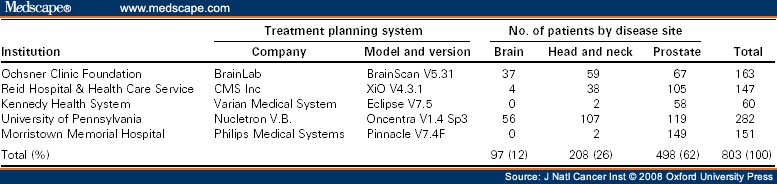
What is SSD in radiation therapy?
Machine Operations • SSD: distance to the patient’s skin from the source (or target, TSD) of the radiation • SSD technique: placing isocenter on the patient’s skin, SSD = 100 cm • SSD is source-surface or source- skin-distance
What does it mean to sign a radiation therapy document?
Signing the document means: Your team gave you information about your treatment options. You choose to have radiation therapy. You give permission for the health care professionals to deliver the treatment. You understand the treatment is not guaranteed to give the intended results. Simulating and planning treatment.
How long does radiation therapy take to work for cancer?
Typically, people have treatment sessions 5 times per week, Monday through Friday. This schedule usually continues for 3 to 9 weeks, depending on your personal treatment plan. This type of radiation therapy targets only the tumor. But it will affect some healthy tissue surrounding the tumor.
What does Sad mean in radiology?
SAD: distance from the source of the radiation to the axis of the beam or isocenter • SAD technique: the isocenter is at some depth within the patient on a modern linac, SSD will read less than 100 cm on the patient • Isocentric technique 2. Machine Operations
What is SSD technique in radiotherapy?
Purpose: Source to surface distance (SSD) plays a very important role in external beam radiotherapy treatment verification. In this study, a simple technique has been developed to verify the SSD automatically with lasers. The study also suggests a methodology for determining the respiratory signal with lasers.
What is SSD and sad in radiotherapy?
Modern photon beam radiotherapy is carried out with a variety of beam energies and field sizes under one of two set-up conventions: a constant source to surface distance (SSD) for all beams or an isocentric set-up with a constant source to axis distance (SAD).
How do you calculate equivalent square field size?
There are various formulae for equivalent square. The simplest is E=4A/P where A is the area of the field and P is the perimeter. This works OK for slightly irregular fields, especially ones defined with blocks.
How should you report a 3 D radiation therapy plan?
Use CPT code 77290 to report complex simulation for three (3) or more treatment areas, or any number of treatment areas if any of the following are involved: particle, rotation or arc therapy; complex blocking; custom shielding blocks; brachytherapy simulation; hyperthermia probe, verification; any use of contrast ...
What is sad setup?
SAD setup uses a constant distance between the source and isocenter. This allows for rotation around a fixed isocenter, and is therefore much more common for modern-era radiation therapy. SAD is a fixed value for any given machine (80 cm for Co-60, 100 cm for linac).
How does SSD increase PDD?
The percentage depth dose (PDD) increases with SSD due to the effects of inverse square law. NO dependance on the SAD or SSD. and hν constant TMR decreases with increasing z. constant TMR increases with increasing hν.
What is field size in radiotherapy?
field size is defined as “the projection, on a plane. perpendicular to the beam axis, of the distal end of the. collimator as seen from the front size.”
How do you calculate equivalent area?
Therefore, the equivalent area of base material is equal to the second materials area multiplied by the transformation factor (or moduli ratio which is the second material's modulus divided by the base material's modulus).
How do you calculate TMR?
The following equations are used for TMR calculations:TMR = dose at depth in tissue for field size (D_dx) / dose at depth of maximum dose for the same field size (D_dmax).Dose at depth = dose at isocenter * (TMR_depth in tissue / TMR_depth of isocenter) * inverse square correction.More items...
What is the standard measure of energy in Radiation Treatment?
The radiation dose absorbed by a person (that is, the amount of energy deposited in human tissue by radiation) is measured using the conventional unit rad or the SI unit gray (Gy).
How many times can you bill 77263?
77263 is only billable once per course of treatment.
What is the difference between 77385 and 77386?
CPT 77385 is often appropriate for breast or prostate cancer diagnoses because critical structures are not in the immediate area. CPT 77386 may be appropriate for the left breast, depending on the location of the tumor and what tissues may be impacted.
What is the best way to make sure radiation is treated the same?
To make sure that the radiation treats the same precise place in the body each treatment day, an immobilization device such as a mold or mask may be designed to help the patient lie in the same position every day. For example, a mask may be required for treatment of the head and neck region.
How long does radiation treatment last?
The treatment is given each day, Monday through Friday, for 1 to 8 weeks depending on the type of cancer and the reason for the treatment.
What is a radiation oncologist?
The radiation oncologist is a physician who has completed a residency in radiation oncology. The radiation oncologist is responsible for determining the role of radiation therapy in a patient’s care, planning the treatment, and evaluating the patient for the response to the treatment.
What is the treatment for a tumor?
The other method of delivering radiation treatment is called brachytherapy. In this method, a source of radiation in the shape of needles or seeds is implanted in the body. This treatment is often given before or after external beam irradiation as a way of increasing the radiation dose to only the tumor.
What is the role of radiation therapist?
The radiation therapists are responsible for the simulation procedure and the daily treatments.
How often do radiation oncologists meet with patients?
After all fields are treated and treatment is complete for the day, the patient may dress and go home. Once a week, the radiation oncologist meets with the patient to determine how well the patient is reacting to the treatment and to provide answers to questions from the patient or family.
How long do brachytherapy implants stay in place?
Some of the implants stay in place permanently, whereas others are removed after 2 or 3 days.
What to expect when getting radiation therapy?
What to Expect When Having Radiation Therapy. It is normal to feel worried or overwhelmed when you learn that you will need radiation therapy. However, learning more about this type of cancer treatment may help you feel more prepared and comfortable.
How long does radiation therapy last?
It is the most common radiation therapy treatment for cancer. Each session is quick, lasting about 15 minutes. Radiation does not hurt, sting, or burn when it enters the body.
What type of doctor is responsible for radiation therapy?
Radiation oncologist. This type of doctor specializes in giving radiation therapy to treat cancer. A radiation oncologist oversees radiation therapy treatments. They work closely with other team members to develop the treatment plan. Radiation oncology nurse.
What is simulation in radiation therapy?
Simulating and planning treatment. Your first radiation therapy session is a simulation. This means it is a practice run without giving radiation therapy. Your team will use imaging scans to identify the tumor location.
Why is it important to be in the same position for radiation?
It is important for your body to be in the same position for each treatment. Your radiation oncology team cares about your comfort. Talk with the team to find a comfortable position that you can be in every time you come in for radiation therapy.
How often should you check for radiation?
During your treatment, your radiation oncologist will check how well it is working. Typically, this will happen at least once a week. If needed, they may adjust your treatment plan.
What is informed consent for radiation?
Giving permission for radiation therapy. If you choose to receive radiation therapy, your health care team will ask you to sign an "informed consent" form. Signing the document means: Your team gave you information about your treatment options. You choose to have radiation therapy.
Abstract
To develop a novel approach to accurately verify patient set up in proton radiotherapy, especially for the verification of the nozzle – body surface air gap and source-to-skin distance (SSD), the consistency and accuracy of which is extremely important in proton treatment.
Background
Wilson theorized that fast protons could be used for treating deep-seated tumors while sparing adjacent normal tissues due to the unique physical properties in 1946 [ 1 ], and according to the PTCOG website ( https://www.ptcog.ch) as of December 2017, more than 170,000 patients worldwide have been treated with proton therapy.
Methods
A Mevion S250 (Mevion Medical Systems, Littleton, MA, USA) proton system has been clinically used to treat patients since 2015 in our department.
Results
The result comparison of the air gap and SSD for the phantom is presented as a box and whisker plot in Fig. 5.
Discussion
The values of the air gap and SSD calculated from the CT body surfaces with the developed methodology and calculation program agreed well with the corresponding TPS values within about 0.5 mm, validating the methodology with the digital round-off accuracy of about 0.5 mm.
Conclusions
We have developed an optical surface imaging based methodology to automatically derive the values of the air gap and SSD for proton treatments. The methodology was evaluated and validated using both phantom and clinical patient data.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
How much radiation should a pacemaker receive?
Ideally, pacemakers should not lie in the path of a treatment field and should only receive scattered radiation dose of less than 2 Gy . The cardiologist should be consulted to ascertain the required level of monitoring during and after the treatment.
What is the goal of external beam radiotherapy?
The goal of treatment planning of external beam radiotherapy is to produce a dose distribution within the patient that will destroy the tumour while sparing as much healthy tissue as possible. The planning role is usually carried out by radiographers, physicists, or technologists with expertise in producing either an optimum plan, or a selection of compromise plans for the clinician to approve. The planner must have sufficient clinical knowledge to understand where compromises may have to be made, either in sparing some of the target volume dose or in accepting higher than desirable doses to radiosensitive healthy tissue.
Why is it important to have the dose and dose per fraction available at the time of planning?
However, it is important to have the dose and dose per fraction available at the time of planning as the dose limits to critical structures will depend on the dose rate. Much of radiotherapy dose and fractionation is based largely on clinical results evaluated over decades.
What happens if you take a serial dose?
In a serial organ, if any part of the organ receives a dose above its threshold then there will be total loss of function, e.g. paralysis in the case of the spinal cord. In a parallel organ, part of the organ may be severely damaged but the rest continues to function.
What is the complexity of a treatment plan?
The complexity of a treatment plan is likely to increase, especially when an organ at risk (OAR), also referred to as a critical structure, lies adjacent to the planning target volume (PTV), and the prescribed dose greatly exceeds the tolerance dose of the OARs.
What is a wedge in a megavoltage treatment machine?
Megavoltage treatment machines have integral beam modifying techniques which are referred to as wedges (see Chapter 8). They alter the uniform dose distribution of the radiation beam in a simple and controlled manner to produce a dose gradient across the field.
How to reduce side effects of radiation?
You can reduce the risk of side effects by following these tips: Wash the treated skin gently every day with warm water. Washing helps remove bacteria from your skin, which can cause an infection.
How long after radiation treatment do you have side effects?
Some side effects occur weeks, months, or years after your last radiation treatment. This can happen even if you had no side effects during treatment. To catch these side effects early, dermatologists recommend the following: Watch your treated skin for signs of change.
How to avoid skin irritation from radiation?
To avoid irritating your skin, skip the washclothes, sponges, and loofahs. Instead, use your hands to gently splash water on the treated skin.
How to protect skin from radiation?
During radiation therapy: Be gentle and protect your skin. You want to start doing the following on the day you begin radiation therapy and continue until you’ve stopped radiation and your skin feels normal. Bathing and shaving: Skin can become very sensitive during radiation therapy.
What to do if you don't remember sunscreen?
Your care team will recommend skin care products that you can use, including sunscreen. If you don’t remember getting a recommendation for sunscreen, ask someone on your care team which sunscreen you should use. Seek shade when outdoors.
What to do if you have a rash after radiation?
Watch your treated skin for signs of change. After treatment, it’s important to pay close attention to the skin that was treated with radiation therapy. If you see redness, a rash, or any other change, call your oncologist or dermatologist.
Can radiation cause redness?
Some people develop redness, sores, or scabs during radiation therapy. If you need to care for a wound, be sure to follow the directions you’re given. Doing so can help your skin recover more quickly and avoid a serious reaction. Skip the antiperspirant and talcum powder.