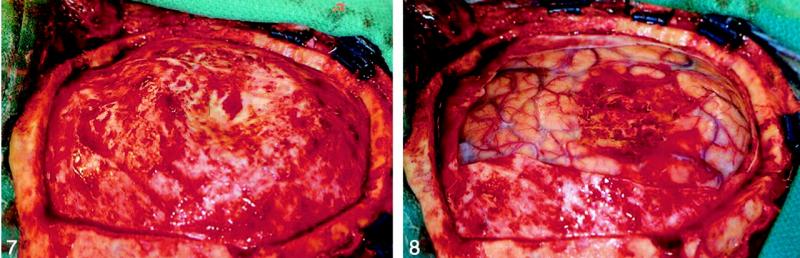
Treatment will be needed if the tumor begins to grow or cause symptoms. For most healthy adults, surgery is the next step. A neurosurgeon will perform a craniotomy to safely remove the brain tumor. However, surgery might not be the best option for meningiomas
Meningioma Brain Tumor
A condition in which a (usually) non-cancerous tumor develops from the membrane that surround the brain and spinal cord.
Full Answer
What is the best treatment for meningioma?
Your doctor may have you come in for a brain scan every three to six months for the first year. Since the vast majority of meningiomas are benign (noncancerous), they are most commonly treated with surgery. Total removal of a meningioma is preferred since it lessens the chances of the tumor returning.
Does radiation work on meningioma tumors?
After surgery, radiation is often recommended to delay the return of grade II and III meningiomas. Treatments may also include chemotherapy, or clinical trials. Clinical trials, with new chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or immunotherapy drugs, may also be available and can be a possible treatment option.
Why are Most meningiomas removed through surgery?
Surgery is the most common treatment for a meningioma. If a meningioma is benign and in a part of the brain where neurosurgeons can safely completely remove it, surgery is likely to be the only treatment needed. For some, total resection surgery is all that is needed for treatment, followed by periodic imaging to monitor any recurrence of a tumor.
What is a meningioma of the brain?
The major goal of radiation treatment is to kill meningioma tumor cells while minimizing damage to surrounding normal brain tissue. Radiation therapy for meningiomas involves externally beaming from a machine high energy X-rays at the tumor site (known as external beam radiation). There are variations of radiation therapy and the type chosen is based on factors used for …

Do all meningiomas need treatment?
Immediate treatment isn't necessary for everyone with a meningioma. A small, slow-growing meningioma that isn't causing signs or symptoms may not require treatment.Mar 4, 2022
When does a meningioma need surgery?
If a meningioma requires treatment, surgery is usually the preferred method, especially if the tumor is relatively large, fast-growing or causing symptoms. The goal of meningioma surgery is to remove as much of the tumor as safely possible, which can vary depending on the tumor's size and location.
At what size should a meningioma be removed?
Ideally, surgical removal of meningioma entails removal of a one-centimeter margin all the way around the tumor.Oct 11, 2018
What happens if meningioma is left untreated?
If you leave a meningioma untreated, it can grow as large as a grapefruit can cause persistent headaches, nausea, loss of neurological function, weakness and/or numbness and tingling on one side of the body, seizures, hearing or vision loss, balance problems, and muscle weakness.
How long is hospital stay after meningioma surgery?
The hospital stay after surgery for a meningioma can range from a few days to a couple of weeks, depending on how large the tumor is, where it's located, and the type of procedure used to remove it.
What is the prognosis for meningioma?
The 10-year survival rate for malignant meningioma is almost 61%. The person's age and whether the tumor is cancerous affect survival rates for meningioma, along with other factors. The 5-year survival rate for malignant meningioma is almost 78% for children ages 0 to 14 and more than 83% in people ages 15 to 39.
Can an MRI tell if a meningioma is benign?
Highlights. MRI has a promising role in predicting meningioma grade which can directly impact future management protocols. Hyperostosis of the adjacent skull was the only significant CT feature in benign meningiomas. MRI has an 79% specificity and 92% negative predictive value in detecting meningioma brain invasion.
Should I worry about a meningioma?
Often, meningiomas cause no symptoms and require no immediate treatment. But the growth of benign meningiomas can cause serious problems. In some cases, such growth can be fatal. Meningiomas are the most common type of tumor that originates in the central nervous system.Dec 15, 2021
How safe is meningioma surgery?
Although surgery for meningiomas is generally safe, there are some risks whenever performing a craniotomy. These include: Infection 1-2% Seizures which can require taking medication.
How often should a meningioma be checked?
With active surveillance, you will need to be examined and have an MRI or CT scan of the head periodically. This is usually done three to six months after the first brain scan, then every 6 to 12 months depending on the concern for regrowth, assuming that the meningioma does not grow or cause symptoms during this time.Nov 5, 2020
What does a meningioma headache feel like?
They are often described as dull, "pressure-type" headaches, though some patients also experience sharp or "stabbing" pain. They can be localized to a specific area or generalized. They can be made worse with coughing, sneezing or straining.May 20, 2020
How can I shrink my meningioma naturally?
Several observational and experimental studies found that taking certain foods and supplements including Vitamin D-rich foods, fish, Curcumin, fresh fruits (avocado and apricot) and vegetables, and Vitamin E supplements as part of the diet may help in reducing the risk of meningioma or help with reducing symptoms such ...Jan 21, 2021
What are the different grades of meningioma?
What are the grades of meningiomas? 1 Grade I meningiomas are low grade tumors and are the most common. This means the tumor cells grow slowly. 2 Grade II atypical meningiomas are mid-grade tumors. This means the tumors have a higher chance of coming back after being removed. The subtypes include choroid and clear cell meningioma. 3 Grade III anaplastic meningiomas are malignant (cancerous). This means they are fast-growing tumors. The subtypes include papillary and rhabdoid meningioma.
What is a grade 1 meningioma?
Grade I meningiomas are low grade tumors and are the most common. This means the tumor cells grow slowly. Grade II atypical meningiomas are mid-grade tumors. This means the tumors have a higher chance of coming back after being removed.
What is the most common type of meningioma?
Meningiomas are more common in females, but grades II and III occur more often in males. They are most common in black people, followed by white people, and then Asian-Pacific Islanders. The meningiomas tend to occur in people around 60 years old, with the risk increasing with age.
What is the survival rate for atypical meningioma?
The relative 5-year survival rate for atypical and anaplastic meningioma is 63.8% but know that many factors can affect prognosis. This includes the tumor grade and type, traits of the cancer, the person’s age and health when diagnosed, and how they respond to treatment.
What is the goal of surgery?
The goal of surgery is to obtain tissue to determine the tumor type and to remove as much tumor as possible without causing more symptoms for the person. Most people with atypical and anaplastic meningiomas receive further treatments.
Where do meningiomas form?
Meningiomas form along the dura mater, the ou termost layer of tissue that covers and protects the brain and spinal cord. The dura mater is one of three layers that form the meninges. Meningiomas arise from meningeal cells. As a result, they tend to occur along the surface of the brain.
Is chemotherapy a clinical trial?
Clinical trials, with new chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or immunotherapy drugs, may also be available and can be a possible treatment option. The role of chemotherapy or clinical trials after radiation therapy is unclear.
How to treat meningioma?
Try to stay healthy during your treatment for a meningioma by taking care of yourself. Eat a diet rich in fruits and vegetables, and get moderate exercise daily if your doctor allows it. Get enough sleep so that you wake feeling rested. Reduce stress in your life by focusing on what's important to you.
What are the factors that determine the treatment for meningioma?
The treatment you receive for a meningioma depends on many factors, including: The size and location of your meningioma. The rate of growth or aggressiveness of the tumor. Your age and overall health. Your goals for treatment.
Why is meningioma so difficult to diagnose?
A meningioma can be difficult to diagnose because the tumor is often slow growing. Symptoms of a meningioma may also be subtle and mistaken for other health conditions or written off as normal signs of aging.
How to diagnose meningioma?
To diagnose a meningioma, a neurologist will conduct a thorough neurological exam followed by an imaging test with contrast dye, such as: Computerized tomography (CT) scan. CT scans take X-rays that create cross-sectional images of a full picture of your brain. Sometimes an iodine-based dye is used to augment the picture.
How does radiation therapy work?
Radiation therapy uses a large machine to aim high-powered energy beams at the tumor cells. Advances in radiation therapy increase the dose of radiation to the meningioma while reducing radiation to healthy tissue. Radiation therapy options for meningiomas include:
Can a surgeon remove a meningioma?
Surgeons work to remove the meningioma completely. But because a meningioma may occur near many delicate structures in the brain or spinal cord, it isn't always possible to remove the entire tumor. In those cases, surgeons remove as much of the meningioma as possible.
Can you get radiation for a malignant tumor?
If the tumor is atypical or malignant, you'll likely need radiation . Surgery may pose risks including infection and bleeding. The specific risks of your surgery will depend on where your meningioma is located. For instance, surgery to remove a meningioma that occurs around the optic nerve can lead to vision loss.
What is the treatment for meningioma?
Radiation Therapy. The major goal of radiation treatment is to kill meningioma tumor cells while minimizing damage to surrounding normal brain tissue. Radiation therapy for meningiomas involves externally beaming from a machine high energy X-rays at the tumor site (known as external beam radiation). There are variations of radiation therapy and the ...
What is the best treatment for a tumor?
Surgery. In most cases, if a tumor is causing symptoms, surgery would be the first treatment choice, barring other complications. Complete removal of the tumor is the goal, as this allows the best chance for the least likelihood of tumor recurrence, increased patient survival time, and the potential easing or complete disappearance of symptoms.
Why is chemo called a systemic treatment?
Chemotherapy is called a systemic treatment because the drug enters the bloodstream, travels through the body, and can kill cancer cells throughout the body. Due to what is commonly called the “blood barrier” it can be difficult for medications to reach affected areas of the brain.
When is radiation therapy used?
Radiation therapy is also used as a treatment option when tumors are inoperable, in locations where the risk of surgery is considered too high, or the patient is not a good surgical risk. Two variations of external beam radiation often employed in these cases are stereotactic radiosurgery and stereotactic radiotherapy.
What is stereotactic radiotherapy?
Stereotactic radiotherapy is similar to stereotactic radiosurgery, except that instead of one high dose of radiation, the dose is broken down into smaller amounts of radiation and administered over several sessions to achieve the desired total dose of radiation (also known as fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy).
Can you have more than one treatment for a tumor?
In some cases, more than one treatment option may be used, not only when the tumor is first treated, but also over time should the tumor progress and/or recur. In deciding the particular course of treatment for a patient, the benefits of each treatment option or combination of treatment options are weighed against the associated risks.
Is stereotactic radiosurgery surgery?
Stereotactic radiosurgery is not actually surgery, but rather a delivery of a very intense dose of radiation, much higher than the daily dose received with conventional radiation. It is given in a single dose that is delivered by either a Gamma Knife machine or a linear accelerator.
What is the treatment for meningioma?
At University of Utah Health, we typically use stereotactic radiation therapy , which can stop the growth of your meningioma.
Why do meningiomas need surgery?
The majority of meningiomas are removed through surgery because of the patient’s significant symptoms and tumor size. Doctors often recommend surgery when tumors are too large to be treated with radiation.
How to tell if you have a meningioma?
When meningiomas are large enough to compress your brain tissue or nerves, the most common symptoms are: 1 headaches, 2 weakness in an arm or leg, and 3 vision changes.
What is a meningioma?
A meningioma is a common skull base tumor that is a mass of abnormal cells growing in the thin tissue known as the meninges covering the brain and spinal cord. As the tumor grows inward, it may press on your brain. If it grows outward, the skull can thicken. You may have more than one meningioma, ...
How to monitor meningioma growth?
For some patients, the best course of treatment may be to monitor the meningioma’s growth over time through imaging tests. If your symptoms change, you should let your doctor know immediately.
Where is meningioma located?
Suprasellar meningioma — This is located near the pituitary gland and optic nerves. It commonly presents with visual loss.
What are the symptoms of meningiomas?
When meningiomas are large enough to compress your brain tissue or nerves, the most common symptoms are: headaches, weakness in an arm or leg, and. vision changes. Other symptoms include : personality changes, seizures, nausea,
How to tell if you have a meningioma?
The symptoms of a meningioma depend on its location. Generally speaking, a meningioma may cause: 1 headaches that are more intense in the mornings 2 changes in vision 3 loss of hearing 4 loss of smell 5 confusion 6 seizures
Where does meningioma start?
A meningioma is a tumor that starts in the space between the skull and brain or the spine and spinal cord. It is the most common type of primary brain tumor. When brain cancer is primary, this means that the tumor originated in the brain. The outlook for a person with a meningioma depends on many factors, including the size of the tumor.
What is the most common grade of meningioma?
the person’s age. the amount of tumor that remains after surgery. A doctor grades meningiomas 1–3. Grade 1 is the most common type, and it grows slowly. People with grade 2 meningiomas have a higher chance of the tumor returning after surgery to remove the initial tumor.
How long do meningiomas live?
They are highest for people with grade 1 tumors.#N#For people with grade 2 or 3 meningiomas, experts use the relative 5-year survival rate. This describes the percentage of people who live for at least 5 years after receiving their meningioma diagnosis. The 5-year survival rate for grade 2 and 3 meningiomas is almost 64%.#N#It is worth keeping in mind that doctors base all survival rates on averages of past data, and they may not consider recent advances in detection and treatment.
What is a grade 1 meningioma?
Summary. A meningioma is a type of tumor that develops in the meninges — three membrane layers surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Grade 1 meningiomas may not require treatment. Instead, the doctor may monitor the tumor and the person’s overall health once or twice a year.
What are the three membranes of the brain?
The meninges are three membrane layers that surround the brain and spinal cord. The layers are called dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. Meningiomas are the most common type of primary brain tumor. They grow on the dura mater, which is the outermost layer of the meninges.
What is the outermost layer of the meninges?
They grow on the dura mater, which is the outermost layer of the meninges. The cells that line the dura mater are called meningeal cells. When these cells mutate, their genetic code changes, and this can affect how the cells function. As a result, they can transform into tumor cells.
How to diagnose brain meningioma?
To diagnose a brain meningioma, you’ll begin by meeting with your doctor for a physical exam. You’ll talk about your symptoms, and your doctor may test your motor skills and senses. Your doctor will likely order imaging tests, such as an MRI or a CT scan.
What are the symptoms of meningioma?
If you have a brain meningioma, you may experience: 1 Balance problems 2 Muscle jerking 3 Difficulty speaking 4 Changes in your ability to smell 5 Weakness or numbness on one side of your body
What happens if a meningioma grows outward?
If the meningioma grows inward, it may put pressure on brain tissue, nerves and blood vessels. If it grows outward, it can press against the skull. Meningiomas may be noncancerous (benign) or, rarely, cancerous (malignant).
What is a meningioma tumor?
Dr. Couldwell: A meningioma is usually a benign tumor that occurs from the covering of the brain. Now, the covering of the brain covers the entire brain, and it's attached to the inside of the skull. It's called the meninges. It's sort of like a thick piece of paper in thickness, and it's attached everywhere on the skull and inside ...
What is the base of the skull?
The skull base is a complicated area of your head. It's where all the nerves and the arteries . . . so all the nerves that serve things like vision, moving your eyes, facial sensation, hearing, swallowing, etc., they all traverse the base of the skull.
Can meningioma recur after surgery?
You can have recurrence after surgery, and you can have recurrence after radiation.
Can MRI detect meningioma?
And the imaging is so good nowadays. If they get an MRI, that will detect usually a significant meningioma.
What is the best treatment for meningioma?
The standard treatment for brain tumors is surgery, radiation, chemotherapy and/or targeted therapies. Your treatment team will recommend the best treatment for meningioma depending on the location of the tumor, whether it has spread, its grade, and your general health and fitness. At UTHealth Neurosciences you can expect the latest advancements in diagnosis and treatment, as well as access to international multicenter clinical trials.
What are the symptoms of meningioma?
Symptoms may include headaches, nausea and/or vomiting, seizures, double vision, drowsiness or lethargy, mood or personality changes, loss of motor function, weakness or numbness, speech difficulty, and/or memory loss.
What is a grade 2 meningioma?
Grade 2 atypical meningiomas are mid-grade tumors, which have a higher chance of recurrence after they are removed. They include choroid and clear-cell meningioma. Grade 3 anaplastic meningiomas are fast-growing malignant tumors. They include papillary and rhabdoid meningiomas.
How do you know if you have a meningioma?
Symptoms of meningioma appear depending on the location of the tumor. Some symptoms, such as headaches or a change in cognition, may appear slowly and worsen over time. Other signs, such as a seizure or loss of motor function, may appear suddenly. As a meningioma begins to grow in an area of the brain or spinal cord, pressure increases on the tissue. Symptoms may include headaches, nausea and/or vomiting, seizures, double vision, drowsiness or lethargy, mood or personality changes, loss of motor function, weakness or numbness, speech difficulty, and/or memory loss.
Where do meningiomas develop?
Meningiomas develop in the brain or spinal cord from the surrounding membranes called meninges. These membranes serve as a protective barrier between the brain and skull, as well as between the spine and spinal cord. Most meningiomas are benign, but they can cause significant health problems if they grow large enough to put pressure on ...
What is the phone number for UTHealth Neurosciences?
To ask us a question, schedule an appointment, or learn more about us, please call (713) 486-8000, or click below to send us a message.
Can meningioma be caused by radiation?
Causes of Meningioma. The cause of meningioma is not known, although research has shown that mening iomas are more common in women. However, higher-grade tumors ( Grades 3 and 4) occur more often in men. Exposure to radiation, especially in childhood, is the only known environmental risk factor for developing meningioma.

Diagnosis
Treatment
- The treatment you receive for a meningioma depends on many factors, including: 1. The size and location of the meningioma 2. The rate of growth or aggressiveness of the tumor 3. Your age and overall health 4. Your goals for treatment
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Alternative Medicine
- Alternative medicine treatments aren't typically effective in the treatment of meningioma, but some may help provide relief from treatment side effects or help you cope with the stress of having a meningioma. Alternative medicine therapies that may be helpful include: 1. Acupuncture 2. Hypnosis 3. Massage 4. Meditation 5. Music therapy 6. Relaxation exercises Discuss options …
Coping and Support
- Being diagnosed with a meningioma can be overwhelming. As you come to terms with your diagnosis, your life can be turned upside down with visits to doctors and surgeons as you prepare for your treatment. To help you cope, try to: 1. Learn everything you can about meningiomas. Ask your health care team where you can get more information about meningiomas and your treatm…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- You're likely to start by seeing your primary provider. If your provider suspects that you may have a brain tumor, such as a meningioma, you may be referred to specialists who treat brain disorders (neurologists and neurosurgeons). Here's some information to help you prepare for your appointment.