Medication
History of Leukemia. In the 18th century, Thomas Fowler created a solution comprising arsenic trioxide and potassium bicarbonate, and called it Fowler's solution. This solution became a standard remedy to treat Hodgkin's disease, anemia, and leukemia. However, in the early 20th century, arsenic was replaced by radiation therapy.
Procedures
Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects your blood cells and bone marrow. As with other types of cancer, there’s currently no cure for leukemia. People with leukemia sometimes experience...
Therapy
People with acute leukemias need to be treated immediately, to destroy the disease and eliminate symptoms. Those with chronic leukemia may not need to start treatment right away; in some cases, doctors prefer to monitor patients’ health closely and start treatment after the onset of symptoms.
Nutrition
Targeted antibody treatment has also advanced leukemia treatment. In the 1980s, scientists found that cancerous B cells (a type of white blood cell) contained a particular type of protein called an antigen. This specific type of antigen was named CD20. By 1990, Rituxan (rituximab) had been developed.
What is the history of leukemia treatment?
Is there a cure for leukemia?
When should you start treatment for leukemia?
What are the latest advancements in leukemia treatment?

How was leukemia treated in the past?
In the 1940s and 1950s treatment of leukemia was based on single agent chemotherapy. In the 1960s multi-agent chemotherapy began and dramatically increased survivorship (Kersey 1997 ). In the 1970s and 1980s pre-symptomatic therapy for central nervous system leukemia also improved treatment.
When did they find a treatment for leukemia?
In 1948, Sidney Farber reported the first rational treatment for acute leukemia.
Did they find a cure for leukemia?
As with other types of cancer, there's currently no cure for leukemia. People with leukemia sometimes experience remission, a state after diagnosis and treatment in which the cancer is no longer detected in the body. However, the cancer may recur due to cells that remain in your body.
What is the newest treatment for leukemia?
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently approved two new treatments for some adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML): enasidenib (Idhifa®), a drug that targets aberrant forms of the IDH2 protein; and liposomal cytarabine-daunorubicin CPX-351 (Vyxeos™), a two-drug chemotherapy combination encapsulated ...
Who found the cure for leukemia?
Yet Emil J Freireich, M.D., 88, who achieved legendary status as a pioneer in the early history of oncology triumphs, still comes to work every day, attending meetings and participating in the center's medical education program.
How long can you live with leukemia?
Survival rates by typeTypeAge rangeSurvival rateAcute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)This type of leukemia is most common in older adults, but it can be diagnosed at any age. Most deaths occur in people ages 65 to 84.Relative survival rate for all ages 5 years after diagnosis is about 29.5% .4 more rows•Aug 18, 2021
Can leukemia be prevented?
Although the risk of many adult cancers can be reduced by lifestyle changes (such as quitting smoking), there is no known way to prevent most childhood cancers at this time. Most children with leukemia have no known risk factors, so there is no sure way to prevent these leukemias from developing.
What are the six signs of leukemia?
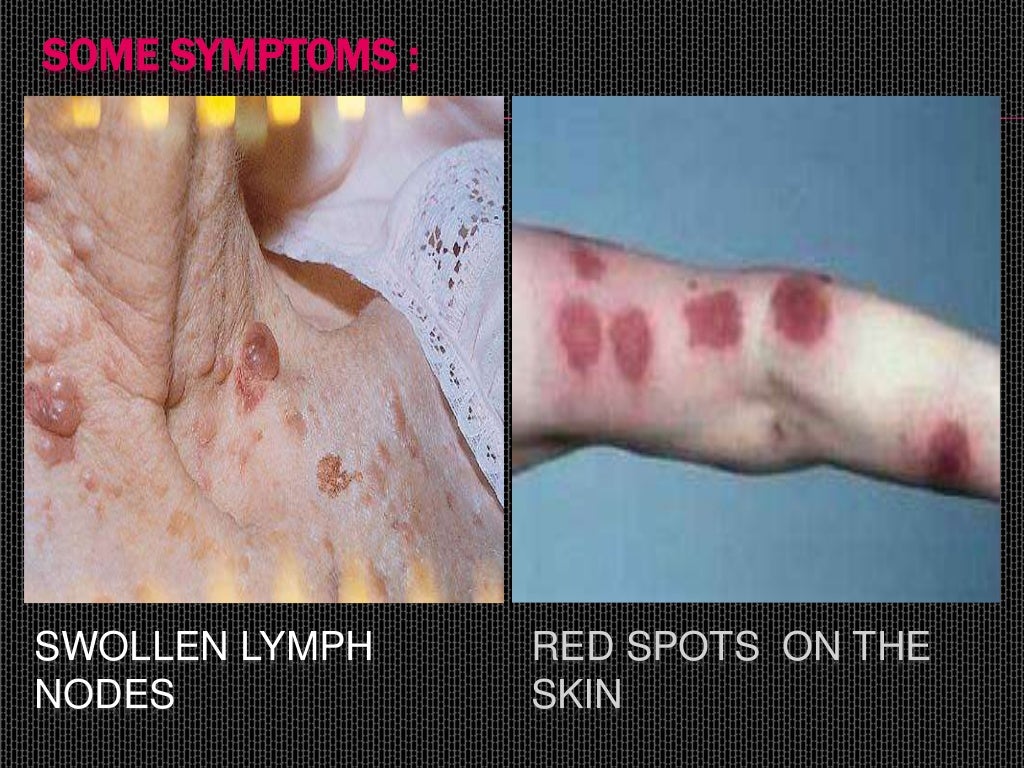
Fatigue. Fatigue is an extreme form of tiredness. ... Fever and night sweats. People with leukemia can often experience fever, which is when body temperature is higher than normal. ... Easy bruising or bleeding. ... Aching in bones or joints. ... Frequent infections. ... Unexplained weight loss. ... Shortness of breath. ... Additional symptoms.
Will leukemia come back?
You may be relieved to finish treatment, but find it hard not to worry about the leukemia coming back. (When leukemia comes back after treatment, it is called a relapse or recurrence.) This is a very common concern in people who have had leukemia. For other people, the leukemia may not go away completely.
Where is the best hospital to treat leukemia?
The Leukemia Center at MD Anderson is one of the world's most-recognized treatment centers for leukemia and blood disorders. Research by MD Anderson doctors has pioneered new standards of care for all types of leukemia.
What are some future treatment possibilities for leukemia?
Novel anti-leukemia therapies, such as inhibitors of FLT3 and IDH1/2 mutations in certain AML cells. Genetically modified immune (T) cells. New antibody formulations. Oral chemotherapy substitutes for IV chemotherapy.
What gender does leukemia affect the most?
Gender: Men are more likely than woman to develop leukemia. Age: The risk of most leukemias increase with age. The median age of a patient diagnosed with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is 65 years and older.
What exams would be Performed?
As mentioned, your doctor will be requiring to perform series of exams to come up with the best treatment plan. Some of these exams may be anything from the following:
Treatment of Leukemia
Keep in mind that the treatment procedure for leukemia would be dictated by a number of different factors. Your doctor will be determining your options for leukemia treatment based on overall health and age, type of leukemia that you have and whether it began spreading in several parts of your body.
What is HPSCT?
A bone marrow transplant, or HPSCT, is the process of replacing blood cells in the body. To do this, healthy blood stem cells are injected into the body. These stem cells travel to the bone marrow where they replace the current stem cells called hematopoietic stem cells.
How is it done?
Receiving stem cells is similar to receiving a blood transfusion. A needle may be inserted into a large vein in your arm, or you may have a central venous catheter placed in a blood vessel in the right side of your chest and the stems cells will flow into your heart.
What are the side effects and risks?
Complications may occur, but not everyone will experience them. Complications may include:
What is chemotherapy?
Chemotherapy uses strong drugs or chemicals, sometimes in combination, to damage or kill cancer cells. This treatment is systemic, which means chemotherapy drugs attack cancer cells, which tend to be fast-growing. However, these drugs can also affect healthy cells.
How is it given?
Chemotherapy can be given orally as a pill, capsule, or liquid, but most of the time, the drugs are given intravenously, through a catheter or central line. This is a port-like device attached to one of your veins that allows you to receive intravenous drugs.
Which types of leukemia may be treated with this?
All four main types of leukemia may be treated with chemotherapy. In ALL, AML, and CLL, it’s the first and main treatment. For CML, targeted therapies are typically used first, followed by chemotherapy.
What are the side effects and risks?
As with any medical treatment, there are side effects with chemotherapy depending on the drug used, dosage, and how long you take it.
What is the treatment for leukemia?
Chemotherapy (drug treatment to destroy leukemia cells) is the mainstay of leukemia treatment, and may incorporate multiple types of drugs. Radiation and surgery are contemplated only for cases in which leukemia cells have collected in definitive areas.
Where are clinical trials being conducted for leukemia?
Doctors at some medical centers including the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center are conducting clinical trials to test novel vaccines for leukemia.
How does radiation kill leukemia?
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill leukemia cells by damaging the genetic material they contain . This treatment can be used adjunctively to chemotherapy to control disease or eradicate local areas of disease. Some patients receive targeted radiation from a large machine aimed at the spleen, brain or other parts of the body where leukemia cells have collected. This type of therapy takes place five days a week for several weeks. Others may receive radiation directed to the whole body. These sessions are given once or twice a day for a few days, usually before a stem cell transplant.
What is the drug used for minimal residual leukemia?
Dose-intensive, curative chemotherapy for minimal residual leukemia. Pioneered clinical trials of the drug tipifarnib, known by its trade name Zarnestra, which blocks an enzyme called farnesyltransferase, which modifies certain cellular proteins so that they can attach to cellular membranes or other structures.
How long does radiation therapy last?
This type of therapy takes place five days a week for several weeks. Others may receive radiation directed to the whole body.
What organ is removed to help fight infection?
In some cases of CLL, for example, doctors may recommend surgery to remove the spleen, an organ located in the abdomen behind the ribs that removes and destroys old red blood cells and helps fight infection. The procedure, called a splenectomy, is helpful if the spleen is destroying red blood cells and platelets.
How many drugs are given for leukemia?
Depending on the type of leukemia, you may receive a single drug or a combination of two or more drugs. The medications may be prescribed as pills, or as fluids administered through a needle or tube inserted into a vein; through a tube inserted in the chest; or through injection into the cerebrospinal fluid.
Who first described leukemia?
Leukemia was first described by anatomist and surgeon Alfred-Armand-Louis-Marie Velpeau in 1827. A more complete description was given by pathologist Rudolf Virchow in 1845. Around ten years after Virchow's findings, pathologist Franz Ernst Christian Neumann found that the bone marrow of a deceased person with leukemia was colored "dirty green-yellow" as opposed to the normal red. This finding allowed Neumann to conclude that a bone marrow problem was responsible for the abnormal blood of people with leukemia.
How long does it take for leukemia to develop?
Chronic leukemia is characterized by the excessive buildup of relatively mature, but still abnormal, white blood cells. Typically taking months or years to progress, the cells are produced at a much higher rate than normal, resulting in many abnormal white blood cells.
What type of cell is involved in lymphocytic leukemia?
Most lymphocytic leukemias involve a specific subtype of lymphocyte, the B cell. In myeloid or myelogenous leukemias, the cancerous change takes place in a type of marrow cell that normally goes on to form red blood cells, some other types of white cells, and platelets.
How does leukemia cause cancer?
Leukemia, like other cancers, results from mutations in the DNA. Certain mutations can trigger leukemia by activating oncogenes or deactivating tumor suppressor genes, and thereby disrupting the regulation of cell death, differentiation or division.
How many people died from leukemia in 2010?
In 2010, globally, approximately 281,500 people died of leukemia. In 2000, approximately 256,000 children and adults around the world developed a form of leukemia, and 209,000 died from it. This represents about 3% of the almost seven million deaths due to cancer that year, and about 0.35% of all deaths from any cause.
What are the causes of leukemia?
Risk factors include smoking, ionizing radiation, some chemicals (such as benzene ), prior chemotherapy, and Down syndrome.
What are the symptoms of leukemia?
Symptoms may include bleeding and bruising, fatigue, fever, and an increased risk of infections. These symptoms occur due to a lack of normal blood cells. Diagnosis is typically made by blood tests or bone marrow biopsy. The exact cause of leukemia is unknown.
How long does leukemia last?
Over 55 years, the five-year survival rate for leukemia has risen from 14 percent to 66 percent in the United States. A disease that was once considered a death sentence can now be treated and, in some cases, cured. However, leukemia research hasn’t stopped.
How can bone marrow be used to treat leukemia?
Scientists hypothesized that they could treat leukemia by replacing diseased bone marrow with healthy marrow capable of creating the stem cells that develop into healthy blood cells. By the middle of the 20th century, researchers found that such transplants were effective in treating disease in rats and other animals.
What are the different types of leukemia?
These discoveries paved the way for the definitions of the four major subtypes of leukemia: 1 Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL, also known as acute lymphoblastic leukemia) 2 Acute myeloid leukemia (AML, also known as acute myeloblastic leukemia) 3 Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) 4 Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML, also known as chronic myelogenous leukemia)
How long can you live with CML?
In addition, some forms of leukemia — especially CML — still remained resistant to treatment. An adult diagnosed with CML could expect to live for just a year or less , unless they were still young enough to risk a bone marrow transplant. Even then, death rates were high.
What was Ehrlich's work on stem cells?
This was the earliest definition of what we now know as “stem cells.”. Ehrlich’s work also led to classifications of types of leukemia by which cells were affected.
What is the color of bone marrow in leukemia?
Other doctors found that people with leukemia had bone marrow that was yellowish-green, instead of the normal, healthy red. Leukemia wasn’t just a disease of the organs: The bones were involved as well. This destruction of the bone marrow accounted for the anemia (lack of red blood cells) that went along with leukemia.
What did Paul Ehrlich do to help scientists?
In 1877, a German medical student named Paul Ehrlich developed a stain that let scientists see the details of blood cells.
What is the treatment for leukemia?
Traditionally, leukemia is primarily treated with chemotherapy or radiation therapy. Stem cell transplants may also be used in conjunction with chemotherapy, particularly in children. Immunotherapy and targeted therapies are newer treatments for certain types of leukemia.
How does immunotherapy help with leukemia?
Depending on the type of immunotherapy, treatment may help: boost your T-cells (T-cell transfer therapy) preserve the integrity of immune cells by helping prevent them from responding too strongly to leukemia cells ( immune checkpoint inhibitors)
What are the treatments for cancer?
For this reason, standard treatments tend to include: chemotherapy (sometimes with stem cell transplant) radiation therapy. Due to the risk of lifelong side effects, researchers are looking into other options, such as targeted therapies and immunotherapies.
How does targeted therapy work?
As the name suggests, this treatment approach works by targeting genes or proteins that may be helping cancerous cells grow.
What is car T cell therapy?
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy is a newer type of immunotherapy for childhood ALL. Your body already has T-cells, but when you have cancer, they may not work as they should. With CAR T-cell therapy, some T-cells are removed and genetically modified with receptors to fight cancer more effectively.
What is the survival rate for leukemia?
The overall 5-year survival rate for leukemia is estimated at 63.7 percent. Trusted Source. . As new, earlier treatments have emerged, the death rate for this type of cancer is also declining. In 2020, leukemia made up only 3.8 percent.
Can leukemia recur?
However, the cancer may recur due to cells that remain in your body. The exact outlook depends on the type of leukemia, the stage of the disease, and your age. But research and advances in treatments point to the possibility of a cure that makes leukemia unlikely to recur. Immunotherapies and targeted therapies are of particular interest ...
Who was the first person to treat acute leukemia?
In 1948, Sidney Farber reported the first rational treatment for acute leukemia. 5 Aware of anecdotal evidence that children with acute leukemia who were given the then-new vitamin, folic acid, became worse, Farber reasoned that if folic acid metabolism could be blocked that perhaps they would improve.
Who discovered leukemia in 1845?
But the real origin of the understanding of leukemia as an entity occurred quite fortuitously in the same year, 1845, by the great German pathologist, Rudolf Virchow, and the British pathologist, John Bennett.
What happened to Dr Gloor?
Instead, he was fired from his job in Naegeli's clinic and was banished to a clinic in one of the outlying cantons, where he spent the rest of his career.
When did acute leukemia become gloomy?
Nonetheless, the outlook in acute leukemia remained very gloomy through the 1950s and the 1960s. In the 1960s Boggs, Wintrobe, and Cartwright reviewed the acute leukemias and discussed the response to therapy, which then consisted of 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) and methotrexate.
Can leukemia be differentiated into hematopoietic stem cells?
Thus one could take a muscle biopsy on a patient with leukemia, grow up the myoblasts in that muscle, and then allow them to differentiate into hematopoietic stem cells, stem cells that are now autologous, but completely free of the mutations causing malignancy.
Was Metzger cured?
It is possible that Mr Metzger was not cured, but it was a very long remission. Arsenic, one of the components of RAT, continued to play a role in the treatment of leukemia for quite a long time. We used to think, even in the 1950s and 1960s, that the use of arsenic in the treatment of leukemia was really quite quaint.
Who named the disorder leukemia?
Virchow named the disorder leukemia and John Bennett named it leukocypenia. This difference in nomenclature, the beginning of many conflicts about nomenclature in this field, resulted in vigorous and acrimonious debate over many years.
What was the treatment for leukemia in the 1940s?
Further, in the 1940s more and more new treatments such as aminopterin, 6-mercaptopurin, and 6- mercaptopurine came about.
What is the history of leukemia?
History of Leukemia. Leukemia is a type of blood cancer and is characterized by the presence of excess number of white blood cells in the blood. Although this disease has been around for centuries together, it was officially diagnosed only in 1845 by John Hughes... Leukemia is a type of blood cancer and is characterized by the presence ...
What are the causes of leukemia?
Exposure to radiation via atomic bomb explosion or medical treatments such as chemotherapy and high amount of pesticides are also risk factors that can lead to leukemia. People suffering from Down syndrome are also prone to this blood disease. The oldest and primary treatment for leukemia was arsenic.
What was the name of the chemical that was used to treat Hodgkin's disease?
In the 18th century, Thomas Fowler created a solution comprising arsenic trioxide and potassium bicarbonate, and called it Fowler’s solution. This solution became a standard remedy to treat Hodgkin’s disease, anemia, and leukemia. However, in the early 20th century, arsenic was replaced by radiation therapy.
Why are industrialized countries more susceptible to leukemia?
Industrialized nations are more susceptible to leukemia because people residing in such nations are constantly coming in contact with chemicals, such as high levels of benzene and formaldehyde ( at workplaces).
Where does the word "leukemia" come from?
The word leukemia comes from the Greek words ‘leukos’ and ‘heima’, which mean white blood and refers to excess white blood cells in the body. Leukemia is a type of cancer of the blood and bone marrow, and comprises a broad spectrum of diseases. It is characterized by the abnormal production and multiplication of blood cells in the body, ...
Can leukemia be cured?
Acute myelogenous leukemia (Erythroleukemia) Further, in 1970 it was confirmed that leukemia could be cured, and by the 1980s and 1990s the patients cured were around 70%. This increased the hopes of all the patients worldwide.
When was leukemia first discovered?
June 4, 2012. Leukemia, a malignant cancer of the blood, was named in 1847 by Dr. Rudolf Virchow, a German politician whose wide-ranging interests led him to significant discoveries in cell biology, pathology and anthropology.
When did the chemical approach to leukemia start?
The first suggestion to readers of The Times that a chemical approach might work was on April 13, 1946, when an anonymous reporter noted that because some of the chemicals tested and rejected for malaria treatment “destroy white blood cells, they may yet have their uses in leukemia.”.
How much did the Dutch give for the most satisfactory treatise on leukemia?
On March 5, 1927, The Times reported that a “Dutch gentleman” had offered an award of 25,000 guilders “for the most satisfactory treatise on the treatment of leukemia.”.
Is radium used for leukemia?
On May 3, 1915, The Times reported that radium “has also been found effective in leukemia,” but then acknowledged that “patients might even succumb to the poisons released into the system.”. Still, this was the first mention of a treatment, radiation therapy, that today remains one of the treatments for the illness. Image.
Can leukemia be cured?
The many types of leukemia can be successfully treated, and sometimes cured, with chemotherapy, stem cell transplants and biological therapies that enhance the body’s immune system. NICHOLAS BAKALAR. Advertisement. Continue reading the main story.

Diagnosis
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment
Specialist to consult
Overview
Classification
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Signs and symptoms
- A diagnosis of leukemia may be devastating — especially for the family of a newly diagnosed child. With time you'll find ways to cope with the distress and uncertainty of cancer. Until then, you may find it helps to: 1. Learn enough about leukemia to make decisions about your care. Ask your doctor about your leukemia, including your treatment options and, if you like, your prognosis. As …
Causes
- Start by seeing your family doctor if you have signs or symptoms that worry you. If your doctor suspects you have leukemia, you may be referred to a doctor who specializes in diseases of the blood and bone marrow (hematologist). Because appointments can be brief, and because there's often a lot of information to discuss, it's a good idea to be prepared. Here's some information to …
Diagnosis
Leukemia is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called blasts or leukemia cells. Symptoms may include bleeding and bruising, bone pain, fatigue, fever, and an increased risk of infections. These symptoms occur due to a lack of normal blood cells. Diagnosis is typically made by blood tests or bone marrow biopsy.
Treatment
Clinically and pathologically, leukemia is subdivided into a variety of large groups. The first division is between its acute and chronic forms:
• Acute leukemia is characterized by a rapid increase in the number of immature blood cells. The crowding that results from such cells makes the bone marrow unable to produce healthy blood cells resulting in low hemoglobin and low platelets. Immediate treatment is required in acute leuk…
Prognosis
The most common symptoms in children are easy bruising, pale skin, fever, and an enlarged spleen or liver.
Damage to the bone marrow, by way of displacing the normal bone marrow cells with higher numbers of immature white blood cells, results in a lack of blood platelets, which are important in the blood clotting process. This means people with leukemia may easily become bruised, bleed ex…
Epidemiology
There is no single known cause for any of the different types of leukemias. The few known causes, which are not generally factors within the control of the average person, account for relatively few cases. The cause for most cases of leukemia is unknown. The different leukemias likely have different causes.
Leukemia, like other cancers, results from mutations in the DNA. Certain mutations can trigger le…