
The IRS allows you to change your filing status for a tax return you’ve already filed if no more than three years have passed since the original tax filing deadline. For example, if you filed as a single taxpayer last year, but now realize you qualified for head of household, you need to make the change on an IRS Form 1040-X.
Full Answer
When should I change my tax withholding date?
When You Should Change Your Withholding Tax. In the U.S. tax system, individuals may either withhold paying their taxes until the April 15th deadline of the following calendar year or they may take the pay-as-you earn (PAYE) approach, in which estimated tax is paid out throughout the year before taxes are ultimately due.
When can the Commissioner change a taxpayer’s method of taxation?
The Commissioner may do so even when the taxpayer changed from an impermissible to a permissible method. The Service may change the taxpayer back to its former method in the taxable year the taxpayer changed without consent, or if the statute of limitations is closed for that year, in the earliest open year.
When should I file my tax return after changing my name?
You should wait to file your return until after the name change process has been completed to avoid any complications that could arise if the name on the return does not match the SSN on file with the SSA.
When can a taxpayer request a change to a previously controverted method?
Where the service has changed its position with respect to a particular method of accounting (i.e., it recognizes the permissibility of a method which it previously viewed as impermissible), a taxpayer may request that the examiner allow a change to the previously controverted method in the years under examination via formal or informal claim.
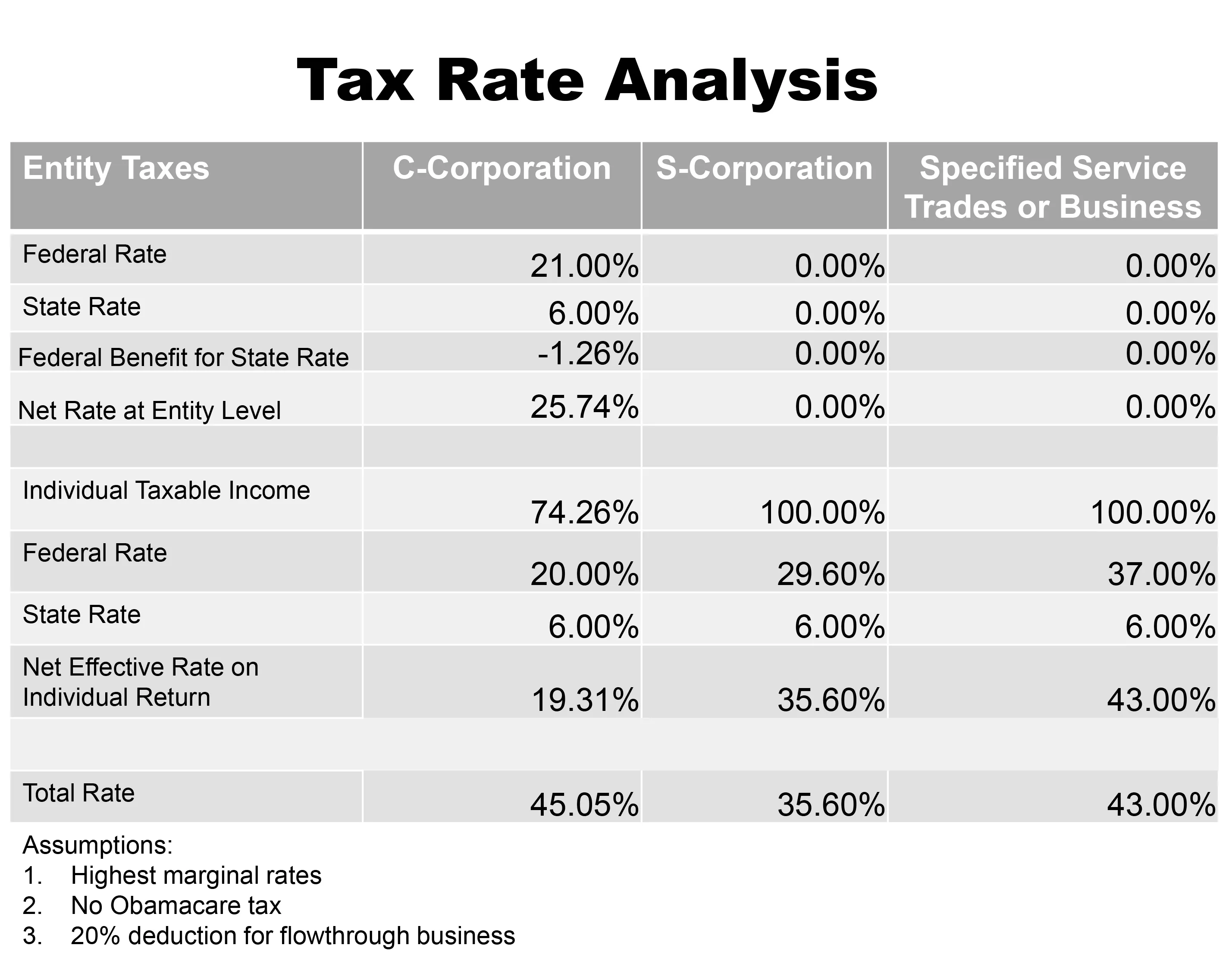
When can I change my tax deductions?
As soon as you realize a major life event is going to take place, you can make the adjustments, as long as the event is going to happen in the same tax year. If you have a major life event, you can change your withholdings at any time and aren't restricted by the usual withholding rules.
Can we change tax regime in between financial year?
Anytime in the financial year before the ITR filing, you cannot switch to another regime.
How often can you change accounting methods for tax purposes?
2015-13, a taxpayer may not request an automatic method change for the same item that was the subject of an accounting method change within the past five years. A taxpayer also generally cannot request a method change for the final year of its trade or business.
Will there be tax changes in 2021?
Higher standard deductions Standard deductions increased in 2021. For those whose filing status is single, married filing separately, and head of household, the amount increased by $150 from 2020. For joint filers qualifying widows or widowers, it increased by $300.
Can I change my tax regime in mid year?
Only salaried individuals can opt out of any of the regimes every year. Also, the taxpayer is free to choose a different regime than he/she chose for TDS deduction with the employer, i.e. the employee can use a different regime than the one he opted for before while filing an ITR.
Can we switch between old and new tax regime every year Quora?
Yes, you can switch between new and old tax regime in every financial year provided you do not have business income.
When Should form 3115 be filed?
File after the first day of the year of the change There are no specific deadlines for the form. However, the earlier you file your Form 3115, the more time the IRS has to solve any issues. Generally, you submit the form after the first day of the year of the change.
What is considered a change in accounting method?
A change in the characterization of an item may constitute a change in method of accounting if the change has the effect of shifting income from one period to another. For example, a change from treating an item as income to treating the item as a deposit is a change in method of accounting.
Can you switch from cash basis to accrual?
To convert to accrual, subtract cash payments that pertain to the last accounting period. By moving these cash payments to the previous period, you reduce the current period's beginning retained earnings. Cash receipts received during the current period might need to be subtracted.
What is the new tax law for 2022?
Single Filers: The maximum deduction is reduced at $68,000 in 2022 (up from $66,000 in 2021) and is completely eliminated at $78,000 or more (up from $76,000). Married Filing Jointly: The maximum deduction is reduced at $109,001 (up from $105,001 in 2021) and is completely eliminated at $129,000 (up from $125,000).
How can I reduce my taxable income 2021?
6 Ways to Lower Your Taxable IncomeSave for Retirement. Retirement savings are tax-deductible. ... Buy tax-exempt bonds. ... Utilize Flexible Spending Plans. ... Use Business Deductions. ... Give to Charity. ... Pay Your Property Tax Early. ... Defer Some Income Until Next Year. ... Need a Loan?
What are the new tax rates for 2021?
2021 federal income tax bracketsTax rateTaxable income bracketTax owed10%$0 to $19,90010% of taxable income12%$19,901 to $81,050$1,990 plus 12% of the amount over $19,90022%$81,051 to $172,750$9,328 plus 22% of the amount over $81,05024%$172,751 to $329,850$29,502 plus 24% of the amount over $172,7503 more rows
Your Monthly Child Tax Credit Payments May Increase or Decrease Your Refund
For the first time in history, the IRS sent the child tax credit as monthly payments to qualifying families. Depending on the amount of your monthly child tax credit payments received in 2021, you may receive a bigger tax refund, get a smaller refund than expected—or even owe additional taxes.
2021 Recovery Rebate Tax Credit for Third Stimulus Payments
For 2021, you may qualify for the Recovery Rebate Tax Credit. This is the case if you haven’t received the third economic impact payment (also known as a stimulus payment) or received only a partial payment (less than the full stimulus payment amount of $1,400),
What is the standard deduction for 2020?
Standard deduction. The standard deduction reduces your taxable income. For the 2020 tax year (that's the tax return you'll file in 2021), the standard deduction is $12,550 for single filers and married filers filing separately, $25,100 for married filers filing jointly and $18,800 for heads of household. (Go here for help deciding whether ...
How much can you deduct on student loans?
The student loan interest deduction lets you deduct up to $2,500 from your taxable income if you paid interest on student loans in 2020. If you fall into the 22% tax bracket, for example, the maximum student loan interest deduction would put $550 back in your pocket.
What is the EIC tax credit?
Earned Income Tax Credit. The Earned Income Tax Credit (EIC or EITC) is a refundable tax credit for low- and moderate-income workers. The amount depends on income and number of children. People without kids can qualify. For 2020, the earned income tax credit ranges from $538 to $6,660. The amount depends on income and number of children.
How much is the Earned Income Tax Credit 2020?
The amount depends on income and number of children. People without kids can qualify. For 2020, the earned income tax credit ranges from $538 to $6,660. The amount depends on income and number of children.
What are the tax changes related to?
Tax changes related to the government's ongoing response to the coronavirus. Tax changes related to annual adjustments in tax rules and thresholds that could affect what you can claim and how you file.
When is the tax deadline for 2021?
The tax-filing deadline this year is May 17, 2021 (it's usually on or around April 15). If you get an extension, you'll have until October 15, 2021, but remember that a tax extension only gets you more time to file, not more time to pay. Read more here.
Can you deduct student loan interest?
Student loan interest is deductible if your modified adjusted gross income, or MAGI, was less than $70,000 in the past tax year. The maximum deduction is $2,500. If your MAGI was between $70,000 and $85,000, you can deduct a reduced amount of interest that you paid.
Why is there a marriage penalty?
A marriage penalty exists when two individuals filing a joint return pay more tax than the sum of their individual tax liabilities calculated as if they were filing as single taxpayers. One reason this occurs is because the MFJ income tax brackets and standard deduction are not always equal to twice the single income tax bracket and standard deduction.
What is the only tax filing status for married filing separately?
Once you get married, the only tax filing statuses that can be used on your tax return are Married Filing Jointly (MFJ) or Married Filing Separately (MFS). Marriage tax benefits for filing taxes together are the following:
How does marriage affect taxes?
Marriage can affect taxes in many ways. While everyone’s situation is different, there are some tax benefits of marriage that help you pay less in taxes. Plus, you’ll have tax options as spouses that single filers don’t. Other tax changes after marriage are related to paperwork you should complete. Whether you’re looking to find out how marriage ...
How much gain can you exclude from income when selling a home?
If you are selling a home, the amount of gain that can be excluded from income doubles from $250,000 to $500,000. Be cautious, though: if only one of you owned the home before the marriage, the $500,000 exclusion applies only if you both lived in the home as your main home for at least two years.
Can you defer IRA distributions?
However, spouses have a special option, which may ultimately mean you can defer the distributions longer and if you are in a lower income tax bracket at the time of distribution, paying less tax on the distribution. When you name your spouse as the beneficiary of your IRA, your spouse can treat the inherited IRA as their own.
Can you claim child tax credit on MFS?
You can claim deductions for children and childcare expenses. Child tax credit and credit for other dependents are both permitted on an MFS tax return. Child and dependent care credit is generally not permitted on an MFS return. You can file for the Earned Income Tax Credit (if you qualify).
Can a spouse take an inherited IRA?
When you name your spouse as the beneficiary of your IRA, your spouse can treat the inherited IRA as their own. If it’s a Traditional IRA, your spouse may be able to put off taking distributions longer than a non-spouse. If it’s a Roth IRA, your spouse won’t need to make RMDs during their lifetime.
What is a 941 X?
Employers who have included amounts covered by the exception or the transition rule in individuals’ wages or compensation can take steps to correct taxable wages and employment taxes. Instructions for Form 941-X, Adjusted Employer's Quarterly Federal Tax Return or Claim for Refund.
What changes to fringe benefits affect a business' bottom line?
One of these changes is to qualified moving expenses.
When can you deduct transition rule?
To qualify for the transition rule, the payments or reimbursements must be for qualified expenses which would have been deductible by the employee if the employee had directly paid them before Jan. 1, 2018. The employee must not have deducted them in 2017.
Who pays for moving expenses in 2018?
An employer pays a third party in 2018 for qualified moving services provided to an employee prior to 2018. An employer reimburses an employee in 2018 for qualified moving expenses incurred prior to 2018.
Can you exclude moving expenses from your income?
Exception. Generally, members of the U.S. Armed Forces can still exclude qualified moving expense reimbursements from their income if: They are on active duty. They move pursuant to a military order and incident to a permanent change of station.
How many years of adjustment for IRC 481?
In general – Unless specifically noted otherwise, the IRC 481 (a) adjustment period is one taxable year (year of change) for a negative IRC 481 (a) adjustment and four taxable years (year of change and next three taxable years) for a positive IRC 481 (a) adjustment.
What is IRM 4.11.6.1?
(1) Renamed IRM 4.11.6.1, References for Changes in Accounting Methods, to Program Scope and Objectives to conform to the rules described in IRM 1.11.2.2.5, Address Management and Internal Controls. Added new subsections for Background, Authority, Roles and Responsibilities, and Related Resources and rearranged content accordingly.
What is clear reflection of income?
Clear Reflection of Income: If a taxpayer has not used a method of accounting regularly or if the method employed does not clearly reflect income, the Service will make the computation under a method that , in the opinion of the Commissioner, clearly reflects income.
What is the accounting method?
Neither the Code nor the regulations specifically define the term "method of accounting." In general, an accounting method is a set of rules used to determine when and how a taxpayer takes income and expenses into account for federal income tax purposes.
What is the purpose of IRM?
Purpose : This IRM serves as a reference guide for procedures on changes in accounting methods. It acts as an index, providing guidance for examination activity and refers the reader to supporting references. It is not intended to be an exclusive research tool.
When does a taxpayer take a net negative IRC 481?
When a taxpayer uses the voluntary method change procedures or a regulation provision , it generally takes a net negative IRC 481 (a) adjustment into account in the year of change. A taxpayer generally takes a net positive IRC 481 (a) adjustment into account over four years (year of change and next three taxable years).
What is a change in method of accounting?
A change in the characterization of an item may constitute a change in method of accounting if the change has the effect of shifting income from one period to another. For example, a change from treating an item as income to treating the item as a deposit is a change in method of accounting.
What is practice unit?
263, Regs. Sec. 1.263 (a)- 5, and other authorities relevant to costs incurred in connection with certain business transactions. It includes illustrative examples, flowcharts, questionnaires, documentation lists, and legal authority citations and sets forth the following three - step process for examining and determining the appropriate tax treatment of such costs:
Who must take costs into account for tax purposes?
IRS guidance and judicial precedent have generally established that the party "directly and proximately" receiving the services or benefits (e.g., loan proceeds) must take the costs into account for tax purposes, even if another party engaged the provider, indirectly benefited from the services, or paid the fees and expenses.
Is Y a legal entity?
Since Y directly benefited from the advisory services, Y is the proper legal entity to take the investment banker's fees into account as a deduction or as a capital expenditure, as appropriate. This is true even though X initially paid the investment banker on Y' s behalf.
Do tax rules follow book treatment?
The tax rules governing the treatment of these costs are complex, generally do not follow book treatment, and may require an extensive, facts - and - circumstances analysis to meet the subjective technical requirements and extensive documentation standards. Consequently, the area has historically generated significant uncertainty ...
What is a significant modification?
For nonrecourse debt instruments, a modification that releases, substitutes, adds, or otherwise alters a substantial amount of the collateral for, a guarantee on, or other form of credit enhancement for a nonrecourse debt instrument is a significant modification.
What is the general rule used to determine if a debt modification has occurred?
If a significant modification of a debt has occurred, an adviser should analyze the tax consequences to the borrower and the debt holder of the deemed exchange.
What is modification in a contract?
In general, a modification means any alteration, including any deletion or addition, in whole or in part, of a legal right or obligation of the issuer or a holder of a debt instrument, whether the alteration is evidenced by an express agreement (oral or written), conduct of the parties, or otherwise.
How is gain or loss measured?
Gain or loss to the holder/lender is measured by the difference between the issue price of the new debt and the tax basis of the old debt. The holder can have a different tax basis than the adjusted issue price. For instance, the holder could have bought the debt from the original lender at a discount.
What happens to debt restructuring in recession?
This has led to a substantial increase in debt restructuring activity.#N#Debt restructuring can trigger unforeseen tax consequences. A significant modification of a debt may result in the modification’s being treated as a deemed exchange.#N#The regulations provide five specific rules and one general rule for determining whether a modification is significant. If none of the specific rules apply in a particular situation, the general rule is used to make the determination.#N#If a significant modification of a debt has occurred, an adviser should analyze the tax consequences to the borrower and the debt holder of the deemed exchange. In determining the consequences, a key point is whether the debt is publicly traded.
What happens if a debt is modified?
If the debt is modified and the resulting instrument is not characterized as debt for tax purposes (and is instead treated as equity for tax purposes), the transaction would be treated as an exchange of the old debt instrument for equity of the issuer.
How long does it take to determine if a property is publicly traded?
In each case, the time period for determining whether the property is publicly traded is the 31-day period ending 15 days after the issue date of the debt instrument.
What is a common modification during financial hardships?
Common modifications during financial hardships During a period of financial hardships, a debtor may seek to restructure existing debt with more favorable terms . It is important to understand both the short-term and the long-term cash tax impact before finalizing the modification. Although not an exhaustive list, ...
What is an exercised conversion instrument?
Exercising conversion features A debt instrument may allow the issuer to convert the instrument into equity of the issuer. If the option is exercised, the issuer will realize COD income to the extent the adjusted issue price of the debt instrument exceeds the fair market value of the associated equity.
What happens if a significant modification occurs?
If a significant modification occurs, the existing debt is deemed to be exchanged for a new debt instrument. If, however, a significant modification does not occur, the existing debt is not deemed to be exchanged, thereby limiting any income tax consequences. A modification is a “significant modification” if the legal rights or obligations are ...
What happens if a non-traded debt instrument is significantly modified?
Thus, if a non-traded debt instrument is significantly modified, there is, generally, minimal COD income realized in the debt-for-debt exchange if there is no reduction in the principal amount and the stated interest is at least the AFR. If the debt is publicly traded in the 15 days before or after the modification, ...
When does a debtor realize a material amount of COD income?
Thus, if a debtor significantly modifies a publicly traded debt when the trading price is low ( e.g., during a business decline, an economic downturn, etc.), the debtor may realize a material amount of COD income.
What is a modification in a law?
A modification is a “significant modification” if the legal rights or obligations are altered and the degree to which they are altered are economically significant. The regulations provide bright-line tests for changes in the: Yield ( e.g., interest rate) Timing of payments. Obligor or security. Recourse nature of a debt instrument.
What is the AFR for 2020?
In an exchange of non-traded debt, the issue price of a new debt is generally equal to the stated principal amount if the stated interest is above the applicable federal rate (AFR). The long-term May 2020 AFRs is 1.15%. Thus, if a non-traded debt instrument is significantly modified, there is, generally, minimal COD income realized in ...
