Explore
Aug 14, 2021 · Shock therapy, known medically as electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), is a treatment for major depressive disorder (MDD), bipolar disorder, and other psychiatric conditions. ECT is generally offered when other treatments are ineffective or there is a need for rapid response.
What is shock therapy used to treat?
The cornerstone of the treatment of hypovolemic shock is the administration of adequate amounts of the right kinds of intravenous fluids. Focus is on classification of shock (reversible shock, irreversible or fatal shock, hypovolemia), the heart in shock, respiration, drugs (steroids, vasoactive drugs), and disseminated intravascular coagulation. If edema is a problem, …
What is the first aid treatment for shock?
Apr 29, 2021 · Shock: First aid. Shock is a critical condition brought on by the sudden drop in blood flow through the body. Shock may result from trauma, heatstroke, blood loss, an allergic reaction, severe infection, poisoning, severe burns or other causes. When a person is in shock, his or her organs aren't getting enough blood or oxygen.
What should I do if a patient is in shock?
May 11, 2022 · Potassium peroxymonosulfate is commonly known as non-chlorine shock, and as the name suggests, is a chemical that can shock your pool without any chlorine. Non-chlorine shock can be used at any time of the day, and you can swim in your pool 15 minutes after using it. However, because it is chlorine-free, it won’t prevent algae growth.
What is the prognosis of shock shock treatment for depression?
1. Lay the Person Down, if Possible. Elevate the person's feet about 12 inches unless head, neck, or back is injured or you suspect broken hip or leg bones. Do not raise the person's head. Turn ...

When do you consider ECT electroconvulsive therapy?
Who is a good candidate for ECT?
What is shock therapy and is it effective?
When would you use shock therapy?
- Severe depression, particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to eat.
- Treatment-resistant depression, a severe depression that doesn't improve with medications or other treatments.
Can ECT change your personality?
Is ECT worth the risk?
What was shock therapy was this the best way?
What does shock therapy do for muscles?
Why do we give shock to patients?
Can ECT damage your brain?
What does ECT do to the brain?
Shock Therapy: Process, Preparation, Outcomes and more
Krystina is a Technical Writer with a background in healthcare. She has spent the last 10 years working for an internationally recognized medical facility where she found her passion for making complicated topics easier to understand.
The Electroconvulsive Therapy Process
An ECT treatment regimen will typically include sessions two to three days a week for a total of six to 12 treatments. The schedule works out to about one month of treatment, although the course may continue for longer.
How to Prepare for Your Treatment
ECT sessions generally do not require much preparation, though you will need to go over the specifics with your doctor. Your doctor may give you orders to follow based on other health conditions you have or medications you take.
Potential Outcomes of Shock Therapy
Most people who undergo ECT will see a noticeable change in their symptoms. Some people will notice an immediate improvement after one session. However, it is more common to not see or feel a significant difference in symptoms for several sessions.
Summary
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can be used to treat major depressive disorde r, bipolar disorder, and other psychiatric conditions. It is often considered when other treatments have not helped.
A Word From Verywell
If you are wondering if shock therapy might be a treatment option for you, discuss it with your psychiatrist. While ECT can provide lasting relief from the symptoms of MDD, bipolar disorder, and similar conditions, it's not the right choice for everyone.
Frequently Asked Questions
Even though ECT has been around for nearly 90 years, scientists still are not quite sure why or how it benefits some people with depression.
What is shock therapy?
"Shock therapy" was so-called, as an electric shock is used to induce a controlled seizure intended as a treatment , primarily for mood disorders, although other conditions may be treated as well. Shock therapy is now known as electroconvulsive therapy or ECT.
Does shock help with depression?
Shock treatment for depression often produces a dramatic improvement in symptoms, especially in elderly individuals, sometimes during the first week of treatment. While it is estimated many of these patients will experience a future return of depression symptoms, the prognosis for each episode of depression is good. Mania also often responds well to shock treatment. The picture is not as bright for schizophrenia, which is more difficult to treat and is characterized by frequent relapses.
What is the name of the drug that is used to treat seizures?
A paralyzing agent called succinylcholine is then administered to prevent the seizure from spreading to your body. The electrodes are then applied to your head with conducting jelly and a brief shock (less than 2 seconds) is administered.
Is electroconvulsive therapy effective?
Electroconvulsive therapy has also shown effectiveness in treating other disorders such as neuroleptic malignant syndrome (a rare, severe, adverse reaction to antipsychotic medication). Shock treatment for depression and other disorders is indicated when the patient needs rapid improvement because the patient is:
Can ECT cause memory loss?
You will likely experience short-term memory loss around the time of the procedure. With multiple treatments, this may increase. Adverse cognitive effects tend to be the most concerning factors around ECT and tend to affect the frequency and duration of treatments and whether ECT is offered at all. Your vital signs will be monitored closely ...
What to do when someone is in shock?
If you suspect a person is in shock, call 911 or your local emergency number. Then immediately take the following steps: Lay the person down and elevate the legs and feet slightly, unless you think this may cause pain or further injury. Keep the person still and don't move him or her unless necessary.
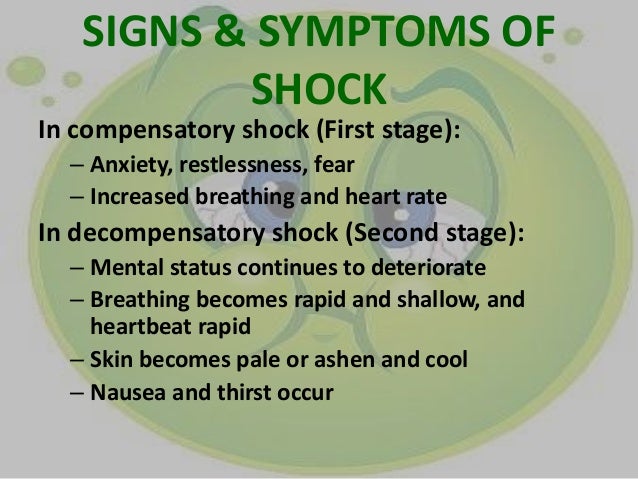
What happens when you are in shock?
When a person is in shock, his or her organs aren't getting enough blood or oxygen. If untreated, this can lead to permanent organ damage or even death. Signs and symptoms of shock vary depending on circumstances and may include: Cool, clammy skin. Pale or ashen skin.
What is shock in medical terms?
Shock is a critical condition brought on by the sudden drop in blood flow through the body. Shock may result from trauma, heatstroke, blood loss, an allergic reaction, severe infection, poisoning, severe burns or other causes. When a person is in shock, his or her organs aren't getting enough blood or oxygen.
How do you know if you're in shock?
Signs and symptoms of shock vary depending on circumstances and may include: Cool, clammy skin. Pale or ashen skin. Bluish tinge to lips or fingernails (or gray in the case of dark complexions) Rapid pulse. Rapid breathing. Nausea or vomiting.
How to do CPR on a person who is not breathing?
Lay the person down and elevate the legs and feet slightly , unless you think this may cause pain or further injury. Keep the person still and don't move him or her unless necessary. Begin CPR if the person shows no signs of life, such as not breathing, coughing or moving.
How to treat a broken hip?
1. Lay the Person Down, if Possible. Elevate the person's feet about 12 inches unless head, neck, or back is injured or you suspect broken hip or leg bones. Do not raise the person's head. Turn the person on side if they are vomiting or bleeding from the mouth. 2.
How to call 911 for a broken hip?
Call 911. 1. Lay the Person Down, if Possible. Elevate the person's feet about 12 inches unless head, neck, or back is injured or you suspect broken hip or leg bones. Do not raise the person's head. Turn the person on side if they are vomiting or bleeding from the mouth. 2.
How to protect yourself from a syringe?
4. Keep Person Warm and Comfortable 1 Loosen restrictive clothing. 2 Cover with a coat or blanket. 3 Keep the person still. Do not move the person unless there is danger. 4 Reassure the person. 5 Do not give anything to eat or drink.
How to help a child who is not breathing?
Do not raise the person's head. Turn the person on side if they are vomiting or bleeding from the mouth. 2. Begin CPR, if Necessary. If the person is not breathing or breathing seems dangerously weak: For a child, start CPR for children. For an adult, start adult CPR.
How to treat a swollen ear?
1. Lay the Person Down, if Possible 1 Elevate the person's feet about 12 inches unless head, neck, or back is injured or you suspect broken hip or leg bones. 2 Do not raise the person's head. 3 Turn the person on side if they are vomiting or bleeding from the mouth.
Terminology
Mechanism
- The brain is still not well understood, nor is the reason for the treatment effects ECT (shock) therapy has on some individuals. It is known that ECT affects hormones, neuropeptides, neurotrophic factors, and neurotransmitters in the brain. All of this may come together to explain how ECT works in treatment.
Preparation
- A full physical is generally needed before shock therapy. Because general anesthesia will be administered, one should not eat or drink 8-12 hours before the shock treatment. This helps to prevent any vomiting during the procedure. Other exams like an electrocardiogram (ECG) may also be given before ECT to ensure the procedure is safe and appropriate.
Treatment
- Shock therapy is performed in a hospital, sometimes in an area specifically set aside for this treatment. An intravenous (IV) is inserted to provide anesthetic medication. Vital signs are taken initially and continuously throughout the shock therapy treatment. An anesthesiologist administers anesthesia and after you are asleep, places a tube in your throat to help you breathe…
Results
- When you awake from the anesthesia, you may be confused and tired. You will likely experience short-term memory loss around the time of the procedure. With multiple treatments, this may increase. Adverse cognitive effects tend to be the most concerning factors around ECT and tend to affect the frequency and duration of treatments and whether ECT is offered at all. Your vital si…
Uses
- It is most common to see shock therapy used in severe cases of depression. Shock therapy is also performed to improve the condition of the following disorders:1
Risks
- The complications associated with ECT / shock therapy are often related to electrode placement with bilateral placement (an electrode by each temple) typically showing greater unwanted cognitive effects than unilateral placement (one electrode at the temple and the other on the forehead). Risks of shock therapy include slow heart beat (bradycardia) and rapid heartbeat (tac…
Prognosis
- Shock treatment for depression often produces a dramatic improvement in symptoms, especially in elderly individuals, sometimes during the first week of treatment. While it is estimated many of these patients will experience a future return of depression symptoms, the prognosis for each episode of depression is good. Mania also often responds well to shock treatment. The picture i…