Mayoclinic.org
1. Lose extra pounds and watch your waistline...
2. Exercise regularly...
3. Eat a healthy diet...
4. Reduce sodium in your diet...
5. Limit the amount of alcohol you drink...
6. Quit smoking...
7. Cut back on caffeine...
8. Reduce your stress...
Learn More...Top10homeremedies.com
1. Lemons...antioxidant...
2. Watermelon seeds...helps widen the blood capillaries...
3. Garlic...helps relax blood vessels by stimulating the production of nitric oxide and hydrogen sulfide...
4. Banana...rich source of potassium...
5. Celery...
6. Coconut Water...
7. Cayenne Pepper...
8. Onion Juice...
Learn More...Medicalnewstoday.com
1. Walk and exercise regularly...
2. Reduce your sodium intake...
3. Drink less alcohol...
4. Eat more potassium-rich foods...
5. Cut back on caffeine...
6. Learn to manage stress...
7. Eat dark chocolate or cocoa...
8. Lose weight...
Learn More...What medications bring down diastolic blood pressure?
- Alpha blockers. Alpha blockers prevent the hormone norepinephrine (noradrenaline) from tightening the muscles in the walls of smaller arteries and veins, which causes the vessels to remain open and relaxed. ...
- Alpha-beta blockers. Alpha-beta blockers work similarly to beta blockers. ...
- Central-acting agents. ...
- Vasodilators. ...
- Aldosterone antagonists. ...
What medications lower diastolic pressure?
Some commonly used calcium channel blockers include:
- amlodipine (Norvasc)
- diltiazem (Cardizem, Tiazac)
- felodipine
What are the most common medications for hypertension?
The following list includes most of the commonly prescribed combination drugs used for hypertension:
- Moduretic (amiloride and hydrochlorothiazide)
- Lotrel (amlodipine and benazepril)
- Tenoretic (atenolol and chlorthalidone)
- Lotensin HCT (benazepril and hydrochlorothiazide)
- Ziac (bisoprolol and hydrochlorothiazide)
- Capozide (captopril and hydrochlorothiazide)
- Vaseretic (enalapril and hydrochlorothiazide)
- Lexxel (felodipine and enalapril)
What is the best medication for diastolic dysfunction?
Treatment and Prevention
- Lifestyle. Quit smoking: If you need nicotine patches to succeed, make it temporary, and slowly taper down the dosage to zero.
- Medications. Medications for conditions that put you at risk for diastolic dysfunction include those to control diabetes, blood pressure, LDL and HDL cholesterol, triglycerides, and obesity.
- A Word From Verywell. ...
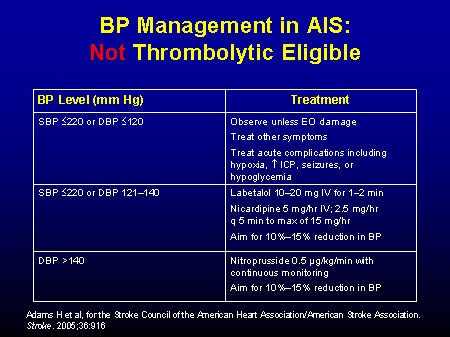
Which medicine works best on diastolic pressure?
What medications treat diastolic hypertension?Calcium channel blockers. Norvasc (amlodipine) ... Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. Prinivil, Zestril (lisinopril) ... Water pills or diuretics. Chlorthalidone. ... Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) Atacand (candesartan) ... Beta-blockers. Tenormin (Atenolol)
How do you treat high diastolic blood pressure?
Follow the 20 tips below to help lower your overall blood pressure, including diastolic blood pressure.Focus on heart-healthy foods. ... Limit saturated and trans fats. ... Reduce sodium in your diet. ... Eat more potassium. ... Lay off the caffeine. ... Cut back on alcohol. ... Ditch sugar. ... Switch to dark chocolate.More items...
Should you treat diastolic hypertension?
Although treatment is not recommended in young people in isolated diastolic hypertension, treatment should be individualized according to the underlying cardiovascular disease in the elderly.
What is the first drug of choice for hypertension treatment?
Generally, ACE inhibitors should remain the initial treatment of choice for hypertension. Angiotensin II receptor antagonists or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) are used for patients who are unable to tolerate ACE inhibitors.
Does amlodipine lower diastolic blood pressure?
Titration of amlodipine 5 to 10 mg daily resulted in a statistically significant decrease in both systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure for both age subgroups.
Does losartan lower diastolic pressure?
Diastolic pressure was reduced by 16.8 mm Hg with losartan and by 16.6 mm Hg with atenolol.
Why is my diastolic BP high?
Smoking, consuming alcohol, obesity, and high blood fat may lead to IDH. Additionally, certain groups of people have an increased risk of IDH, including younger males and people with diabetes or previous cardiovascular events.
Why is my diastolic pressure always high?
Endocrine and kidney conditions Hypothyroidism is one of the common causes of IDH. The raised diastolic pressure is the consequence of excessive arteriolar narrowing. Endocrine diseases producing significant degrees of aldosterone, parathyroid hormone, or corticosteroids can cause IDH.
What is the treatment of diastolic dysfunction?
Medications — water pills can often help to alleviate the edema that is caused by diastolic dysfunction, and other medications can help to treat underlying medical problems like high blood pressure, diabetes or other heart conditions such as atrial fibrillation.
What is the safest blood pressure medications?
Methyldopa, which works to lower blood pressure through the central nervous system, has the lowest risk of harming the mother and developing fetus. Other possible safe options include labetalol, beta-blockers, and diuretics.
What are the 4 best blood pressure drugs?
Many medications used in the past to lower blood pressure may not be the best choice for lowering your blood pressure today. The four classes of medications recommended by the most recent guidelines and research are thiazide diuretics, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, and calcium channel blockers.
Which beta blocker is best for hypertension?
Propranolol and atenolol have been studied most intensely in hypertension. For secondary prevention of myocardial infarction, the evidence is best for timolol. Sotalol is probably the best antiarrhythmic among the beta-blockers.
What is the best treatment for diastolic hypertension?
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers have been shown to be effective in improvement of measures of diastolic function and are recommended as first-line agents in the control of hypertension in patients with diastolic heart failure.
What is diastolic dysfunction?
Diastolic dysfunction is present in half of patients with hypertension and has been shown to be associated with increased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, as well as the development of heart failure. With the high prevalence of hypertension and its associated complications, treatment of diastolic dysfunction in hypertension is an important and desirable goal. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers have been shown to be effective in improvement of measures of diastolic function and are recommended as first-line agents in the control of hypertension in patients with diastolic heart failure. Beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and diuretics have also shown some efficacy in improved indices of diastolic filling. However, the independent impact of these pharmacologic interventions on prognosis and outcome in diastolic dysfunction has yet to be clarified. The Irbesartan in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (I-PRESERVE) study, Candesartan in Heart Failure: Assessment in Reduction of Mortality and Morbidity (CHARM-Preserved) trial and the Losartan Intervention For End-point Reduction in Hypertension (LIFE) Study all failed to show improved morbidity and mortality with these drugs although, the LIFE study showed reduced heart failure hospitalization in hypertensive patients with normal in-treatment diastolic function. The Trial Of Preserved Cardiac function heart failure with an Aldosterone anTagonist (TOPCAT) is an on-going large, international study evaluating the effect of spironolactone on cardiovascular mortality, aborted cardiac arrest, or hospitalization for diastolic heart failure. This and other studies will provide further insight into the pathophysiology and management of patients with diastolic dysfunction.
What are the best medications for high blood pressure?
Other common options include angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers, according to the Cleveland Clinic.
What is the name of the drug that reduces blood pressure?
This type of medication, also called a water pill, reduces blood pressure by increasing urine output. Other drugs, called first-line drugs, may also be an early choice. These include a different type of drug, called an ACE inhibitor. People with diabetes are often started on an ACE inhibitor.
What is the first number on a blood test for stage 1 hypertension?
Your doctor could diagnose you with stage 1 hypertension if your diastolic pressure is consistently 80 to 90, or your systolic blood pressure (the first or top number) is 130 to 139. Systolic pressure is higher because it occurs during the force of a heartbeat.
What happens if your diastolic pressure is higher than normal?
If your diastolic pressure is higher than normal, you have diastolic hypertension and need treatment. Of the two numbers that measure your blood pressure, the second (or lower) one indicates your blood pressure between heartbeats. That's your diastolic pressure. If it's higher than normal, you have diastolic hypertension and need treatment, ...
What is the normal blood pressure?
This pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). Normal blood pressure is less than 120 over 80, and high blood pressure is 140 over 90 or higher, according to the American Heart Association (AHA). Your doctor could diagnose you with stage 1 hypertension if your diastolic pressure is consistently 80 to 90, ...
Why is hypertension important?
Treating hypertension is important because it may prevent a stroke or heart attack, kidney disease or heart failure, according to the Cleveland Clinic, and treatment with lifestyle changes generally starts any time someone's blood pressure is consistently higher than 120 over 80.
Why is it important to treat hypertension?
Treating hypertension is important because it may prevent a stroke or heart attack, kidney disease or heart failure, according to the Cleveland Clinic , and treatment with lifestyle changes generally starts any time someone's blood pressure is consistently higher than 120 over 80. "Even for patients with stage 1 hypertension, treatment usually starts with lifestyle changes before medications," says Dr. Bungo.
What are the best ways to prevent hypertension?
So, precautions people diagnosed with hypertension should take include avoiding the following triggers: smoking, drinking alcohol and eating foods with a lot of salt and fat; and introducing exercises and a diet that is rich in vegetables and fruits.
What is the first stage of hypertension?
Of course, the first stage of hypertension is defined as a milder condition and the treatment includes beta blockers (that tranquilize the nerve response to the heart), angiotensin II receptor blockers ...
Is an alpha blocker a diuretic?
Also, diuretics are the obligatory medications, and they are followed by the same types of the drugs that are previously mentioned, but an alpha blocker could be included in the treatment, since there is a danger of acute problems, such as stroke or heart attack.
Is hypertension a health problem?
As already mentioned, hypertension is often related with and can lead to other health problems, such as a risk of coronary artery disease, a prior heart attack or stroke, and the heart failure, diabetes, a kidney disorder and anatomical problems, for example, an enlarged left chamber of the heart.
What is it called when diastolic pressure is elevated?
When only the diastolic pressure is elevated, the condition is called isolated diastolic hypertension. The condition may be a normal consequence of aging or seen in some diseases, such as diabetes mellitus.
How to reduce blood pressure?
Listen to music, take a stroll in the park, take up gardening, dance, etc. Deep breathing and meditation may also help reduce blood pressure.
What does the number on the bottom of the blood pressure chart mean?
The number on the bottom represents your diastolic blood pressure, which is the force exerted on your arteries when your heart relaxes and fills with blood. Elevated systolic or diastolic pressure is called hypertension or high blood pressure. When only the diastolic pressure is elevated, the condition is called isolated diastolic hypertension.
What causes a rise in blood pressure?
Obesity: Weight gain or obesity (especially abdominal obesity) can cause a rise in blood pressure. Aim to maintain a body mass index between 18.5 and 24.9 kg/m2.
How to avoid hypertension?
Men should limit themselves to 2 drinks a day and women to 1 drink a day. Caffeine: Drinking too much coffee or consuming caffeinated products in excess can contribute to hypertension.
Can caffeine cause hypertension?
Caffeine: Drinking too much coffee or consuming caffeinated products in excess can contribute to hypertension. If you have high blood pressure, don’t have anything with caffeine just before exercising. Smoking: Smoking causes plaque buildup in the walls of your arteries and leads to high blood pressure.
Does age affect blood pressure?
Age: The risk of hypertension increases with age. Sex: Men and women are at equal risk of developing hypertension. But while men are more likely to develop high blood pressure before the age of 55, women tend to develop it after menopause.
What is the best medication for hypertension?
It’s been shown to be a great additive medication for resistant hypertension.”. Centrally acting agents, such as clonidine (Catapres, Kapvay), guanfacine (Intuniv) or methyldopa. These medications help slow your heart rate and keep your blood vessels from constricting by interfering with signals from the brain.
What is the best treatment for blood vessels?
Angiotensin-receptor blockers, such as losartan (Cozaar) or valsartan (Diovan). ARBs help block angiotensin and relax the blood vessels.
What is the role of a vasodilator in the kidney?
Vasodilators relax the muscles in the blood vessel walls, enabling blood to flow more easily. Loop diuretics, such as bumetanide (Bumex) or ethacrynic acid (Edecrin). These diuretics act on a different part of the kidney than thiazide diuretics. “Loop diuretics are secondary players,” Ajithan says.
What is the best medicine for kidneys?
Thiazide diuretics (“water pills”), such as hydrochlorothiazide (Microzide) and chlorothiazide (Diuril). Thiazide diuretics help relieve pressure on your blood vessels by prompting the kidneys to remove excess fluid and salt from your body. Calcium channel blockers, such as amlodipine (Norvasc) or diltiazem (Cardizem). ...
How do beta blockers help your heart rate?
Beta blockers help slow your heart rate by reducing the amount of stress hormones (such as adrenaline) in the body. The drugs might be used in people with an abnormal heartbeat or a history of heart attack. “Beta blockers are good at helping the heart remodel.
What to do if blood pressure isn't lowering?
If a medication isn’t doing enough to reduce your blood pressure after one month, your doctor may increase the dose or add another drug to your regimen. Medications in this arsenal include: Beta blockers, such as atenolol (Tenormin) or metoprolol (Lopressor).
What is the standard blood pressure for a high blood pressure patient?
First Lines of Defense. When you’re initially diagnosed with high blood pressure – typically defined as a measurement at or above 130/80 millimeters of mercury (mmHg) – your doctor will consider if you have any underlying conditions.
What are some examples of blood pressure medications?
Examples are spironolactone (Aldactone, Carospir) and eplerenone (Inspra). How well a drug works for you can depend on your age, sex, race, blood pressure level and overall health.
What are some examples of medications that can cause high blood pressure?
Examples include hydralazine and minoxidil. Aldosterone antagonists. These medications are often used with other drugs, such as a diuretic. Aldosterone antagonists block the hormone aldosterone, which sometimes causes salt and fluid retention, contributing to high blood pressure.
What are some examples of ACE inhibitors?
There are several ACE inhibitors available. Examples include enalapril (Vasotec, Epaned), lisinopril (Prinivil, Zestril, Qbrelis) and ramipril (Altace). Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs). These drugs block the action of angiotensin, a chemical in your body that narrows your arteries and veins.
What are some examples of beta blockers?
Examples of beta blockers include metoprolol (Lopressor, Toprol-XL), nadolol (Corgard) and atenolol (Tenormin). Renin inhibitors. Renin is a substance produced by your kidneys that triggers a series of steps that increases blood pressure.
What are some examples of calcium channel blockers?
Examples of calcium channel blockers include amlodipine (Norvasc), diltiazem (Cardizem, Tiazac, others), nifedipine (Adalat CC, Procardia) and verapamil (Verelan, Calan). Beta blockers. These drugs work by blocking the effects of the hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline.
What are the different types of diuretics?
There are three types of diuretics: thiazide, loop and potassium-sparing. Examples of diuretics include chlorothiazide (Diuril), bumetanide (Bumex) and amiloride (Midamor). If diuretics aren't enough to lower your blood pressure, your doctor might recommend adding other blood pressure medications to your treatment.
How well do drugs work?
How well a drug works for you can depend on your age, sex, race, blood pressure level and overall health. Combining two drugs usually works better than a single drug to get your blood pressure under control. Sometimes additional medication is needed to achieve your blood pressure goal.
Does RAAS cause diastolic dysfunction?
Hypertensive patients are at increased risk of developing LV hypertrophy and myocardial fibrosis, which cause diastolic dysfunction. Because the activation of rennin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) has been shown to induce LV hypertrophy and myocardial fibrosis, the RAAS may play a central role in the pathogenic process from hypertension to diastolic HF. Inhibitors of RAAS have been considered as a treatment option for these patients, and the angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB) have been of interest because they antagonize the effects of angiotensin II more completely. However, the Irbesartan in Heart Failure with Preserved Systolic Function (I-PRESERVE) trial reported that treatment with irbesartan did not reduce the risk of death or hospitalization for cardiovascular causes among 4,128 patients who had HF with a preserved LV ejection fraction. The degree of improvement of diastolic dysfunction was associated with the extent of systolic blood pressure reduction, whether a RAAS inhibitor or non-RAAS blood pressure lowering was used. Amlodipine is a potent and well-tolerated calcium channel blocker, and seems to be appropriate for achieving more aggressive systolic blood pressure target and improving diastolic dysfunction in hypertensive patients, because amlodipine is clinically very useful for controlling systolic blood pressure. Assessment of diastolic function by echocardiography will be helpful to determine whether addition of amlodipine or an ARB to standard therapy is more beneficial to hypertensive patients with diastolic dysfunction. The investigators hypothesize that amlodipine added to standard therapy will be superior to valsartan in improving diastolic dysfunction by lowering systolic blood pressure more effectively in hypertensive patients, and try to examine this hypothesis in a prospective, open-label, randomized comparison study using blinded echocardiographic evaluation for end point.
Is amlodipine good for blood pressure?
Amlodipine is a potent and well-tolerated calcium channel blocker, and seems to be appropriate for achieving more aggressive systolic blood pressure target and improving diastolic dysfunction in hypertensive patients, because amlodipine is clinically very useful for control ling systolic blood pressure.