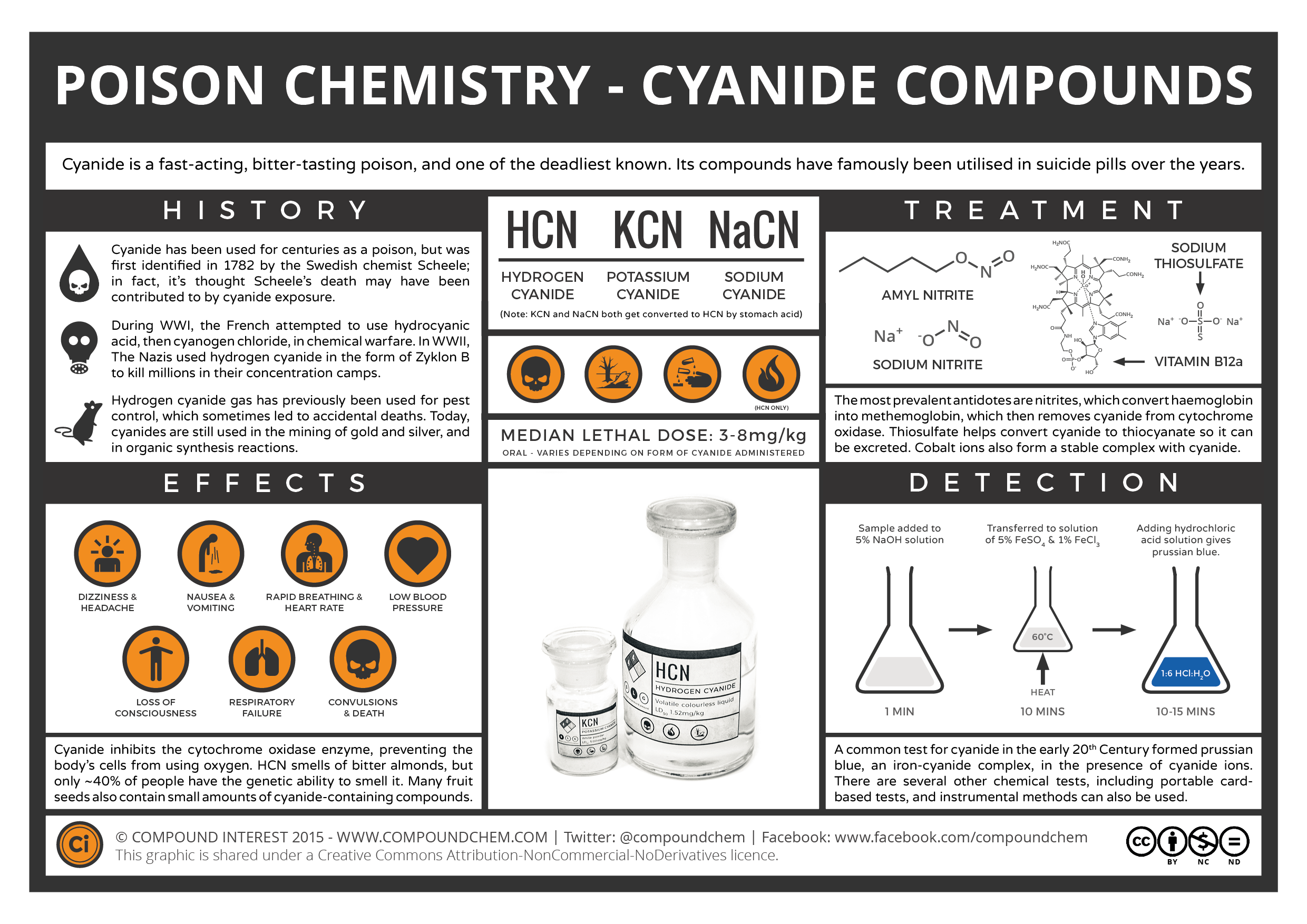
Which chemical treatment produces a white-appearing latent print?
Sep 12, 2012 · Latent heat of fusion (or enthalpy of fusion) is a characteristic of a substance, rather than a chemical bond. If you mean enthalpy of reaction then the lowest absolute values are for the bonds in ...
What is agent white phosphorus?
Jul 25, 2021 · Which chemical treatment produces a white-appearing latent print? A)Ninhydrin B)Iodine fuming C)Superglue fuming D)Physical developer
What are the treatment options for white phosphorus exposure?
Nov 19, 2018 · Blue and yellow combine to make white light. In another design (right), UV light (depicted as purple) excites red, green, and blue phosphors to make white. To make LEDs that are more pleasing to ...
How is white phosphorous (WP) removed from skin?
Which chemical treatment produces a white appearing latent print. Superglue fumimg. What is more important for fingerprint ID,ridge patterns or ridge characteristics. Ridge characteristics. Give two examples of a porous surface. Skin Cardboard Cloth Paper. Which latent print method involves sublimation.

What chemical treatment produces a white latent print?
Cyanoacrylate, also called super glue, fuming is a chemical method for the detection of latent fingermarks on non-porous surfaces such as glass, plastic etc. The method relies on the deposition of polymerized cyanoacrylate ester on residues of latent fingermarks.Jul 18, 2017
What does ninhydrin detect on a latent print?
Ninhydrin is used on a latent print to detect: protein material. Physical developer contains: silver nitrate.
What does iodine fuming react with?
Fingerprints can be developed using a number of chemical and physical methods. In this activity, fingerprints will be developed chemically in iodine vapor. Iodine is toxic by ingestion and inhalation. It reacts violently with reducing materials, sulfur, iron, alkali metals, metal powders, and phosphorus.
Which chemical method produces a reddish brown print?
Iodine combines with carbohydrates in patent prints to give a brownish print.
Which chemical test turns the print white?
Super glue reacts with the traces of amino acids, fatty acids, and proteins in the latent fingerprint and the moisture in the air to produce a visible, sticky white material that forms along the ridges of the fingerprint. The final result is an image of the entire latent fingerprint.
Does ninhydrin destroy DNA?
This research shows that ninhydrin does not significantly affect the recovery of profiles; however, the quantity of DNA may be reduced after treatment. ... ... This research shows that ninhydrin does not significantly affect the recovery of profiles; however, the quantity of DNA may be reduced after treatment.
What does the superglue react with in the fingerprint?
Super glue reacts with the traces of amino acids, fatty acids, and proteins in the latent fingerprint and the moisture in the air to produce a visible, sticky white material that forms along the ridges of the fingerprint.
Why is iodine fuming rarely used anymore?
The temporary nature of iodine developed latents, requiring fixing agents that preclude further processing techniques, probably results in the low use of this process. While iodine fuming is often considered archaic and not considered in many cases, its use should not be completely discarded.Jun 7, 2016
What is super glue fuming?
Cyanoacrylate or super glue fuming uses the vapors of super glue to develop latent fingerprints. Super glue fuming is an easy and effective way to make fingerprints visible. Super glue fuming can be performed on old or new fingerprints and can then be further enhanced by using dyes or powders.
WHAT IS fingerprint oil made of?
Most black fingerprint powders contain rosin, black ferric oxide and lampblack. Many also contain inorganic chemicals such as lead, mercury, cadmium, copper, silicon, titanium and bismuth.Sep 2, 2002
What chemicals are in fingerprints?
Forensic scientists rely on four primary chemicals to reveal and collect fingerprints: iodine, cyanoacrylate, silver nitrate and ninhydrin. These chemicals react to substances within the fingerprint, such as oil and sweat, making the print change color so analysts can see it better.May 15, 2018
What chemical gets rid of fingerprints?
Or, use a white vinegar solution (1/4 cup mixed with one gallon of water). Soak the cloth, wring it out and wipe fingerprints off the sliding glass door. Buff with a dry microfibre cloth.Dec 4, 2017
What does red phosphor do to white LEDs?
Most red phosphors boost color quality in white LEDs by filling in red tones, but they also emit broadly, spilling out of the visible spectrum and into the infrared range, wasting energy and causing the light from their LEDs to score poorly in luminous efficacy.
What colors make white light?
Blue and yellow combine to make white light. In another design (right), UV light (depicted as purple) excites red, green, and blue phosphors to make white. To make LEDs that are more pleasing to consumers for home use, scientists are developing new phosphors.
How many lumens does a 15W LED light have?
That’s because LEDs are more energy efficient. A 15-to-20-W LED can produce the same brightness as a 100-W incandescent, roughly 1,500 lumens. LEDs are also less fragile and can last tens of thousands of hours longer.
What color is white LED light?
The various types of white LED lights are classified as a reddish-orange “warm white” (about 3,000 K), a neutral or faintly blue “cool white” (about 4,000 K), and a blue-white “daylight” (about 6,000 K). One approach to making white light calls for blending the blue, green, and red outputs of three single-color LEDs, ...
What is a phosphor LED?
In this design, referred to as a phosphor-converted LED, the blue light excites the phosphor powder, which is usually encapsulated in the outer casing. The light emitted by the yellow phosphor combines with the blue light emitted by the LED to produce white light.
Do incandescent lights have good color?
That means the perceived colors of objects viewed under incandescent lighting appear “correct,” or very close to their appearance in daylight. To put it in lighting parlance, incandescents have a color rendering index (CRI) of 100, the same as sunlight.
How to remove white phosphorus from skin?
Vigorous irrigation with cold water is the best way to remove white phosphorous embedded in the skin. Remove visible particles of white phosphorus while washing with large amounts of cold water or while the area is submerged in cold water.
What is white phosphorus?
Turns dark on exposure to light. DESCRIPTION: White phosphorus is a toxic substance produced from phosphate-containing rocks. White phosphorus is used industrially to manufacture chemicals used in fertilizers, food additives, and cleaning compounds. It has been used in the past as a pesticide and in fireworks.
What temperature does phosphorus ignite?
Phosphorus ignites at approximately 86°F (30°C) in air; the ignition temperature is higher when the air is dry. Phosphorus reacts violently with oxidants, halogens, some metals, nitrites, sulfur, and many other compounds, causing a fire hazard. The agent burns rapidly, releasing dense, white irritating fumes.
What is the purpose of decontamination?
INTRODUCTION: The purpose of decontamination is to make an individual and/or their equipment safe by physically removing toxic substances quickly and effectively . Care should be taken during decontamination, because absorbed agent can be released from clothing and skin as a gas. Your Incident Commander will provide you with decontaminants specific for the agent released or the agent believed to have been released.
How long does it take for a burn to heal from phosphorus?
TIME COURSE: Exposure to white phosphorus may cause immediate burns that heal slowly. Systemic toxicity from white phosphorus exposure is classically divided into 3 phases. The first phase, the gastrointestinal phase, occurs a few minutes to 8 hours following white phosphorus exposure. Shock during this phase may be severe enough to cause death in 24 to 48 hours. The second phase, the asymptomatic phase, follows the first phase and lasts for 8 hours to 3 days. The third phase, the multi-organ failure and central nervous system injury phase, may begin 4 to 8 days after the second phase begins, and may end in death.
What is chemical resistant gloves?
Chemical-resistant gloves (outer). Chemical-resistant gloves (inner). Chemical-resistant boots with a steel toe and shank. Coveralls, long underwear, a hard hat worn under the chemical-resistant suit, and chemical-resistant disposable boot-covers worn over the chemical-resistant suit are optional items.
How long does the second phase of a syringe last?
The second phase, the asymptomatic phase, follows the first phase and lasts for 8 hours to 3 days . The third phase, the multi-organ failure and central nervous system injury phase, may begin 4 to 8 days after the second phase begins, and may end in death.
What chemicals are used to disinfect wastewater?
Specialized chemicals such as chlorine, hydrogen peroxide, sodium chlorite, and sodium hypochlorite (bleach) act as agents that disinfect, sanitize, and assist in the purification of wastewater at treatment facilities. There are several distinct chemical unit processes, including chemical coagulation, chemical precipitation, chemical oxidation, ...
How does chemical stabilization work?
Chemical Stabilization. This chemical wastewater treatment process works in a similar fashion as chemical oxidation. Sludge is treated with a large amount of a given oxidant, such as chlorine. The introduction of the oxidant slows down the rate of biological growth within the sludge and also helps deodorize the mixture.
What is the primary objective of wastewater treatment?
The primary objective of wastewater treatment processes is to purify the water and make certain that it is safe for subsequent use once it has been returned to the environment as part of the water cycle. Wastewater treatment involves a number of stages involving processes that are mechanical (physical)-based, biological-based, chemical-based, ...
How to remove metals from wastewater?
Chemical precipitation is the most common method for removing dissolved metals from wastewater solution containing toxic metals. To convert the dissolved metals into solid particle form, a precipitation reagent is added to the mixture. A chemical reaction, triggered by the reagent, causes the dissolved metals to form solid particles. Filtration can then be used to remove the particles from the mixture. How well the process works is dependent upon the kind of metal present, the concentration of the metal, and the kind of reagent used. In hydroxide precipitation, a commonly used chemical precipitation process, calcium or sodium hydroxide is used as the reagent to create solid metal hydroxides. However, it can be difficult to create hydroxides from dissolved metal particles in wastewater because many wastewater solutions contain mixed metals.
Where does wastewater come from?
Wastewater originates from homes, businesses, industry, as well as storm drains and rainwater runoff. Generally, wastewater contains around 99.9% water by weight with the remaining 0.1% representing dissolved solids or other suspended materials. This material may include excrement, detergents from washing clothes and dishes, food scraps, grease, oils, plastics, salts, sand, grit, and heavy metals. Some wastewaters from industrial or agricultural processes may also contain chemicals that may be hazardous to the environment or to public health and which need to be neutralized or removed from the water before it can be safely reintroduced into the environment. The primary objective of wastewater treatment processes is to purify the water and make certain that it is safe for subsequent use once it has been returned to the environment as part of the water cycle.
What is wastewater treatment?
The initial stage of wastewater treatment involves mechanical processes, which remove some 20-30% of solids in the water. First, the wastewater is directed to a screen or a sieve drum that filters out impurities that are relatively coarse, such as leaves, textiles, paper, or other large materials. A series of screens are used with various degrees ...
How does alkaline chlorination work?
The pollutants then undergo structural modification, becoming less destructive compounds. Alkaline chlorination uses chlorine as an oxidant against cyanide. However, alkaline chlorination as a chemical oxidation process can lead to the creation of toxic chlorinated compounds, and additional steps may be required. Advanced oxidation can help remove any organic compounds that are produced as a byproduct of chemical oxidation, through processes such as steam stripping, air stripping, or activated carbon adsorption.
