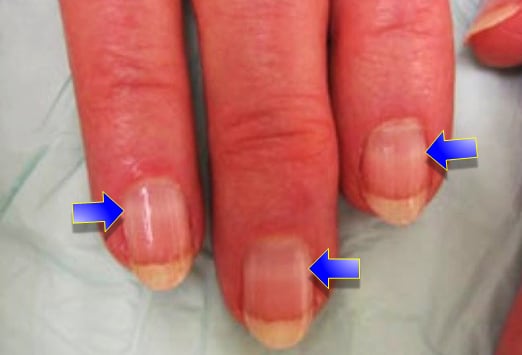
The currently recommended treatment is 2-3-dimercapto-1-propanesulfonate (DMPS) or meso 2, 3-dimer-captosuccinic acid (DMSA). These are more water soluble than BAL, and can be administered orally with lower toxicity [Mazumder et. al. 2001]. All known chelating agents have adverse side effects and should be used with caution.
Full Answer
What is DMSA used for in toxicology?
DMSA for Heavy Metals & Mercury Poisoning. DMSA is a sulfhydryl-containing substance that binds to mercury, lead, cadmium and zinc. It is a water-soluble, non-toxic, orally administered metal chelator that has been in use as an antidote for heavy metal toxicity and mercury poisoning treatment since the 1950s.
What is the efficacy of DMPS in the treatment of arsenic poisoning?
Significant improvement of symptoms and signs of chronic arsenic poisoning has been demonstrated in a prospective single blind, placebo-controlled trial with DMPS [Mazumder et al. 2001].
Is DMSA an antidote for lead poisoning?
DMSA has been FDA-approved as an antidote for lead poisoning in children in 1991, but has also been used for the treatment of mercury intoxication. Poison centers list DMSA as an antidote for arsenic and mercury, or as a general antidote for heavy metal exposure [10].
Is Bal appropriate as a treatment for systemic arsenic poisoning?
These results raise the question as to the appropriateness of BAL as the treatment for systemic arsenic poisoning. Either DMSA or DMPS, when given sc or po, will protect rabbits against the lethal systemic effects of subcutaneously administered Lewisite .

Does DMSA remove arsenic?
The combination of alpha lipoic acid and DMSA has proved to be beneficial against arsenic-mediated toxicity due to the additional benefits obtained from the chelating nature of lipoic acid as well as its ability to augment cellular GSH levels [69].
Does DMSA chelate arsenic?
DMPS (unithiol) and DMSA (succimer), dithiol water-soluble analogs of BAL, were developed in the Soviet Union and China in the late 1950s. These three agents have remained the mainstay of chelation treatment of arsenic and mercury intoxication for more than half a century.
Which antidote used in arsenic poisoning is?
Dimercaprol (2, 3 dimercaptopropanol, also known as British anti Lewisite or BAL), was previously the most frequently recommended chelating agent for arsenic. The currently recommended treatment is 2-3-dimercapto-1-propanesulfonate (DMPS) or meso 2, 3-dimer-captosuccinic acid (DMSA).
What is the treatment for arsenic?
There is no effective treatment for arsenic toxicity. There is increasing evidence that chelation therapy may benefit some people who were poisoned with arsenic. Chelation therapy involves putting a chemical called a chelating agent into the bloodstream.
What is DMPS chelation?
Abstract. DSMA and DMPS are chelating agents that are effective for treating heavy metal intoxication in humans. DMSA, an orphan drug, was approved by the U.S. FDA in January 1991 for treating childhood lead poisoning and is expected to be the drug of choice for this.
What are the side effects of DMSA?
Although DMSA it is known to be a safe agent when used in correct clinical settings, there have been reports of GI upsets, skin reactions, mild neutropenia, and elevated liver enzymes. A rare side effect reported is mucocutaneous eruptions and toxic epidermal necrosis that resolves when DMSA is discontinued.
What is the best antidote for poison?
IntroductionPoisonAntidoteFluoride (acute) and hydrofluoric acidCalcium borogluconateHeparinProtamine sulfateIronDeferoxamineLeadCalcium disodium EDTA OR Calcium disodium EDTA + dimercaprol OR Meso-2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid (Succimer) OR d-Penicillamine29 more rows
Which type of antidote is used when the nature of poison is unknown?
The most commonly used non-specific binding agent is activated charcoal. Specific binders include chelating agents, bioscavenger therapy and immunotherapy.
Can someone recover from arsenic poisoning?
Most cases of acute arsenic poisoning occur from accidental ingestion of insecticides or pesticides and less commonly from attempted suicide. Small amounts (<5 mg) result in vomiting and diarrhoea but resolve in 12 hours and treatment is reported not to be necessary.
What are the key factors in the initial management of acute arsenic intoxication?
Most frequently, removal from exposure is the key management intervention for arsenic effects due to overexposure. Gut decontamination and hemodynamic stabilization are key factors in the initial management of acute arsenic intoxication.
What is the OSHA standard for arsenic?
OSHA is the federal regulatory agency responsible for enforcing federal workplace health standards. OSHA’s standard for arsenic also requires that medical examinations be provided for all employees exposed to levels of inorganic arsenic above the action level of 5 micrograms per meter cubed for at least 30 days per year.
How long after exposure to arsenic can you use chelation?
In animal models, the efficacy of chelation therapy generally declines as the time elapsed since exposure increases. If patients are treated within several hours after arsenic ingestion, chelation is likely to be beneficial.
What is the best chelating agent for arsenic?
Dimercaprol (2, 3 dimercaptopropanol, also known as British anti Lewisite or BAL), was previously the most frequently recommended chelating agent for arsenic. The currently recommended treatment is 2-3-dimercapto-1-propanesulfonate (DMPS) or meso 2, 3-dimer-captosuccinic acid (DMSA).
Is arsenic exposure asymptomatic?
Patients presenting to their primary care providers with a history of arsenic exposure will vary widely in their clinical condition. Some will be asymptomatic. Some will just be beginning to show signs of arsenic-associated disease, and others will have more established disease. The care provided, including any referrals made, ...
Can you have gastric lavage after arsenic poisoning?
Aggressive intravenous fluid replacement therapy may be life–saving in severe poisoning. Gastric lavage may be useful soon after an acute ingestion to prevent further absorption.
Can vitamin A be used for keratosis?
Studies suggest that the use of vitamin A analogs ( retinoids) may be useful in treating pre-cancerous arsenical keratoses [Elmariah et al. 2008]. Recovery from chronic arsenic toxicity, particularly from the resulting peripheral neuropathy, may take months and may not be complete.
What are the side effects of DMPS?
Side effects in people who have generally tolerated DMPS include dizziness and weakness, the lowering of blood pressure, and flu-like symptoms.
What happens when you mix bentonite clay with water?
When you mix bentonite clay with water, it creates a large negatively charged surface area. When the body is in a tub of warm water, the warm water opens up the pores of the skin, and the positively charged toxic particles are drawn through the pores of the skin, to be absorbed by the clay.
How long does an IV treatment last?
Typically, twenty to thirty or even more IV treatments are needed to eliminate toxins from the body, and the sessions last anywhere from 90 minutes to 3 hours. Side effects may include dizziness, headache, mild nausea, or irritation at the IV site.
What are the health effects of heavy metals?
Heavy metal toxicity or poisoning can lead to any number of health conditions including autoimmune disease, cardiovascular disease, chronic pain, chronic fatigue, numerous neuromuscular disorders and diabetes.
Is DMPS an experimental drug?
DMPS can also be taken orally, intravenously, or as a suppository, though it is most commonly given as an infusion or injection. It is an experimental drug, and has NOT been approved by the FDA.
Is oral DMSA safe?
Oral administration is generally safer, because a patient can monitor the dose and test for side effects. The side effects of DMSA include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, appetite loss and rashes. As with other chelating drugs, kidney and liver function needs to be closely monitored.
Is DMSA safer than DMPS?
DMSA comes in capsule or suppository form, and is considered to be much safer than DMPS. In research studies, DMSA was proven to be three times less toxic than DMPS. DMSA is commonly prescribed orally. Oral administration is generally safer, because a patient can monitor the dose and test for side effects.
