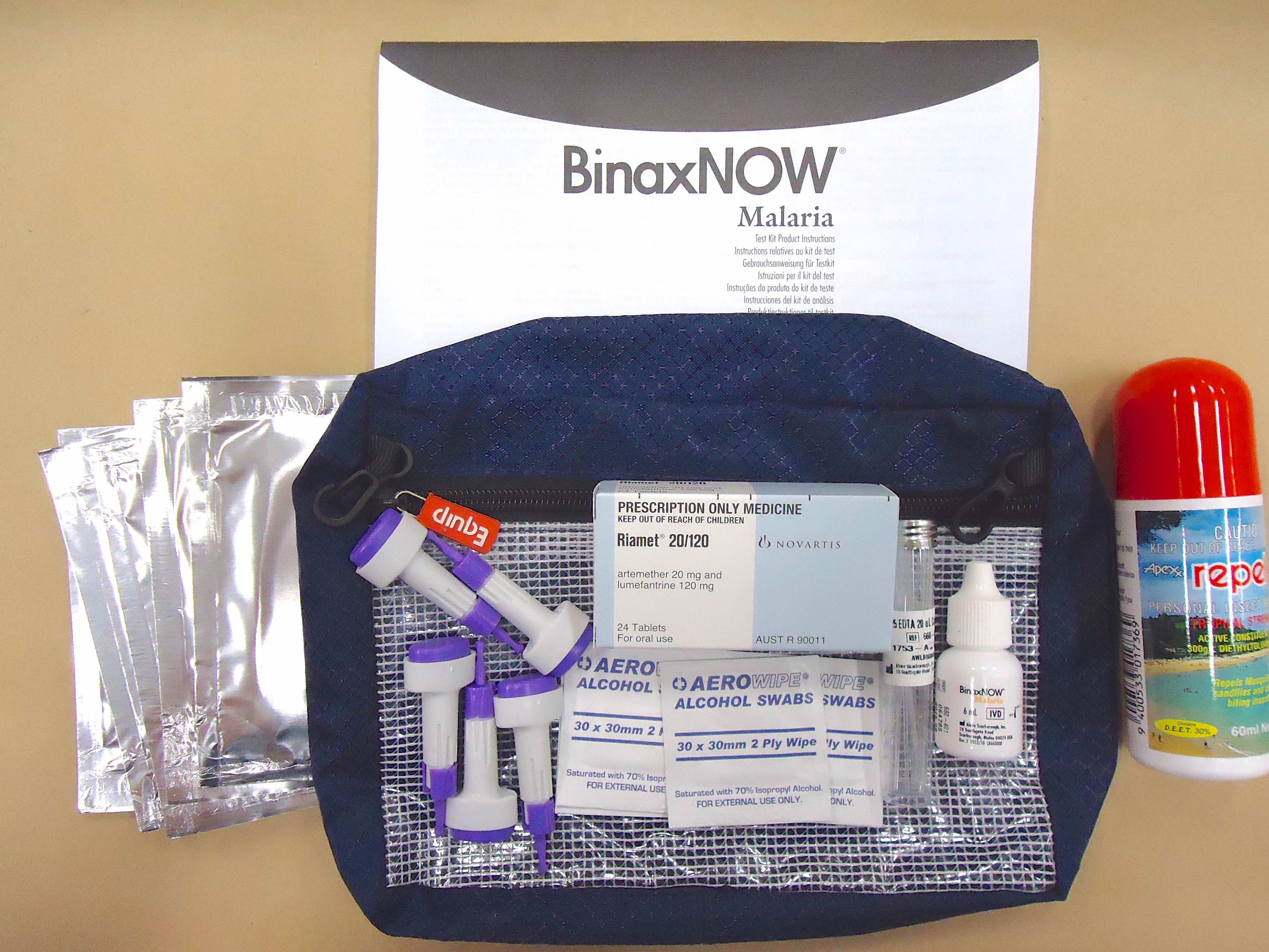
Which drug is used for malaria chemoprophylaxis?
Table 4-10. Drugs used in the prophylaxis of malariaDRUGUSAGEAtovaquone-proguanilProphylaxis in all areasChloroquineProphylaxis only in areas with chloroquine-sensitive malariaDoxycyclineProphylaxis in all areas1 more row
What drugs are used for chemoprophylaxis?
Pre-exposure Prophylaxis Doxycycline, Mefloquine, other drugs listed above. Mefloquine taken weekly for 2 weeks prior to travel. Doxycycline is taken daily for 2 days prior to travel. Both drugs are taken for the duration of travel and for 4 weeks after return.
Which medicine is best for treating malaria?
Medications. The most common antimalarial drugs include: Chloroquine phosphate. Chloroquine is the preferred treatment for any parasite that is sensitive to the drug.
What is the drug used in short term chemoprophylaxis?
falciparum endemic areas, doxycycline 100mg once a day is now recommended as the drug of choice for short term prophylaxis....Malaria Prophylaxis.Drugs and Dosage for ChemoprophylaxisDrugsProguanilDosage200 mg daily< 2 yrs: 50 mg/day; 2-6 yrs: 100 mg/day; 7-9 yrs: 150 mg/day; >9 yrs: 200 mg/dayPros and ConsUsed in combination5 more columns
How does chemoprophylaxis work malaria?
An experimental approach involves preventing the parasite from binding with red blood cells by blocking calcium signalling between the parasite and the host cell. Erythrocyte-binding-like proteins (EBLs) and reticulocyte-binding protein homologues (RHs) are both used by specialized P.
Which of the above drugs may used for causal prophylaxis in malaria?
Doxycycline, a synthetically derived tetracycline, is a highly effective drug for the prevention of malaria. In studies conducted in non-immune populations, the dosage used was 100mg daily, resulting in greater than 95% efficacy against P.
What are the names of malaria drugs?
chloroquine (Aralen),doxycycline (Vibramycin, Oracea, Adoxa, Atridox),quinine (Qualaquin),mefloquine (Lariam),atovaquone/proguanil (Malarone),artemether/lumefantrine (Coartem), and.primaquine phosphate (Primaquine).
What antibiotics are used to treat malaria?
Doxycycline: This daily pill is usually the most affordable malaria drug. You start taking it 1 to 2 days before your trip and continue taking it for 4 weeks afterward.
What is the latest treatment for malaria?
Artemether-lumefantrine (Coartem™) is the preferred follow-on treatment but adequate alternatives are atovaquone-proguanil (Malarone™), quinine plus doxycycline or clindamycin, or mefloquine.
Is ivermectin used to treat malaria?
Ivermectin is widely used in mass drug administrations for controlling neglected parasitic diseases, and can be lethal to malaria vectors that bite treated humans. Therefore, it could be a new tool to reduce plasmodium transmission.
Is doxycycline used to prevent malaria?
Doxycycline is an antibiotic that also can be used to prevent malaria. It is available in the United States by prescription only. It is sold under multiple brand names and it is also sold as a generic medicine. It is available in tablets, capsules, and an oral liquid formulation.
What is malaria agent?
Malaria is caused by a single-celled parasite of the genus plasmodium. The parasite is transmitted to humans most commonly through mosquito bites.
Overview
Medications
In choosing the agent, it is important to weigh the risk of infection against the risks and side effects associated with the medications.
An experimental approach involves preventing the parasite from binding with red blood cells by blocking calcium signallingbetween the parasite and the host cell. Erythrocyte-binding-like proteins (EBLs) and reticulocyte-binding protein h…
Strategies
• Risk management
• Bite prevention—clothes that cover as much skin as possible, insect repellent, insecticide-impregnated bed nets and indoor residual spraying
• Chemoprophylaxis
• Rapid diagnosis and treatment
Vaccines
In November 2012, findings from a Phase III trials of an experimental malaria vaccine known as RTS,S reported that it provided modest protection against both clinical and severe malaria in young infants. The efficacy was about 30% in infants 6 to 12 weeks of age and about 50% in infants 5 to 17 months of age in the first year of the trial.
The RTS,S vaccine was engineered using a fusion hepatitis B surface protein containing epitopesof …
Risk factors
Most adults from endemic areas have a degree of long-term infection, which tends to recur, and also possess partial immunity (resistance); the resistance reduces with time, and such adults may become susceptible to severe malaria if they have spent a significant amount of time in non-endemic areas. They are strongly recommended to take full precautions if they return to an endemic area.
History
Malaria is one of the oldest known pathogens, and began having a major impact on human survival about 10,000 years ago with the birth of agriculture. The development of virulence in the parasite has been demonstrated using genomic mapping of samples from this period, confirming the emergence of genes conferring a reduced risk of developing the malaria infection. References to the disease can be found in manuscripts from ancient Egypt, India and China, illustrating its wid…
See also
• Malaria prevention
• Mosquito control