What is Flow equalization in wastewater treatment?
Feb 21, 2022 · Flow equalization usually involves construction of large basins to collect and hold wastewater streams, from which the wastewater is pumped to treatment facilities at a constant rate. These basins usually are located after pretreatment facilities such as screens, comminutors, and grit chambers.
What is an equalization basin?
Equalization (EQ) Basins are designed to provide consistent influent flow to downstream processes by retaining high flow fluctuations. Due to the additional retention time, aeration and mixing are required to prevent the raw wastewater from becoming septic and to maintain solids in suspension. Aeration Industries’ Aire-O 2 Triton ® aerator ...
How is the effluent regulated in a wastewater treatment plant?
Equalization Basin for Wastewater Treatment. From Application. 0. Providing consistent flow and loading to a biological process is important to maintain optimal treatment. Equalization (EQ) Basins are designed to provide consistent influent flow to downstream processes by retaining high flow fluctuations. Due to the additional retention time ...
What is a waste water basin and how does it work?
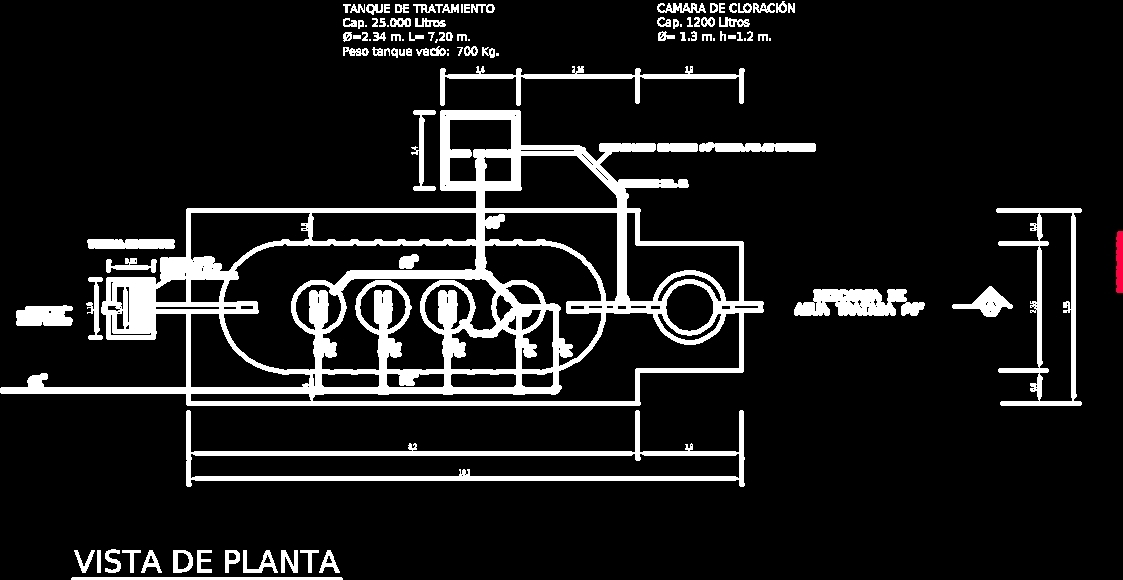
The grit is then removed and washed before disposal at a landfill. In-Line Equalization Basin. The in-line basin has a volume of 2.5 million gallons. It provides equalization of diurnal flow variation to achieve a constant or nearly constant flow rate and wasteload through the downstream treatment processes. Off-Line Stormwater Basins

How is carbon removed from wastewater?
In the traditional wastewater treatment process, activated sludge is commonly used for the removal of carbon, and it involves complex steps with anaerobic, aerobic, or anoxic conditions during 5–8 h of treatment and it also produces a high volume of sludge.Jan 15, 2014
What is the function of the equalization basin in a wastewater treatment plant?
Equalization (EQ) Basins are designed to provide consistent influent flow to downstream processes by retaining high flow fluctuations. Due to the additional retention time, aeration and mixing are required to prevent the raw wastewater from becoming septic and to maintain solids in suspension.
What is removed in the aeration basin from the wastewater?
Aeration brings water and air in close contact in order to remove dissolved gases and to oxidize dissolved metals, including iron, hydrogen sulfide, and volatile organic chemicals (VOCs).Sep 9, 2020
What is equalization process in wastewater treatment?
Flow equalization is the process of controlling hydraulic velocity, or flow rate, through a wastewater treatment system. The equalization of flow prevents short term, high volumes of incoming flow, called surges, from forcing solids and organic material out of the treatment process.
Where is the location of equalization basin?
These basins usually are located after pretreatment facilities such as screens, comminutors, and grit chambers.Feb 21, 2022
What is flow equalization basin?
A flow equalization basin (FEB) is a constructed storage feature used to capture and temporarily store peak stormwater flows. Water managers can move water from FEBs to Stormwater Treatment Areas (STAs) at steady rates to optimize STA performance and help achieve water quality improvement targets.
What is removed by the grit and sand removal process?
Grit removal is the process used to remove sand, silt and grit from water. Grit (and sand) removal is often found in the headworks of wastewater treatment plants (WWTP).
What is removed in the secondary clarifiers?
When the wastewater enters the two Secondary Clarifiers, it still contains lots of microorganisms from the Aeration Basins and looks brown and murky. The Secondary Clarifiers are identical to the Primary Clarifiers; materials in the wastewater sink and float and rotating arms remove this material from the water.
Where is the treated water released discharged from the Lansing wastewater treatment plant?
The combined sewer system works fine on dry days, when both storm water and sewage get treated at the plant and released into the Grand River, a Lake Michigan tributary that flows from Jackson, through Lansing, Grand Rapids, Grand Haven and out to the big lake.Feb 28, 2019
What is the position of equalization basin in offline equalization process?
The basins are normally located near the head end of the treatment works, preferably downstream of preliminary treatment facilities such as bar screens and grit chambers and before primary treatment and biological treatment is appropriate.
Why equalization is required in industrial waste treatment?
The purpose of equalization is to provide adequate damping of organic fluctuations in order to prevent shock loading of biological treatment. It also provide adequate pH control or to minimize the chemical requirements for neutralization.
What is the difference between neutralization and equalization?
Flow Equalization is the damping of flow rate and concentration variations so that a constant or near-constant stream is achieved to the plant. Neutralization is the process of blending acid or caustic into the waste stream to adjust the basin's pH level.
What is the last process control that takes place at the wastewater treatment plant?
Dechlorination is the last process control that takes place at the wastewater treatment plant. Before the treated water is discharged into a tributary of the Neshaminy Creek, Sodium Bisulfite is added to remove any chlorine residual. The Sodium Bisulfite reacts very quickly with the chlorine residual to form non-toxic chloride, thus protecting the Neshaminy Creek from chlorine toxicity.
Why is chlorine added to wastewater?
Many of these pathogenic organisms are removed in the preceding plant processes. Chlorine is added to the treated wastewater to kill essentially all of the remaining pathogenic organisms before being discharged to the receiving stream. This process, termed disinfection, prevents the spread of waterborn disease. Chlorine solution is added at the head of the chlorine contact tank, which is a maze configuration to provide mixing and contact time. Adequate chlorine is added to ensure disinfection of the treated wastewater. This is controlled by the amount of residual chlorine remaining at the end of the contact tank.
How does nitrification work?
The nitrification system consists of two plastic media trickling filters and two clarifiers. The clear effluent from the activated sludge clarifiers is pumped to the top of the 21.5 foot trickling filters and distributed over the plastic media. The nitrogen in the wastewater is oxidized to nitrite and nitrate by a population of microorganisms attached to the plastic filter media. The slime layer increases in thickness and eventually washes off (termed sloughing). These solids that are sloughed off settle in the nitrification clarifiers and are wasted to the gravity thickeners. The clear effluent flows to the denitrification process from July through October and to the chlorination system from November to June. We are only required to denitrify from July to October.
What is activated sludge?
The activated sludge process is an aerobic biological process. The goal of this process is to remove the carbonaceous waste contained in wastewater by providing an environment for bacteria and other microorganisms to grow and consume the organic waste. It consists of two aeration tanks and two clarifiers. In the aeration tanks, the return sludge
What is denitrification process?
The denitrification system is a biological process by which nitrates are removed from the wastewater and converted to nitrogen gas. The first stage is an anoxic mixing tank where the dissolved oxygen is kept below 2.0 ppm and a carbon source is added to the wastewater. Diluted corn syrup and/or a manufactured glycerin product is used at the Lansdale plant as a carbon source.
What is grit chamber?
The grit chambers are designed to slow the velocity of the wastewater down so that grit, sand, and other abrasive materials can settle to the bottom. The grit is then removed and washed before disposal at a landfill.
What is a bar screen in wastewater treatment plant?
The bar screen is made of parallel steel bars spaced about a quarter inch apart. It is designed to screen out rags, wood, plastics and other floating objects that could clog pipes or disable pumps if not removed. These solids are washed, compacted and then sent to a landfill.
Where is the Aldie Wastewater Treatment Plant located?
The Aldie Wastewater Treatment Plant, located inAldie , Virginia, is an extended aeration facilitywhich treats an average of 0.0031 MGD with adesign flow of 0.015 MGD. This technology waschosen because it would allow the area to meetpermit requirements while minimizing land use.The plant consists of an influent chamber whichdirects the flow to two parallel aeration basins,parallel clarifiers, and a UV disinfection system.
Where are package treatment plants used?
They are most often used inremote locations such as trailer parks, highway restareas, and rural areas.
What is an oxidation ditch?
Oxidation ditches are suitable for facilities thatrequire nutrient removal, have limitations due to thenature of the site, or want a biological system thatsaves energy with limited use of chemicals unlessrequired for further treatment. Oxidation ditchtechnology can be used to treat any type ofwastewater that is responsive to aerobicdegradation. In addition, systems can be designedfor denitrification and phosphorous removal.
What is sequencing batch reactor?
sequencing batch reactor (SBR) is a variation ofthe activated sludge process. As a fill and draw orbatch process, all biological treatment phases occurin a single tank. This differs from the conventionalflow through activated sludge process in that SBRsdo not require separate tanks for aeration andsedimentation (Kappe, 1999). SBR systems containeither two or more reactor tanks that are operated inparallel, or one equalization tank and one reactortank. The type of tank used depends on thewastewater flow characteristics (e.g. high or lowvolume). While this setup allows the system toaccommodate continuous influent flow, it does notprovide for disinfection or holding for aeratedsludge.
What is extended aeration?
The extended aeration process is one modificationof the activated sludge process which providesbiological treatment for the removal ofbiodegradable organic wastes under aerobicconditions. Air may be supplied by mechanical ordiffused aeration to provide the oxygen required tosustain the aerobic biological process. Mixing mustbe provided by aeration or mechanical means tomaintain the microbial organisms in contact withthe dissolved organics. In addition, the pH must becontrolled to optimize the biological process andessential nutrients must be present to facilitatebiological growth and the continuation of biologicaldegradation.
What are the components of an oxidation ditch?
Key components of a typical oxidation ditchinclude a screening device, an influent distributor(with some systems), a basin or channel, aerationdevices (mechanical aerators, jet mixers, ordiffusers, depending on the manufacturer), asettling tank or final clarifier (with some systems),and an RAS system (with some systems).Typically , the basin and the clarifier areindividually sized to meet the specific requirementsof each facility. These components are often builtto share a common wall in order to reduce costs andsave space (Lakeside, 1999).Concrete tanks are typically used when installingpackage plant oxidation ditches. This results inlower maintenance costs as concrete tanks do notrequire periodic repainting or sand blasting.Fabricated steel or a combination of steel andconcrete can also be used for construction,depending on site conditions (Lakeside, 1999).
What is a package plant?
Package plants are pre-manufactured treatmentfacilities used to treat wastewater in smallcommunities or on individual properties .Accordingto manufacturers, package plants can bedesigned to treat flows as low as 0.002 MGD or ashighas 0.5 MGD,although they more commonlytreatflows between 0.01 and 0.25 MGD (Metcalfand Eddy, 1991).
What is the process of wasting activated sludge?
Digester – This is where the activated sludge is sent from the RAS pit if it is not sent back to the oxidation ditch. This process is called wasting and is a necessary part of keeping an activated sludge plant healthy. Once in the digester the sludge is allowed to settle and concentrate.
What is the process of oxidation ditch?
Most of the wastewater treatment process happens in the oxidation ditch. Secondary Clarifier – The effluent from the oxidation ditch enters the secondary clarifiers.