
What is the most common application of heat treatment?
The most common application is metallurgical. Heat treatments are also used in the manufacture of many other materials, such as glass. Heat treatment involves the use of heating or chilling, normally to extreme temperatures, to achieve a desired result such as hardening or softening of a material.
What types of metals can be heat treated?
About 80% of heat treated metals are different grades of steel. Ferrous metals that can be heat treated include cast iron, stainless steel and various grades of tool steel.
What are the different types of heat treatment in machining?
Types of Heat Treatment and Their Purposes in Machining. 1 Hardening. Hardening involves the heating of the metal material to a specific temperature. This temperature is the point at which the elements present ... 2 Tempering. 3 Annealing. 4 Normalizing.
What is the best book to learn about heat treatment?
Reed-Hill, Robert (1994). Principles of Physical Metallurgy (3rd ed.). Boston: PWS Publishing. Wikimedia Commons has media related to Heat treatment.

What heat treatment would produce the highest strength?
After the hardening (830-860o C and oil quench) process, the tempering temperature determines the properties obtained: the highest tensile and yield strength is obtained after tempering at 450 oC, while the highest impact strength is seen after tempering at 650 oC.
Which process of heat treatment gives better accuracy?
Annealing is carried out to soften the metal. It makes the metal more suitable for cold working and forming. It also enhances the metal's machinability, ductility and toughness. Annealing is also useful in relieving stresses in the part caused due to prior cold working processes.
Which steel is best for heat treatment?
The plain medium-carbon steels have low hardenabilities and can successively heat treated only in thin sections and with very rapid quenching rates. High Carbon steel have carbon contents between 0.6-1.4 wt%. these are the hardest strongest but least ductile among the carbon steels.
What materials should be heat treated?
Although iron and steel account for the vast majority of heat treated materials, alloys of aluminum, copper, magnesium, nickel and titanium may also be heat treated.
In which type of heat treatment process we get better mechanical properties for steel?
TEMPERING. Tempering is a method of heat treating used to increase the resilience of iron-based alloys like steel. Iron-based metals are very hard, but they are often too brittle to be useful for most purposes.
What is the most important heat treatment for hardening steels?
martensite formationAnswer. The most important heat treatment for steels is martensite formation by heating steel into the austenite region and quenching.
Can high carbon steel be heat treated?
When steel with a medium to high carbon content is subjected to heat treatment, it can be hardened. Depending on steel's carbon content, they can be heated to specific temperatures (780 oC to 850 oC) and then quenched in oil or water to cool them quickly.
What is the best steel for hardening?
Carbon is the most important hardening element in steel or cast iron.1045 carbon steel (0.45%carbon). ... 4140/709M alloy steel (0.40%carbon). ... 4340 alloy steel (0.40%carbon). ... EN25 alloy steel (0.30%carbon). ... EN26 alloy steel (0.40%carbon). ... XK1340 carbon steel (0.40%carbon). ... K245 tool steel (0.65% carbon).More items...•
Can you heat treat stainless steel?
Types of stainless steel Austenitic stainless steels cannot harden via heat treatment. Instead, these steels work harden (they attain hardness during their manufacture and formation). Annealing these stainless steels softens them, adds ductility and imparts improved corrosion resistance.
Does heat treating metal make it stronger?
Heat treating can improve wear resistance by hardening the material. Metals (including steel, titanium, inconel, and some copper alloys) can be hardened either on the surface (case hardening) or all the way through (through hardening), to make the material stronger, tougher, more durable and more resistant to wear.
Can plastic be heat treated?
Heat treating plastics is a procedure to bond the particles, to polish it and to avoid cracking during the production process. After polymers go through heat treating, their mechanical and thermal properties improve. Moreover, the method removes internal stresses of the material.
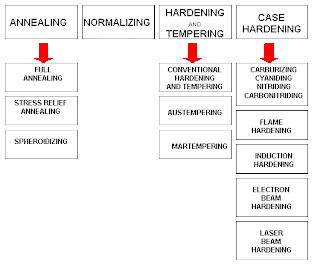
How many types of heat treatment are there?
4 TypesWhat are the 4 Types of Heat Treating Processes? Common types of heat treating methods include annealing, hardening, quenching, and stress relieving, each of which has its own unique process to produce different results.
What is the purpose of heat treating metals?
grain size and composition) is one of the most effective factors that can determine the overall mechanical behavior of the metal. Heat treatment provides an efficient way to manipulate the properties of the metal by controlling the rate of diffusion and the rate of cooling within the microstructure. Heat treating is often used to alter the mechanical properties of a metallic alloy, manipulating properties such as the hardness, strength, toughness, ductility, and elasticity .
How does heat treatment work?
These tend to consist of either cooling different areas of an alloy at different rates, by quickly heating in a localized area and then quenching, by thermochemical diffusion, or by tempering different areas of an object at different temperatures, such as in differential tempering.
What color is tempered steel?
Very hard tools are often tempered in the light to the dark straw range, whereas springs are often tempered to the blue. However, the final hardness of the tempered steel will vary, depending on the composition of the steel. Higher-carbon tool steel will remain much harder after tempering than spring steel (of slightly less carbon) when tempered at the same temperature. The oxide film will also increase in thickness over time. Therefore, steel that has been held at 400˚F for a very long time may turn brown or purple, even though the temperature never exceeded that needed to produce a light straw color. Other factors affecting the final outcome are oil films on the surface and the type of heat source used.
What is a heat treating schedule?
Complex heat treating schedules, or " cycles," are often devised by metallurgists to optimize an alloy's mechanical properties. In the aerospace industry, a superalloy may undergo five or more different heat treating operations to develop the desired properties. This can lead to quality problems depending on the accuracy of the furnace's temperature controls and timer. These operations can usually be divided into several basic techniques.
What is the process of heating something to alter it?
Process of heating something to alter it. Heat treating furnace at 1,800 °F (980 °C) Heat treating (or heat treatment) is a group of industrial, thermal and metalworking processes used to alter the physical, and sometimes chemical, properties of a material. The most common application is metallurgical. Heat treatments are also used in the ...
Why is heat treatment called an arrest?
This temperature is referred to as an "arrest" because at the A temperature the metal experiences a period of hysteresis.
What is differential hardening?
Some techniques allow different areas of a single object to receive different heat treatments. This is called differential hardening. It is common in high quality knives and swords. The Chinese jian is one of the earliest known examples of this, and the Japanese katana may be the most widely known. The Nepalese Khukuri is another example. This technique uses an insulating layer, like layers of clay, to cover the areas that are to remain soft. The areas to be hardened are left exposed, allowing only certain parts of the steel to fully harden when quenched.
What is the most common heat treatment process?
The most common heat treatment process of all, hardening is used to increase the hardness of a metal. In some cases, only the surface may be hardened. A work piece is hardened by heating it to the specified temperature, then cooling it rapidly by submerging it into a cooling medium. Oil, brine or water may be used.
Why do we heat treat?
There are various reasons for carrying out heat treating. Some procedures make the metal soft, while others increase hardness. They may also affect the electrical and heat conductivity of these materials.
How many heat treatment steps are there for metal?
For instance, some super alloys used in the aircraft manufacturing industry may undergo up to six different heat treating steps to optimise it for the application.
Which media absorbs heat the fastest?
The sequence of cooling media named above is in decreasing order of effective rate of cooling. Brine absorbs heat fastest, while air is the slowest. It is also possible to use furnaces in the cooling process.
What are the factors that affect the final outcome of a metal treatment?
These include the time of heating, time of keeping the metal part at a certain temperature, rate of cooling, surrounding conditions, etc. The parameters depend on the heat treatment method, type of metal and part size. Over the course of this process, the metal’s properties will change.
What is heat treating?
Heat treating can be applied to the part before to make the material more machinable, or the components may be machined before the final hardening and heating stages. Heat treating can affect a number of different aspects of the metal including strength, hardness, toughness, machinability, formability, ductility, and elasticity.
Why is heat treatment important?
The heat treatment can be an essential part of the precision machining process to transform metals and ensure your pieces and parts perform as you need them to. Talk to one of our qualified precision engineers about your requirements and how to find the right method of heat treating for your precision engineering project.
Why is steel treated in air cooled?
The heat treating in normalization causes smaller austenitic grains, while air cooling produces more refined ferritic grains. This process improves machinability, ductility, and strength of the steel.
Why is case hardening used?
High heat is used in combination with other elements and chemicals to produce a hardened outer layer. Because hardening can make metals more brittle, case hardening can be useful for applications that require a flexible metal with a durable wear layer.
Why do we use tempering?
Tempering is a method of heat treating used to increase the resilience of iron-based alloys like steel. Iron-based metals are very hard, but they are often too brittle to be useful for most purposes. Tempering can be used to change the hardness, ductility, and strength of metal, which usually makes it easier to machine. The metal will be heated to a temperature below the critical point as lower temperatures reduce brittleness while maintaining hardness. For increased plasticity with less hardness and strength, higher temperatures are required.
How does heat treat metal?
Heat treating addresses those deficiencies by bringing the metal into a reliable solution with fine particles to strengthen the metal. Once the metal is thoroughly heated to the right temperature to produce a solid solution, it is quickly quenched to trap the particles in solution.
What happens when metal is heated to the right temperature?
Once the metal is thoroughly heated to the right temperature to produce a solid solution, it is quickly quenched to trap the particles in solution. In precipitation hardening, impurity particles are added to the metal alloy to increase strength further.
Why do people heat treat metal?
Long before many of today’s technological advances, people have heat-treated metals to improve their physical and chemical properties for a given application . In the middle ages, blacksmiths forged and tempered metals (albeit in a relatively crude fashion) to create blades, tools, and goods for everyday life.
What is the alternative to high temperature carburizing?
The alternative to the high temperature carburizing/carbonitriding is nitriding/nitrocarburizing. It also produces hardened surface layers and similar wear resistances, but it diffuses nitrogen throughout the surface layer (not carbon), and it uses sub-critical processing temperatures.
How deep is case hardening?
These processes create hardened surface layers range from 0.01 to 0.25 in. deep, depending on processing times and temperatures. Making the hardened layer thicker incurs higher costs due to additional processing times, but the part’s extended wear life can quickly justify additional processing costs. Material experts can apply these processes to provide the most cost-effective parts for specific applications.
What are the properties of quenching and tempering?
For parts with additional heat treat processes used to modify surface properties, quench and temper determine a part’s core properties such as hardness, strength, and ductility.
What is the advantage of carburizing steel?
As mentioned, the advantage of carburization is a deep wear resistance layer with high hardness. This is ideal for gears, blades, and cutting tools. Carburization creates hard, durable parts from lower cost alloyed steels and low carbon steels, such as 1008, 1018, and 8620.
What is induction hardening?
That’s because in induction hardening, heating is carried done by via magnetic coils designed to match the part’s geometry .
What steels are martensitic?
Not all ferrous alloys are eligible for this hardening mechanism, but martensitic stainless steels such as 17-4, 15-5, and 13-8 are excellent candidates, as well as maraging steels. (The term “maraging” combines the two words "martensitic" and "aging.".
What are the two methods of surface heat treatment?
Make the surface of steel quickly get high temperature. The main methods of surface heat treat are flame quenching and induction heat treatment. The oxyacetylene, ethylene oxide and etc are the most useful heat sources.
What is chemical heat treatment?
Chemical Heat Treatment. It is to change the chemical composition, structure, properties of steel material surface. It can change the chemical composition of the surface layer of the steel material. It is a big difference between chemical heat treatment and surface heat treatment. The way of chemical heat treatment is to heat ...
How does heat treatment change the chemical composition of steel?
It is to change the chemical composition, structure, properties of steel material surface. It can change the chemical composition of the surface layer of the steel material. It is a big difference between chemical heat treatment and surface heat treatment. The way of chemical heat treatment is to heat the material in a medium (gas, liquid, solid) containing carbon, nitrogen or other alloying elements for a long time. To make the carbon, nitrogen, boron and chromium elements get into its surface layer. After that, also need other heat treatments sometimes, such as quenching and tempering. Carburizing, nitriding are the main methods of chemical heat treatment.
What is thermomechanical treatment?
The way of thermomechanical treatment needs pressure processing deformation and heat treatment effectively combining. It will make the steel material get good hardness and toughness. The heat treatment performed in a vacuum atmosphere or in a vacuum is referred to as a vacuum heat treatment. It not only can prevent the alloy steel material ...
How does heat treatment affect steel?
Heat treatment is one of the most important processing for the production of machine fittings and mold base. It can control all kinds of properties of steel material. Such as wear resistance, corrosion resistance, magnetic properties and so on. Use the right heat treatment processing to the gear wheel, its useful life would longer than the general ones. By the way, adding some alloy elements to low-quality carbon steel would make it improve the properties. Then it can use to instead of some heat-resistant steel and stainless steel. And almost all of the alloy steel needs to be through heat treatment before the use. Heat treatment is one of the most effective technological skill to maximizing the potential properties of steel. The purpose of make steel been through heat treatment is to get the desired structure and properties. Truly understand the influence of heat treatment on the properties of steel. Then make an effective and right heat treatment way is really important.
Why is steel heat treated?
The purpose of make steel been through heat treatment is to get the desired structure and properties.
What temperature should steel be kept at?
The steel after quenching is kept warm for a long time at a suitable temperature above room temperature and below 650 ° C and then cooled. These four steps will evolve different heat treatment according to the different temperature and the way of cooling.
Why use heat treated metal?
Using effectively heat-treated metal parts ensures the effective and cost-effective running of machines. Furthermore, the product will be a lot more efficient, even for the toughest applications. Also, there may be the need for extremely hard metals for some applications.
How does heat treatment improve mechanical properties?
Conclusion. Heat treatment of metals is a great way of improving the mechanical properties of metals. Asides from the physical, it can also improve the electrical and magnetic properties of a metal. This further improves the compatibility of the part with other materials.
Why do we heat treat steel?
This is another heat treatment process that helps to increase the resilience of steel. Iron-based alloys are usually hard but often too brittle for certain applications. Tempering helps to alter the hardness, brittleness, and ductility of the metal. This is in a bid to make the machining process easier.
What is the process of making metal harder?
This usually made the metal a lot harder and less brittle. This is a basic process called heat treatment of metals. Modern machining and metalworking processes are now more precise and sophisticated. Many different techniques help shape metals for various purposes.
What would happen if metals were not heat treated?
Without the heat treatment of metals, there may be nothing like metal parts for devices and equipment. Even if they existed, they wouldn’t function in the right manner. For example, non-ferrous metal parts would be too weak for several applications.
What happens to the microstructure of a metal when it is hot?
While the metal is hot, the microstructure changes . This is the physical structure of the metal. The change in the structure ultimately results in a change in the physical properties of the metal. The ‘soak time’ is the amount of time used to heat the metal.
What temperature does heat treatment go to?
The first step involves the heating of the metal or alloy to the required temperature. Sometimes, the temperature goes up to 2400°F. It is held at the temperature for a specified amount of time before cooling.
What are the different types of heat treatment?
Types of Heat Treatment. 1. Annealing. Annealing is one of the most important processes of heat treatment. It is one of the most widely used operations in the heat treatment of iron and steel and is defined as the softening process.
Why is heat treatment done?
The heat treatment is done to improve the machinability. To improve magnetic and electrical properties. To increase resistance to wear, heat and corrosion, ...
What is tempered steel?
It is an operation used to modify the properties of steel hardened by quenching for the purpose of increasing its usefulness. Tempering or draw results in a reduction of brittleness and removal of internal strains caused during hardening. Steel must be tempered after the hardening process.
What is the purpose of normalizing steel?
Normalizing. Normalizing: The main aim of normalizing is to remove the internal stresses developed after the cold working process. In this, steel is heated 30 – 50°C above its upper critical temperature and cooling it in the air. It improves mechanical and electrical properties, machinability & tensile strength.
How to reheat steel?
The reheating is done in a bath of oil or molten lead or molten salt. The specimen is held in the bath for a period of time till attains the temperature evenly , the time depends on the composition and desired quality of steel. Now the specimen is removed from the bath and allow to cool slowly in still air.
What is the name of the atom that makes a material hard?
Due to this, a nitrogen atom is deposited and makes material hard. Induction hardening and Flame hardening objects are heated by an oxy-acetylene flame.
What temperature is steel heated to?
The steel is heated to a temperature of about 40° to 50°C above its upper critical temperature. It is held at this temperature for a short duration. The steel is then allowed cool in still air at room temperature, which is known as air quenching.
What aircraft uses heat treating material?
It is used in the manufacture of advanced commercial aircraft such as the Boeing 777, Airbus 380, and military aircraft such as the Boeing UCAV or the Boeing F/A-18 E/F. When used in conjunction with aluminum alloys, the term ‘heat treating’ is generally restricted ...
What is the purpose of heat treating aluminum?
When used in conjunction with aluminum alloys, the term ‘heat treating’ is generally restricted to solution heat treatment, quenching, and subsequent aging of aluminum alloys to increase strength and hardness . These usually are referred to as the ‘heat-treatable’ alloys to distinguish them from those alloys in which no significant strengthening can be achieved by heating and cooling. The latter, generally referred to as ‘non-heat-treatable’ alloys, depend primarily on cold work to increase strength.
What is age hardening alloy?
Age-hardening alloys are precipitation strengthened indicated by heat-treatment tempers (T-tempers). Depending on the alloying elements, strengthening of aluminum can be achieved by heat treatment or by solid solution strengthening (often in conjunction with work hardening).
What is a non-heat treatable alloy?
These usually are referred to as the ‘heat-treatable’ alloys to distinguish them from those alloys in which no significant strengthening can be achieved by heating and cooling. The latter, generally referred to as ‘non-heat-treatable’ alloys, depend primarily on cold work to increase strength.
Is zinc a good addition to aluminum?
Zinc confers little solid solution strengthening or work hardening to aluminum, and no significant technical benefits are obtained by the addition of just zinc to aluminum. However, the addition of copper and/or magnesium with zinc results in attractive compositions for heat treating or natural aging. Usually, other elements, such as chromium, are also added in small quantities.
Is magnesium good for aluminum?
The main benefit to adding magnesium to aluminum-copper alloys is the increased strength possible following solution heat-treatment and quenching. In both casting and wrought alloys, as little as 0.05 percent magnesium is effective in changing aging characteristics.
Is aluminum a good material?
Aluminum’s many desirable properties, such as high strength-to-weight ratio, good corrosion resistance, ease of processing, and low cost, make it a very widely used material in many applications. Because of this wide use, designers are often challenged with selecting the “best choice” from numerous alloys and several heat-treating processing ...
What is heat treatment of steel?
Heat Treatment of steels is called the heating and cooling process to achieve certain microstructural features for a wide range of applications. If required properties and microstructural features do not match with criteria than the process is said to be defective.
How to prevent defects in heat treatment?
First and foremost, a method to prevent these usual defects of heat treatment is to perform heat treatment of steel in Vacuum or molten salts or a protective atmosphere. The protective atmosphere includes dried producer gas or dissociated products of ammonia.
Why is steel hard after heat treatment?
After heat treatment, not getting desired hardness or strength can become a cause of stress. Following are common reasons for lower hardness and stress in steel after heat treatment; Lower hardening temperature. For higher hardness and strength, martensitic formation is very important.
Why do steels need martensitic formation?
Martensitic steels are commonly used in the defense industry, powder metallurgy, and cutting tools industry. These types of steel undergo a series of heat treatments for achieving desired hardness and strength. After heat treatment, not getting desired hardness or strength can become a cause of stress.
What is Brinell hardness test?
The Brinell hardness test is commonly used in industry for large parts that do not have surface finished. Rockwell hardness test is used for finished parts which are considered non-destructive in nature and will not affect surface features of steel parts. For Laboratory testing and specific hardness of phases in steel, the Vicker hardness test is used.
How does slow heating and cooling affect steel?
In the case of slow heating and cooling, steel will get enough time to release stresses by bringing change in dimensions. With severe cooling, heat distribution in the sample will not be uniform bringing step-wise changes to cause the development of internal stresses.
Who wrote the book Heat Treatment?
Heat treatment: Principle and Techniques by C.P Sharma.
Overview
Techniques
Complex heat treating schedules, or " cycles," are often devised by metallurgists to optimize an alloy's mechanical properties. In the aerospace industry, a superalloy may undergo five or more different heat treating operations to develop the desired properties. This can lead to quality problems depending on the accuracy of the furnace's temperature controls and timer. These operation…
Physical processes
Metallic materials consist of a microstructure of small crystals called "grains" or crystallites. The nature of the grains (i.e. grain size and composition) is one of the most effective factors that can determine the overall mechanical behavior of the metal. Heat treatment provides an efficient way to manipulate the properties of the metal by controlling the rate of diffusion and the rate of cooling within th…
Effects of composition
The specific composition of an alloy system will usually have a great effect on the results of heat treating. If the percentage of each constituent is just right, the alloy will form a single, continuous microstructure upon cooling. Such a mixture is said to be eutectoid. However, If the percentage of the solutes varies from the eutectoid mixture, two or more different microstructures will usually form sim…
Effects of time and temperature
Proper heat treating requires precise control over temperature, time held at a certain temperature and cooling rate.
With the exception of stress-relieving, tempering, and aging, most heat treatments begin by heating an alloy beyond a certain transformation, or arrest (A), temperature. This temperature is referred to as an "arrest" because at the A temperature the metal experiences a period of hystere…
Specification of heat treatment
Usually the end condition is specified instead of the process used in heat treatment.
Case hardening is specified by hardness and case depth. The case depth can be specified in two ways: total case depth or effective case depth. The total case depth is the true depth of the case. For most alloys, the effective case depth i…
Furnace types
Furnaces used for heat treatment can be split into two broad categories: batch furnaces and continuous furnaces. Batch furnaces are usually manually loaded and unloaded, whereas continuous furnaces have an automatic conveying system to provide a constant load into the furnace chamber.
Batch systems usually consist of an insulated chamber with a steel shell, a hea…
See also
• Carbon steel
• Carbonizing
• Diffusion hardening
• Induction hardening
• Retrogression heat treatment
The Benefits
Heat Treatment Process Steps
Phase Diagrams
Common Heat Treatment Methods
What Metals Are Suitable For Heat Treating?
- Although ferrous metals account for the majority of heat treated materials, alloys of copper, magnesium, aluminium, nickel, brass, and titanium may also be heat treated. About 80% of heat treated metals are different grades of steel. Ferrous metals that can be heat treated include cast iron, stainless steel and various grades of tool steel. Process...