What is the best treatment for acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
The main treatment for acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) in adults is typically long-term chemotherapy (chemo)....Different combinations of chemo drugs might be used, but they typically include:Vincristine.Dexamethasone or prednisone.An anthracycline drug such as doxorubicin (Adriamycin) or daunorubicin.
How much does it cost to treat acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
Total mean cost of the entire treatment was US $103250 (US $55196-166039) per patient, 53% of which were basic hospital costs and 47% patient-specific costs.
How long is treatment for acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
Treatment for acute lymphocytic leukemia can be a long road. Treatment often lasts two to three years, although the first months are the most intense. During maintenance phases, children can usually live a relatively normal life and go back to school. And adults may be able to continue working.
Can acute lymphoblastic Leukaemia be cured?
The medical community considers a person cured of acute lymphocytic leukemia if they're in total remission for 10 years. Up to 98% of children with ALL go into remission in about a month after treatment and 9 in 10 can be cured.
Is leukemia treatment covered by insurance?
Medicare covers many of the costs of care relating to leukemia. As with other cancer, doctors customize treatment options for people based on their medical history and type of cancer.
How much does a leukemia surgery cost?
The costs of the transplantation varied between $25,531 and $44,087. Costs of follow-up amounted to $4,167. Relapse treatment, mainly consisting of reinduction therapy, costs on average $24,338. The total average weighted costs of AML patients amounted to $104,386.
How long are you in hospital with leukemia?
Patients will often need to stay in the hospital for 3 to 4 weeks during treatment. However, depending on the situation, many patients can leave the hospital.
How serious is acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
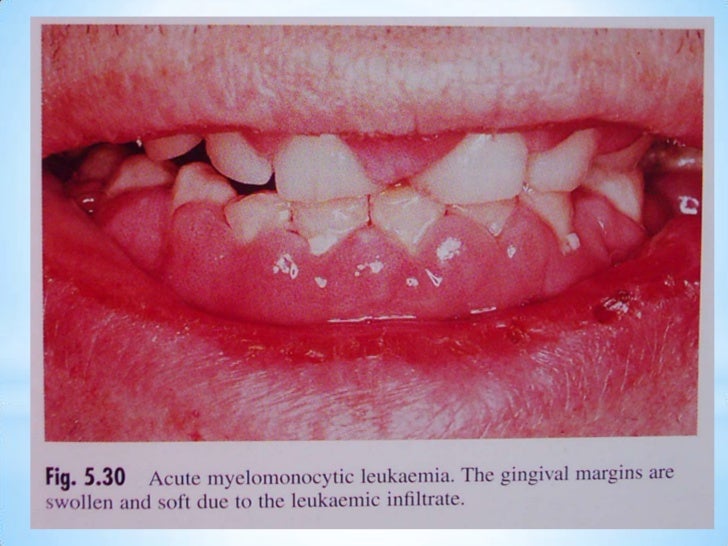
Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) is also called acute lymphoblastic leukemia. “Acute” means that the leukemia can progress quickly, and if not treated, would probably be fatal within a few months. "Lymphocytic" means it develops from early (immature) forms of lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell.
Is acute leukemia is curable?
Although AML is a serious disease, it is treatable and often curable with chemotherapy with or without a bone marrow/stem cell transplant (see the Types of Treatment section). It is important to remember that statistics on the survival rates for people with AML are an estimate.
How long can you live with acute lymphocytic leukemia?
The 5-year survival rate for people age 20 and older is 40%. The 5-year survival rate for people under age 20 is 89%. Recent advances in treatment have significantly lengthened the lives of people with ALL. However, survival rates depend on several factors, including biologic features of the disease and a person's age.
How quickly does acute lymphoblastic leukemia progress?
Acute leukemias — which are incredibly rare — are the most rapidly progressing cancer we know of. The white cells in the blood grow very quickly, over a matter of days to weeks. Sometimes a patient with acute leukemia has no symptoms or has normal blood work even a few weeks or months before the diagnosis.
Can you live a normal life with leukemia?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) can rarely be cured. Still, most people live with the disease for many years. Some people with CLL can live for years without treatment, but over time, most will need to be treated. Most people with CLL are treated on and off for years.
What are the treatments for acute lymphoblastic leukemia?
Some treatments are standard (the currently used treatment), and some are being tested in clinical trials. A treatment clinical trial is a research study meant to help improve current treatments or obtain information on new treatments for patients with cancer . When clinical trials show that a new treatment is better than the standard treatment, the new treatment may become the standard treatment. Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial. Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment.
Which type of cell fights infection?
Granulocytes ( white blood cells) that fight infection and disease. A lymphoid stem cell becomes a lymphoblast cell and then one of three types of lymphocytes (white blood cells): B lymphocytes that make antibodies to help fight infection.
What is the name of the cancer that is caused by the bone marrow making too many lymphocytes?
Adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). Adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL; also called acute lymphocytic leukemia) is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow. This type of cancer usually gets worse quickly if it is not treated.
What is the disease that affects the white blood cells?
Adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). Leukemia may affect red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Previous chemotherapy and exposure to radiation may increase the risk of developing ALL.
Can leukemia cause side effects?
Treatment for adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia may cause side effects. For information about side effects that begin during treatment for cancer, see our Side Effects page. Side effects from cancer treatment that begin after treatment and continue for months or years are called late effects. Late effects of treatment for ALL may include ...
Can leukemia cause bleeding?
These leukemia cells are not able to fight infection very well. Also, as the number of leukemia cells increases in the blood and bone marrow, there is less room for healthy white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets. This may cause infection, anemia, and easy bleeding.
Do clinical trials include patients who have not received treatment?
Some clinical trials only include patients who have not yet received treatment . Other trials test treatments for patients whose cancer has not gotten better. There are also clinical trials that test new ways to stop cancer from recurring (coming back) or reduce the side effects of cancer treatment.
Induction
The goal of induction chemotherapy is induce remission. Remission is when doctors are no longer able to find signs of your cancer. The induction phase can take up to 4 weeks, during which time you’ll stay in the hospital.
Intensification and consolidation
The intensification and consolidation phase consists of additional chemotherapy to destroy lingering cancer cells that may be in your body, but aren’t detectable. You may also receive a bone marrow transplant at this time. This stage may last several months.
Maintenance
The maintenance phase involves taking a lower dose of chemotherapy drugs for typically about 2 years to prevent relapse. Medications may include:
Bone marrow transplant
Chemotherapy damages healthy cells in your body that divide quickly like the cells in your bone marrow that produce blood cells. A bone marrow transplant helps replace these damaged bone marrow cells.
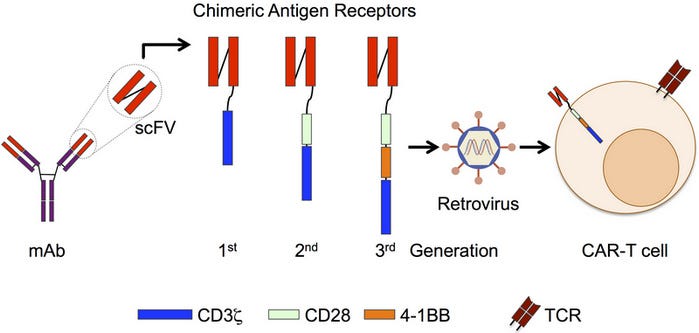
CAR T cell therapy
A type of immunotherapy called CAR T-cell therapy is a new treatment available for adults up to age 25. It’s sometimes used when ALL doesn’t respond to other treatments.
Supportive care
This helps address the side effects of treatment, especially when cancer is aggressive or not responding to treatments. This can include antibiotics, as well as red blood cell and platelet transfusions.
Low risk
For low-risk children, an allogeneic bone marrow transplant may be performed after remission if there’s a poor response to chemotherapy.
How long does it take to cure leukemia?
Complete therapy for ALL typically continues for two to three years.
How long does it take to get chemo for all?
Chemotherapy. Treatment of ALL is usually urgent and needs to be given within days, and sometimes the same day, as the diagnosis is made. The first phase of treatment, called induction chemotherapy, requires that patients remain in the hospital for approximately four weeks.
What chromosomes should be translocated to BMT?
Patients with the Philadelphia chromosome or with the translocation involving chromosomes 4 and 11 , should go on to BMT. At UCSF Medical Center, allogeneic transplantation — which uses stem cells or bone marrow from a matched brother or sister — is preferred and considered the standard therapy for ALL.
What is the procedure called when you have abnormal cytogenetics?
Stem cell transplantation. Stem cell transplantation , also called blood or marrow transplantation (BMT), is performed only in patients who have abnormal cytogenetics, chromosome testing or other high-risk ALL features.
What is the most common drug used for induction treatment of all?
The most common drugs used for induction treatment of ALL are daunorubicin, vincristine, prednisone, asparaginase and sometimes cyclophosphamide. Intensive supportive care accompanies the chemotherapy, including transfusion of red blood cells and platelets. Antibiotics are needed both preventatively and as treatment for both bacterial ...
How does a doctor relate to chemo?
The relationship with a doctor is a very personal one, built on communication and trust. In choosing a doctor, the "chemistry" between the two of you must work . Coping with Chemotherapy. Each person experiences side effects from chemotherapy differently, and different chemotherapy drugs cause different side effects.
Can stem cell transplants be used for all patients?
Stem cell transplantation is not typically performed to treat ALL unless abnormal cytogenetics are present. Chemotherapy agents used during consolidation include the same agents used during induction, as well as Ara-C, etoposide, methotrexate and 6-mercaptopurine.
What are the services offered by the American Cancer Society?
These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, nutritional advice, rehab, or spiritual help. The American Cancer Society also has programs and services – including rides to treatment, lodging, and more – to help you get through treatment.
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
Why is it important to discuss treatment options?
It’s important to discuss all of your treatment options and their goals and possible side effects, with your treatment team to help make the decision that best fits your needs. Some important things to consider include: It’s also very important to ask questions if there is anything you’re not sure about.
How long does ALL treatment last?
Treatment of ALL typically lasts for about 2 years. It is often intense, especially in the first few months of treatment, so it's important that you are treated in a center that has experience with this disease. The treatment approach for children with ALL can be slightly different from that used for adults.
Can you continue cancer treatment?
Whether or not you continue treatment, there are still things you can do to help maintain or improve your quality of life.
Is treatment information given here official policy of the American Cancer Society?
The treatment information given here is not official policy of the American Cancer Society and is not intended as medical advice to replace the expertise and judgment of your cancer care team. It is intended to help you and your family make informed decisions, together with your doctor.
ALL treatment plans
Newly diagnosed adult ALL patients typically undergo chemotherapy, which is given in three phases. Depending on the features of the patient’s cancer, targeted therapy may also be prescribed.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy drugs kill cancer cells, control their growth or relieve disease-related symptoms. Chemotherapy may involve a single drug or a combination of two or more drugs, depending on the type of cancer and how fast it is growing.
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy drugs are designed to stop or slow the growth or spread of cancer. This happens on a cellular level. Cancer cells need specific molecules (often in the form of proteins) to survive, multiply and spread. These molecules are usually made by the genes that cause cancer, as well as the cells themselves.
Stem cell transplantation
A stem cell transplant (also known as a bone marrow transplant) is a procedure that replaces cancerous bone marrow with new, healthy bone marrow stem cells. Stem cell transplants are usually given after an intense round of chemotherapy that kills the patient’s existing bone marrow cells and prepares the body for transplant.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses powerful beams of energy to kill cancer cells. Since leukemia cells travel in the blood stream, there is no distinct tumor to target with radiation therapy. Instead, radiation may be used when the disease has spread to the central nervous system.
CAR T-cell therapy
T cells are a type of immune system cell. They help the immune system respond to disease and directly kill diseased cells. In Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, T cells are modified so they can recognize and attack cancer cells.
Clinical trials
As a top-ranked cancer center, MD Anderson offers multiple clinical trials for ALL. Many of these cannot be found anywhere else. Trials explore new drug combinations and new drugs, including targeted therapies and immunotherapies.
What is acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)?
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia causes your bone marrow (spongy tissue in bones) to make too many immature white blood cells (lymphoblasts). These abnormal cells crowd out healthy red and white blood cells and platelets in the blood and bone marrow, making it difficult for the body to fight infection and disease.
Facts and stats
About 60% of acute lymphoblastic leukemia occurs in children. Other key things to know about ALL:
Causes and risk factors
Researchers believe acute lymphoblastic leukemia occurs due to genetic mutations (changes) that affect blood cell production. The exact cause of these changes is not known.
Symptoms
Some children and adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia may not experience symptoms. Many symptoms can feel like the flu, but don’t improve with time.
Types
B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma: Starts in immature cells that ordinarily develop into B-cell lymphocytes. B-cell ALL is the most common subtype.
Diagnosing
To diagnose acute lymphoblastic leukemia, your doctor performs a thorough physical exam and checks your body for swollen lymph nodes (small glands that help your body fight infection). Your doctor also asks about your health history and family health history.
Treatments
Treatment options for acute lymphoblastic leukemia depend on your overall health and how well you respond to treatment. ALL is not divided into stages, which doctors use to describe the extent of cancer in other forms of the disease.
Blood cell creation
The body produces millions of blood cells each day. Most develop in the bone marrow, the spongy interior of bones that contains immature stem cells.
How is leukemia classified?
While there are many types of leukemia, they are typically classified by the type of stem cell that has turned cancerous, either lymphoid or myeloid.
About ALL
ALL forms from lymphoid stem cells. These disease cells multiply rapidly and are poor at fighting infection. They also crowd out healthy cells, leaving people with ALL weak and prone to infection.
ALL risk factors
A risk factor is anything that increases the risk of developing a disease. Knowing a disease’s risk factors can be an important step towards catching it early. It's important to note that not everyone with risk factors will develop the disease.
Why choose MD Anderson for your leukemia treatment?
Choosing the right cancer center may be the most important decision you can make as a leukemia patient. At MD Anderson’s Leukemia Center and Stem Cell Transplantation and Cellular Therapy Center, you’ll get treatment from one of nation’s the largest, most experienced leukemia teams at a top-ranked cancer center.