Individuals qualify for monoclonal antibody treatment if:
- they have tested positive for COVID-19, and
- it has been 10 days or less since symptoms first started, and
- they have other health conditions that put them at higher risk.
How often can you get monoclonal antibodies?
Jan 06, 2022 · Individuals qualify for monoclonal antibody treatment if: they have tested positive for COVID-19, and it has been 10 days or less since symptoms first started, and they have other health conditions that put them at higher risk.
How effective is the monoclonal treatment?
Dec 23, 2021 · If monoclonal antibody therapy is administered quickly enough after a known exposure to Covid-19, it is possible that the treatment could help the body ward off the virus and avoid infection. Once someone tests positive, monoclonal antibodies significantly reduce the likelihood of hospitalization due to severe Covid-19 symptoms.
What are the dangers of monoclonal antibodies?
Dec 21, 2021 · When do I need to get the treatment in order for it to work? The monoclonal antibody treatments are meant for mild to moderate COVID cases in adults and children over 12 to prevent the progression...
How safe is monoclonal antibodies?
Mar 01, 2022 · The therapy for COVID-19 works best when given early in the COVID-19 illness. This is only recommended for those considered high risk for severe illness. It is important to seek treatment early as you can only receive monoclonal antibodies if …
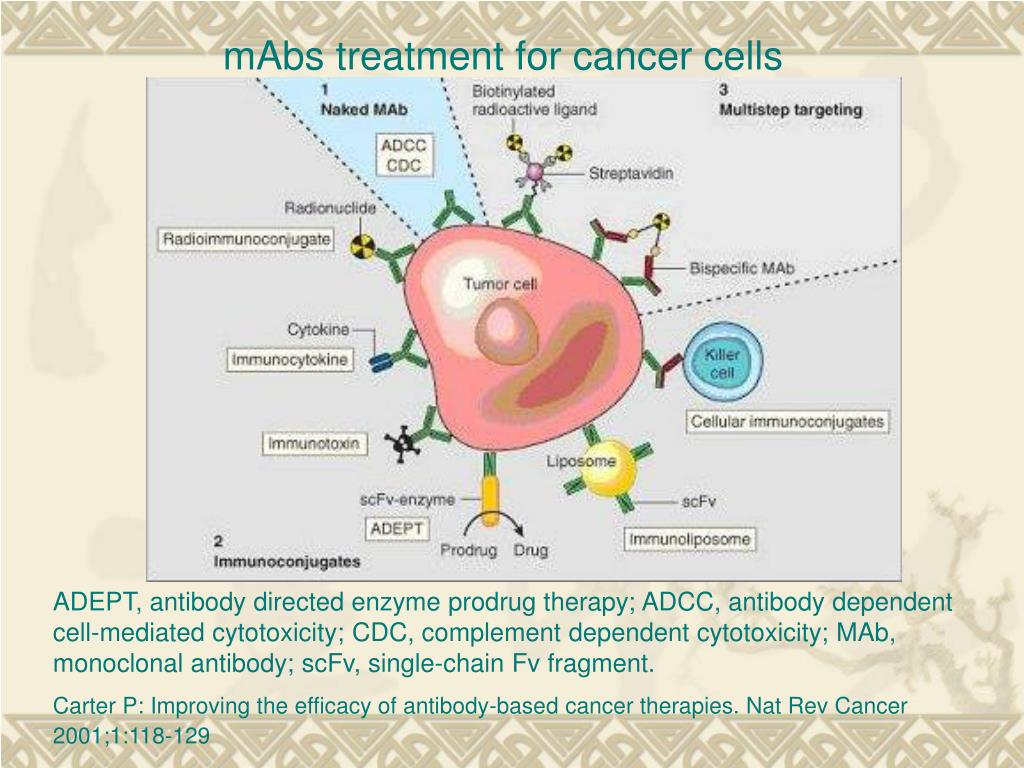
What is a monoclonal antibody for COVID-19?
Monoclonal antibodies are laboratory-produced molecules that act as substitute antibodies that can restore, enhance or mimic the immune system's attack on cells. Monoclonal antibodies for COVID-19 may block the virus that causes COVID-19 from attaching to human cells, making it more difficult for the virus to reproduce and cause harm. Monoclonal antibodies may also neutralize a virus.Mar 31, 2022
Can I get the COVID-19 vaccine if I was treated with monoclonal antibodies or convalescent plasma?
If you were treated for COVID-19 symptoms with monoclonal antibodies or convalescent plasma, you should wait 90 days before getting a COVID-19 vaccine.
How long does it take for antibodies to develop after exposure to COVID-19?
It can take days to weeks after an infection for your body to make antibodies.Feb 24, 2022
How long do COVID-19 antibodies last?
At this time, it is unknown for how long antibodies persist following infection and if the presence of antibodies confers protective immunity.Jan 31, 2022
Should you still get the COVID-19 vaccine if you were treated with monoclonal antibodies?
If you were treated for COVID-19 with monoclonal antibodies or convalescent plasma, there is no need to delay getting a COVID-19 vaccine.Feb 17, 2022
Do I need the COVID-19 vaccine if I still have antibodies?
Yes, the COVID-19 vaccines are recommended, even if you had COVID-19.Nov 23, 2021
Is it possible to develop immunity to COVID-19 after being exposed?
In addition, the hope is that people who've been exposed to COVID-19 also develop an immunity to it. When you have immunity, your body can recognize and fight off the virus. It's possible that people who've had COVID-19 can get sick again -- and maybe infect other people.Jan 21, 2022
What does a positive antibody test result mean for COVID-19?
A: A positive antibody test result could mean you previously had a SARS-CoV-2 infection or COVID-19. A positive antibody test could also mean the test is detecting antibodies in your blood in response to your COVID-19 vaccine.Feb 24, 2022
What is the COVID-19 antibody test?
COVID-19 antibody tests can help identify people who may have been infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus or have recovered from a COVID-19 infection.Feb 24, 2022
Do people produce COVID-19 antibodies after infection?
Most people who've recovered from COVID-19 do make antibodies against the virus.Jan 21, 2022
How long does immunity last after the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine?
Antibodies able to block the omicron coronavirus variant last four months after a third dose of Pfizer-BioNTech's vaccine, according to a study published Jan. 22 by bioRxiv.Jan 25, 2022
Should you get the COVID-19 vaccine if you already had COVID-19 and recovered?
If I already had COVID-19 and recovered, do I still need to get a COVID-19 vaccine? You should get a COVID-19 vaccine even if you already had COVID-19. Getting a COVID-19 vaccine after you recover from COVID-19 infection provides added protection to your immune system.
What does a monoclonal IV do?
If monoclonal antibody therapy is administered quickly enough after a known exposure to Covid-19, it is possible that the treatment could help the body ward off the virus and avoid infection. Once someone tests positive, monoclonal antibodies significantly reduce the likelihood of hospitalization due to severe Covid-19 symptoms.
How and when to get a monoclonal IV
If you are at high risk of severe Covid-19 progression and have been exposed to someone who has tested positive for Covid-19, or if you have developed Covid-19 symptoms, you should contact your doctor.
Let Drip Hydration Bring Monoclonal IV Treatment to Your Home
If you are in need of monoclonal antibody IV therapy, reach out to Drip Hydration today. Our medical experts can consult with you to create a personalized treatment plan. We offer both Covid-19 testing as well as monoclonal antibody treatment.
What are monoclonal antibodies?
Antibodies are naturally produced by your body to fight off infections. When your body is introduced to a new virus such as COVID-19, it does not have the antibodies to fight it off. That is where monoclonal antibodies come in. Monoclonal antibodies are created in a laboratory. They can target a particular virus or infection such as COVID-19.
How does monoclonal antibody therapy work?
Monoclonal antibodies are given by IV or a single-dose injection to people diagnosed with COVID-19. This therapy uses COVID-19 antibodies to help a person’s body fight off the infection. The injection is a lower dosage than the infusion therapy.
What monoclonal antibody therapies for COVID-19 are available?
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved emergency use authorization for five antibody infusion therapies:
Is monoclonal antibody therapy effective against the Omicron variant?
So far, it appears only one of the monoclonal antibody treatments – sotrovimab – is effective against the Omicron variant for outpatient treatment. Most of the other monoclonal antibody treatments have limited or no effectiveness against the Omicron variant .
Who should get monoclonal antibody therapy?
Monoclonal antibody treatment is now available for three specific uses:
Who is at high risk for severe illness from COVID-19?
While anybody can get very sick or even die from COVID-19, those most at risk include:
What COVID-19 treatment is available for people diagnosed with COVID-19?
If you are diagnosed with COVID-19 but aren’t sick enough to be hospitalized, you may think there isn’t much you can do. It is important to:
COVID-19 VEKLURYTM (remdesivir)
Following the recent statement from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel about therapies for the COVID-19 Omicron variant, CMS created HCPCS code J0248 for VEKLURY™ (remdesivir) antiviral medication when administered in an outpatient setting.
COVID-19 Monoclonal Antibody Products
The FDA authorized the following investigational monoclonal antibody product under EUA for pre-exposure prophylaxis of COVID-19:
Important Update about Viral Variants
On April 16, 2021, the FDA revoked the EUA for bamlanivimab, when administered alone , due to a sustained increase in COVID-19 viral variants in the U.S. that are resistant to the solo product.
Medicare Coverage for COVID-19 Monoclonal Antibody Products
During the COVID-19 public health emergency (PHE), Medicare will cover and pay for these infusions (when furnished consistent with their respective EUAs) the same way it covers and pays for COVID-19 vaccines.
Coding for the Administration of COVID-19 Monoclonal Antibody Products
CMS identified specific code (s) for each COVID-19 monoclonal antibody product and specific administration code (s) for Medicare payment:
Medicare Payment for Administering COVID-19 Monoclonal Antibody Products
To ensure immediate access during the COVID-19 PHE, Medicare covers and pays for these infusions and injections in accordance with Section 3713 of the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act (CARES Act) .
Billing for Administering COVID-19 Monoclonal Antibody Products
Health care providers can bill on a single claim for administering COVID-19 monoclonal antibody products, or submit claims on a roster bill.
What antibody is used to block the virus?
Monoclonal antibodies against COVID-19 attach to the virus to block it from entering human cells. The monoclonal antibody protein also “marks” the virus to be broken down by the immune system and cleared from the body.
What is the function of antibodies?
Antibodies are proteins that exist in our bodies as part of our immune system to recognize and defend against harmful viruses and bacteria. Monoclonal antibodies are made in a laboratory and designed to target a specific virus or bacteria.
Can monoclonal antibodies cause nausea?
Most people tolerate monoclonal antibody infusions very well. Some people may experience infusion-related side effects, such as nausea and dizziness, that are short-lived and go away on their own. As with any medication, there is the potential for mild or more severe allergic reactions, which are uncommon.