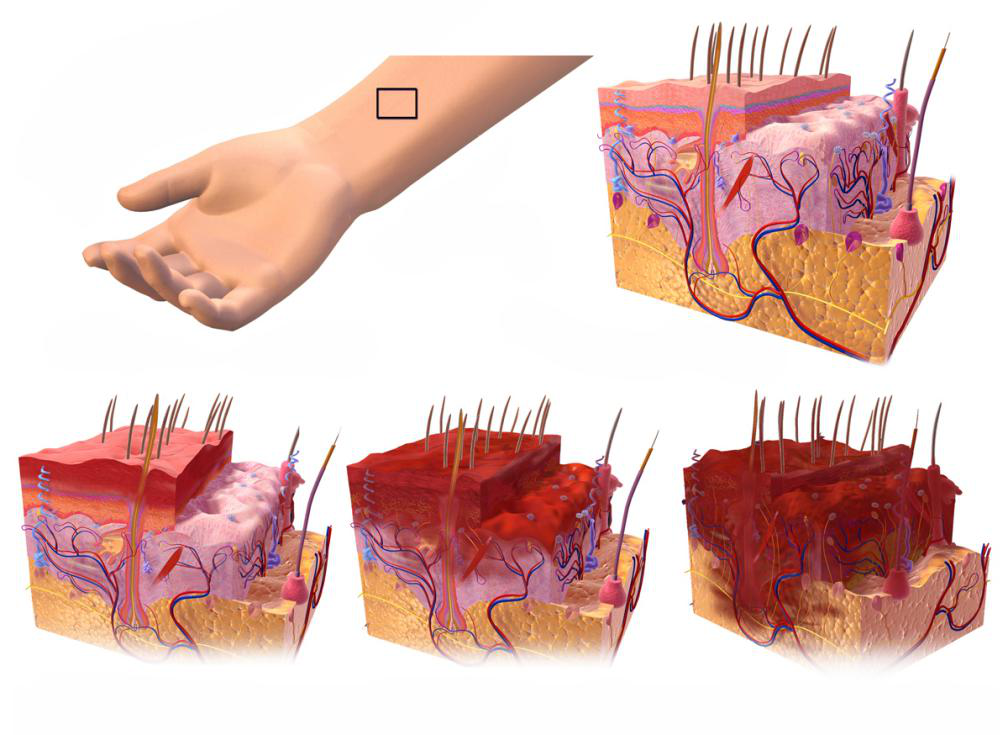
What is included in the treatment area for caustic substance toxicity?
There are many important aspects of chemically treating kerosene fractions with sodium hydroxide solutions (caustic) for the removal of naturally occurring contaminants in the production of jet fuels. A treating process consisting of several steps is often necessary to meet acidity, mercaptan, and other specifications required for the upgrading ...
What is the best way to dilute caustic solution?
Applications Caustic soda is used to maintain or increase pH. Increasing pH with caustic soda precipitates magnesium (Mg 2+) and suppresses calcium (Ca 2+) in high-hardness waters such as seawater, reduces corrosion, and neutralizes acid gases such as carbon dioxide (CO 2) and hydrogen sulfide (H 2 S).. Typical concentrations range from 0.25 to 4 lbm/bbl [0.7 to 11.4 …
How does a caustic injection system work?
· The vast majority of caustic chemicals are acidic or alkaline substances that damage tissue by accepting a proton (alkaline substance) or donating a proton (acidic substance) in an aqueous solution. ... In the treatment area, patients suspected of ingesting a caustic substance should be triaged to a high priority for prompt evaluation and ...
How to treat Caustic ingestion in the stomach?
We studied 239 patients who ingested caustic soda (NaOH) from 1957 to 1994. Data were collected from the medical records of the patients and from interviews with them and analyzed by software and by statistical tests of association. The results showed that more women than men ingested caustic substances (57%, n=153).

How is caustic soda used in water treatment?
Caustic soda is often used in wastewater treatment to raise the pH of water. It does this by absorbing water and carbon dioxide, and is commonly an integral component of water treatment.
How do you increase the pH of a sewage treatment plant?
Common chemicals used to increase alkalinity and pH include:Calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide (as lime slurry)Sodium hydroxide (caustic soda)Sodium carbonate (soda ash) or sodium bicarbonate.Magnesium hydroxide or magnesium bicarbonate.
Does caustic soda increase alkalinity?
Common chemicals used to increase alkalinity and pH include: Calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide (as lime slurry) Sodium hydroxide (caustic soda)
How do you reduce alkalinity in wastewater treatment?
Add sodium bisulfate and muriatic acid to lower the alkalinity of the wastewater. High alkalinity levels for domestic wastewater are 200 ppm and above. For industrial wastewater, these levels are very high. For example, high alkalinity levels can reach a figure of 500 ppm or more in the beverage industry.
How do you treat acidic wastewater?
Traditionally, sodium hydroxide (caustic soda) and calcium hydroxide (lime) have been used to neutralise acidic wastewater. However, these compounds are reactive and can cause high pH levels if not controlled correctly. The Magmex range is the environmentally friendly answer for acidic wastewater treatment.
Why is alkalinity important in wastewater treatment?
The biological wastewater treatment process also generates hydrogen ions, and so alkalinity is needed to keep the pH of the solution in the required range. If the alkalinity is too low then the extra hydrogen ions are not removed, the pH drops, and the speed of the wastewater treatment slows or even stops.
What is the pH of caustic soda?
pH values for bases like sodium hydroxide, ammonia and more.BaseNormalitypHSodium hydroxide (caustic soda)N14.0Sodium hydroxide0.1 N13.0Sodium hydroxide0.01 N12.0Sodium metasilicate0.1 N12.623 more rows
How do you add caustic soda to water?
ALWAYS add CAUSTIC SODA to water; NEVER add water to CAUSTIC SODA. CAUSTIC SODA is a strong alkali and produces a strong base solution when mixed with water. The reaction generates heat.
Which process is used to treat highly acidic and alkaline water?
Soda ash/sodium hydroxide injection This treatment method is used if water is acidic (low pH). Soda ash (sodium carbonate) and sodium hydroxide raise the pH of water to near neutral when injected into a water system. Unlike neutralizing filters, they do not cause hardness problems in treated water.
How is alkalinity removed from water?
The feed of a mineral acid will neutralize the alkalinity of water. Hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid or a combination of these can be used. This process converts the bicarbonates and carbonates present into carbonic acid.
How is sodium bicarbonate used in water treatment?
Many waters with a pH <6.5 are acidic, soft, and corrosive. Thus, sodium compounds like sodium bicarbonate are added during water treatment in order to raise the pH level of the water by chemically neutralizing the acidity as well as to soften the water.
Why is caustic soda stronger than soda ash?
Explanation: soda ash is considered to be a simple base whereas caustic soda is a weak salt of carbonic acid. ... sodium metal reacts with water to give sodium hydroxide and hydogerwhile sodium hydroxide reacts with carbonic acid to form caustic soda and water.
What causes low pH in wastewater?
If the influent pH is satisfactory, then the low effluent pH is usually caused by nitrification in combination with low natural alkalinity in the wastewater. If ammonia removal is required, then nitrification must continue.
What chemicals are used to adjust pH?
To raise the pH of an acidic liquid, sodium carbonate (soda ash), ammonium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide (lime) or magnesium hydroxide can also be used. To lower the pH of a base liquid, phosphoric acid, hydrochloric acid (HCI), nitric acid or carbon dioxide can be used, in addition to sulfuric.
How does pH affect wastewater treatment?
As a chemical component of the wastewater, pH has direct influence on wastewater treatability – regardless of whether treatment is physical/chemical or biological. Because it is such a critical component of the makeup of the wastewater, it is therefore critically important to treatment.
What is the pH of sewage water?
Raw wastewater generally has a pH near neutral (7.0), although it may vary between 6 and 8.
What is caustic ingestion?
In adults, caustic ingestions are frequently intentional ingestions of large amounts by suicidal people and are life-threatening . Common sources of caustics include solid and liquid drain and toilet bowl cleaners. Industrial products are usually more concentrated than household products and thus tend to be more damaging.
What is the treatment for esophageal perforation?
Esophageal or gastric perforation is treated with antibiotics and surgery (see Acute Perforation ). IV corticosteroids and prophylactic antibiotics are not recommended. Strictures are treated with bougienage or, if they are severe or unresponsive, with esophageal bypass by colonic interposition.
Is perforation a surgical procedure?
Perforation is treated surgically. (See also General Principles of Poisoning .) Worldwide, 80% of caustic ingestions occur in young children; these are usually accidental ingestions of small amounts and are often benign. In adults, caustic ingestions are frequently intentional ingestions of large amounts by suicidal people and are life-threatening.
Why do we do endoscopy?
Endoscopy. Because the presence or absence of intraoral burns does not reliably indicate whether the esophagus and stomach are burned, meticulous endoscopy is indicated to check for the presence and severity of esophageal and gastric burns when symptoms or history suggests more than trivial ingestion.
Is magnesium carbonate soluble in water?
As magnesium carbonate is relatively soluble (approximately 70 mg ·L –1 ), an excess of lime will lead to the following reaction: And if amounts of reagent are precisely adjusted, the water’s alkalinity will be reduced to the theoretical solubility applicable to the CaCO 3 + Mg (OH) 2 system which ranges from 2 to 3°F under normal temperature ...
What is settling zone?
a zone where recirculated crystals, water to be treated and lime are thoroughly combined; a settling zone from which the crystals that have been formed are removed and partially returned to the 1 st zone.
What is NaClO bleach?
Sodium hypochlorite (NaClO) is the active ingredient in commercial liquid bleach , which is commonly available in 6, 12 and 15 percent solutions. Sodium hypochlorite has a relatively short shelf life that depends on sunlight, temperature, vibration and the starting concentration. Increases in any of these shorten life.
Is sodium hypochlorite a carcinogen?
In addition, chlorination of drinking water with sodium hypochlorite can oxidize organic contaminants, producing trihalomethanes, which are considered carcinogenic and are subject to regulation.
What is the pH of sodium hypochlorite?
Sodium hypochlorite is a clear, slightly yellowish solution with a characteristic odor. As a bleaching agent it is usually a 5 percent sodium hypochlorite with a pH of about 11. More concentrated solutions (10 to 15 percent) have a pH of about 13. Sodium hypochlorite is unstable.
How is sodium hypochlorite produced?
The chemical also can be produced by adding chlorine gas to caustic soda, producing sodium hypochlorite, water and salt. The advantage of salt electrolysis system in formation of sodium hypochlorite is that no transport or storage of chemical is required.
What is the active ingredient in bleach?
The community had been using chlorine gas and ammonia as primary and secondary disinfectants. Sodium hypochlorite (NaClO) is the active ingredient in commercial liquid bleach, which is commonly available in 6, 12 and 15 percent solutions.
Is hydrogen gas explosive?
The hydrogen gas produced is explosive, and as a result ventilation is required. This process is slow, and a buffer of extra hypochlorous acid needs to be used. The maintenance and purchase of the electrolysis system is much more expensive than sodium hypochlorite.
Is monochloramine a disinfectant?
Monochloramine has a much longer shelf life and has no known negative health effects. It is a much weaker disinfectant and usually it is not used for primary disinfection. It is, however, perfect for secondary disinfection (the prevention of recontamination of drinking water in the distribution system).
co-current line
The old lines comprised co-current regenerated, fixed ion exchange beds: the water to be treated and the regenerating solution percolate from the top downwards through the resin bed.
countercurrent line
Almost all lines currently offered are of the countercurrent type. The first countercurrent systems available during the 1970s and 1980s were of the air or water blocking type.
water softening
A cation exchanger is used and regenerated using a sodium chloride solution (figure 81).
carbonate removal
This system uses a carboxylic resin that has previously been regenerated using acid in order to obtain the R-H form (figure 83).
demineralisation
The following description of the most commonly found exchanger groups uses the notation given below:
