Ledipasvir-sofosbuvir is approved for the treatment of HCV genotypes 1, 4, 5, or 6 starting at 3 years of age, with the pangenotypic regimens sofosbuvir-velpatasvir and glecaprevir-pibrentasvir approved starting at ages 6 and 12 years, respectively.
When should antiviral therapy be used to treat hepatitis C (HCV)?
Aug 20, 2015 · When to Start HCV Treatment: The Intersection of Guidelines and Real-World Practice. Treatment for hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is changing at a pace almost too rapid for the average physician to keep up with. Until recently, HCV treatment required weekly interferon injections plus oral ribavirin for up to a year and was effective in only ...
What are the possible treatment outcomes for hepatitis C (HCV)?
receive treatment with new DAA therapy.[5] This treatment priority ranking is no longer used in the AASLD-IDSA HCV Guidance; instead, the current guidance emphasizes that all persons, except for those with a short (i.e. less than 12 months) life expectancy, should receive treatment for chronic HCV infection.[5] The
Should we defer treatment for hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection?
Apr 19, 2021 · Ledipasvir-sofosbuvir is approved for the treatment of HCV genotypes 1, 4, 5, or 6 starting at 3 years of age, with the pangenotypic regimens sofosbuvir-velpatasvir and glecaprevir-pibrentasvir approved starting at ages 6 and 12 years, respectively. [ 5] Treatment Readiness Assessing Readiness Figure 1.
Why scale up HCV treatment in injectable drugs?
Oct 09, 2019 · Treatment for hepatitis C is now done with all-oral medications. These pills, called antiviral medications, are usually taken once per day. The provider treating your hepatitis C may recommend one or a combination of two to three medications to be taken for about 12 weeks.
When should I start treatment for Hep C?
Who is eligible for HCV treatment?
What is the first line of treatment in hepatitis?
What are the first steps that you would take in planning an HCV intervention?
Does Medi-Cal cover Hep C treatment?
What type of medication is used to cure the majority of cases of chronic HCV?
What is HCV medical term?
How long should I take entecavir?
What is the best treatment for hep C?
Why is there no vaccine for hep C?
How long does hep C take to damage liver?
What the Hepatitis C Guidelines Say
According to joint guidelines from the AASLD (American Association for the Study of Liver Disease) and the IDSA (Infectious Diseases Society of America), HCV treatment should be considered in all chronically infected patients except those with short life expectancies due to comorbid conditions.
The Intersection of HCV Treatment Guidelines and Real-World Practice
I practice medicine in the state of California where new MediCal (Medicaid) guidelines released July 1, 2015, are largely concordant with the AASLD/IDSA guidelines in listing the indications for treatment and coverage by MediCal.
A View from the Clinic
This morning in clinic, I saw a patient with chronic HCV infection who has a long history of injecting methamphetamines and who is currently injecting. He has been under my care for three years and is well engaged with our clinic, using our behavioral health services and, intermittently, substance-use counseling.
How old do you have to be to get HCV?
Many persons living with chronic HCV infection in the United States are over 50 years of age. With the availability of new, highly effective, safe, well-tolerated regimens, it is likely that more interest and experience will accumulate in treating persons with advanced age.
Is ribavirin contraindicated for HCV?
[ 5] Available data from animal studies indicate that ribavirin has significant teratogenic and embryocidal adverse effects. [ 7] Accordingly, the use of ribavirin is contraindicated in women who are pregnant, women who may become pregnant, or men whose female partners are pregnant or trying to conceive. [ 8, 9] Persons with chronic HCV who are of reproductive age and are to receive a regimen that includes ribavirin should be advised to use two forms of contraception during treatment and for at least 6 months following the end of treatment. [ 10] With DAA therapy, decompensated cirrhosis, renal failure, and recent or active substance use (e.g. drugs and alcohol) are not contraindications to treatment. [ 11, 12, 13] Indeed, multiple studies involving persons with past or current injection-drug use have shown very good adherence and excellent SVR rates with HCV DAA therapy. [ 14, 15, 16, 17]
Is DAA therapy covered by Medicare?
Although the high cost of these medications remains a concern, the cost of DAA therapy has significantly decreased over the past several years, and many states are now covering DAA therapy for all Medicaid and Medicare patients without restriction. Nevertheless, some state Medicaid plans continue to have fibrosis, sobriety, and prescriber restrictions for DAA therapy. [ 20] These restrictions are not in step with AASLD-IDSA HCV Guidance and represent a suboptimal and short-sighted approach to care. [ 21, 22, 23] If possible, DAA therapy should be initiated in all persons with chronic HCV and not deferred due to ongoing substance use or fibrosis requirements.
How long after hepatitis C treatment can you be cured?
Sustained virologic response (or SVR): If the hepatitis C virus is not detected in your bloodstream three months after treatment, you are considered cured. This is called a sustained virologic response and the data has indicated that you will stay free of the virus indefinitely.
How to treat hepatitis C?
The purpose of taking medications to treat hepatitis C is to: 1 Clear the virus from your bloodstream 2 Slow the advancement of inflammation and scarring of your liver 3 Lower your chances of developing cirrhosis or liver cancer
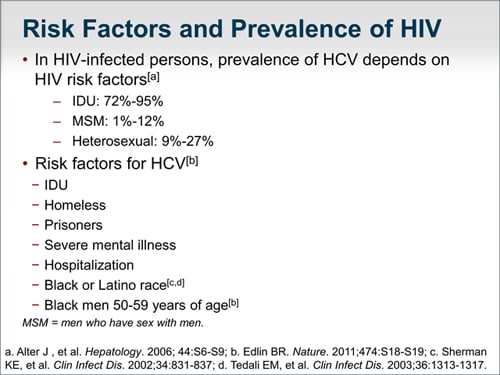
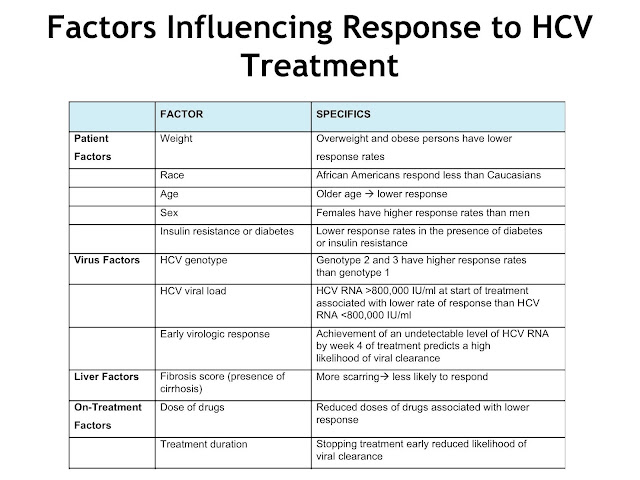
What are the factors that affect hepatitis C?
The most important factors that impact treatment results include: 1 Taking medications as prescribed and not missing doses 2 Your hepatitis C genotype 3 The presence of cirrhosis (severe scarring of the liver)
How long does it take to cure hepatitis C?
This treatment is for adults with chronic hepatitis C genotypes 1 through 6, and treatment duration can be as little as eight weeks. Results from early trials showed that 92 to 100 percent.
What is the first drug to treat hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C treatment today. In 2016, sofosbuvir/velpatasvir (Epclusa) was developed as the first drug therapy to treat all hepatitis C genotypes in tablet form. The side effects are considered low (headache and fatigue).
When was hepatitis C first discovered?
Those who will develop this disease may take some comfort in knowing that today’s hepatitis C treatments differ extremely from what was available when it was first discovered in 1989.
Is hepatitis C 100 percent curable?
Regardless of your genotype, there are now more treatment options than ever. More exciting is the possibility that eventually most genotypes of hepatitis C will be 100 percent curable. Last medically reviewed on March 9, 2018.
When was Sofosbuvir approved?
In July 2017 , sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir (Vosevi) was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat chronic hepatitis C of all genotypes. This fixed-dose combination pill prohibits the development of the specific protein NS5A.
What is the HBV primary care workgroup?
The HBV Primary Care Workgroup includes members in the United States from hepatology, infectious diseases, pharmacy, primary care, and public health. [ 37] The 2020 HBV Primary Care Workgroup Guidance was first released in early 2020 and is accessible on this web site (Hepatitis B Online), with the aim to have regular updated versions posted online. [ 37] The goal of this document is to provide simplified, up-to-date, and readily accessible HBV management guidance for primary care medical providers. Note, this guidance does not incorporate HBeAg status in the initial decision-making process, but persons positive for HBeAg are recommended to undergo monitoring of HBeAg for evidence of HBeAg seroconversion. The 2020 HBV Primary Care Workgroup Guidance recommends initiating HBV treatment in the following situations. [ 37]
What is the AASLD for HBV?
The AASLD defines immune-active chronic HBV as persistent elevation of ALT at least 2 times greater than the upper limit of normal (or evidence of significant histologic disease) plus elevated HBV DNA above 2,000 IU/mL if HBeAg negative or above 20,000 IU/mL if HBeAg positive. [ 4] If this occurs in HBeAg-negative patients after a period in the inactive carrier phase, this is called reactivation.For persons who do not have cirrhosis or any special condition that warrants HBV treatment, the main indication for therapy would be evidence of immune activity, as reflected by persistent (at least 6 months) elevations in both ALT and plasma HBV DNA levels. The evidence to support the benefit of antiviral treatment in reducing the risk of clinical events (cirrhosis and HCC-related mortality) is found primarily in patients who have met criteria for immune-active disease. [ 12] These include observational studies as well as randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared a control group (no treatment or placebo) with either interferon-based therapy or an oral nucleoside or nucleotide analogue agent. Seven RCTs involving 3,463 patients followed for a mean of 28 months demonstrated that antiviral therapy significantly reduced the risk of decompensated liver disease and cirrhosis. [ 12] Further, in 35 observational studies of 59,201 patients followed for a mean of 60 months, antiviral therapy versus control was associated with a decreased risk of HCC, cirrhosis and all-cause mortality. [ 12]
What is EASL in hepatitis?
European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL) The European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL) hepatitis B clinical practice guidelines is the major hepatitis B guidance for Europe and this document was primarily written by gastroenterology and hepatology specialists. [ 35] .
What are the factors that determine a person's HBV?
The decision to treat persons with chronic HBV therefore typically incorporates the following three factors: (1) cirrhosis status, (2) evidence of hepatic inflammation, as measured by alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels or liver biopsy, and (3) ongoing HBV replication as indicated by serum HBV DNA levels.
Is cirrhosis a histologic diagnosis?
Cirrhosis is thus a histologic diagnosis, and refers to an advanced stage of fibrosis that has extended beyond the portal triad to form bridges of scar that eventually results in the distortion of hepatic architecture. Liver biopsy can have limitations, including undersampling and misclassification. [ 13] .
What is considered a decompensated cirrhosis?
Persons with cirrhosis are considered to have decompensated cirrhosis if certain liver-related complications develop, including jaundice, ascites, esophageal variceal bleeding, hepatic encephalopathy, or impaired hepatic synthetic function (as reflected by elevated prothrombin time or total bilirubin). Decompensated cirrhosis is formally defined as a Child Pugh score of 7 or greater (class B or C). Because antiviral therapy has been shown to improve transplant-free survival in patients with decompensated cirrhosis, they should also be started on oral antiviral therapy regardless of ALT or HBV DNA levels. Patients with more advanced disease should also be referred for liver transplantation, if eligible.
What is a child Pugh score?
Decompensated cirrhosis is formally defined as a Child Pugh score of 7 or greater (class B or C). Because antiviral therapy has been shown to improve transplant-free survival in patients with decompensated cirrhosis, they should also be started on oral antiviral therapy regardless of ALT or HBV DNA levels.
