...
Executive Summary.
| In | Out |
|---|---|
| Freshwater, Treated Water | Treated Water |
How is ion exchange chromatography used for purification of water?
In the context of water purification, ion-exchange is a rapid and reversible process in which impurity ions present in the water are replaced by ions released by an ion-exchange resin. The impurity ions are taken up by the resin, which must be periodically regenerated to restore it to the original ionic form.
What are the application of ion exchange?
Miscellaneous analytical uses of ion exchange include the dissolving of sparingly soluble salts like calcium sulfate, the determination of total dissolved salts in natural waters (by passing them through hydrogen-loaded, cation-exchange resins and titrating the acid formed), and the identification of minute traces of ...
Which is the process of water softening treatment works based on ion exchange process?
In the ion exchange process, sodium ions are used to coat an exchange medium in the softener. The exchange medium can be natural “zeolites” or synthetic resin beads that resemble wet sand. As hard water passes through a softener, the calcium and magnesium trade places with sodium ions (Figure 1).
Is ion exchange a chemical or physical process?
reversible chemical reactionIon exchange is a reversible chemical reaction where dissolved ions are removed from solution and replaced with other ions of the same or similar electrical charge. Not a chemical reactant in and of itself, IX resin is instead a physical medium that facilitates ion exchange reactions.Nov 28, 2017
What is the mechanism of ion exchange process?
Ion exchange is a chemical reaction in which free mobile ions of a solid, the ion exchanger, are exchanged for different ions of similar charge in solution. The exchanger must have an open network structure, either organic or inorganic, which carries the ions and which allows ions to pass through it.
What is ion exchange water softener?
Cation exchange water softeners remove the calcium and magnesium ions found in hard water by exchanging them with sodium (or potassium) ions. Once all the ions are fully exchanged, the water softener undergoes a regeneration process to flush the system of excess ions and recharge with new sodium ions.Feb 15, 2022
How ion exchangers help in water treatment using cationic and anionic ion exchangers?
They exchange the anionic portion of the minerals and they are known as anion exchanger. Uses of Ion-exchange Resin – Water treatment by ion-exchange resin includes softening deionization and de-alkalization of water. Therefore, hard water can be converted into soft water by making use of ion-exchange resins.
How does ion exchange method remove hardness of water?
Hard water in this process is first passed by cation ion exchange resin which causes substitution of all cations with H+ ions. Now the water after passing through this reaches at the bottom of tank where it treated with anionic resin which substitutes OH− ions with Cl−ions and SO4−2 ions.
What is ion exchange?
Ion exchange is a water treatment process commonly used for water softening or demineralization, but it also is used to remove other substances from the water in processes such as dealkalization, deionization, denitrification, and disinfection. With many other overlapping technologies available, it is important to determine whether ion exchange is ...
What is the process of exchange of ions?
Ion exchange describes a specific chemical process in which unwanted dissolved ions in water and wastewater — like nitrate, fluoride, sulfate, and arsenic — are exchanged for other ions with a similar charge. Ions are atoms or molecules containing a total number of electrons that are not equal to the total number of protons.
How much is the ion exchange resin market?
The global market for ion exchange resins, which was estimated at $1.54 billion in 2014, was projected in 2016 to be $2.46 billion by 2022, a compound annual growth rate of roughly 6%, according to Stratistics MRC, a Maryland-based market research firm. Their analysts see increased nuclear power demand and stringent environmental regulations driving the market. This is particularly seen in the power generation and wastewater treatment markets.
What is resin exchange capacity?
Resin materials have a finite exchange capacity. Each of the individual exchange sites will become full with prolonged use. When unable to exchange ions any longer, the resin must be recharged or regenerated to restore it to its initial condition. The substances used for this can include sodium chloride, as well as hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, or sodium hydroxide.
What is specialized resin?
Specialized resins have been designed to treat various contaminants of concern, including boron, perchlorate, and uranium. There are many resins designed for these purposes, such as strong base/strong anion resin, which is used to remove nitrates and perchlorate. Ion exchange is used extensively in water softening, where it’s considered a solid, ...
What is the ion exchange process?
The Ion Exchange process can be used in a variety of ways when it comes to water purification and softening. Although different water treatment products utilize this process in different ways, the action itself remains the same: unwanted ions that are dissolved in the water are replaced with new beneficial or harmless ions of an equivalent charge.
What is the difference between a cation and an anion?
A Cation is an atom with a positive charge, whereas an Anion is an atom with a negative charge. When it comes to the resins used, their composition is normally made up of microbeads that are very permeable. Typically, the microbeads are created out of different polymers like polystyrene.
How to restore resin?
Restoration is done by having a solution poured into the resin. This solution is typically made up of an acid or salt and is able to renew itself by replacing all of the anions and cations within the resin. Then the ions that are “dirty” get tossed out.
What is a cation resin?
A Cation Resin can be used in ion exchange systems for dealkalization or demineralization, depending on whether it’s a weak acid cation or a strong acid cation. A Chelating Resin is often used to remove heavy metals such as mercury or cobalt from drinking water.
What are some examples of resins?
A good example is a chelating resin. This resin is frequently used when Mercury and Cobalt metals need to be removed. Also, resins known as magnetic exchange are often utilized ...
What is the purpose of ion exchange?
Ion exchange is a process used extensively in nuclear facilities, industrial processes and medical and pharmaceutical operations to control the purity and pH of water by removing undesirable ions ...
What is ion exchange?
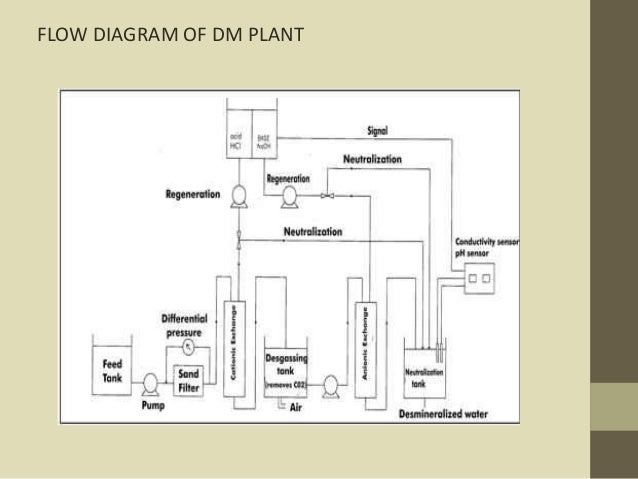
An ion exchange is the reversible exchange of ions between a liquid and a solid. This process is generally used to remove undesirable ions from a liquid and substitute acceptable ions from the solid (resin). The devices in which ion exchange occurs are commonly called demineralizers. This name is derived from the term demineralize, ...
What is the process of removing impurities from water?
The devices in which ion exchange occurs are commonly called demineralizers. This name is derived from the term demineralize, which means the process whereby impurities present in the incoming fluid (water) are removed by exchanging impure ions with H and OH ions, in the formation of pure water.
What are the two types of ion exchange resins?
There are two general types of ion exchange resins: those that exchange positive ions , called cation exchange resins, and those that exchange negative ions , called anion exchange resins. A cation is an ion with a positive charge. Common cations include Ca +2, Mg +2, Fe +2, and H +1. A cation resin is one that exchanges positive ions. An anion is an ion with a negative charge. Common anions include Cl -1, SO4 -2, and OH -1 . An anion resin is one that exchanges negative ions. Chemically, both types are similar and belong to a group of compounds called polymers, which are extremely large molecules that are formed by the combination of many molecules of one or two compounds in a repeating structure that produces long chains. A demineralizer is a vessel, usually with a volume of several cubic feet, that contains the resin.
What is the difference between a cation and an anion?
Common cations include Ca +2, Mg +2, Fe +2, and H +1. A cation resin is one that exchanges positive ions. An anion is an ion with a negative charge. Common anions include Cl -1, SO4 -2, and OH -1 . An anion resin is one that exchanges negative ions. Chemically, both types are similar and belong to a group of compounds called polymers, ...
What is a demineralizer?
A demineralizer is a vessel, usually with a volume of several cubic feet, that contains the resin. A demineralizer may contain an intimate mixture of both cation exchange resins and anion exchange resins and is called a mixed bed. Two-bed demineralizers have two vessels, the first containing cation resin followed by a separate vessel containing ...
What is the diameter of a resin?
Physically, ion exchange resins are formed in the shape of very small beads, called resin beads, with an average diameter of about 0.5 millimeters. Wet resin has the appearance of damp, transparent, amber sand and is insoluble in water, acids, and bases.
What happens to the exchange medium after softening?
After softening a large quantity of hard water, the exchange medium becomes coated with calcium and magnesium ions. When this occurs, the exchange medium must be recharged or regenerated (Figure 1). To recharge the softener with sodium ions, a softener is backflushed with a salt brine solution.
Why is it important to recharge water softeners?
This is important because recharging the beads with salt too early wastes salt and water. Recharging too late causes performance to fall off.
How much sodium is added to water?
During the softening process, sodium is released from the exchange media into the output water. For every grain of hardness removed from water, 8 mg/1 (ppm) of sodium is added. People on restricted sodium intake diets should account for increased levels of sodium in softened water.
What chemicals are used to soften water?
Two types of chemicals used to soften water for home laundry are Sal Soda and Calgon.
Is hard water a problem?
Ask your supplier for a copy of the latest water test results. Hard water is considered a nuisance water problem. Hardness removal is not a necessity to protect your health, but water softening is popular because most people prefer softened water for bathing, cleaning and washing.
Why is my white shirt dingy?
Through time, clothes washed in hard water may look dingy and feel harsh and scratchy. White clothing continually washed in hard water gradually will become dingy.
What is a water softener?
Standard water softeners are cation exchange devices. Cations refer to positively charged ions dissolved in the water. Cation exchange involves the replacement of the hardness ions with a nonhardness ion. Water softeners usually use sodium (Na+) as the exchange ion.
What is a cation exchanger?
Cation exchangers can be classified as either strong acid cation (SAC) resins or weak acid cation (WAC) resins, both of which are extensively used for demineralization. SAC resins are also commonly used for softening, while WAC resins are used for dealkalization applications.
What is an IX resin?
Most commonly, IX resins take the form of tiny, porous microbeads, though they are sometimes available as a sheet-like membrane . IX resins are fashioned from organic polymers, such as polystyrene, which form a network of hydrocarbons that electrostatically bind a large number of ionizable groups.
What is ion exchange?
Ion exchange is a process in which ions of a particular species in solution are replaced by ions with a similar charge but of different species attached to an insoluble resin. In essence, ion exchange is a sorption process and can also be considered a reversible chemical reaction. The common appli cations of ion exchange are water softening ...
What is an organic ion exchange resin?
An organic ion exchange resin consists of an organic or inorganic network structure with attached functional groups that can exchange their mobile ions for ions of similar charge from the surrounding medium. Each resin has a distinct number of mobile ion sites that set the maximum quantity of exchanges per unit of resin.
What is the exchange capacity of weak base resins?
Consequently, weak base resins exhibit minimum exchange capacity above a pH of 7.0. These resins merely sorb strong acids: they cannot split salts.
Why are strong acid resins called that?
Strong acid resins are so named because their chemical behavior is similar to that of a strong acid. The resins are highly ionized in both the acid (R-SO3H) and salt (R-SO3Na) form. They can convert a metal salt to the corresponding acid by the reaction (Equation 3.42):
What is an ion exchange system?
Ion exchange systems are used for efficient removal of dissolved ions from water. Ion exchangers exchange one ion for another, hold it temporarily, and then release it to a regenerant solution. In an ion exchange system, undesirable ions in the water supply are replaced with more acceptable ions.
What are the ions in water?
All natural waters contain, in various concentrations, dissolved salts which dissociate in water to form charged ions. Positively charged ions are called cations; negatively charged ions are called anions. Ionic impurities can seriously affect the reliability and operating efficiency of a boiler or process system.
How does a demineralizer work?
In a conventional demineralizer system, regenerant flow is in the same direction as the service flow, down through the resin bed. This scheme is known as co-current operation and is the basis for most ion exchange system designs. During the regeneration of a co-current unit, the contaminants are displaced through the resin bed during the regeneration. At the end of the regeneration, some ions, predominately sodium ions, remain in the bottom of the resin bed. Because the upper portion of the bed has been exposed to fresh regenerant, it is highly regenerated. As the water flows through the resin during service, cations are exchanged in the upper portion of the bed first, and then move down through the resin as the bed becomes exhausted. Sodium ions that remained in the bed during regeneration diffuse into the decationized water before it leaves the vessel. This sodium leakage enters the anion unit where anion exchange produces caustic, raising the pH and conductivity of the demineralized water.
When was zeolite used in water softeners?
In 1905 , Gans, a German chemist, used synthetic aluminosilicate materials known as zeolites in the first ion exchange water softeners. Although aluminosilicate materials are rarely used today, the term "zeolite softener" is commonly used to describe any cation exchange process.
What is zeolite softening?
Sodium zeolite softening is the most widely applied use of ion exchange. In zeolite softening, water containing scale-forming ions, such as calcium and magnesium, passes through a resin bed containing SAC resin in the sodium form. In the resin, the hardness ions are exchanged with the sodium, and the sodium diffuses into the bulk water solution. The hardness-free water, termed soft water, can then be used for low to medium pressure boiler feedwater, reverse osmosis system makeup, some chemical processes, and commercial applications, such as laundries.
Where is the underdrain system located?
The underdrain system, located at the bottom of the vessel, retains ion exchange resin in the tank, evenly collects the service flow, and evenly distributes the backwash flow. Uneven collection of water in service or uneven distribution of the backwash water can result in channeling, resin fouling, or resin loss.
What is the process of demineralization of water?
Demineralization of water is the removal of essentially all inorganic salts by ion exchange.
How does ion exchange work?
Ion exchange water treatment works by removing material from the water through the use of water processes such as water softening, and water deionization. These systems work by exchanging specific ions for other ions. When it comes to water softeners, magnesium and calcium ions are replaced by sodium ions.
What are ions in water?
Ions are electrically charged molecules, and are formed as pollutants dissolve in water. Natural areas of water have a balance of positively and negatively charged ions. Ions are what determine the TDS and conductivity of the water. The greater presence of ions results in higher TDS and conductivity.
What happens when you replace all cations dissolved in water?
If you replace all cations dissolved in water by H+ ions and all anions by OH– ions, these will recombine and form new molecules of water. To do this, you need a cation exchange resin in the H form and an anion exchange resin in the OH form. All cations and anions will be exchanged, and in this case the net result is a complete “disappearance” of the ionic contaminants. The cation exchange reactions will be:
What are the ions in water?
The soluble, ionised substances are present in water as ions, which are electrically charged atoms or molecules. The positively charged ions are called cations, and the negatively charged ions are called anions. Because water is globally neutral electrically (otherwise you would get an electric shock when you put your hand in water) the number of positive charges is identical to the number of negative charges.
What are the two substances that dissolve in water?
Among the substances dissolved in water, hardness is very commonly found. Hardness is a popular word to represent principally calcium and magnesium dissolved in the water; these ions can precipitate under certain conditions and form the scale that you may have seen in your boiling pan, and that can obstruct pipes and damaged water boilers. The “softening” of water is the exchange of the hardness cations (Ca++ and Mg++) for another cation that cannot form scale because it is much more soluble: the sodium ion Na+.
What happens when resins are exhausted?
When the resins are exhausted, you can bring them back to the fresh state and start over again. Regeneration of ion exchange resins is a reversal of the exchange reactions shown above. For instance, the softening resin is regenerated with sodium (Na+) ions supplied by a salt (common salt: NaCl) solution. The regeneration reaction is:
Is drinking water a good idea?
In many cases, these substances cause no problem. Drinking water containing some salinity is much better for health than ultra-pure water. For specific applications, however, these foreign substances are regarded as impurities and must be removed from water.

What Exactly Is Ion Exchange?
Removing Ionic Contaminants
Recharging Resins
Exchange Resins Market
Ion Exchange in Drinking Water Treatment
Food Processing
Is Ion Exchange Right For Your Needs?
- Although ion exchange and biological treatmentare widely recognized as the two leading technologies for denitrification, ion exchange is typically used to treat for nitrates in groundwater, while biological treatment is typically used to treat surface water. Ion exchange can also be used in the removal of arsenicand other metalloids and metals. Oth...