Sewage treatment
| Synonym | Wastewater treatment plant (WWTP), water ... |
| Position in sanitation chain | Treatment |
| Application level | City, neighborhood [1] |
| Management level | Public |
Full Answer
What work do they do at a sewage treatment plant?
What are the rules and regulations around sewage treatment plants?
- Legal Compliance. For starters, you’ll need to make sure your sewage treatment plant is legally compliant – particularly if you’ve moved into a property with an old model.
- Consent to Discharge. ...
- Planning Permission. ...
How does a sewage treatment plant actually work?
You’re basically:
- growing the organisms in a suspension and retaining them
- mixing the wastewater with the biomass
- aerating this “mixed liquor” so the bacteria can get to work
- settling out the mixed liquor suspended solids (MLSS)
- sending return activated sludge (RAS) to the reactor basin
- sending waste activated sludge (WAS) to be dewatered and treated accordingly
How much does a sewage treatment plant cost?
- Sewage in a plant is treated to a safe level
- Does not harm the environment
- Reliable and modern solution
- Cost effective over time
- Compact system
- Improve resale value of premises
- Safer and poses lower risk to health
- Simple and easy installation
Why do we need sewage treatment plants?
Maintenance of Sewage Water Treatment Plants:
- Clarifies should not be clogged with solid waste
- There is no biological growth in your aerators
- The growth of the filaments is zero in the aeration tanks
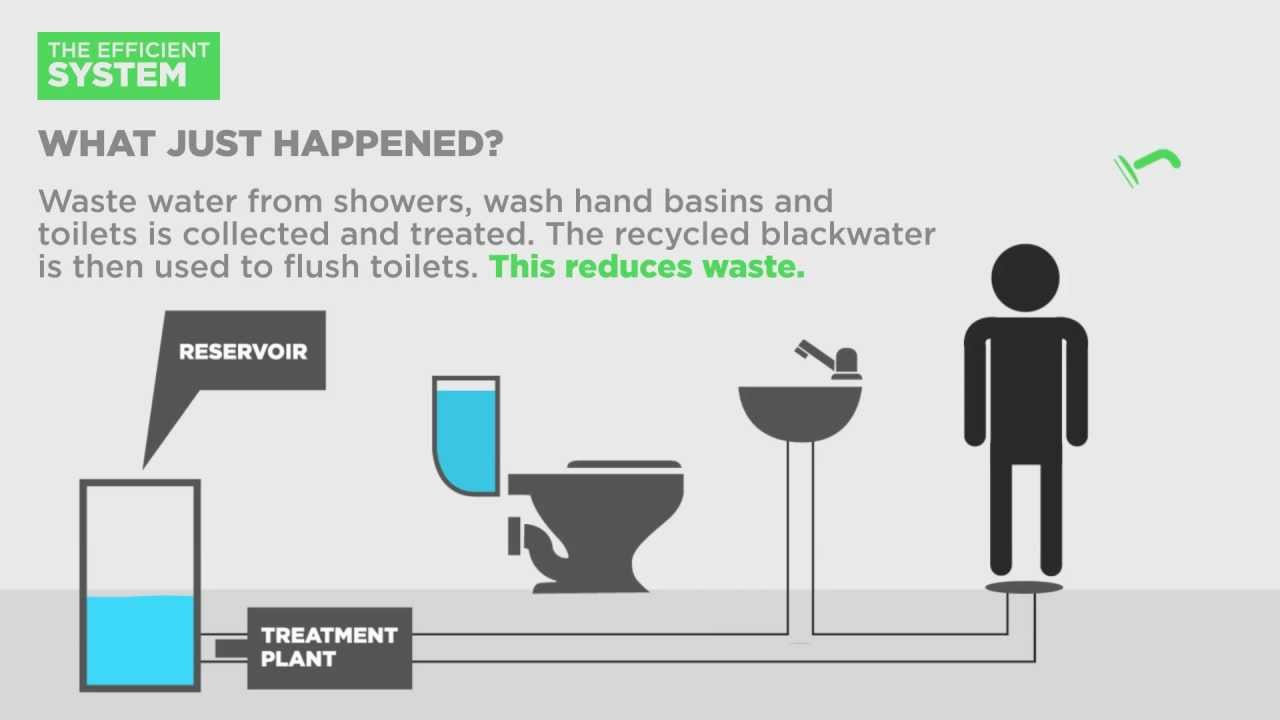
Where is sewage treatment used?
For domestic wastewater (also called municipal wastewater or sewage), the treatment plant is called a sewage treatment plant. For industrial wastewater, treatment either takes place in a separate industrial wastewater treatment plant, or in a sewage treatment plant (usually after some form of pre-treatment).
What are sewage treatment plants used for?
Most treatment plants were built to clean wastewater for discharge into streams or other receiving waters, or for reuse. Years ago, when sewage was dumped into waterways, a natural process of purification began.
How many types of areas are commonly used in the treatment of wastewater?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment.
Are sewage treatment plants good for the environment?
It removes various solids, which includes everything from rags and sticks to sand and smaller particles found in wastewater. It reduces organic material and pollutants by the controlled action of helpful bacteria and other microorganisms that consume organic matter in wastewater.
What are the advantages of sewage treatment?
There are many benefits to a modern wastewater treatment system:Rids Potential Diseases. Wastewater treatment systems eliminate disease-causing bacteria and kills harmful organisms. ... Low-Cost. ... Minimal Odour Emissions. ... No Water Bills. ... Little Maintenance. ... Break Down Solids Faster. ... Less Wasteful.
Do we drink sewage water?
If the recycled water is intended for human consumption, the next stage is to put it through further treatment before mixing it with natural water supplies. However, sewage water which has gone through wastewater treatment forms 'recycled water' which is clean enough for some agricultural and industrial usage.
What are the 4 stages of sewage treatment?
4-Step Wastewater Sludge Treatment ProcessStep 1 – Sludge Thickening. The first step in the sewage sludge treatment plan is called thickening. ... Step 2 – Sludge Digestion. After amassing all the solids from the sewage sludge begins the sludge digestion process. ... Step 3 – Dewatering. ... Step 4 – Disposal.
What are the 3 types of water treatment plant?
Types of Water Treatment PlantsWastewater Treatment Plant (WWTP) ... Sewage Treatment Plants (STPs) ... Effluent Treatment Plants (ETP's) ... Demineralization (DM) Treatment Plants. ... Reverse Osmosis (RO) Water Treatment.
How many types of sewage treatment plants are there?
4 Types of Sewage Treatment Plants.
How close to a house can a sewage treatment plant be?
At least 10 meters away from any habitable building.
Do sewage plants smell?
The very nature of wastewater makes it a smelly venture. While wastewater treatment plants do smell, it's important to reduce those smells for several reasons. First, you don't want people who live nearby to constantly complain to the town or city about the odors.
What are the disadvantages of sewage treatment plant?
Disadvantages of a sewage treatment plantRoutine pumping out. ... Smelly. ... Bacteria. ... Space. ... Installation costs. ... Power. ... Sporadic use. ... Treated water absorption.More items...
How is sewage treated in a package plant?
In the first stage, raw sewage enters the system and larger particles are settled out or broken up mechanically to increase their surface area and make them more accessible to the aerobic bacteria.
What is the final step in sewage treatment?
During this period, aerobic bacteria reduce the sewage into simple compounds. The final step is the settling or clarification chamber. Treated sewage from the aeration process is emptied into this chamber where the heavier solids in the sewage settle.
What is aerobic treatment?
In this process, oxygen-using bacteria attack and break down the organic portions of the sewage into simpler inorganic compounds . Aerobic treatment is preferred because it is rapid and relatively odor free.
Why is aerobic treatment preferred over anaerobic treatment?
Aerobic treatment is preferred because it is rapid and relatively odor free. It also provides greater solids reduction. Septic tank systems rely on the anaerobic (without oxygen) breakdown process that is less efficient. It produces the characteristic septic odor.
What is the second phase of anaerobic treatment?
Anaerobic treatment chambers require periodic pumping of sludge. The second phase of the treatment consists of mechanical aeration. Oxygen-containing air is mixed and blended with mixtures of solids and liquid. During this period, aerobic bacteria reduce the sewage into simple compounds.
How do package plants maintain aerobic conditions?
It produces the characteristic septic odor. Package plants maintain aerobic conditions by introducing air into the tank. This can be done in either of two ways. Some manufacturers use an external air compressor to bubble air through the sewage.
What are the three methods of handling waste from a rural residence?
There are three generally recognized methods of handling wastes from a rural residence. They are the stabilization lagoon, the septic tank and the individual aerobic treatment plant.
Where can sewage be treated?
Sewage can be treated close to where the sewage is created , which may be called a "decentralized" system or even an "on-site" system (in septic tanks, biofilters or aerobic treatment systems ). Alternatively, sewage can be collected and transported by a network of pipes and pump stations to a municipal treatment plant.
What is wastewater treatment plant?
The term "sewage treatment plant" (or "sewage treatment works" in some countries) is nowadays often replaced with the term wastewater treatment plant or wastewater treatment station . Strictly speaking, the latter is a broader term that can also refer to industrial wastewater.
Why is wastewater treated?
The pretreatment has the following aims: to remove constituents that may pose risks to the sewerage system and its workers; prevent toxic or inhibitory compounds to the microorganisms in the biological stage in the municipal treatment plant; hinder beneficial use of the produced sewage sludge; or that will still be present in the final effluent from the treatment plant. : 59 Some industrial wastewater may contain pollutants which cannot be removed by sewage treatment plants. Also, variable flow of industrial waste associated with production cycles may upset the population dynamics of biological treatment units.
What is wastewater used for?
Physical, chemical, and biological processes are used to remove contaminants and produce treated wastewater (or treated effluent) that is safe enough for release into the environment.
What is municipal wastewater treatment?
Sewage treatment (or domestic wastewater treatment, municipal wastewater treatment) is a type of wastewater treatment which aims to remove contaminants from sewage.
How much of the world's wastewater is treated?
At the global level, an estimated 52% of municipal wastewater is treated. However, wastewater treatment rates are highly unequal for different countries around the world. For example, while high-income countries treat approximately 74% of their municipal wastewater, developing countries treat an average of just 4.2%.
How does sewage water go through a bar screen?
The influent in sewage water passes through a bar screen to remove all large objects like cans, rags, sticks, plastic packets, etc. carried in the sewage stream. This is most commonly done with an automated mechanically raked bar screen in modern plants serving large populations, while in smaller or less modern plants, a manually cleaned screen may be used. The raking action of a mechanical bar screen is typically paced according to the accumulation on the bar screens and/or flow rate. The solids are collected and later disposed in a landfill, or incinerated. Bar screens or mesh screens of varying sizes may be used to optimize solids removal. If gross solids are not removed, they become entrained in pipes and moving parts of the treatment plant, and can cause substantial damage and inefficiency in the process. : 9
How to keep a treatment plant from overloaded?
Try to use cleaning products little and often so your treatment plant is not overloaded .
Why use a waste disposal unit?
Only use a waste disposal unit if your plant is specifically designed to accept higher organic loads.
How to get rid of bacteria in plants?
Try to spread your clothes washing throughout the week. Stick to the same washing, dishwasher and other cleaning products as the bacteria will work more efficiently with products it is used to treating. Think before you put anything down the sink, toilet or drains. Desludge your plant when required.
How to contact KEE for sewer service?
Request a quote for a maintenance contract or call KEE on: 01296 634500. Book a Visit / Service. Call now.
What can you not put down the toilet?
Don’ts. Don’t put sanitary towels, tampons, cotton wool or cotton wool buds, incontinence pads or any baby, cleaning or facial wipes down the toilet. Don’t flush rubber products or other non-biodegradable products down the toilet. Don’t pour fat, grease or cooking oil down the sink or drains. Fats suffocate the bacteria and inhibit ...
Can you leave a plant on while away?
Leave your plant switched on while you are away or on holiday. Switching off your plant can cause damage to the motor and moving parts as well as kill the biomass.
Can you use chlorine in a plant?
Don’t allow rainwater, groundwater or large volumes of water ( such as those from a swimming pool or Jacuzzi) into the plant . Chlorine kills the bacteria and the excessive water will increase the flow rate through the plant, not allowing sufficient treatment time.
Why upgrade wastewater treatment system?
Enhanced treatment systems enable some wastewater plants to produce discharges that contain less nitrogen than plants using conventional treatment methods . Upgrading wastewater treatment systems is often expensive for municipalities and rate payers, but upgrades can pay for themselves or end up saving a plant money.
How to maintain a septic system?
Homeowners are responsible for maintaining their septic systems in most cases. To protect and maintain their system, homeowners should: 1 Have their system inspected regularly and pump their tank as necessary 2 Use water efficiently 3 Not dispose of household hazardous waste in sinks or toilets 4 Avoid driving vehicles or placing heavy objects on their drainfield 5 Visit EPA's decentralized wastewater (septic) systems webpage to learn more about septic systems and EPA's SepticSmart Week Program 6 Consult EPA's guide on maintaining septic systems for more information: Homeowner's Guide to Septic Systems (PDF) (9 pp, 3 MB, About PDF)
What is the source of nitrogen and phosphorus in wastewater?
Wastewater contains nitrogen and phosphorus from human waste, food and certain soaps and detergents. Once the water is cleaned to standards set and monitored by state and federal officials, it is typically released into a local water body, where it can become a source of nitrogen and phosphorus pollution. Some wastewater treatment plants are able ...
How does a septic system contribute to nutrient pollution?
Septic systems can easily become a source of nutrient pollution if not properly maintained. Most homes and businesses send their wastewater to a treatment plant where many pollutants are removed from the water. Wastewater treatment facilities in the United States process approximately 34 billion gallons of wastewater every day.
What percentage of homes in the US have septic systems?
Septic Systems. Approximately 20 percent of homes in the United States use septic systems that locally treat their wastewater. When a septic system is improperly managed, elevated nitrogen and phosphorus levels can be released into local water bodies or ground water.
Who is responsible for septic system maintenance?
Homeowners are responsible for maintaining their septic systems in most cases. To protect and maintain their system, homeowners should: Have their system inspected regularly and pump their tank as necessary. Use water efficiently. Not dispose of household hazardous waste in sinks or toilets.
What causes a septic system to fail?
Common causes of septic system failure include aging infrastructure, inappropriate design, overloading with too much wastewater in too short a period of time and poor maintenance.
Where does wastewater end up in a combined sewer system?
The wastewater and the combined sewer both end up at the treatment plant. Of course, in the case of combined sewer systems, the sewage treatment plant has more work to do, as all the surface water has to be cleaned as well.
How is wastewater drained?
Waste water is drained through pipe systems and thus enters the public sewerage system . Here we differentiate between two types of drainage. In the combined sewer system, domestic and commercial wastewater is fed into a sewer together with rainwater that accumulates on sealed surfaces (e.g. streets and roofs).
How does a separate sewer system work?
The separate sewer system divides the media. Dirty water is fed into one sewer, surface water into another. Because of the low dirt load, the collected surface water is usually discharged into neighbouring waters (lakes or rivers). The wastewater and the combined sewer both end up at the treatment plant. Of course, in the case of combined sewer ...
What is the process of metabolising organic compounds in wastewater?
This process is called Biological nutrient removal.
What is the process of cleaning a toilet called?
Rakes filter everything that is not permeable as solid matter in the wastewater. This can be toilet paper, wet wipes, but also a toothbrush or other things that do not belong in a toilet. This process is called pretreatment.
What is municipal sewage?
Municipal wastewater, or sewage, refers to water that has been used in urban and suburban area homes or businesses for washing, bathing, and flushing toilets. Municipal wastewater also may include water from industrial sources.
How much sewage sludge does Pennsylvania produce?
This means that Pennsylvania's POTWs generate approximately 300,000 tons of sewage sludge (dry weight basis) each year.
What is biosolids in sewage?
The term "biosolids" also helps to distinguish sewage sludge from industrial sludge by emphasizing that the former is produced by a biological process.
What is biosolids in wastewater treatment?
The industry defines biosolids as sewage sludge that has undergone sufficient treatment for stabilization and pathogen reduction, and that is of sufficiently high quality to be land applied. The term is intended to distinguish high-quality, treated sewage sludge from raw sewage sludge and from sewage sludge that contains large quantities of environmental pollutants. The term "biosolids" also helps to distinguish sewage sludge from industrial sludge by emphasizing that the former is produced by a biological process. The term has been criticized by some as an attempt to disguise the real nature of sewage sludge, thereby making land application of this material less objectionable to the general public. Although "biosolids" undoubtedly does not conjure up the same negative images as does "sewage sludge" or simply "sludge," it is a legitimate and functional term when correctly used to make the distinction described above. In this document, "sewage sludge" will be used to refer to wastewater treatment solids generally, and "biosolids" will be used to refer specifically to material that is suitable for land application.
How are sludge solids concentrated?
Sludge solids are concentrated either by settling due to gravity or by introducing air, which causes sludge solids to float.
How does incineration affect sewage?
Sewage sludge incineration reduces the volume of the material to be disposed of, completely destroys pathogens, decomposes most organic chemicals, and recovers the small amount of heat value contained in sewage sludge. The residual ash is a stable, relatively inert, inorganic material that has just 10 to 20% of the original sludge's volume. Most trace metals in the sewage sludge become concentrated in the ash (a five- to tenfold increase in concentration). This material most commonly is landfilled, although it potentially could be used in construction materials.
What is primary treatment?
Primary treatment involves gravity sedimentation and flotation processes that remove approximately half of the solid material that enters this stage. Solid material (both organic and inorganic) that settles out during this stage of treatment is drawn from the bottom and constitutes the primary sludge. In most POTWs, the floating material (oil, grease, wood, and vegetable matter) that is skimmed from the water surface during primary treatment is disposed of separately and does not become part of the primary sludge.
Can you use liquids in a washing machine?
Do use liquids, not powders in washing machines and dishwashers; do try to spread your clothes washing throughout the week.
Can you put bleach down the toilet?
Don’t use household bleach and strong chemicals indiscriminately or have a “spring cleaning” day; don’t tip bottles of medicine, mouth wash etc. down the toilet because these can harm the bacteria inside the wastewater (sewage) plant; don’t keep changing your brands of cleaners and washing powders; don’t pour any garden chemicals, paint or car engine oil down the drains.
Overview
Available process steps
Sewage treatment often involves two main stages, called primary and secondary treatment, while advanced treatment also incorporates a tertiary treatment stage with polishing processes. Different types of sewage treatment may utilize some or all of the process steps listed below.
Preliminary treatment (sometimes called pretreatment) removes coarse mater…
Terminology
The term "sewage treatment plant" (STP) (or "sewage treatment works" in some countries) is nowadays often replaced with the term wastewater treatment plant (WWTP). Strictly speaking, the latter is a broader term that can also refer to industrial wastewater.
The terms "water recycling center" or "water reclamation plants" are also in use.
Purposes and overview
The overall aim of treating sewage is to produce an effluent that can be discharged to the environment while causing as little water pollution as possible, or to produce an effluent that can be reused in a useful manner. This is achieved by removing contaminants from the sewage. It is a form of waste management.
With regards to biological treatment of sewage, the treatment objectives can include various de…
Types of treatment processes
Sewage can be treated close to where the sewage is created, which may be called a "decentralized" system or even an "on-site" system (on-site sewage facility, septic tanks, etc.). Alternatively, sewage can be collected and transported by a network of pipes and pump stations to a municipal treatment plant. This is called a "centralized" system (see also sewerage and pipes and inf…
Design aspects
The "per person organic matter load" is a parameter used in the design of sewage treatment plants. This concept is known as population equivalent (PE). The base value used for PE can vary from one country to another. Commonly used definitions used worldwide are: 1 PE equates to 60 gram of BOD per person per day, and it also equals 200 liters of sewage per day. This concept is also used as a comparison parameter to express the strength of industrial wastewater compare…
Environmental impacts
Sewage treatment plants can have significant effects on the biotic status of receiving waters and can cause some water pollution, especially if the treatment process used is only basic. For example, for sewage treatment plants without nutrient removal, eutrophication of receiving water bodies can be a problem.
Reuse
Increasingly, people use treated or even untreated sewage for irrigation to produce crops. Cities provide lucrative markets for fresh produce, so are attractive to farmers. Because agriculture has to compete for increasingly scarce water resources with industry and municipal users, there is often no alternative for farmers but to use water polluted with sewage directly to water …