What is stem cell therapy for Type 1 diabetes?
The stem cell therapy research is being led by a biotech company called Vertex. They’re running an early-stage clinical trial in the US testing a new approach to replacing the beta cells that are destroyed by the immune system in type 1 diabetes. Transplants of cells taken from donor pancreas already exist, called islet transplants.
Where do stem cells for diabetes come from?
Stem cells for the treatment of diabetes are able to come from a variety of sources. These include foetal tissue from: Embryos. The placenta. Umbilical cord. Bone marrow. Blood cells.
What is an example of stem cell research in diabetes?
In one example of diabetes stem cell research, researchers took cells from human intestine cells and disabled a gene which enabled the cells to produce insulin. Where do stem cells come from?
Can stem cells help treat insulin deficiency?
Engraftment of mature insulin producing cells derived from induced pluripotent stem cells may represent the most promising treatment strategy for diabetic patients with impaired β-cell function. These cells are easily accessible and have been shown to closely mimic endogenous β-cell function in vivo.

Where did the researchers get the stem cells?
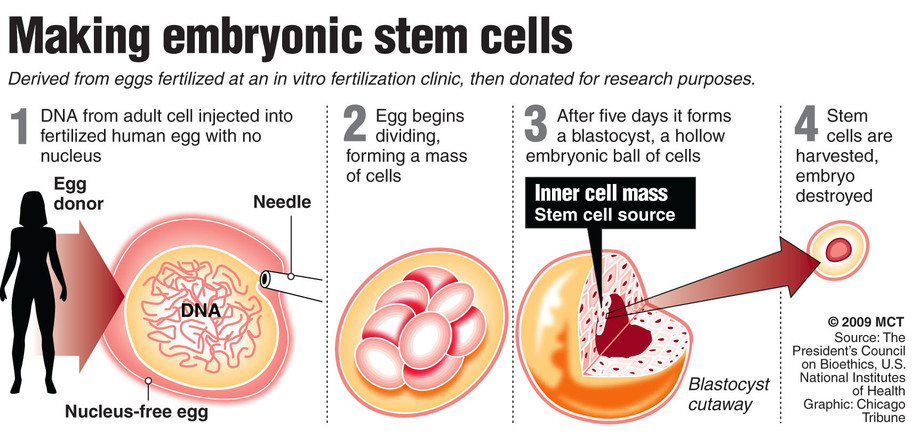
The embryonic stem cells used in research today come from unused embryos. These result from an in vitro fertilization procedure. They are donated to science. These embryonic stem cells are pluripotent.
Where do they collect stem cells?
The largest concentration of blood stem cells is in your bone marrow. However, the blood stem cells can be moved or "mobilized" out of the bone marrow into the bloodstream (peripheral blood) where they can be easily collected. Most transplants these days use stem cells collected from the bloodstream.
Where do stem cells come from for injections?
The answer is simple: from the patient's very own bone marrow or adipose (fat) tissue, depending on the procedure. For stem cell treatment for back, knee, shoulder or joint pain, adult stem cells are harvested from the patient's own bone marrow.
What type of stem cells are used to treat diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes patients require daily blood testing and insulin shots. Scientists have successfully used pluripotent stem cells to produce glucose-responding cells that release insulin, like beta cells. Clinical trials of these cells are underway.
How are stem cells harvested from a donor?
Stem cells are collected using a procedure called apheresis, where only the stem cells are separated and collected during donation. The remaining blood components are safely returned to the donor. This is a non-surgical procedure and takes approximately four to six hours.
Can stem cells be harvested from blood?
Stem cells normally circulate in the blood in very small quantities and can be collected from the blood through a small catheter inserted into a patient's vein. The number of circulating stem cells in the blood is increased in patients whose bone marrow is recovering from chemotherapy.
Do stem cells come from umbilical cords?
Umbilical cord blood contains blood-forming stem cells, which can renew themselves and differentiate into other types of cells. Stem cells are used in transplants for patients with cancers like leukemia and lymphoma. Cord Blood can be used to treat over 80 other life- threatening diseases.
Which country has the most advanced stem cell therapy?
List of countries by stem cell research trialsRankCountry/TerritoryNumber of clinical trials1United States1362Iran653South Korea404Australia1810 more rows
Can diabetes be cured by stem cell therapy?
While stem cell therapy has yet to cure type 1 diabetes, there are documented cases where patients have gone years without needing insulin injections. Some clinical trials are using cord blood stem cells specifically to treat diabetes.
What are the ethical issues of stem cell research?
Table 1Phase of researchEthical issues1. Payment to oocyte donors2. Medical risks of oocyte retrieval3. Protecting reproductive interests of women in infertility treatmentUse of stem cell lines derived at another institutionConflicting legal and ethical standards5 more rows
How much does stem cell therapy for diabetes cost?
What is the cost of the stem cell treatment for Diabetes Mellitus? The price for our Stem Cell Therapy for Diabetes can vary from $8,000 USD and $10,900 USD depending on the personal and medical needs of our patients.
What is stem cell?
What are stem cells? Stem cells are a form of cell that is yet to develop a specific set of traits. However, what stem cells have in abundance is the potential to develop into a number of different forms.
What is stem cell research?
Stem cell research allows researchers to grow specific varieties of human cells in the lab and research how they behave and interact under different conditions. Stem cells open up a wide spectrum of diabetes research possibilities.
How did insulin produce beta cells?
In 2004, the University of Pittsburgh grew insulin producing beta cells by introducing two genes ‘cdk’ and ‘cyclin d’ via a virus. The researchers were able to deactivate the virus and also prevent stem cells from growing further. The research could lead to a better availability of beta cells for future research purposes.
What is the best treatment for diabetes?
Islet cell transplants are one form of procedure that has proven effective. In type 1 diabetes, the body’s immune system becomes programmed to attack the beta cells, so the patient must take immuno-suppressant drugs to prevent this happening.
Can the immune system destroy beta islet cells?
The way in which the immune system causes the destruction of precious beta islet cells within the pancreas of type 1 diabetics is generally understood to be the key. The ultimate goal, which has so far proved elusive, is a cure for diabetes, which could potentially be available for both types of diabetes through stem cell research.
Can progenitor cells divide?
Like stem cells, progenitor cells are able to take on the form of a number of different types of mature human cells, however, unlike stem cells, progenitor cells cannot divide indefinitely. Progenitor stem cells have been used to grow insulin producing cells, under lab conditions, from intestinal cells and undeveloped pancreatic cells.
Can stem cell replacement be used for type 1 diabetes?
To cure type 1 diabetes, stem cell replacement needs to be more than simply a case of swapping insulin-producing cells from a healthy pancreas with those destroyed by diabetes in a diabetic patient. Numerous complications preclude this as a simple treatment.
What are stem cells used for?
You may wonder what stem cells are, how they're being used to treat disease and injury , and why they're the subject of such vigorous debate.
What is stem cell therapy?
Stem cell therapy, also known as regenerative medicine, promotes the repair response of diseased, dysfunctional or injured tissue using stem cells or their derivatives. It is the next chapter in organ transplantation and uses cells instead of donor organs, which are limited in supply.
How many cells are in an embryo?
Embryonic stem cells. These stem cells come from embryos that are three to five days old. At this stage, an embryo is called a blastocyst and has about 150 cells. These are pluripotent (ploo-RIP-uh-tunt) stem cells, meaning they can divide into more stem cells or can become any type of cell in the body.
What are the master cells of the body?
Stem cells are the body's master cells. All other cells arise from stem cells, including blood cells, nerve cells and others. Stem cells are the body's raw materials — cells from which all other cells with specialized functions are generated. Under the right conditions in the body or a laboratory, stem cells divide to form more cells called ...
Why are adult stem cells more likely to contain abnormalities?
Adult stem cells also are more likely to contain abnormalities due to environmental hazards, such as toxins, or from errors acquired by the cells during replication.
What are perinatal stem cells?
Perinatal stem cells. Researchers have discovered stem cells in amniotic fluid as well as umbilical cord blood. These stem cells also have the ability to change into specialized cells. Amniotic fluid fills the sac that surrounds and protects a developing fetus in the uterus.
What type of cells are used to test for drugs?
Test new drugs for safety and effectiveness. Before using investigational drugs in people, researchers can use some types of stem cells to test the drugs for safety and quality. This type of testing will most likely first have a direct impact on drug development first for cardiac toxicity testing.
Why is blood sugar elevated in stem cells?
In diabetes, blood sugar is elevated either because the pancreas does not produce enough insulin ...
Why are transplants less effective in type 2 diabetes?
Transplants generally are less effective in type 2 diabetes patients because they require more islets due to their resistance to insulin.
What happens when you lose beta cells?
In type 1 diabetes, the body’s immune system attacks the beta cells in the pancreas. When the beta cells are lost there is not sufficient insulin for proper control of glucose levels. Resulting high sugar levels in the blood can cause damage to the kidneys, eyes, nervous system, and other organs. People of all body types can be diagnosed ...
What hormones are released into the bloodstream when blood sugar levels reach a certain threshold?
Most importantly, these include beta cells, which produce a hormone known as insulin that is released into the bloodstream when blood sugar levels reach a certain threshold, signaling other cells in the body to take up sugar, a major energy source for the body’s cells.
Why do diabetics need insulin?
Type 1 diabetes patients are given insulin to help them control their glucose levels. These patients, however, often struggle to optimally balance their blood sugar and they need to monitor their blood sugar multiple times a day.
What happens when you have type 2 diabetes?
In type 2 diabetes, cells in the body become resistant to insulin. They don’t respond well to the insulin released by beta cells. The beta cells produce more insulin to signal the other cells, but eventually are not able to compensate. As with type 1, high blood sugar levels in type 2 diabetes can cause serious damage to the body.
How to control diabetes type 2?
Type 2 diabetes can sometimes be controlled with diet and exercise. However, many people with type 2 diabetes eventually have to take insulin injections to control blood sugar levels and/or other medications to deal with complications from the disease.
How long does it take for insulin to be secreted in mice?
The researchers found that when they transplanted the new cells into mice that could not produce insulin, the cells began secreting the hormone within a few days. Better yet, they helped control the animals’ blood sugar for months.
How many beta cells can be produced in a few weeks?
If it does get to that point, Millman has plans for mass-producing the cells. He and his team can already generate more than a billion beta cells in just a few weeks.
Is diabetes a cure?
Diabetes is manageable with proper care, but no cure is yet available. Some scientists believe that transforming stem cells into insulin-secreting cells might offer hope. Stem cell researchers are attempting to crack diabetes. A new study, which features in the journal Stem Cell Reports, highlights research from Washington University School ...
Did the stem cells produce enough insulin?
In some cases, the cells produced too much insulin, while in others, they did not produce enough.
Can blood sugar rise?
Eventually, blood sugar levels rise, and it is no longer possible for the body to keep them within a normal, healthy range. Increased blood sugar can lead to a host of potentially serious health problems.
Does type 2 diabetes produce insulin?
In type 2 diabetes, which is the most common type, the body either does not produce enough insulin or does not respond to it properly. Although the insulin-producing pancreas can initially create more of this hormone to make up for the deficit, it cannot keep up over time.
Making strides with stem cells
The research is being led by a biotech company called Vertex. They’re running an early-stage clinical trial in the US testing a new approach to replacing the beta cells that are destroyed by the immune system in type 1 diabetes.
Safety and side effects
Being able to make new beta cells in the lab that can help people with type 1 to make their own insulin again is hugely exciting.
The quest to keep cells safe
For stem cell therapy to offer hope for everyone with living with type 1 diabetes, we need treatments other than immunosuppression drugs to protect transplanted cells from the immune system. That’s why we’re funding research to develop and test treatments called immunotherapies.
What about type 2 diabetes?
Stem cells therapies at the moment are being tested in people with type 1 diabetes and frequent hypos and hypo unawareness , for whom this pioneering treatment could be life-saving.
Can I take part?
Vertex is only recruiting people to take part in their study in the US and Canada. But if you’re interested in getting involved in research, you can search for studies near you on our take part in research page.
You make our work possible
Someone is diagnosed with diabetes every two minutes. Your donation can change lives.
What is stem cell research?
Stem cell research holds great promise for biomedical science—from helping us better understand how diseases develop and spread, to serving as accurate screens for new drugs, to developing cell-based therapies for diabetes, heart failure, Parkinson’s disease, and many other conditions that affect millions of Americans.
How many types of stem cells are there?
There are 2 basic types of human stem cells: embryonic stem (ES) cells and non-embryonic, or “adult” stem cells. Just a few years ago, scientists discovered how to make a third type, by reprogramming ordinary skin cells that have already “grown up” into those that look and act like cells from an embryo. These cells have been named induced ...
Why are iPS cells important?
The ability to create iPS cells is a significant breakthrough, since the reprogramming technique is relatively simple to perform with standard laboratory methods, and because skin cells are easy to gather and grow.