
Antiretroviral drugs work by blocking different stages of this cycle. When used in combination, they function as a biochemical tag team—one that is able to suppress the multitude of viral mutations that can exist within a single HIV population.
Full Answer
When should antiretroviral therapy for HIV be started?
Jul 18, 2021 · The goal of HIV medicines is to prevent HIV from multiplying. There are six classes of drugs used in antiretroviral therapy. These drugs generally fall into classes according to the phase of the HIV life cycle inhibited by them.
When to start antiretroviral therapy in HIV-infected patients?
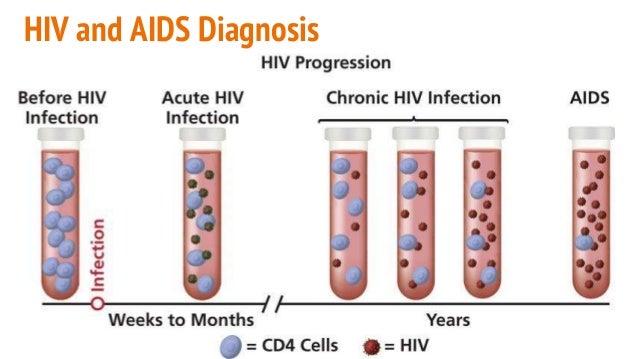
HIV virions enter the CD4+ T-cells and utilize the CD4 cells as the machinery for reproduction of new virions. The currently approved antiretroviral drugs aim at halting viral replication at 6 different stages of the HIV life cycle. Table 2 lists the drugs approved by …
When to start antiretroviral therapy?
HIV treatment involves taking medicine that reduces the amount of HIV in your body. HIV medicine is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). There is no effective cure for HIV. But with proper medical care, you can control HIV. Most people can get the virus under control within six months.
How to start antiretroviral therapy?
Apr 10, 2022 · The benefits of antiretroviral therapy are a greater ease of use, a lower risk of HIV drug resistance, and fewer treatment-related side effects.
What are the goal of antiretroviral therapy?
The goals of antiretroviral treatment are to improve the quality of life of the HIV infected, reduce HIV related morbidity and mortality, and restore or preserve their immune function through maximal suppression of viral replication.
What do antiretroviral medications do for someone with HIV?
Antiretroviral therapy prevents the virus from multiplying, which reduces the amount of HIV in the body. This gives the immune system a chance to produce more CD4 cells.
What are the five goals of antiretroviral therapy?
Thus, once initiated, ART should be continued, with the following key treatment goals:Maximally and durably suppress plasma HIV RNA;Restore and preserve immunologic function;Reduce HIV-associated morbidity and prolong the duration and quality of survival; and.Prevent HIV transmission.Jan 28, 2016
What is the meaning of antiretroviral drugs?
Antiretroviral drugs are medications for the treatment of infection by retroviruses, primarily HIV. Different classes of antiretroviral drugs act at different stages of the HIV life cycle. Combination of several (typically three or four) antiretroviral drugs is known as Highly Active Anti-Retroviral Therapy (HAART).
What is HIV treatment?
HIV treatment involves taking medicine that reduces the amount of HIV in your body. HIV medicine is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). There is n...
When should I start treatment?
Start Treatment As Soon As Possible After Diagnosis HIV medicine is recommended for all people with HIV, regardless of how long they’ve had the vir...
What if I delay treatment?
HIV will continue to harm your immune system. This will put you at higher risk for developing AIDS. Learn more about AIDS and opportunistic infecti...
What are the benefits of taking my HIV medicine every day as prescribed?
Treatment Reduces the Amount of HIV in the Blood The amount of HIV in the blood is called viral load. Taking your HIV medicine as prescribed will h...
Does HIV medicine cause side effects?
HIV medicine can cause side effects in some people. However, not everyone experiences side effects. The most common side effects are Nausea and vom...
Will HIV treatment interfere with my hormone therapy?
There are no known drug interactions between HIV medicine and hormone therapy. Talk to your health care provider if you are worried about taking HI...
What if my treatment is not working?
Your health care provider may change your prescription. A change is not unusual because the same treatment does not affect everyone in the same way.
Sticking to my treatment plan is hard. How can I deal with the challenges?
Tell your health care provider right away if you’re having trouble sticking to your plan. Together you can identify the reasons you’re skipping med...
What are the goals of antiretroviral therapy?
The key goals of antiretroviral therapy are to: 1 achieve and maintain suppression of plasma viremia to below the current assays’ level of detection; 2 improve overall immune function as demonstrated by increases in CD4+ T cell count; 3 prolong survival; 4 reduce HIV associated morbidity; 5 improve overall quality of life; and 6 reduce risk of transmission of HIV to others
What was the disease of the 1980s?
The 1980s saw the devastation of the newly emerging and deadly disease of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome or AIDS. The identification of the retrovirus - now known as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) - as the causative pathogen in the mid-1980s was the key milestone in the control of this disease.
When was Zidovudine first used?
This in turn halts the conversion of viral RNA into double stranded DNA. Zidovudine was first approved in 1987 for patients with advanced HIV (CD4 count <200 cells/mm3) or with AIDS defining conditions,1followed by the approval of didanosine, zalcitabine, stavudine, and lamivudine.
Does Atazanavir increase AUC?
Atazanavir undergoes rapid oral absorption. When unboosted, the area under the concentration time curve (AUC) is increased by almost 70% when given with a light meal compared to approximately 35% with a high fat meal. When given with ritonavir, the AUC of atazanavir is increased by almost 2.5-fold.
What happens after HIV enters the cell?
Reverse Transcription– After cell entry as HIV is a retrovirus, the virus’s RNA template transcribes into a double-stranded viral DNA in the presence of the enzyme reverse transcriptase. Integration –The viral double-stranded DNA produced after reverse transcription is then transported into the cellular nucleus.
Does Ritonavir cause nausea?
Gastrointestinal side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain are common, most likely because of the higher dosage of ritonavir used. Rash was also reported in up to 18% of patients in clinical trials accompanied by joint pain, fever, and myalgia.
What cells do HIV enter?
HIV virions enter the CD4+ T- cells and utilize the CD4 cells as the machinery for reproduction of new virions. The currently approved antiretroviral drugs aim at halting viral replication at 6 different stages of the HIV life cycle. Table 2lists the drugs approved by the FDA within each drug class. Table 2.
Why is it important to take HIV medication?
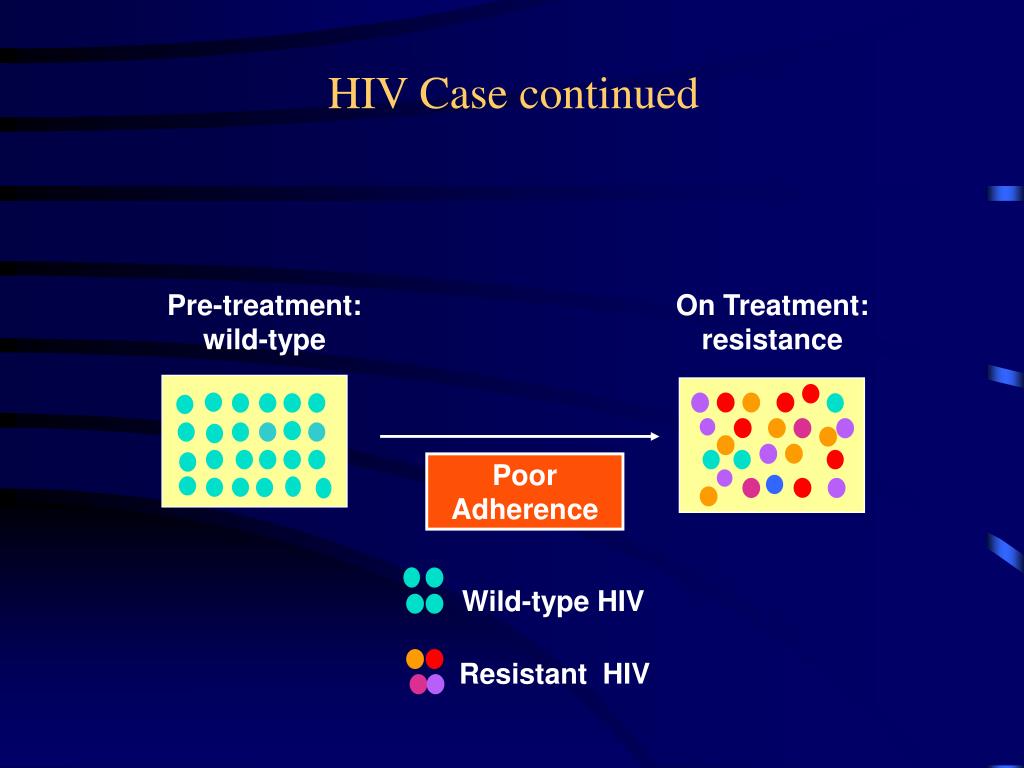
Taking HIV medication consistently, as prescribed, helps prevent drug resistance. Drug resistance develops when people with HIV are inconsistent with taking their HIV medication as prescribed. The virus can change (mutate) and will no longer respond to certain HIV medication. If you develop drug resistance, it will limit your options ...
How long does it take to get rid of HIV?
There is no effective cure for HIV. But with proper medical care, you can control HIV. Most people can get the virus under control within six months. Taking HIV medicine does not prevent transmission ...
Does HIV harm the immune system?
HIV will continue to harm your immune system. This will put you at higher risk for developing AIDS. Learn more about AIDS and opportunistic infections. This will put you at higher risk for transmitting HIV to your sexual and injection partners.
Can HIV be transmitted through sex?
If you have an undetectable viral load, you have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to an HIV-negative partner through sex. Having an undetectable viral load may also help prevent transmission from injection drug use.
Can I take pills at work?
A busy schedule. Work or travel away from home can make it easy to forget to take pills. It may be possible to keep extra medicine at work or in your car. But talk to your health care provider first. Some medications are affected by extreme temperatures and it is not always possible to keep medications at work.
Can you take a medicine if you missed it?
Missing a dose. In most cases, you can take your medicine as soon as you realize you missed a dose. Then take the next dose at your usual scheduled time (unless your pharmacist or health care provider has told you something different).
What are the different types of antiretroviral therapy?
Combination antiretroviral therapy works by blocking several stages of the HIV life cycle. There are currently six classes of antiretroviral drugs, each classified by the stage of the cycle they inhibit: 1 Entry/attachment inhibitors 2 Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) 3 Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) 4 Protease inhibitors 5 Integrase inhibitors 6 Pharmacokinetic enhancers ("boosters")
What was the life expectancy of a 20 year old man with HIV?
Prior to 1996, the average life expectancy of a 20-year-old man newly infected with HIV was a mere 19 years. 1 While the antiretroviral drugs of the time managed to slow the progression of the disease, drug resistance developed quickly, and people would often find themselves with few if any treatment options after a few short years.
How many classes of antiretroviral drugs are there?
Drug Classes. Combination antiretroviral therapy works by blocking several stages of the HIV life cycle. There are currently six classes of antiretroviral drugs, each classified by the stage of the cycle they inhibit: Entry/attachment inhibitors. Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs)
Do antiretroviral drugs kill viruses?
Antiretroviral drugs do not kill the virus; rather, they block different stages of the virus's life cycle. By doing so, the virus is unable to replicate and make copies of itself. If treatment continues without interruption, the viral population will drop to a point where it is undetectable (meaning not zero but below the level of detection with current testing technologies).
How does HIV affect the immune system?
HIV causes disease by depleting immune cells, called CD4 T-cells, that the body needs for an effective immune response. As their numbers are depleted, the body's ability to fight disease diminishes, leaving it vulnerable to an ever-widening range of opportunistic infections .
Is HIV undetectable?
On the other hand, if the virus is fully suppressed and remains undetectable, a person with HIV has a "effectively zero" chance of passing the virus to others, according to a landmark study published in May 2019 in The Lancet. 6. Undetectable HIV Equals Zero Risk of Transmission .
How do antiretroviral drugs work?
Once new viral particles are released, the cycle starts anew. Antiretroviral drugs work by blocking different stages of this cycle. When used in combination, they function as a biochemical tag team—one that is able to suppress the multitude of viral mutations that can exist within a single HIV population.
What is the NIH?
NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit www.nih.gov. NIH…Turning Discovery Into Health®.
Can HIV be suppressed without medication?
Rather, it would allow a person living with HIV to keep latent virus suppressed without daily medication. Today, people living with HIV typically must take ART—a daily regimen usually of three or more antiretroviral drugs—to stay healthy and prevent transmitting the virus to others.
What Is Antiretroviral Therapy?
How It Works
Side Effects
Tests
Other Treatments
Talk to Your Doctor
Summary
- Antiretroviral therapy is used to control HIV. It relies on drugs that inhibit points of the viral replication cycle so the virus cannot make copies of itself and infect immune system cells. Antiretroviral drugs are usually given daily in the form of a pill, which may contain a combination of drugs. These medications may have side effects. The drug...
A Word from Verywell