What are XO inhibitors for gout?
One such option is the xanthine oxidase inhibitor (XO inhibitors) class of medications. These drugs present a powerful opportunity to reduce the chances of a gout attack. This article will review the members of the class, how they work, and what costs and concerns must be considered before using them. What are xanthine oxidase inhibitors?
How do xanthine oxidase inhibitors work?
Xanthine oxidase inhibitors are urate-lowering drugs used in the treatment of gout. Urate is the salt form of uric acid. At low levels, uric acid circulates harmlessly through our bloodstream and is excreted by our kidneys.
Does oxypurinol inactivate xanthine oxidoreductase?
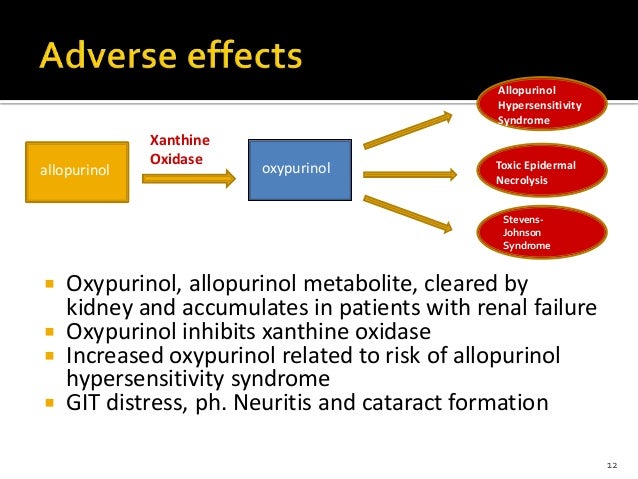
Allopurinol and its primary breakdown product oxypurinol inactivate xanthine oxidoreductase, the enzyme complex made up of xanthine oxidase and the sister version of XO, xanthine dehydrogenase. Consequently, in the setting of allopurinol, xanthine oxidase cannot act on its two substrates to produce urate.

Which of the following drugs inhibits xanthine oxidase and is used for treatment of gout?
Allopurinol. Allopurinol, a xanthine oxidase inhibitor, is commonly used for the treatment of hyperuricemia and gout.
Which of the following drug are xanthine oxidase inhibitor?
An xanthine oxidase inhibitor is any substance that inhibits the activity of xanthine oxidase, an enzyme involved in purine metabolism....Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors.DrugTargetTypeFebuxostatUDP-glucuronosyltransferase 2B7enzymeFebuxostatCytochrome P450 1A2enzymeFebuxostatCytochrome P450 2C8enzymeFebuxostatCytochrome P450 2C9enzyme14 more rows
What is a xanthine oxidase inhibitor used for?
Xanthine oxidase inhibitors are primarily used in the clinical prevention and treatment of gout associated with hyperuricemia. The archetypal xanthine oxidase inhibitor, Allopurinol has been shown to have other beneficial effects such as a reduction in vascular reactive oxygen species and mechano-energetic uncoupling.
What drug is the first non purine inhibitor of xanthine oxidase for the treatment of gout?
As a non-purine selective XO inhibitor, febuxostat inhibits both oxidized and reduced types of XO. It does not inhibit enzymes involved in purine or pyrimidine metabolism, as does allopurinol.
Does allopurinol inhibit xanthine oxidase?
Allopurinol was effective in inhibiting xanthine oxidase activity in vivo as measured by the dramatic reduction of uric acid production.
Is Febuxostat a xanthine oxidase inhibitor?
Febuxostat: a selective xanthine oxidase inhibitor for the treatment of hyperuricemia and gout.
Does allopurinol bind to xanthine oxidase?
Allopurinol and its metabolite oxypurinol are analogs of hypoxanthine and xanthine, respectively, and prevent the formation of UA by binding to XO and inhibiting it [22].
Which medication used in the treatment of gout prevents the conversion of xanthine to uric acid?
Allopurinol was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 1966 for treatment of gout and remains a mainstay in the therapy of primary and secondary hyperuricemia. The mechanism relates to the inhibition of XO-catalyzed formation of uric acid from hypoxanthine and xanthine.
What is inhibited by allopurinol?
Allopurinol is an inhibitor of xanthine oxidoreductase (XOR) and inhibits the generation of uric acid (UA) as the final product of purine catabolism, as well as the resulting generation of superoxide (O2(-)), in humans.
Which of the following drugs used in the treatment of gout has as its primary effect the reduction of uric acid synthesis?
Allopurinol (Zyloprim, Aloprim) It is the most effective therapy for lowering serum uric acid.
What type of inhibitor is allopurinol?
Allopurinol is in a class of medications called xanthine oxidase inhibitors. It works by reducing the production of uric acid in the body. High levels of uric acid may cause gout attacks or kidney stones.
Is allopurinol a substrate for xanthine oxidase?
Allopurinol is also a substrate for xanthine oxidase and the product of the reaction, oxypurinol (alloxanthine), is also an inhibitor.
How do xanthine oxidase inhibitors work?
Xanthine oxidase inhibitors are medications prescribed for the treatment of gout, a painful condition caused by excessive uric acid levels in the blood ( hyperuricemia ). Uric acid is a waste product from the metabolization of purine, an essential chemical compound in the body, also found in many foods.
How are xanthine oxidase inhibitors used?
Xanthine oxidase inhibitors may be administered as oral tablets or intravenous (IV) injections, and are approved by FDA to prevent and treat the following conditions:
