Medication
6 rows · Mar 08, 2021 · The table presents a list of the 6 most popular antibiotics for cystitis: Phosfomycin. ...
Procedures
Amoxicillin Traditionally, amoxicillin has been one of the most common antibiotics used to treat cystitis, but the University of Maryland Medical Center reports that 25 percent of E. coli strains are now resistant to this antibiotic. It can, however, be used to treat cystitis caused by Enterococcus species and Staphylococcus saprophyticus.
Nutrition
Oct 24, 2019 · Usually, a single dose of. antibiotics. with a special drug is enough to relieve the symptoms. Alternatively, there are. antibiotics. that are taken for 3, 5 or 7 days. The studies found the following: A one- to three-day treatment was enough to relieve the symptoms in most women who had uncomplicated cystitis. Taking.
See more
Mar 08, 2021 · A list of the 6 most common antibiotics for cystitis is presented in the table: Fosfomycin. Considered the most effective broad spectrum antibiotic, used in acute cases. In the form of a suspension, it is rapidly transported by the blood stream to the inflamed area and begins to act on the site of the infection.
How to treat cystitis naturally at home?
Mar 21, 2018 · TMP, trimethoprim; SMX, sulfamethoxazole. Results are shown as percentages. Although the antibiotic resistance to ciprofloxacin, which was increasingly used as an empirical antibiotic for acute cystitis, increased, that to TMP/SMX, which has been used less and less over time, decreased [ 40, 41] ( Fig. 1 ).
Can cystitis be cleared without antibiotics?
5 rows · and proper empiric antibiotic treatment will usually forestall serious complications and provide ...
What are the safest antibiotics for UTI?
Feb 14, 2022 · Cystitis refers to infection of the lower urinary tract, or more specifically the urinary bladder.[1][2] It may be broadly categorized as either complicated or uncomplicated (simple). Uncomplicated cystitis refers to a lower urinary tract infection (UTI) in either men or non-pregnant women who are otherwise healthy. Complicated cystitis, on the other hand, is associated with …
Are there UTI treatment without antibiotics available?
Oct 01, 2011 · Guidelines recommend three options for first-line treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis: fosfomycin, nitrofurantoin, and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (in regions where the prevalence of...
Can you take amoxicillin for cystitis?
In studies of uncomplicated cystitis, a 3-day regimen of amoxicillin-clavulanate and a 7-day regimen of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole have been shown to be superior to a single-dose regimen of amoxicillin-clavulanate.
What is the first choice antibiotic for UTI?
First-line antibiotics for acute, uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs) typically include: Fosfomycin. Nitrofurantoin. Trimethoprim or sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim)May 28, 2021
Do antibiotics clear up cystitis?
Antibiotics are very effective Antibiotics can quickly relieve the symptoms of cystitis and clear up the infection by killing the bacteria.Feb 14, 2006
Which antibiotics are first-line to treat E coli cystitis?
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or trimethoprim should be used as first-line therapy because of its low cost and efficacy for uncomplicated urinary tract infections in women unless the prevalence of resistance to these agents among uropathogens in the community is greater than 10% to 20%.
What is the strongest antibiotic for UTI?
What antibiotics can treat a UTI? Not all antibiotics work for treating UTIs, but several do. Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, nitrofurantoin, and fosfomycin are the most preferred antibiotics for treating a UTI.Nov 17, 2020
What is the safest antibiotic for UTI?
Simple infection Drugs commonly recommended for simple UTIs include: Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim, Septra, others) Fosfomycin (Monurol) Nitrofurantoin (Macrodantin, Macrobid)Apr 23, 2021
What is the fastest way to get rid of cystitis?
Things you can try yourselftake paracetamol up to 4 times a day to reduce pain.give children liquid paracetamol – follow the instructions on the bottle.drink plenty of water.hold a hot water bottle over your lower tummy.avoid having sex.avoid drinks that may irritate your bladder, like fruit juices, coffee and alcohol.More items...
Can I take Flucloxacillin for cystitis?
Flucloxacillin is used to treat bacterial infections in the upper and lower respiratory tract infections, such as bronchitis, tonsillitis and pneumonia; urinary tract infections such as cystitis and urethritis; skin and soft tissue infections such as boils and abscesses; and infected wounds and burns.
Is 3 day antibiotic enough for UTI?
Women and children with straightforward UTIs usually take a 3-day course of treatment. Men and pregnant women with straightforward UTIs usually take a 7-day course of treatment. People with particularly severe or complicated UTIs, or a catheter, usually take a 14-day course of treatment.
Can azithromycin treat cystitis?
Macrolides (for example, clarithromycin, azithromycin, and erythromycin), used more often with some STD-caused urinary problems. Fosfomycin (Monurol), a synthetic phosphonic acid derivative, is used for acute cystitis but not in more complicated UTIs.
Is azithromycin good for UTI?
Azithromycin is a medicine used to treat many types of bacterial infections. It's commonly prescribed for infections of the lungs, throat, sinuses, ears, skin, urinary tract, cervix, or genitals. This medicine is in a class of drugs called macrolide antibiotics. It works by stopping the growth of bacteria.Nov 24, 2020
Is ciprofloxacin best for UTI?
Ciprofloxacin is considered to be the standard treatment for patients with complicated urinary tract infections (UTI). This multicentre, randomized clinical study was designed to compare a once-daily regimen with 500 mg to the usual twice-daily regimen with 250 mg orally for 7-20 days.
Which antibiotics are suitable for treatment?
The choice of antimicrobial agent is empirical due to a predictable range of pathogens that cause inflammation.
List of antibiotics for cystitis in women
The choice of a drug depends not only on the causative agent of the disease, but also on the form of its course. In the acute and chronic course, different antibiotics can be prescribed for the treatment of cystitis in women with an individual treatment regimen.
Antibiotics for chronic cystitis
When the infection progresses to the chronic stage, empiric antibiotic therapy is unacceptable. Surely, before prescribing antibacterial drugs, it is necessary to conduct a microbiological study of urine. The resistance of the bacterial strain to specific medicinal agents is also studied with him.
Contraindications
Antibiotics for cystitis in women should be used after studying the clinical picture of the disease, conducting diagnostic studies and decoding analysis for the susceptibility of the pathogen of the pathology to the effects of a certain group of substances. Self-medication with antibiotic therapy is unacceptable.
How to take antibiotics correctly
When treating bladder inflammation with antibiotics, it is necessary to follow a number of rules for the use of antibacterial drugs that will help you undergo a course of therapy without harming the body and maintaining your health:
Additional treatment
A heavy drinking regime is recommended with the exception of alcoholic beverages, soda, strong and sweet tea and coffee. Compliance with the basic principles of the 5th Pevzner diet is shown.
What antibiotics are used for cystitis?
Fluoroquinolones. Another class of antibiotics that are widely used to treat cystitis are fluoroquinolones such as ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin.
What causes cystitis in women?
MedlinePlus also reports that cystitis usually occurs in sexually active women between 20 to 50 years of age and is commonly caused by bacteria such as E. coli 1. Antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment against cystitis, therefore the type of antibiotic and length of treatment depend on the overall condition of the patient and the amount ...
What are the side effects of doxycycline?
Doxycycline is commonly prescribed to treat cystitis caused by chlamydia and mycoplasma species and is available in tablet and suspension form. The University of Maryland Medical Center warns pregnant women and children against the use of doxycyline. The common side effects include: 1 changes in skin color 2 sunburn 3 sore mouth 4 upset stomach 5 diarrhea 6 according to Merck Manuals Online Medical Library
How does fluoroquinolone work?
Fluoroquinolones work by killing the bacteria that cause the infection and are available in capsule or tablet form to be taken orally. Nausea, vomiting, stomach pain and heartburn are the common side effects, as described by the Merck Manuals Online Medical Library .
What is doxycycline used for?
Doxycycline is commonly prescribed to treat cystitis caused by chlamydia and mycoplasma species and is available in tablet and suspension form. The University of Maryland Medical Center warns pregnant women and children against the use of doxycyline. The common side effects include: changes in skin color. sunburn.
Does amoxicillin cause diarrhea?
Common side effects include nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, according to Merck Manuals Online Medical Library. Traditionally, amoxicillin has been one of the most common antibiotics used to treat cystitis, but the University of Maryland Medical Center reports that 25 percent of E. coli strains are now resistant to this antibiotic.
What is a UTI?
What is a urinary tract infection (UTI)? UTIs are common infections that happen when bacteria, often from the skin or rectum, enter the urethra, and infect the urinary tract. The infections can affect several parts of the urinary tract, but the most common type is a bladder infection (cystitis).
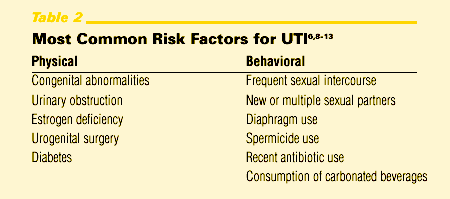
What are the factors that increase the risk of UTI?
Other factors that can increase the risk of UTIs: A previous UTI. Sexual activity, and especially a new sexual partner. Changes in the bacteria that live inside the vagina (vaginal flora), for example caused by menopause or use of spermicides. Pregnancy.
Why are UTIs more common in women?
UTIs are more common in women and girls because their urethras are shorter and closer to the rectum, which makes it easier for bacteria to enter the urinary tract.
Can a toddler have a UTI?
While fever is the most common sign of UTI in infants and toddlers, most children with fe ver do not have a UTI. Talk to a doctor if you are concerned. See a doctor right away if your child is younger than 3 months old and has a fever of 100.4 °F (38 °C) or higher.
Can antibiotics cause diarrhea?
However, any time you take antibiotics, they can cause side effects. Side effects can range from minor reactions, such as a rash, to very serious health problems, such as antibiotic-resistant infections or C. diff infection, which causes diarrhea that can lead to severe colon damage and death. Call your doctor if you develop any side effects ...
Does pyelonephritis increase during pregnancy?
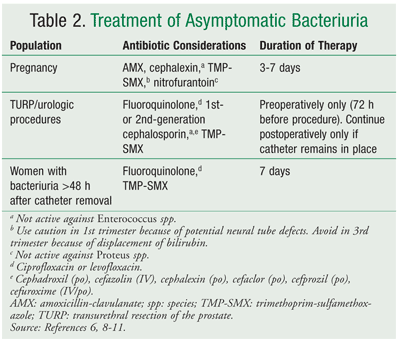
Although the rates of asymptomatic bacteriuria areroughly the same among pregnant and non-pregnantwomen, various anatomical and hormonal changesgreatly increase the rates of pyelonephritis in pregnantwomen. During pregnancy the kidneys enlarge and aremore engorged with blood, the ureters dilate, the bladderenlarges and is unable to contract as strongly, and loosevesicourethral junctions and a growing gravid uterusconspire to prevent efficient emptying of the bladder. Acute pyelonephritis in pregnancy, in addition tomaternal morbidity, carries higher rates of pretermbirth, subsequent low birth weight infants, and higherinfant morbidity and mortality, which compel cliniciansto keep a low threshold of suspicion about pregnantwomenAcute whopyelonephritis present with in urinary pregnant concerns. women warrantsparenteral antibiotics initially, usually delivered IV inthe inpatient setting. “Mild to moderate” pyelonephritis,in the absence of urosepsis, can be treated with 1 or 2days of IV antibiotics and a transition to an oral 10- to14-day regimen (based on culture sensitivity results), pro-vided a patient is afebrile and hasshown clinical improve-ment (Table 6). Ceftriaxone, cefepime, nitrofurantoinandamoxicillin/clavulanate have Class B pregnancy riskclassification. The Class B status means they are reason-ably safe to use, especially in the second and thirdtrimester, because fetal harm is possible but unlikely. For patients in whom these ideal regimens are con-traindicated, others can be considered. Parenterally,ampicillin 1 to 2 g IV every 6 hours plus gentamicin 1.5mg/kg IV every 8 hours can be used. Ampicillin and gen-and D, respectively. If thecausative organism is resistant tonitrofurantoin and amoxicillin/clavulanate, trimethoprim/sulfa -me thoxazole double-strength(TMP/SMX), 1 tablet PO every 12hours can be used. TMP/SMX hasa Class D pregnancy, classification,which denotes known evidence of fetal risk; however,the risk may (as is the case in acute pyelonephritis) out-weigh the fetal risk in serious maternal conditions.
Is pyelonephritis a bacterial infection?
Acute uncomplicated pyelonephritis is a common seri-ous bacterial infection in women and has the highestincidence in women ages 15 to 29. Although acutepyelonephritis can occur in men, children, and preg-nant women, it is rare and outside the scope of IDSAantibiotic treatment guidelines.
Can empiric antibiotics help with cystitis?
Urgent message: Proper empiric antibiotic treatment in womenwith acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis can preventunnecessary morbidity and provide urgent relief from these commongenitourinary infections.
What is the first line of treatment for cystitis?
Guidelines recommend three options for first-line treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis: fosfomycin, nitrofurantoin, and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (in regions where the prevalence of Escherichia coli resistance does not exceed 20 percent).
What is the most important tool for diagnosing acute uncomplicated cystitis?
The history is the most important tool for diagnosing acute uncomplicated cystitis, and it should be supported by a focused physical examination and urinalysis. It also is important to rule out a more serious complicated UTI. By definition, the diagnosis of acute uncomplicated cystitis implies an uncomplicated UTI in a premenopausal, nonpregnant woman with no known urologic abnormalities or comorbidities ( Table 1 5).
What is the most common bacterial infection in women?
Urinary tract infections are the most common bacterial infections in women. Most urinary tract infections are acute uncomplicated cystitis. Identifiers of acute uncomplicated cystitis are frequency and dysuria in an immunocompetent woman of childbearing age who has no comorbidities or urologic abnormalities.
Is cystitis normal in women?
The physical examination of patients with acute uncomplicated cystitis is typically normal, except in the 10 to 20 percent of women with suprapubic tenderness. 10 Acute pyelonephritis should be suspected if the patient is ill-appearing and seems uncomfortable, particularly if she has concomitant fever, tachycardia, or costovertebral angle tenderness.
Can beta-lactam be used for cystitis?
Beta-lactam antibiotics are not recommended as first-line therapy for acute uncomplicated cystitis because of widespread E. coli resistance rates above 20 percent. Fluoroquinolone resistance usually is found to be below 10 percent in North America and Europe, but with a trend toward increasing resistance over the past several years. 16 To preserve the effectiveness of fluoroquinolones, they are not recommended as a first-tier option. Fosfomycin and nitrofurantoin have retained high rates of in vitro activity in most areas. 16
Can you self diagnose UTI?
Two recent studies have shown that some women who self-diagnose a UTI may be treated safely with telephone management. Women who have had acute uncomplicated cystitis previously are usually accurate in determining when they are having another episode. In one study of 172 women with a history of recurrent UTI, 88 women self-diagnosed a UTI based on symptoms, and self-treated with antibiotics. 8 Laboratory evaluation showed that 84 percent of the urine samples showed a uropathogen, 11 percent showed sterile pyuria, and only 5 percent were negative for pyuria and bacteriuria. Another small, randomized controlled trial compared outcomes of acute uncomplicated cystitis in healthy women managed by telephone versus in the office. 9 There were no differences in symptom score or satisfaction. The authors concluded that the short-term outcomes of managing suspected UTIs by telephone were comparable with those managed by usual office care.