Nutrition
There are 10 drugs currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating TB. Of the approved drugs, the first-line anti-TB agents that form the core of treatment regimens are: isoniazid (INH) rifampin (RIF) ethambutol (EMB) pyrazinamide (PZA) TB Regimens for Drug-Susceptible TB.
What drugs are used to treat tuberculosis (TB)?
What are Antituberculosis agents? Antituberculosis agents are drugs used to treat tuberculosis, an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This infection mainly affects the lungs but can also affect many other organ systems. Many classes of drugs, with different mechanism of action have activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
What are antituberculosis agents?
M. tuberculosis (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) is the etiological agent of TB and currently more than one-third of the world population is suffering from TB. For the treatment of TB, administration of multiple antibiotics such as isoniazid, rifampicin, pyrazinamide and ethambutol is required for a long period of time to kill bacteria.
What is Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
It is very important that people who have TB disease are treated, finish the medicine, and take the drugs exactly as prescribed. If they stop taking the drugs too soon, they can become sick again; if they do not take the drugs correctly, the TB bacteria that are still alive may become resistant to those drugs.
Why is it important to finish treatment for tuberculosis (TB)?
What is used for the treatment of tuberculosis?
The usual treatment is: 2 antibiotics (isoniazid and rifampicin) for 6 months. 2 additional antibiotics (pyrazinamide and ethambutol) for the first 2 months of the 6-month treatment period.
What is the main agent for tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious disease caused by infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) bacteria. It is spread through the air when a person with TB disease of the lungs or throat coughs, speaks or sings, and people nearby breathe in these bacteria and become infected.
Which agent is used for the treatment of tuberculosis rifampin?
Rifampin (Rifadin) Rifampin is used in combination with at least 1 other antituberculous drug for the treatment of active TB. It inhibits DNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity in bacterial cells but not in mammalian cells. Cross-resistance may occur.
Which drugs are used for first-line treatment of tuberculosis?
First-line agents for treatment of active TB consist of isoniazid, a rifamycin (rifampin or [less frequently] either rifapentine or rifabutin), pyrazinamide, and ethambutol; in addition, moxifloxacin is a first-line agent when administered in combination with isoniazid, rifapentine, and pyrazinamide [6].
What is a causative agent?
Causative agents in infection are pathogens. Pathogens are micro-organisms that are capable of causing diseases or infections. If micro-organisms from a person's own body cause an infection, it is called an endogenous infection.
What are the causative agent of tuberculosis and malaria?
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The bacteria usually attack the lungs, but TB bacteria can attack any part of the body such as the kidney, spine, and brain.
What is ethambutol used to treat?
Ethambutol is used to treat tuberculosis (TB). It is used with other medicines for TB. This medicine may also be used for other problems as determined by your doctor.
Is ciprofloxacin used for tuberculosis?
Ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, levofloxacin and sparfloxacin are currently the most commonly used agents used against Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB), with in vitro minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of 0.1 to 4 mcg/ml.
How does ethambutol treat TB?
Ethambutol is used with other medications to treat tuberculosis (TB). Ethambutol is an antibiotic and works by stopping the growth of bacteria. This antibiotic treats only bacterial infections. It will not work for viral infections (such as common cold, flu).
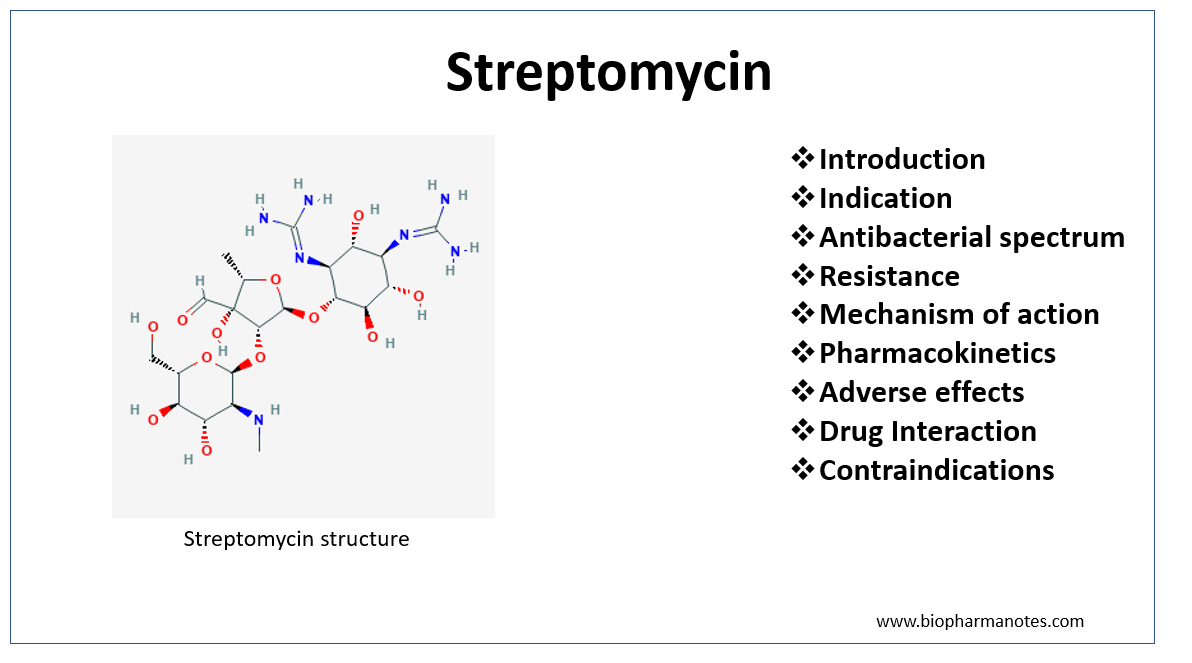
Is streptomycin used for tuberculosis?
Streptomycin was the first antibiotic to be used against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It was used for years in monotherapy regimens, thereby resulting in the appearance of resistance and the relegation of its use. The resistance detected against drugs currently employed has led to a renewed interest in streptomycin.
Is streptomycin still used to treat tuberculosis?
With the development of more effective anti TB medicines such as rifampicin and isoniazid, streptomycin was replaced in the initial treatment of TB, but is still widely used in the retreatment of TB.
Are anti TB drugs antibiotics?
With the proper treatment, tuberculosis (TB, for short) is almost always curable. Doctors prescribe antibiotics to kill the bacteria that cause it. You'll need to take them for 6 to 9 months.
What are Antituberculosis agents?
Antituberculosis agents are drugs used to treat tuberculosis, an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This infection mainly affects the lungs but can also affect many other organ systems. Many classes of drugs, with different mechanism of action have activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
How many drugs are given in a chemo treatment for tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis chemotherapy involves giving two to four drugs simultaneously. These drugs work differently so they target the organism in different ways and using a few types of drugs prevents drug resistant strains of Mycobacterium from evolving.
What are the most common medical conditions that increase the risk of tuberculosis?
Persons with the following medical conditions that have been reported to increase the risk of tuberculosis ( ≥ 10 mm): silicosis; diabetes mellitus; prolonged therapy with adrenocorticosteroids; immunosuppressive therapy; some hemat ologic and reticuloendothelial diseases, such as leukemia or Hodgkin’s disease; end-stage renal disease; clinical situations associated with substantial rapid weight loss or chronic undernutrition (including: intestinal bypass surgery for obesity, the postgastrectomy state (with or without weight loss), chronic peptic ulcer disease, chronic malabsorption syndromes, and carcinomas of the oropharynx and upper gastrointestinal tract that prevent adequate nutritional intake). Candidates for preventive therapy who have fibrotic pulmonary lesions consistent with healed tuberculosis or who have pulmonary silicosis should have 12 months of isoniazid or 4 months of isoniazid and rifampin, concomitantly.
How long does LTBI treatment last?
Adults: Treatment of latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI): 300 mg/day or 900 mg twice weekly for 6-9 months in patients who do not have HIV infection (9 months is optimal, 6 months may be considered to reduce costs of therapy) and 9 months in patients who have HIV infection.
How much of ethambutol is excreted in urine?
During the 24-hour period following oral administration of ethambutol hydrochloride tablets approximately 50 percent of the initial dose is excreted unchanged in the urine, while an additional 8 to 15 percent appears in the form of metabolites.
Can you use sirturo for tuberculosis?
Limitations of Use: Do not use SIRTURO for the treatment of latent, extra-pulmonary or drug-sensitive tuberculosis or for the treatment of infections caused by non-tuberculous mycobacteria (1). Safety and efficacy of SIRTURO in HIV-infected patients with MDR-TB have not been established, as clinical data are limited (14).
Does isoniazid inhibit mycoloic acid?
Isoniazid inhibits the synthesis of mycoloic acids, an essential component of the bacterial cell wall. At therapeutic levels isoniazid is bacteriocidal against actively growing intracellular and extracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis organisms.
Does ethhambutol inhibit synthesis?
Ethambutol hydrochloride tablets appear to inhibit the synthesis of one or more metabolites, thus causing impairment of cell metabolism, arrest of multiplication, and cell death.
Does ethambutol help with tuberculosis?
When ethambutol hydrochloride tablets have been used alone for treatment of tuberculosis , tubercle bacilli from these patients have developed resistance to ethambutol hydrochloride by in vitro susceptibility tests; the development of resistance has been unpredictable and appears to occur in a step-like manner. No cross resistance between ethambutol hydrochloride tablets and other antituberculous drugs has been reported. Ethambutol hydrochloride tablets have reduced the incidence of the emergence of mycobacterial resistance to isoniazid when both drugs have been used concurrently. An agar diffusion microbiologic assay, based upon inhibition of Mycobacterium smegmatis (ATCC 607) may be used to determine concentrations of ethambutol hydrochloride in serum and urines
What test is used to test for tuberculosis?
The most commonly used diagnostic tool for tuberculosis is a skin test, though blood tests are becoming more commonplace. A small amount of a substance called tuberculin is injected just ...
How long do you have to take antibiotics for tuberculosis?
For active tuberculosis, you must take antibiotics for at least six to nine months. The exact drugs and length of treatment depend on your age, overall health, possible drug resistance and where the infection is in your body.
How long does ethambutol last?
If you have drug-resistant TB, a combination of antibiotics called fluoroquinolones and injectable medications, such as amikacin or capreomycin (Capastat), are generally used for 20 to 30 months. Some types of TB are developing resistance to these medications as well.
What is the test for TB?
Sputum tests. If your chest X-ray shows signs of tuberculosis, your doctor might take samples of your sputum — the mucus that comes up when you cough. The samples are tested for TB bacteria. Sputum samples can also be used to test for drug-resistant strains of TB.
What test can confirm active tuberculosis?
Blood tests can confirm or rule out latent or active tuberculosis. These tests measure your immune system's reaction to TB bacteria.
Can a TB test be wrong?
Results can be wrong. The TB skin test isn't perfect. Sometimes, it suggests that people have TB when they don't. It can also indicate that people don't have TB when they do. You can have a false-positive result if you've been vaccinated recently with the bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccine.
Can TB drugs cause liver damage?
Serious side effects of TB drugs aren't common but can be dangerous when they do occur. All tuberculosis medications can be toxic to your liver. When taking these medications, call your doctor immediately if you have any of the following:
What are the mechanisms of action of tuberculosis drugs?
For some drugs, the mechanisms of action have not been fully identified.
What is the new drug for TB?
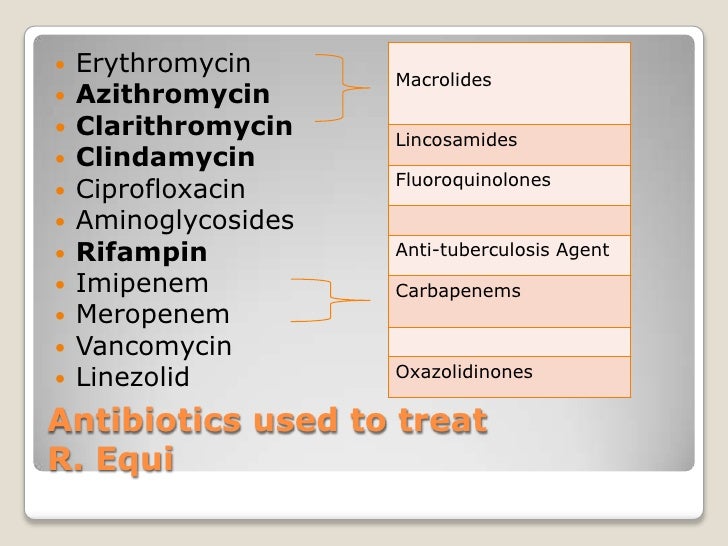
Bedaquiline and Delamanid are new drugs. Ethambutol, Pyrazinamide, Thioamides, Cycloserine, Para-aminosalicylic acid, Streptomycin, and Clofazimine are possibly effective. Kanamycin, Capreomycin and Amikacin are injectable second-line. XDR TB occurs when a Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, ...
What is the treatment for MDR TB?
MDR TB occurs when a Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, two of the most powerful first-line drugs. To cure MDR TB, healthcare providers must turn to a combination of second-line drugs, several of which are shown here. Second-line drugs may have more side effects, the treatment may last much longer, and the cost may be up to 100 times more than first-line therapy. MDR TB strains can also grow resistant to second-line drugs, further complicating treatment.
What drugs target DNA?
Rifamycins, Oxazolidinones and Macrolides act on DNA. Tuberculosis drugs target various aspects of Mycobacterium tuberculosis biology, including inhibition of cell wall synthesis, protein synthesis, or nucleic acid synthesis. For some drugs, the mechanisms of action have not been fully identified.
How long does it take to cure tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis, which results from an infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, can be cured with a combination of first-line drugs taken daily for several months.
Which compounds inhibit ATP synthase?
Thioamides, Nitroimidazoles, Ethambutol, and Cycloserine act on cell wall synthesis. Diarylquinoline inhibits ATP synthase. PAS, Fluoroquinolones, Cyclic Peptides and Aminoglycosides act on the DNA.
Who took the photo of Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
The photo of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, CDC/Dr. Ray Butler, Janice Carr. This illustration is in the public domain. Please credit the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID).
What is the name of the drug that is used to treat TB?
Isoniazid (INH) Rifapentine (RPT) Rifampin (RIF) These medications are used on their own or in combination, as shown in the table below. CDC and the National Tuberculosis Controllers Association (NTCA) preferentially recommend short-course, rifamycin-based, 3- or 4-month latent TB infection treatment regimens over 6- or 9-month isoniazid ...
What should a clinic decide on TB treatment?
Clinicians should choose the appropriate treatment regimen based on drug susceptibility results of the presumed source case (if known), coexisting medical conditions (e.g., HIV. ), and potential for drug-drug interactions. Consultation with a TB expert is advised if the known source of TB infection has drug-resistant TB.
Is 6H a good treatment for TB?
If short-course treatment regimens are not a feasible or an available option, 6H and 9H are alternative, effective latent TB infection treatment regimens. Although effective, 6H and 9H have higher toxicity risk and lower treatment completion rates than most short-term treatment regimens.
