insulin and growth hormone. This resource is part of the Biotechnology collection. Continue reading >>
When was recombinant DNA first used?
Recombinant DNA technology was first developed in the early 1970s, and the first genetic engineering company, Genentech, was founded in 1976. The company isolated the genes for human insulin into E. coli bacteria, which allowed the bacteria to produce human insulin.
What are the four nucleotides that make up DNA?
DNA relies on four different nucleotides - called A, T, G, and C - that are strung together in sequences millions of nucleotides long. These unique sequences are responsible for coding traits, from the color of your eye to a sea turtle's shell. A change to just one or several nucleotides results in a mutation.
How does a bacterial plasmid work?
A bacterial plasmid is cut open using the same restriction enzyme. Restriction enzymes leave ‘sticky ends’, where one of the two DNA strands is longer than the other. Using the same restriction enzyme to cut both the human DNA and bacterial plasmid results in complementary sticky ends that join by base pairing.
Where did insulin come from?
Before genetic engineering, insulin was obtained from pigs and cattle. Due to an increase in the number of diabetics, more insulin is required than ever before.
Why is insulin put in a fermenter?
The bacterial cell is placed in a fermenter to allow reproduction under perfect conditions (warmth, moisture and oxygen). Downstreaming occurs – this is when insulin is extracted, purified and packaged.
How do engineers and scientists work together to produce a protein in the lab?
Explain how engineers and scientists may work together to produce a protein in the lab. The scientists would do biological studies of how protein breaks down and combines with the muscles. Engineers would then create delivery systems to get the protein to the muscle faster and more efficiently.
Why can't hydrophobic amino acids be pushed out of water?
The insoluble, hydrophobic amino acids cannot e pushed out of the water altogether the way oil is, because they are attached to the soluble, hydrophillic amino acids. All they can do is group together, forming a droplet of oil in the middle of the protein with a surrounding shell of soluble amino acids.
How has insulin changed?
Insulin has changed to act faster and be less painful to the patient. instead of painful injections straight into the muscles that take hours to be effective. Patients can now use pumps that directly send insulin into the bloodstream and liver.
What is protein folding?
Protein folding is the process by which a protein structure assumes its functional shape or conformation. All protein molecules are heterogeneous unbranched chains of amino acids. GFP contains a large number of hydrophobic amino acids. Describe how these amino acids would be oriented in the protein.
