
Is it important to treat Parkinson's early?
Clinical trials suggest but have yet to conclusively demonstrate that early treatment can slow disease progression. Both the diminishment of symptoms and the potential for slowing disease progression have large implications for improving patient quality of life.
What is the first thing to do if you have Parkinson's disease?
Here are seven things to do right now, according to experts at the Johns Hopkins Parkinson's Disease and Movement Disorders Center:See a Specialist. ... Give Yourself Time to Adjust. ... Be Honest. ... Boost Activity. ... Stay Engaged. ... Track Your Symptoms. ... Consider Research.
Can Parkinson be cured at early stage?
Parkinson's disease can't be cured, but medications can help control your symptoms, often dramatically. In some more advanced cases, surgery may be advised. Your doctor may also recommend lifestyle changes, especially ongoing aerobic exercise.
At what stage is Parkinson's usually diagnosed?
One clear risk is age: Although most people with Parkinson's first develop the disease after age 60, about 5% to 10% experience onset before the age of 50. Early-onset forms of Parkinson's are often, but not always, inherited, and some forms have been linked to specific gene mutations.
Can you stop Parkinson's from progressing?
Currently, there is no licensed treatment to slow or stop the progression of Parkinson's disease.
What are early warning signs of Parkinson's disease?
10 Early Signs of Parkinson's DiseaseTremor. Have you noticed a slight shaking or tremor in your finger, thumb, hand or chin? ... Small Handwriting. Has your handwriting gotten much smaller than it was in the past? ... Loss of Smell. ... Trouble Sleeping. ... Trouble Moving or Walking. ... Constipation. ... Masked Face. ... Dizziness or Fainting.More items...
Can Parkinson's stay mild?
The primary Parkinson's disease symptoms — tremors, rigid muscles, slow movement (bradykinesia), and difficulty balancing — may be mild at first but will gradually become more intense and debilitating. Parkinson's symptoms can become more severe over a period of 20 years or even longer.
How do you slow down Parkinson's disease?
The Role of Exercise “Movement, especially exercises that encourage balance and reciprocal patterns [movements that require coordination of both sides of your body], can actually slow progression of the disease,” she says.
What age is early onset Parkinson's?
Parkinson's is a progressive disease of the central nervous system. The condition is caused by a loss of cells in the area of the brain that produces dopamine. It's usually diagnosed in people who are in their early 60s. People who are diagnosed before age 50 are said to have early onset Parkinson's.
What are the five 5 signs of Parkinson disease?
Parkinson's signs and symptoms may include:Tremor. A tremor, or shaking, usually begins in a limb, often your hand or fingers. ... Slowed movement (bradykinesia). ... Rigid muscles. ... Impaired posture and balance. ... Loss of automatic movements. ... Speech changes. ... Writing changes.
How long can you live with early onset Parkinson's?
Median survival was 15 years (95% CI: 14.2–15.5) for the whole cohort. Early-onset PD (EOPD) patients (AAO < 50 years) had the longest median survival time.
What are the four cardinal signs of Parkinson's disease?
One of the most prevalent neurological disorders is Parkinson's disease (PD), characterized by four cardinal signs: tremor, bradykinesia, rigor and postural instability.
What is the most important factor in initiating medications for an individual patient?
The most important factor in initiating medications for an individual patient is whether Parkinson’s symptoms are affecting quality of life , or alternatively whether symptoms are affecting work performance.
Why should medication be carefully monitored?
Most experts agree that the medication dosage and the timing of the medication dosage should be carefully monitored in order to maximize the control of potentially responsive Parkinson related symptoms.
Can you use amantadine for Parkinson's?
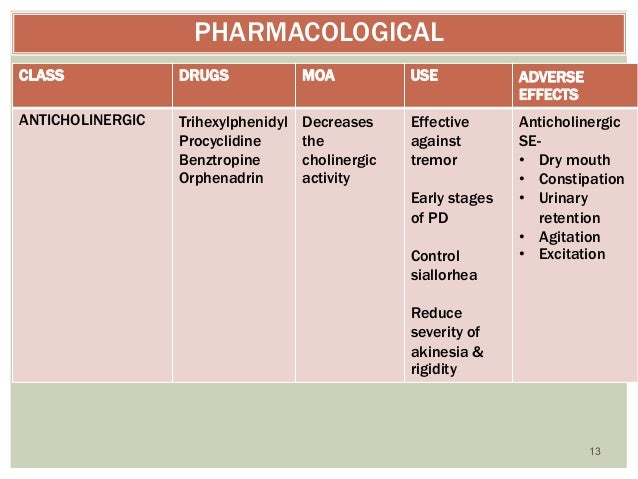
Other drugs such as amantadine may be used early in Parkinson’s disease therapy, however most practitioners reserve amantadine for treatment ofdyskinesia which may or may not occur later in the disease course. Patients should keep in mind that exercise is like a drug, and that a daily routine is often a great symptomatic supplement to any medication regimen. Many practitioners wait to utilize physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy later in the disease, however these modalities can often be powerful treatments when employed early in the disease. Finally, all Parkinson’s disease patients should have a general practitioner and a dermatologist involved with their care. The reason for involving “other doctors” is because with adequate Parkinson’s treatment, they will be far more likely to encounter difficulties with other medical illnesses (heart disease, prostate cancer, breast cancer, melanoma, etc.). Melanoma occurs more frequently in Parkinson’s disease populations.
Can you take levodopa with Parkinson's?
It is in fact rare to remain on this drug without other Parkinson’s drugs for any significant period of time. Dopamine agonists (ropinerole, pramipexole, cabergoline, rotigotine, others) and levodopa (Sinemet, Madopar) are both excellent choices for early Parkinson’s disease therapy.
Can you delay medication for Parkinson's?
Most experts agree that there is no benefit to delaying medication therapy if bothersome symptoms appear, and there may be risks in delaying treatment, especially if a treatment delay results in unsteadiness, falls, and fractures. Over the last 10-20 years the thinking has evolved on when and how to initiate medication therapy for early Parkinson’s ...
Is Sinemet safe for Parkinson's patients?
The best advice we can offer Parkinson’s disease patients is to not fear treatment, and to especially not fear dopaminergic therapy. Sinemet and other Parkinson’s therapies have not been shown to be toxic or to accelerate disease progression. Dopamimergics never “stop working,” however they may require adjustment over time. If Parkinson’s disease symptoms are affecting quality of life, the work performance, or if there exists a risk of falling, treatment should be initiated. Many practitioners will start with a MAO-B drug (selegiline, rasagiline, dissolvable selegiline, other), but Parkinson’s patients should be aware that the symptomatic effects of MAO-B’s are extremely mild. It is in fact rare to remain on this drug without other Parkinson’s drugs for any significant period of time. Dopamine agonists (ropinerole, pramipexole, cabergoline, rotigotine, others) and levodopa (Sinemet, Madopar) are both excellent choices for early Parkinson’s disease therapy. The choice of agent should however, consider the individual’s comprehensive medical picture (age, co-morbidities, types of symptoms, history of neurological/psychiatric issues) as therapy should never be viewed as a “one size fits all.” Finally, patients should remember that if depression, anxiety and other issues persist following dopaminergic treatment, then antidepressant therapy may also be warranted.
What age do you get Parkinson's?
Although most people with Parkinson’s first develop the disease at about age 60, about 5 to 10 percent of people with Parkinson's have "early-onset" disease, which begins before the age of 50. Early-onset forms of Parkinson's are often, but not always, inherited, and some forms have been linked ...
What is the best treatment for Parkinson's disease?
The main therapy for Parkinson's is levodopa, also called L-dopa. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine to replenish the brain's dwindling supply. Usually, people take levodopa along with another medication called carbidopa.
How many symptoms are there of Parkinson's disease?
Parkinson's disease has four main symptoms: Other symptoms may include depression and other emotional changes; difficulty swallowing, chewing, and speaking; urinary problems or constipation; skin problems; and sleep disruptions. Symptoms of Parkinson’s and the rate of progression differ among individuals.
What does Parkinson's disease do to the body?
People with Parkinson's also lose the nerve endings that produce norepinephrine, the main chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls many functions of the body, such as heart rate and blood pressure.
Can you get a blood test for Parkinson's?
There are currently no blood or laboratory tests to diagnose nongenetic cases of Parkinson's disease. Diagnosis is based on a person's medical history and a neurological examination. Improvement after initiating medication is another important hallmark of Parkinson's disease.
Can Parkinson's cause parkinsonism?
A number of disorders can cause symptoms similar to those of Parkinson's disease. People with Parkinson's-like symptoms that result from other causes are sometimes said to have parkinsonism.
Can Parkinson's be diagnosed?
Sometimes people dismiss early symptoms of Parkinson's as the effects of normal aging. In most cases, there are no medical tests to definitively detect the disease, so it can be difficult to diagnose accurately.
Can Parkinson's disease be treated with levodopa?
Firstly, initial treatment for early Parkinson's disease is not restricted to levodopa or dopamine agonists. Amantadine, anticholinergic drugs, selegiline, and non-pharmacological treatments (such as physical therapy) provide symptomatic relief in mildly affected patients. Thus, use of levodopa and dopamine agonists can be delayed until symptoms are clinically disabling.4Whether initial treatment with these alternative agents influences subsequent development of motor complications is unknown.
Is Parkinson's disease a neurodegenerative disease?
Parkinson's disease, a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, affects about 1% of the population over the age of 50. While it has no cure, it is the only neurodegenerative disorder with a range of medical and neurosurgical treatments that substantially reduce clinical symptoms.1However, medical management of early Parkinson's disease is controversial because of the potential risks and benefits to patients. Some clinicians prefer to use levodopa, a dopamine precursor, since it promptly relieves symptoms. Others prescribe dopamine agonists and withhold levodopa because of its long term complications, namely abnormal involuntary movements and potential neurotoxicity. Inevitably, managing the side effects of antiparkinsonian drugs becomes a therapeutic focus along with treating the primary motor abnormalities.1Extended controlled clinical trials are the only means of obtaining evidence based guidance on the use of dopamine agonists or levodopa for the management of early Parkinson's disease.
Is ropinirole good for Parkinson's?
Despite the remaining unanswered questions, ropinirole seems to be an effective treatment for early Parkinson's disease. Although levodopa remains the optimal treatment for Parkinson's disease, ropinirole provides similar improvements in functional abilities while minimising abnormal involuntary movements.
What is the best treatment for Parkinson's disease?
Some studies have even suggested that rasagiline may slow neurological deterioration in addition to controlling symptoms, these studies are very controversial. This is in contrast to dopamine, in which some early studies have suggested disease worsening with the drug. Amantadine is another treatment option for Parkinson's disease, and anticholinergics are used to treat the tremor-predominate form of the disease.
What is the drug class for Parkinson's?
In addition to given dopamine directly (a drug called carbidopa-levodopa), Parkinson's disease patients may benefit from a class of drugs called dopamine agonists. These are drugs that aren't dopamine but have similar effects on the nervous system.
How long does dopamine last on levodopa?
In general, dopamine's potency will wear off after three years. When maximum doses of levodopa no longer control the symptoms, what else is there to turn to?
Does dyskinesia affect quality of life?
While it looks uncomfortable, however, most with dyskinesia prefer it to parkinsonism, and studies suggest that dyskinesia ultimately doesn't have much an impact on quality of life. Some researchers have suggested that dopamine may actually accelerate the disease course while patching over the symptoms.
Is amantadine good for Parkinson's?
This is in contrast to dopamine, in which some early studies have suggested disease worsening with the drug. Amantadine is another treatment option for Parkinson's disease, and anticholinergics are used to treat the tremor-pre dominate form of the disease.
Does levodopa help with Parkinson's?
Levodopa is the most effective medication there is to treat Parkinson's symptoms. That said, it's not without side effects. One of the fears of levodopa use is that it can cause excessive movement called dyskinesia. People with dyskinesia have a writhing movement that is out of their control.
Why is early diagnosis important for Parkinson's disease?
At the first visit, it is important to deal with the patient's misconceptions of the disease and its course, to offer sources of information and to suggest exercises. To make a correct ini ….
What is the best treatment for tremor dominant PD?
Anticholinergic drugs are appropriate for younger patients with tremor-dominant PD. Amantadine is mainly used for dyskinesia control. Catechol-O-methyl-transferase inhibitors and neurosurgery are not treatments of choice for early PD but can be very effective for more advanced disease.
How to help Parkinson's patients?
Many people with Parkinson’s don’t get enough vitamin D. Vitamin D supplementation may help reduce your risk. Stay active. Exercise improves muscle stiffness, mobility, and depression in Parkinson patients. It may also help reduce the risk of getting the disease.
How to reduce risk of Parkinson's?
There are steps you can take that may help reduce your risk, however: Drink caffeine. A study published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease. Trusted Source. found that caffeine can help restore early motor and nonmotor symptoms tied to Parkinson’s.
What is the role of dopamine in Parkinson's disease?
Dopamine is responsible for sending brain signals that control movement. Certain genes are associated with early onset Parkinson’s. According to the National Parkinson Foundation, studies show that 65 percent of people with Parkinson’s who experience onset before age 20 may do so because of a genetic mutation.
What is the effect of levodopa on Parkinson's?
People with early onset Parkinson’s may experience more negative side effects, such as involuntary movements. MAO-B inhibitors can help reduce the breakdown of dopamine in the brain. Catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitors can help extend Levodopa’s effects on the brain.
Why do people with Parkinson's have DBS?
This is because people with early onset Parkinson’s are less likely to have other diseases that may cause complications. DBS is a surgical procedure in which electrodes are placed in specific areas of your brain. These electrodes are connected to a generator. The generator is programmed to send electrical pulses to your brain.
What causes Parkinson's disease at any age?
It’s unclear exactly what causes Parkinson’s at any age. Genetic factors, environmental factors, or some combination of the two may play a role. This condition occurs when cells are lost in the part of the brain that produces dopamine. Dopamine is responsible for sending brain signals that control movement.
What is Parkinson's disease?
Understanding Parkinson’s disease. Parkinson’s is a progressive disease of the central nervous system. The condition is caused by a loss of cells in the area of the brain that produces dopamine. It’s usually diagnosed in people who are in their early 60s. People who are diagnosed before age 50 are said to have early onset Parkinson’s.
What is the treatment for Parkinson's disease?
The treatment of Parkinson’s disease is complex. Levodopa is the main drug used to reduce tremors and muscle stiffness. Whether it modifies the course of the disease or becomes less effective over time is debated, and it can have side effects, so patients and clinicians sometimes prefer to delay starting treatment.
When to start levodopa?
This evidence supports current guidance to start levodopa when symptoms begin to affect the quality of life and confirm that it has insufficient impact on disease progression to justify earlier treatment.
How many people in the delayed start group had levodopa before week 40?
Due to needing symptomatic relief, 87 people in the delayed-start group had levodopa before week 40.
How long did the Levodopa trial last?
This Dutch trial involved 445 participants with a recent diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease, enrolled over five years. About half took levodopa for 80 weeks , and half placebo for the first 40 weeks and levodopa for the last 40 weeks. There was no difference in symptoms between the groups at the end of the study.
How long does it take for UPDRS to change?
The estimated rate of change in progression of the disease, a secondary outcome, was similar in both groups between 4 and 44 weeks (estimated difference in mean UPDRS scores -0.02 points, 95% CI -0.07 to 0.03).
What is the best medication for motor symptoms?
If motor symptoms are not affecting the quality of life, the guideline recommends considering other drugs such as dopamine or monoamine oxidase inhibitors based on individual circumstances and preferences.
Why did the delayed start arm of the trial begin treatment earlier than planned?
Some participants (39%) in the delayed-start arm of the trial began treatment earlier than planned due to increasing symptoms, which might have reduced the difference between the two groups studied.
Diagnosis
- No specific test exists to diagnose Parkinson's disease. Your doctor trained in nervous system conditions (neurologist) will diagnose Parkinson's disease based on your medical history, a review of your signs and symptoms, and a neurological and physical examination. Your doctor …
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- If you've received a diagnosis of Parkinson's disease, you'll need to work closely with your doctor to find a treatment plan that offers you the greatest relief from symptoms with the fewest side effects. Certain lifestyle changes also may help make living with Parkinson's disease easier.
Alternative Medicine
- Supportive therapies can help ease some of the symptoms and complications of Parkinson's disease, such as pain, fatigue and depression. When performed in combination with your treatments, these therapies might improve your quality of life: 1. Massage.Massage therapy can reduce muscle tension and promote relaxation. This therapy, however, is rarely covered by healt…
Coping and Support
- Living with any chronic illness can be difficult, and it's normal to feel angry, depressed or discouraged at times. Parkinson's disease, in particular, can be profoundly frustrating, as walking, talking and even eating become more difficult and time-consuming. Depression is common in people with Parkinson's disease. But antidepressant medications can help ease the symptoms o…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- You're likely to first see your primary care doctor. However, you may then be referred to a doctor trained in nervous system disorders (neurologist). Because there's often a lot to discuss, it's a good idea to prepare for your appointment. Here's some information to help you get ready for your appointment and what to expect from your doctor.