However, Planned Parenthood clinics do offer STI testing and treatment at low cost. Fees are usually scaled according to patient income. Most offices also accept health insurance.
Are there any free STI clinics in my area?
Not every town has an STI clinic. Fortunately, health department clinics aren't the only free clinics around. Local public hospitals and teaching hospitals may also run low-cost or free STI clinics that offer both testing and treatment. If you live or work near a hospital, you can call and ask if they offer these services.
What is an STI prevention program?
STI programs funded by federal, state, and local governments, such as those that receive funding from various federal agencies such as HRSA, the CDC, or the Office of Population Affairs (OPA), are important sites of care for STI prevention and treatment, especially, those who are under- or uninsured.
Where can I get STD testing and treatment?
Local public hospitals and teaching hospitals may also run low-cost or free STD clinics that offer both testing and treatment. If you live or work near a convenient hospital, you can call and ask if they offer these services. However, we do not recommend going through the emergency room unless you are actually having an emergency.
Do health services address the needs of sexually transmitted infections (STIs)?
However, research indicates that health services in many countries may not fully address their SRH needs [3–5]. This is especially true for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and may be heightened in countries with fewer resources dedicated to health care.

How much does it cost to treat a STI?
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) will require treatment costing anywhere from $4 to $9,000 depending on your diagnosis without insurance.
Is STI treatment free in Canada?
Where can I get tested? Testing is free across Canada at family doctors' offices, walk-in clinics, sexual health clinics, and other public health units and community centres.
Is STI treatment free in Ontario?
free confidential sexually transmitted infections ( STI ) testing and treatment. anonymous HIV testing and HIV / AIDS Programs. immunizations for hepatitis A and B and HPV vaccine. pap testing.
How do you get help if you have an STD?
You can get tested and treated at your local health department's STD clinic, a family planning clinic, a student health center, or an urgent care clinic. You can also find a clinic using GetTested and ask if they offer treatment for gonorrhea and chlamydia.
How can I cure an STD without going to the doctor?
There is no proven alternative therapy to treating an STI. Treatment is testing and antibiotics. The most effective complementary treatments of STIs — that is, those that that go along with standard medical treatment — involve prevention and patient counseling.
Do STI tests cost money Canada?
You can get tested for Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, HIV, Syphilis and Hepatitis C free of charge.
What happens if you test positive for an STI?
Positive test results If you test positive for an STI , the next step is to consider further testing and then get treatment as recommended by your doctor. In addition, inform your sex partners. Your partners need to be evaluated and treated, because you can pass some infections back and forth.
What happens if you test positive for STI Ontario?
You need to alert all of your past and present sexual partners if you are diagnosed with an STI . They need to be treated at the same time as you to prevent them from re-infecting you or anyone else. Visit Sexual Health Ontario for tips on how to talk to your sexual partner(s) about an STI .
Do you have to pay for STI tests?
All treatment for sexually transmitted infections is free of charge.
What is the strongest antibiotic for STD?
Single-dose therapy with azithromycin is as effective as a seven-day course of doxycycline (Vibramycin). Doxycycline is less expensive, but azithromycin may be cost-beneficial because it provides single-dose, directly observed therapy. Erythromycin and ofloxacin (Floxin) also may be used to treat C.
What STI Cannot be cured?
Viruses such as HIV, genital herpes, human papillomavirus, hepatitis, and cytomegalovirus cause STDs/STIs that cannot be cured. People with an STI caused by a virus will be infected for life and will always be at risk of infecting their sexual partners.
What is the fastest way to get rid of an STD?
Antibiotics. Antibiotics, often in a single dose, can cure many sexually transmitted bacterial and parasitic infections, including gonorrhea, syphilis, chlamydia and trichomoniasis.
What insurances cover STIs?
Access to prevention, screening, testing and treatment services for STIs is facilitated by private insurance, public coverage such as Medicaid and Medicare, as well as publicly-supported health programs.
What is the most common STI in the United States?
Untreated STIs, particularly chlamydia and gonorrhea, can result in pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women and infertility. It is estimated that HPV, the most common STI in the United States, will be contracted at some point during the lifespan of nearly every sexually active individual.
What is EPT in STI?
Many states have laws allowing expedited partner therapy (EPT), which permits the treatment of partners of patients diagnosed with an STI without examination. The CDC has recommended this practice since 2006 in certain circumstances due to its success in reducing gonorrhea reinfection rates. Currently 39 states and DC allow physicians to provide at least some treatment to the partner of a patient diagnosed with a STI. Among publicly funded clinics, 79% provided expedited therapy for the patient’s partner at the same visit in 2015. However, even in states where EPT has been legalized, many do not allow the patient’s insurance coverage to be billed for the partner’s treatment, which can create a financial barrier to care.
How many sexually transmitted infections will be reported in 2020?
Published: Feb 18, 2020. Sexually transmitted infections encompass many different types of viral and bacterial infections. Every year, an estimated 20 million new sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in the United States. The rates of reported STIs reached record-breaking levels ...
Does Medicare cover STI screening?
The ACA also requires Medicare to cover preventive services that are rated “A” or “B” by the USPSTF without cost-sharing. Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance) covers STI screenings for chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, and/or Hepatitis B once every 12 months for individuals at increased risk for an STI or at certain times during pregnancy for pregnant individuals. Medicare also covers up to two individual 20-30 minute, face-to-face, high-intensity behavioral counseling sessions once each year for sexually active individuals at increased risk for STIs. Additionally, Medicare covers an HIV screening once per year for individuals age 15-65 without regard to perceived risk or for individuals outside of this age range who are at an increased risk for HIV. Medicare Part D is required to cover all approved antiretrovirals (one of “six protected” drug classes), which includes PrEP, but unlike most preventive services covered under Part B, plans are allowed to charge cost sharing for these drugs.
Is confidentiality important for STI screening?
Confidentiality is a crucial factor in the provision of STI screening and treatment services. For minors in particular, it can be a challenge. Although all 50 states and DC allow minors to consent to STI services, 18 states allow physicians to inform a parent or guardian that the minor is seeking these services ( Figure 6 ).
Can syphilis be prevented in pregnancy?
Late or limited prenatal care has been associated with congenital syphilis (when the infection is present in utero or childbirth). Congenital syphilis is preventable in most cases, if women are screened for syphilis and treated early during prenatal care.
What are the consequences of STDs?
Women are not only biologically more susceptible than men to some STDs but also may suffer more serious consequences. Because STDs are less likely to produce symptoms in women, those who have been infected are more likely to go undiagnosed until only after they have developed serious health problems, such as cervical cancer or pelvic inflammatory disease (which in turn can cause chronic pain, infertility and ectopic pregnancy). Additionally, STDs in pregnant women can result in miscarriage, low birth weight and congenital and neonatal infections.
Why are family planning clinics important?
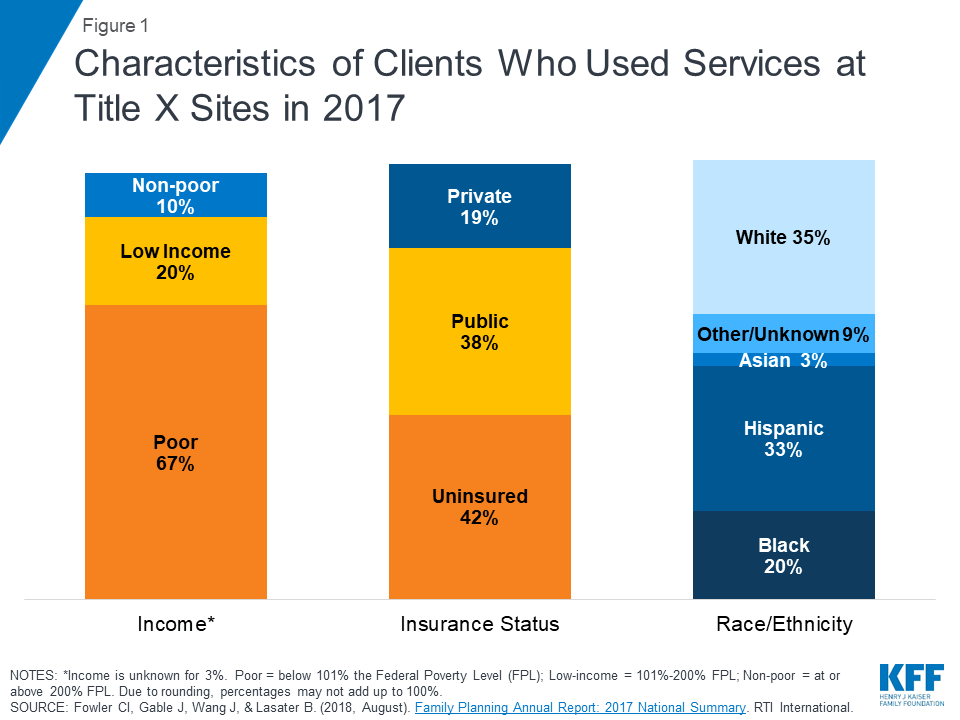
Family planning clinics clearly play an important role in STD service delivery, and many providers are striving to do even more. Yet, many of these same providers feel they are already financially stretched to the limit, and worry simply about maintaining existing services to their current patient population. This is particularly true for family planning clinics that receive Title X funding, since two-thirds of Title X clients are eligible for completely subsidized care, because they have incomes under the federal poverty level. Moreover, federal funding for Title X has not kept pace with the increasing costs of these services: Taking inflation into account, the 2001 funding level of $254 million is 57% lower than the 1980 level. Funding increases in the 1990s were largely earmarked for serving additional clients, rather than meeting the rising costs of service delivery. While Title X clinics can also draw on some of the funds available under the federal Infertility Prevention Program—created in 1992 to support the screening and treatment of chlamydia—funding for the entire program in FY 2002 was only $28 million.
How to check for HIV?
It's a good idea to get tested if you: 1 had a new sexual partner since your last test. 2 had unprotected sex. 3 think your partner may have an STD. 4 are experiencing symptoms — but remember, STDs don't always cause symptoms. 5 if you think you've been exposed to HIV within the last 3-days, call to discuss PEP to prevent HIV infection.
Can you get tested for STDs in person?
Getting tested for sexually transmitted diseases and infections ( STDs/STIs ) is easier than ever either in-person or with at home STD testing kits. It's a good idea to get tested if you: had a new sexual partner since your last test. had unprotected sex. think your partner may have an STD.
Does Planned Parenthood offer STD testing?
Whether online or in-person, Planned Parenthood offers STD care - including at home testing kits. Financial help is available for STD testing and many other services offered at Planned Parenthood. Eligibility depends on things like income, household size, and programs available in your area.
Health Services
Claimed Program This program has been claimed by One Community Health and they are helping to ensure the information is accurate and up-to-date.
Health
Claimed Program This program has been claimed by Women's Empowerment and they are helping to ensure the information is accurate and up-to-date.

What Are Sexually Transmitted Infections?
Prevalence of Sexually Transmitted Infections
- While women still account for the highest reported cases of STIs (driven mainly by high numbers of chlamydia in women), men, in particular gay and bisexual men, saw greater increases in rates of syphilis, chlamydia, and gonorrhea in recent years. Syphilis infection rates nearly doubled among men from 2014 to 2018 (Figure 1). Congenital syphilis rates increased 173% between 20…
Paying For STI Prevention and Treatment Services
- Access to prevention, screening, testing and treatment services for STIs is facilitated by private insurance, public coverage such as Medicaid and Medicare, as well as publicly-supported health programs. The CDC estimates that in 2008 (the most recent estimate available), the annual direct medical costs in the US associated with STIs (including HIV) were nearly $16 billion.
Confidentiality
- Confidentiality is a crucial factor in the provision of STI screening and treatment services. For minors in particular, it can be a challenge. Although all 50 states and DC allow minors to consent to STI services, 18 states allow physicians to inform a parent or guardian that the minor is seeking these services (Figure 6). Confidentiality has long ...
Conclusion
- High rates of STIs continue to be a public health concern. Women, people of color, and youth experience the highest rates of reported infections. Gay and bisexual men account for the majority of the increase between 2000 and 2018. The general public, however, appears to be unaware of the how commonly STIs occur and that their incidence is on the rise. Publicly funde…