Other nitrates medications are approved by the FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) and are used for the acute relief of an attack or acute prophylaxis of angina pectoris due to coronary artery disease. These include nitroglycerin sublingual tablets, Nitrolingual spray, and Nitromist.
Which nitrates are used to treat angina pectoris?
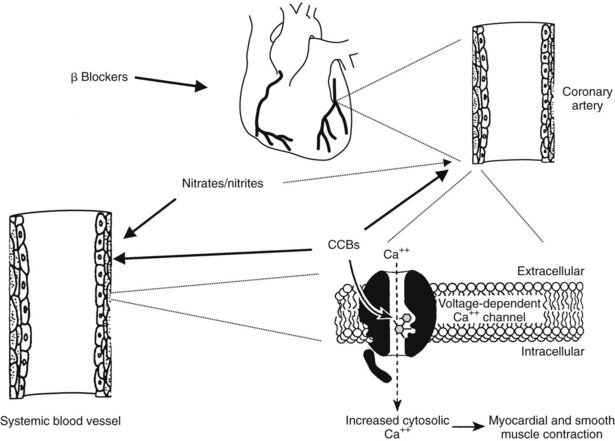
Commonly used nitrates are erythrityl tetranitrate, isosorbidedinitrate, and nitroglycerin. Beta-adrenergic blocking agents, such as propranolol, are used to treat patients who do not respond to weight control and treatment with vasodilators and whose angina significantly limits their activities.
Which medications are used to treat angina pectoris?
Patients with chronic or recurring angina pectoris may get symptomatic relief from long-acting nitrates or calcium channel blockers. Patients with refractory angina may be treated with combinations of all of these drugs in addition to ranolazine, a sodium channel blocker. Patient care
What are beta-adrenergic blocking agents used to treat angina pectoris?
Beta-adrenergic blocking agents, such as propranolol, are used to treat patients who do not respond to weight control and treatment with vasodilators and whose angina significantly limits their activities. These agents decrease the heart rate, blood pressure, and myocardial oxygen consumption and increase the patient's exercise tolerance.
What are the four forms of angina?
Four major forms of angina are identified: 1. stable: predictable frequency and duration of pain that is relieved by nitrates and rest; 2. unstable: pain that is more easily induced and increases in frequency and duration; 3. variant: pain that occurs from unpredictable coronary artery spasm; and 4.

Which classes of drugs are used in the treatment of angina pectoris?
Treatment optionsAspirin. Aspirin and other anti-platelet medications reduce the ability of your blood to clot, making it easier for blood to flow through narrowed heart arteries.Nitrates. ... Beta blockers. ... Statins. ... Calcium channel blockers. ... Ranolazine (Ranexa).
What nitrates are used for angina?
The most commonly used pill form of nitrates is isosorbide dinitrate (Isordil, Sorbitrate). With oral nitrates, the effect on blood vessels begins within approximately 30 minutes and lasts for up to six hours.
Are nitrates used to treat angina pectoris?
Nitrates are useful in the management and treatment of angina. They are a group of medications that cause vasodilation by donating nitric oxide. This activity reviews the indications, action, and contraindications for nitrates as a valuable agent in the management of angina and other cardiovascular diseases.
What is the drug class for nitroglycerin?
Nitroglycerin is in a class of medications called vasodilators. It works by relaxing the blood vessels so the heart does not need to work as hard and therefore does not need as much oxygen.
Why organic nitrates are used in the treatment of angina pectoris?
The role of organic nitrates in the optimal medical management of angina. Organic nitrates are potent vasodilators and are the most widely used antianginal agents during acute events. They selectively dilate epicardial coronaries and also enhance collateral flow; they also inhibit platelet aggregation.
What are nitrates pharmacology?
Nitrates are medications that come under the umbrella of a larger group called vasodilators, which dilate the walls of blood vessels. Nitrates are primarily used to treat angina pectoris, which is pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle; as well as hypertension, and heart failure.
Is nitroglycerin a nitrate or nitrite?
Mechanism of Action of Nitrates Organic nitrates, such as nitroglycerin, isosorbide dinitrate, and isosorbide mononitrate, are rapidly absorbed from several sites, such as the gastrointestinal tract, mucous membranes, and skin, depending on the preparation.
Are nitrates vasodilators?
Nitrates are vasodilators, which means they help widen (dilate) your blood vessels, making it easier for blood to flow through and let more oxygen-rich blood reach your heart.
Is nitroglycerin a nitrate?
Nitroglycerin extended-release capsules are used to prevent chest pain (angina) in people with a certain heart condition (coronary artery disease). This medication belongs to a class of drugs known as nitrates.
What drugs contain nitrates?
Medicines that contain organic nitrates include:Nitroglycerin (such as Nitro-Dur, Nitrolingual, Nitrostat).Isosorbide (such as Dilatrate, Isordil).Nitroprusside (such as Nitropress).Amyl nitrite or amyl nitrate. These are sometimes called "poppers." They are sometimes abused.
Which class of drugs is prescribed for a patient who experiences exertional angina?
Beta-blockers are an appropriate first-line medical treatment to relieve the symptoms of angina.
Is nitroglycerin a beta blocker?
Drugs: Nitrates: nitroglycerin, isosorbide dinitrate. Beta Blockers: propranolol, metoprolol, atenolol. Calcium Channel Blockers: nifedipine, verapamil, diltiazem.
What is a nitrate?
Nitrates are vasodilators that relieve chest discomfort (angina) by improving myocardial oxygen supply, thereby, in turn, dilating epicardial and collateral vessels and thus improving blood supply to the ischemic myocardium. Vasodilators oppose coronary artery spasm, which augments coronary blood flow and reduces cardiac work by decreasing preload and afterload.
Does nitrate help with angina?
Nitroglycerin causes relaxation of vascular smooth muscle by stimulating intracellular cyclic guanosine monophosphate production. Whether administered topically, sublingually, orally, or IV, nitrates ameliorate several pathways of unstable angina and reduce the incidence of symptomatic ischemia. Nitrates lower systemic arterial pressure and decrease venous return to the heart, both of which reduce myocardial wall stress. Similarly, nitrates are excellent coronary vasodilators.
Nitrates, Angina
Nitrates produce a direct, endothelium-independent vasodilatation of the large coronary arteries. In addition, they reduce preload by dilating venous capacitance vessels, which results in decreased myocardial oxygen consumption.
Nitroglycerin (Nitrolingual, Nitrostat, Minitran, Nitro-Bid, Nitro-Dur)
Nitroglycerin causes relaxation of vascular smooth muscle by stimulating intracellular cyclic guanosine monophosphate (GMP). The result is a decrease in blood pressure. Dosage forms include sublingual, transdermal, and intravenous (IV) preparations.
Isosorbide dinitrate (Isordil, Dilatrate SR)
Isosorbide dinitrate relaxes vascular smooth muscle by stimulating intracellular cyclic GMP. It decreases preload and afterload, causing decreased myocardial oxygen demand. Isosorbide dinitrate is used for the treatment and prevention (sustained-release preparations) of variant angina.
Isosorbide mononitrate (ISMO, Imdur, Monoket)
Isosorbide mononitrate is used for the prevention of variant angina. The onset of action of oral isosorbide mononitrate is not sufficiently quick to permit its use as an acute antianginal agent. The half-life is approximately 5 hours.
Why do you need a long nitrate free interval?
Provision of a long nitrate-free interval or low plasma nitrate levels prior to the morning dose prevents the loss of clinical efficacy by preventing the development of tolerance. However, side effects during nitrate therapy are common.
Can nitrates cause headaches?
Headache is the most common side effect of nitrates; often dose-related and reported by up to 82% of patients in placebo-controlled trials. Nearly 10% of patients are unable to tolerate nitrates due to disabling headaches or dizziness.
Is nitrate induced hypotension asymptomatic?
Nitrate-induced hypotension is common, but often asymptomatic. In rare instances, nitrate-induced hypotension is severe and accompanied by marked slowing of the heart rate and syncope. Use of nitrates in patients who experience syncope after administration of nitrates is contraindicated.
Is nitrate a good antianginal?
Nitrates are very effective antianginal and anti-ischaemic agents. Provision of a long nitrate-free interval or low plasma nitrate levels prior to the morning dose prevents the loss of clinical efficacy by preventing the development of tolerance.
How to relieve pain from angina?
The pain is relieved by resting or by administering nitroglycerin, a medication that reduces ischemia of the heart. Patients with angina of effort have an increased risk of heart attack (myocardial infarction).
What is the diagnosis of angina?
Diagnosis. Physicians can usually diagnose angina based on the patient's symptoms and the precipitating factors. However, other diagnostic testing is often required to confirm or rule out angina, or to determine the severity of the underlying heart disease.
What is Prinzmetal's angina?
Prinzmetal's angina a variant of angina pectoris in which the attacks occur during rest, exercise capacity is well preserved, and attacks are associated electrocardiographically with elevation of the ST segment. It is cyclic in nature and is believed to be caused by coronary artery spasm.
Why does angina occur at rest?
Variant angina occurs at rest and is not related to excessive work by the heart muscle. Research indicates that variant angina is caused by coronary artery muscle spasm of insufficient duration or intensity to cause an actual heart attack.
Why do you need a stress test for angina?
Because the symptoms of angina occur during stress, the functioning of the heart may need to be evaluated under the physical stress of exercise. The stress test records information from the electrocardiogram before, during, and after exercise in search of stress-related abnormalities.
What is the pain in the chest called?
Angina is pain, "discomfort," or pressure localized in the chest that is caused by an insufficient supply of blood ( ischemia) to the heart muscle. It is also sometimes characterized by a feeling of choking, suffocation, or crushing heaviness. This condition is also called angina pectoris.
What is stable angina?
stable angina chest pain of cardiac origin that has not changed in character, frequency, intensity, or duration for 60 days. unstable angina chest pain of cardiac origin that is variable, usually increasing in frequency and intensity and with irregular timing. variant angina Prinzmetal's angina.