
What was the first documented case of AIDS?
May 11, 2016 · Congress will not approve the first dedicated funding for AIDS research and treatment until July 1983. November 5: CDC’s “Current Trends Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS): Precautions for Clinical and Laboratory Staffs” lays out the first set of precautions for clinical and laboratory staff working with people exhibiting signs of AIDS.
How do you cure AIDS?
In 1983, scientists discovered the virus that causes AIDS. They later named it human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). The race was on for a treatment to …
What is the prognosis for AIDS?
Jul 14, 2017 · AZT is Developed HIV/AIDS in the 1990s and 2000s HIV Treatment Progresses Sources: In the 1980s and early 1990s, the outbreak of HIV and AIDS swept across the United States and rest of the world,...
What was AIDS called originally?
Oct 12, 2021 · Zidovudine, commonly known as AZT, was introduced in 1987 as the first treatment for HIV. Scientists also developed treatments to reduce transmission during pregnancy. In 1995, President Bill...

How long did it take to develop treatment for AIDS?
It took seven years after HIV was first discovered before the first drug to fight it was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). In those first anxious years of the epidemic, millions were infected.Mar 19, 2017
When did treatment for AIDS become available?
The first antiretroviral drug - a new treatment to prevent the growth of the HIV virus – was introduced on the NHS in 1987, but it wasn't until 1996 when antiretroviral treatment (ART) became more effective that patient outcomes began to improve significantly.
What drug stopped HIV from multiplying?
Also called azidothymidine (AZT), the medication became available in 1987.
What is the name of the drug that shuts down HIV?
Similar to AZT, NNRTIs shut down HIV by targeting the enzymes it needs to multiply. These drugs paved the way to a new era of combination therapy for HIV/AIDS.
How many HIV medications are there?
Today, more than 30 HIV medications are available. Many people are able to control their HIV with just one pill a day. Early treatment with antiretrovirals can prevent HIV-positive people from getting AIDS and the diseases it causes, like cancer.
What drug was approved in 2012?
A study showed that taking a daily dose of antiretrovirals not only helped those who were HIV-positive, but also could protect healthy people from becoming infected. In 2012, the FDA approved the drug Truvada for pre-exposure prophylaxis, or PrEP.
What disease did gay men get?
Others were coming down with a rare type of pneumonia. A year later, the mysterious disease had a name: acquired immune deficiency syndrome, or AIDS.
When did the FDA approve the pill Combivir?
The multiple doses and the drugs’ side effects drove many people to quit their HIV therapy. Then in 1997 , the FDA approved a pill called Combivir that contained two anti-HIV drugs and was easier to take. Nearly 2 decades after the emergence of HIV and AIDS, a dozen antiretroviral drugs were on the market. PrEP.
When was saquinavir approved?
In 1995 , the FDA approved saquinavir, the first in a different anti-HIV (antiretroviral) drug class called protease inhibitors. Like NRTIs, protease inhibitors stop the virus from copying itself, but at a different stage during the infection.
When did the CDC start describing AIDS?
In September of 1982 , the CDC used the term AIDS to describe the disease for the first time. By the end of the year, AIDS cases were also reported in a number of European countries. READ MORE: Pandemics that Changed History. 10.
Where did HIV spread in the 1960s?
In the 1960s, HIV spread from Africa to Haiti and the Caribbean when Haitian professionals in the colonial Democratic Republic of Congo returned home. The virus then moved from the Caribbean to New York City around 1970 and then to San Francisco later in the decade.
How many people have died from HIV in the US?
Today, more than 70 million people have been infected with HIV and about 35 million have died from AIDS since the start of the pandemic, ...
How much does PrEP reduce HIV?
When taken daily, PrEP can reduce the risk of HIV from sex by more than 90 percent and from intravenous drug use by 70 percent, according to the CDC.
How do you detect HIV?
Today, numerous tests can detect HIV, most of which work by detecting HIV antibodies. The tests can be done on blood, saliva, or urine, though the blood tests detect HIV sooner after exposure due to higher levels of antibodies. In 1985, actor Rock Hudson became the first high-profile fatality from AIDS.
When did the first SIV virus occur?
Researchers believe the first transmission of SIV to HIV in humans that then led to the global pandemic occurred in 1920 in Kinshasa, the capital and largest city in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
When was the first antiretroviral drug developed?
AZT is Developed. In 1987, the first antiretroviral medication for HIV, azidothymidine (AZT), became available. Numerous other medications for HIV are now available, and are typically used together in what’s known as antiretroviral therapy (ART) or highly active antiretroviral treatment (HAART).
What is the new class of anti-HIV drugs?
After 1991, several other nucleoside analogs were added to the anti-HIV arsenal, as were a new class of anti-HIV drugs called the non-nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase inhibitors which work in similar ways to the nucleoside analogs but which are more quickly activated once inside the bloodstream.
When did monotherapy start?
Despite this proliferation of drug options, the standard antiviral therapy for HIV-infected individuals between 1986 and 1995 for the most part remained "monotherapy" or treatment with a single drug. Such drugs appeared to be partly efficacious, although there was a great variation in effectiveness among individuals.
What is the class of antiviral drugs that prevents HIV infection?
Next to be developed were the class of antiviral drugs known as protease inhibitors, which were distinctly different from the reverse transcriptase inhibitors in that they do not seek to prevent infection of a host cell, but rather to prevent an already infected cell from producing more copies of HIV.
Why is combination therapy important?
By using more than one drug at a time, combination therapy is able to "pin down" HIV from more than one angle, so that even if one drug fails, another can continue to suppress viral replication.
When was ZDV approved?
From Monotherapy to Combination Therapy. In 1986 the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first antiviral drug zidovudine (ZDV; AZT) for use in preventing HIV replication by inhibiting the activity of the reverse transcriptase enzyme. AZT is part of a class of drugs formally known as nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase ...
What are the targets of HIV?
Transmitted from person to person primarily through blood, semen, and vaginal secretions, HIV's principal targets are the very cells of the immune system (particularly CD4+ t-cells and macrophages) which are intended to clear foreign pathogens from the body.
Can antiretrovirals cure HIV?
A lot of the skepticism about the medical system has returned among many patients, although there is still a recognition that antiretrovirals can help people with HIV stay well longer.".
When was the first HIV test approved?
It caused a 47 percent decline in death rates. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first rapid HIV diagnostic test kit in November 2002.
Who was the first person to have AIDS?
Actor Rock Hudson was the first major public figure to acknowledge he had AIDS. After he died in 1985, he left $250,000 to set up an AIDS foundation. Elizabeth Taylor was the national chairperson until her death in 2011. Princess Diana also made international headlines after she shook hands with someone with HIV.
What was the public response to the AIDS epidemic?
Public response was negative in the early years of the epidemic. In 1983, a doctor in New York was threatened with eviction, leading to the first AIDS discrimination lawsuit. Bathhouses across the country closed due to high-risk sexual activity. Some schools also barred children with HIV from attending.
How many different HIV treatments were there in 2010?
Researchers continued to create new formulations and combinations to improve treatment outcome. By 2010, there were up to 20 different treatment options and generic drugs, which helped lower costs. The FDA continues to approve HIV medical products, regulating: product approval. warnings.
What is the FDA approved drug for HIV?
Recent drug development for HIV prevention. In July 2012, the FDA approved pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP). PrEP is a medication shown to lower the risk of contracting HIV from sexual activity or needle use. The treatment requires taking the medication on a daily basis.
How many people died from AIDS in 1995?
By 1995, complications from AIDS was the leading cause of death for adults 25 to 44 years old. About 50,000 Americans died of AIDS-related causes.
What is PrEP in HIV?
PrEP is shown to reduce the risk for HIV infection by greater than 90 percent.
What was the name of the new class of antiretroviral drugs?
The mid-1990s marked the emergence of another new class of antiretroviral drugs called non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors or NNRTIs. Because they are cheaper and easier to produce than protease inhibitors, they helped scale up antiretroviral therapy in resource-limited settings.
When did NRTI drugs get FDA approval?
In the early 1990s, additional NRTI drugs gained FDA approval. The development of AZT and other NRTIs showed that treating HIV was possible, and these drugs paved the way for discovery and development of new generations of antiretroviral drugs.
What did AZT do?
In the laboratory, AZT suppressed HIV replication without damaging normal cells, and the British pharmaceutical company Burroughs Wellcome funded a clinical trial to evaluate the drug in people with AIDS. Used alone, AZT decreased deaths and opportunistic infections, albeit with serious adverse effects. In March 1987, AZT became the first drug ...
How many antiretroviral drugs are there?
Currently, more than 30 antiretroviral drugs are available, including several fixed-dose combinations, which contain two or more medications from one or more drug classes in a single tablet. Today, many people control their HIV by taking as little as one pill once a day.
What is AZT used for?
In March 1987, AZT became the first drug to gain approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for treating AIDS. AZT, also referred to as zidovudine, belongs to a class of drugs known as nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, or NRTIs.
What is the primary co-receptor used by HIV?
A number of research groups, including NIAID scientists, determined that a different receptor called CCR5 is actually the primary co-receptor used by HIV to infect immune cells. This work laid the foundation for the development of the CCR5- blocking drug maraviroc, which received FDA approval in 2007.
When did saquinavir get FDA approval?
In December 1995, saquinavir became the first protease inhibitor to receive FDA approval. In 1996, results from an NIAID-sponsored trial showed that a three-drug regimen of saquinavir, ddC, and AZT was more effective than two-drug therapy with ddC and AZT. One of the key studies demonstrating the efficacy of triple-drug therapy was ACTG 320, ...
What was the significance of the discovery of NCI researchers in the early days of HIV/AIDS?
The discoveries of NCI researchers in the early days of HIV/AIDS were vital in transforming HIV infection from a fatal diagnosis to the manageable condition it is for many today. Patients with the mysterious immune disorder now known as AIDS had been arriving at the NIH Clinical Center since 1981.
When was AZT approved?
In a randomized trial, it was subsequently shown to improve survival of AIDS patients. In 1987, it became the first drug approved by the U.S. FDA for treatment of the disease. AZT was subsequently shown to markedly reduce the perinatal transmission of HIV.
What enzymes did the NCI develop?
NCI’s strong industry collaborations helped speed patient access to the new drugs. The NCI researchers first focused on a viral enzyme called reverse transcriptase that HIV needs to multiply. They developed an assay to test the utility of drugs against HIV and gathered a number of promising compounds to test.
What enzymes were used to map out the structure of HIV?
NCI scientists helped map out the structure of another essential viral enzyme, the HIV protease, to guide the design of a new class of HIV drugs. When combined with reverse transcriptase inhibitors, protease inhibitors, developed in the mid-1990s, dramatically suppressed replication of the virus, often reducing it to undetectable levels.
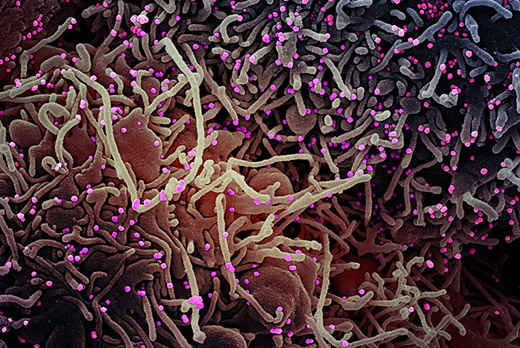
What color are HIV cells?
An HIV-infected T cell (blue, green) interacts with an uninfected cell (brown, purple). Faced with the burgeoning HIV/AIDS epidemic in the 1980s, NCI’s intramural program developed the first therapies to effectively treat the disease.
Who invented AZT?
Azidothymidine (AZT), a compound first synthesized by Jerome Horowitz, Ph.D., in 1964 as an anti-cancer drug, was among the drugs initially tested. In a preliminary clinical trial done largely in the NIH Clinical Center, NCI scientists showed that AZT could improve the immune function of AIDS patients. In a randomized trial, it was subsequently ...
Is AZT effective for AIDS?
Because AZT was not entirely effective by itself, NCI scientists continued to develop and test other drugs to treat AIDS, including the reverse transcriptase inhibitors didanosine (ddI) and zalcitabine (ddC). These became the second and third drugs approved by the FDA for AIDS. Combining AZT with one of these drugs improved the effectiveness ...
in The Beginning
from Monotherapy to Combination Therapy
Still Not A Cure
The Post-Vancouver State of Combination Treatment
References