Medication
How To Cure Appendicitis Naturally
- Garlic. Garlic is an excellent remedy for treating inflammation of your body. ...
- Ginger. Ginger is also rich in its anti inflammatory properties. ...
- Fenugreek Seeds. Fenugreek Seeds are excellent in treating appendicitis. ...
- Castor Oil. ...
- Baking Soda. ...
- Apple Cider Vinegar. ...
- Mint. ...
- Honey And Lemon Juice. ...
- Green Tea. ...
- Buttermilk. ...
Procedures
What antibiotics are used to treat appendicitis without surgery?
- Zosyn (piperacillin and tazobactam)
- Unasyn (ampicillin and sulbactam)
- Timentin (ticarcillin and clavulanate)
- Rocephin (ceftriaxone)
- Maxipime (cefepime)
- Gentamicin (Gentacidin, Garamycin)
- Merrem (meropenem)
- Invanz (ertapenem)
Self-care
What is the best antibiotic for appendicitis? Antibiotics Used for Treating Appendicitis. Zosyn (piperacillin and tazobactam) Unasyn (ampicillin and sulbactam) Timentin (ticarcillin and clavulanate) Rocephin (ceftriaxone) Maxipime (cefepime) Gentamicin (Gentacidin, Garamycin) Merrem (meropenem) Invanz (ertapenem) Can amoxicillin treat appendicitis?
Nutrition
We conclude that CRP does not aid in the diagnosis of appendicitis. Simple appendicitis was seen in spite of normal WBC and CRP. C-reactive protein estimation does not improve accuracy in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis in pediatric patients Int J Surg. 2009 ... Delayed diagnosis of acute appendicitis in children can lead to complications ...
How to cure early symptoms of appendicitis?
How can you treat appendicitis without surgery?
What is the best antibiotic for appendicitis?
Can we improve diagnosis of acute appendicitis?

Where is appendix treated?
Appendicitis is an inflammation of your appendix, in the lower right side of your abdomen, that requires immediate treatment.
Is appendectomy The usual treatment for acute appendicitis?
Today, the standard of care for the treatment of appendicitis remains surgical removal of the appendix (appendectomy), along with intravenous fluids and antibiotics. In fact, appendectomy is one of the most common abdominal operations in the world.
What is the treatment of choice for appendicitis?
Surgical removal of the appendix, an appendectomy, has been the standard of care for treatment of appendicitis for more than 120 years, but treatment with antibiotics is often proposed as an alternative. The participants were randomized to receive either appendectomy or antibiotics first for uncomplicated appendicitis.
Is surgery necessary for acute appendicitis?
Most people with appendicitis need a surgery called an appendectomy. It removes a diseased appendix. If the appendix hasn't yet ruptured, surgery prevents that rupture and keeps infection from spreading. Before surgery, you receive intravenous (IV) antibiotics to treat infection.
Is appendicitis always treated with surgery?
"Now we know that only a small proportion of appendicitis patients need an emergency operation," Salminen said. However, there are two types of appendicitis -- one that always requires surgery and a milder form that can be treated with antibiotics, Salminen explained.
Where is appendix located?
The appendix is a small pouch attached to the large intestine. The appendix is a small, finger-shaped pouch of intestinal tissue located between the small intestine (cecum) and large intestine (colon). The appendix is a small finger-shaped tube that branches off the first part of the large intestine.
Where is appendicitis located?
Appendicitis typically starts with a pain in the middle of your tummy (abdomen) that may come and go. Within hours, the pain travels to your lower right-hand side, where the appendix is usually located, and becomes constant and severe. Pressing on this area, coughing or walking may make the pain worse.
Can appendicitis be treated with antibiotics only?
About 20 to 30 percent of patients with appendicitis have a perforated appendix that needs to be removed, but 70 to 80 percent of patients may only need antibiotics, Salminen added.
How to treat appendicitis?
Appendicitis treatment usually involves surgery to remove the inflamed appendix. Before surgery you may be given a dose of antibiotics to treat infection.
What to do if you have appendix pain?
Make an appointment with your family doctor if you have abdominal pain. If you have appendicitis, you'll likely be hospitalized and referred to a surgeon to remove your appendix.
How long does it take for an appendix to heal?
Expect a few weeks of recovery from an appendectomy, or longer if your appendix burst. To help your body heal: Avoid strenuous activity at first. If your appendectomy was done laparoscopically, limit your activity for three to five days. If you had an open appendectomy, limit your activity for 10 to 14 days.
What does a doctor look for in an appendix?
Your doctor may also look for abdominal rigidity and a tendency for you to stiffen your abdominal muscles in response to pressure over the inflamed appendix (guarding). Your doctor may use a lubricated, gloved finger to examine your lower rectum (digital rectal exam).
What to do if pain medication isn't helping?
Call your doctor if your pain medications aren't helping. Being in pain puts extra stress on your body and slows the healing process. If you're still in pain despite your pain medications, call your doctor.
What tests are done to confirm appendicitis?
Imaging tests. Your doctor may also recommend an abdominal X-ray, an abdominal ultrasound, computerized tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to help confirm appendicitis or find other causes for your pain.
How to diagnose appendicitis?
To help diagnose appendicitis, your doctor will likely take a history of your signs and symptoms and examine your abdomen. Tests and procedures used to diagnose appendicitis include: Physical exam to assess your pain. Your doctor may apply gentle pressure on the painful area. When the pressure is suddenly released, ...
How to diagnose acute appendicitis?
To diagnose acute appendicitis, a doctor will take a medical history and carry out a physical examination. They may also perform the following: a blood test to check for a high white blood cell count, which can signal infection. a urine test to check for urinary tract infections.
What are the symptoms of appendicitis?
Symptoms of acute appendicitis in adults can include: pain around the belly button, which may move to the lower righthand side of the abdomen. a swollen abdomen. vomiting. loss of appetite. fever and chills.
What causes an appendix to burst?
Without prompt treatment, acute appendicitis can cause the appendix to burst. This can lead to a condition called peritonitis.
Why does appendicitis occur?
Causes. Acute appendicitis occurs when something blocks the inside of the appendix. This could be due to: a viral, bacterial, or parasitic infection in the digestive tract, which can enlarge the tissue of the appendix wall. stools causing a blockage in the tube between the large intestine and the appendix. tumors.
How long does it take for an appendix to rupture?
People will need immediate medical care if they have any symptoms of appendicitis. Without treatment, the appendix can rupture or burst within 48–72 hours of a person first experiencing symptoms of acute appendicitis.
What is the pain in the abdomen?
Acute appendicitis is the sudden and severe inflammation of the appendix. It can cause pain in the abdomen, and this pain may occur quickly and worsen within hours.
How long does appendicitis pain last?
With chronic appendicitis, a person may experience continuous abdominal pain that may last for weeks, months, or years. This pain can range from mild to moderate. Trusted Source.
What is the pain of appendicitis?
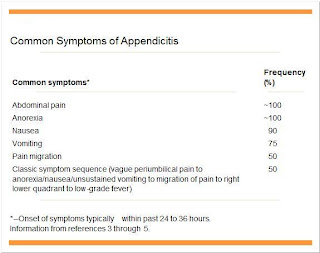
Abdominal pain is the primary presenting complaint of patients with acute appendicitis. The diagnostic sequence of colicky central abdominal pain followed by vomiting with migration of the pain to the right iliac fossa was first described by Murphy but may only be present in 50% of patients.4Typically, the patient describes a peri-umbilical colicky pain, which intensifies during the first 24 hours, becoming constant and sharp, and migrates to the right iliac fossa. The initial pain represents a referred pain resulting from the visceral innervation of the midgut, and the localised pain is caused by involvement of the parietal peritoneum after progression of the inflammatory process. Loss of appetite is often a predominant feature, and constipation and nausea are often present. Profuse vomiting may indicate development of generalised peritonitis after perforation but is rarely a major feature in simple appendicitis. A meta-analysis of the symptoms and signs associated with a presentation of acute appendicitis was unable to identify any one diagnostic finding but showed that a migration of pain was associated with a diagnosis of acute appendicitis.5
How common is appendicitis in England?
Appendicitis is the most common abdominal emergency and accounts for more than 40 000 hospital admissions in England every year .2Appendicitis is most common between the ages of 10 and 20 years, but no age is exempt.3A male preponderance exists, with a male to female ratio of 1.4:1; the overall lifetime risk is 8.6% for males and 6.7% for females in the United States.3Since the 1940s the incidence of hospital admission for acute appendicitis has been falling, but the reason for this decline is not clear.w1
What is the difference between simple appendicitis and complicated appendicitis?
Simple appendicitis—Inflamed appendix, in the absence of gangrene, perforation, or abscess around the appendix. Complicated appendicitis—Perforated or gangrenous appendicitis or the presence of periappendicular abscess.
What is the most common abdominal surgical emergency?
Appendicitis is the most common abdominal surgical emergency
What is a negative appendicectomy?
Negative appendicectomy—Term used for an operation done for suspected appendicitis, in which the appendix is found to be normal on histological evaluation
Where is the tenderness on the right side of the abdomen?
Nausea and vomiting are often present, with associated tenderness located anywhere on the right hand side of the abdomen. Maternal mortality is negligible in cases of simple appendicitis but rises to 4% with advanced gestation and perforation.
Where is the vermiform appendix located?
The vermiform appendix is a tubular structure attached to the base of the caecum at the confluence of the taeniae coli. It is approximately 8-10 cm long in adults and represents the underdeveloped distal end of the large caecum seen in other animals. In humans it is regarded as a vestigial organ, and acute inflammation of this structure is called acute appendicitis
What was the first treatment for appendicitis?
Early treatment of appendicitis focused on surgery. In 1883, Abraham Groves performed the first elective appendectomy [21]. In 1886, Reginald Fitz published the first paper describing early diagnosis and treatment of appendicitis [22]. In 1894, Charles McBurney described an incision parallel to the right rectus muscle oblique at approximately 1-4 inches [4]. This incision, known as the McBurney-McArthur muscle-splitting incision, was found to be associated with the lowest mortality [23]. Four advantages have been described with respect to using this technique: it provides easy direct access to the inflamed organ, drains can be placed laterally with sutures needed only on the peritoneum, the incision can be closed without risk of hernia, and, finally, access to cases of obstruction can be obtained without passing through additional structures [23].
How is appendicitis diagnosed?
Appendicitis has been studied and treated for over a century. Diagnosis is based on imaging findings and clinical presentation. Currently, CT and graded compression color Doppler ultrasonography are generally employed to aid in the diagnosis. MRI has shown great promise as an alternative, with the added advantage of avoiding radiation exposure. Treatment is currently based on surgical intervention although future research looks to focus on more conservative measures such as antibiotics or other modalities. Antibiotic treatment has demonstrated efficacy in the short term but recurrence is likely in the long term. Some newer modalities of treatment have made it possible to forgo surgery by employing endoscopic intervention. Surgical advances with the use of laparoscopy enable same-day discharges, lower cost, fewer complications, and shorter recovery times.
What is the pain of appendicitis?
The initial presentation involves periumbilical colicky pain around the midgut. Localized pain coincides with the parietal peritoneum irritation. The pain intensifies over a period of 24 hours, accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite [6]. In 3.5% of appendicitis presentations, left iliac fossa deep palpation elicits pain in the right iliac fossa, which is termed Rovsing’s sign [9]. If the patient is found to have a positive Rovsing's sign, a barium swallow is then employed to confirm the diagnosis. Barium swallow was initially found to be 95% accurate [10].
How common is appendicitis?
The condition most commonly occurs between the ages of 10 and 20 years with a lifetime risk of 8.6% and 6.7% for males and females respectively. Its diagnosis focuses on clinical presentation and imaging modalities classified according to scoring systems such as the Alvarado scoring system. A number of imaging modalities can be used, with CT being the most common one. For acute appendicitis, surgical intervention is considered to be the gold standard of treatment. However, recent research has focused on other modalities of treatment including antibiotics and endoscopic retrograde appendicitis therapy (ERAT) to avoid surgical complications.
How big is the appendix?
The average size is 1-9 inches. It is held by the mesentery and comprises three layers: organ sera, submucosa, and mucous [5].

Diagnosis
Treatment
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Alternative Medicine
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment