Explore
Metastatic breast cancer is breast cancer that has spread beyond the breast and nearby lymph nodes to other parts of the body (most often the bones, lungs, liver or brain). Although metastatic breast cancer has spread to another part of the body, it’s still breast cancer and treated as breast cancer.
What is metastatic breast cancer and how is it treated?
After a diagnosis of metastatic breast cancer, it’s helpful to take the time you need to gather as much information as possible. Once you are ready, you can make plans and informed decisions about your care, treatment, and quality of life. You may already have a medical oncologist if this is a recurrence of a previous breast cancer diagnosis.
What should I do after a metastatic breast cancer diagnosis?
Distant recurrence: Most commonly, metastatic breast cancer is diagnosed after the original breast cancer treatment. A recurrence refers to the cancer coming back and spreading to a different part of the body, which can happen even years after the original diagnosis and treatment.
Can metastatic breast cancer come back years later?
If metastatic breast cancer is your first breast cancer diagnosis (called de novo metastatic breast cancer), you probably don’t have a medical oncologist. Your primary care physician can recommend an oncologist and other specialists to you so you can put together your medical team.
Do I need a medical oncologist for metastatic breast cancer?
Can you go into remission with Stage 4 metastatic breast cancer?
Metastatic breast cancer may never go away completely. But treatment can control its spread. Cancer may even go into remission at some points. This means you have fewer signs and symptoms of cancer.
How long can you leave with metastatic breast cancer?
While treatable, metastatic breast cancer (MBC) cannot be cured. The five-year survival rate for stage 4 breast cancer is 22 percent; median survival is three years. Annually, the disease takes 40,000 lives.
Can you live 10 years with metastatic breast cancer?
What is the prognosis? While there is no cure for metastatic breast cancer, there are treatments that slow the cancer, extending the patient's life while also improving the quality of life, Henry says. Many patients now live 10 years or more after a metastatic diagnosis.
Can you live 15 years with metastatic breast cancer?
However, survival varies greatly from person to person. About one-third of women diagnosed with metastatic breast cancer in the U.S. live at least 5 years after diagnosis [15]. Some women may live 10 or more years beyond diagnosis [17].
What is the longest anyone has lived with metastatic breast cancer?
She survived for 18 years after the diagnosis of metastatic breast cancer (MBC) while maintaining a good quality of life. To the authors' knowledge, this is the first reported case in the literature with the longest overall survival in a patient with MBC.
Can you live 30 years with metastatic breast cancer?
Many women live for decades with metastatic breast cancer. According to a 2017 article in the journal Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, 34 percent of women diagnosed with metastatic breast cancer have been living with the disease for five years or longer.
Does 5-year survival rate mean you have 5 years to live?
Most importantly, five-year survival doesn't mean you will only live five years. Instead it relates to the percentage of people in research studies who were still alive five years after diagnosis.
Can you live a normal life with metastatic breast cancer?
No one would say that living with metastatic breast cancer is easy. It can be treated, but it cannot be cured. However, many people with metastatic breast cancer can live long lives with excellent quality of life. More and more women and men are living with breast cancer as a chronic disease.
Is metastatic breast cancer a death sentence?
Metastatic breast cancer is not an automatic death sentence. Although most people will ultimately die of their disease, some will live for many years.
What is the 5-year survival rate for metastatic breast cancer?
The 5-year survival rate tells you what percent of people live at least 5 years after the cancer is found. Percent means how many out of 100. The 5-year survival rate for women with metastatic breast cancer is 29%. The 5-year survival rate for men with metastatic breast cancer is 22%.
When does breast cancer spread to brain?
About 10% to 15% of people with stage IV breast cancer have brain metastases. The risk of brain metastasis is usually highest for people with more aggressive subtypes of breast cancer, such as HER2-positive or triple-negative breast cancer.
How long can you live with breast cancer that has spread to the bones?
Some studies suggest that the average 1-year survival rate for people with metastatic bone cancer is 40–59%. However, the American Cancer Society states that people with distant breast cancer are 28% as likely to live for at least another 5 years as those without this condition.
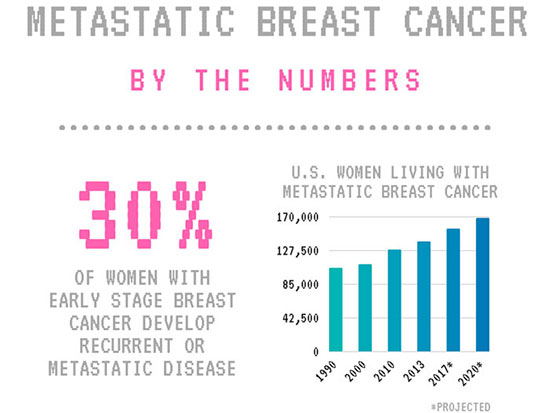
What percentage of women have metastatic breast cancer?
Some people have metastatic breast cancer when they are first diagnosed with breast cancer (about 6 percent of diagnoses in U.S. women and 9 percent of diagnoses in U.S. men) [ 3 ]. This is called de novo metastatic breast cancer.
How many women will have metastatic breast cancer in 2020?
It’s estimated there were more than 168,000 women living with metastatic breast cancer in the U.S. in 2020 [ 1 ]. Men can also get metastatic breast cancer. The risk of metastasis after breast cancer treatment varies from person to person.
What is the line of treatment for breast cancer?
As with hormone therapies, if the first chemotherapy drug (or combination of drugs) stops working and the cancer begins to grow again, a second or third drug can be used. The use of each type of chemotherapy drug (or combination of drugs) for metastatic breast cancer is called a “line” of treatment.
How long do women live after breast cancer?
However, survival varies greatly from person to person. About one-third of women diagnosed with metastatic breast cancer in the U.S. live at least 5 years after diagnosis [ 1 ]. Some women may live 10 or more years beyond diagnosis [ 2 ].
What gene mutations are included in breast cancer treatment?
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network recommends everyone diagnosed with metastatic breast cancer get genetic testing for BRCA1 and BRCA2 inherited gene mutations [ 4 ]. If you have a mutation in one of these genes, a PARP inhibitor may be included in your treatment plan.
How many lines of chemotherapy for breast cancer?
It’s common to get multiple lines of chemotherapy regimens (often 4 or more) over the course of treatment for metastatic breast cancer. Learn more about chemotherapy.
Is metastatic breast cancer a specific type of cancer?
Metastatic breast cancer (also called stage IV or advanced breast cancer) is not a specific type of breast cancer. It’s the most advanced stage of breast cancer. Metastatic breast cancer is breast cancer that has spread beyond the breast and nearby lymph nodes to other parts of the body (most often the bones, lungs, liver or brain).
What is metastatic breast cancer?
Metastatic Breast Cancer. Metastatic breast cancer is when cancer cells have spread from the breast to other parts of the body. It’s classified as advanced (stage 4) breast cancer. Metastatic breast cancer symptoms depend on what area of the body the cells have invaded. Treatment for metastatic breast cancer includes medications to slow ...
Why are meds important for metastatic breast cancer?
Medications are important for metastatic breast cancer to help control its spread. Resistance to therapies may develop, which can lead your care team to recommend a change in treatment. When you start a treatment regimen, you and your care team will see how: The cancer responds to the therapy.
What is the most advanced stage of breast cancer?
Metastatic breast cancer is the most advanced stage of breast cancer. Breast cancer develops when abnormal cells in the breast start to divide uncontrollably. A tumor is a mass or collection of these abnormal cells. Metastasis refers to cancer cells that have spread to a new area of the body. In metastatic breast cancer, cells may spread to the:
Why does metastatic cancer occur?
Most often, metastatic cancer occurs because treatment didn’t destroy all the cancer cells. Sometimes, a few cells remain dormant, or are hidden and undetectable. Then, for reasons providers don’t fully understand, the cells begin to grow and spread again.
What happens if cancer treatment isn't working?
The cancer responds to the therapy. The side effects impact you. If the treatment isn’t working or the side effects are unbearable, your care team can discuss switching the treatment method. They may recommend a different drug, dosage or schedule.
Is breast cancer a primary origin?
Lungs. Healthcare providers name cancer based on its primary origin. That means breast cancer that spreads to other body parts is still considered breast cancer. The cancer cells are still breast cancer cells. Your care team will use breast cancer therapies, even if the cancer cells are in other areas.
Can radiation therapy help with metastatic breast cancer?
Radiation therapy is not a typical treatment for metastatic breast cancer. But your provider may recommend radiation therapy for specific situations. For example, radiation therapy can help ease pain or control cancer growth in a specific area.
How many women will have metastatic breast cancer in 2020?
It’s normal to feel overwhelmed and scared. You’re not alone though. It’s estimated there were more than 168,000 women living with metastatic breast cancer in the U.S. in 2020 [ 1 ]. It may be helpful to talk with others who have metastatic breast cancer.
What is metastasis in breast cancer?
Metastasis is most often found when people report symptoms, such as bone pain, to their health care providers. Based on the symptoms, tests may be done to check if the breast cancer has returned and spread to other organs (metastasized).
How to contact Komen Breast Care?
If you or a loved one needs more information about breast health or breast cancer, call the Komen Breast Care Helpline at 1-877 GO KOMEN (1-877-465-6636). All calls are answered by a trained specialist or oncology social worker in English and Spanish, Monday through Friday from 9:00 a.m. to 10:00 p.m. ET.
What are the most common sites of breast cancer metastases?
Bone Metastases. The bones are one of the most common sites of breast cancer metastases. Bone metastases can damage your bones. Medications to strengthen and protect your bones reduce this damage. LEARN MORE.
Can breast cancer be cured?
Although metastatic breast cancer cannot be cured today, it can be treated. Treatment focuses on extending life and maintaining quality of life. As treatment continues to improve, so does survival.
Is metastatic breast cancer a stage IV?
This section discusses metastatic breast cancer treatment and care. Metastatic breast cancer (also called stage IV or advanced breast cancer) is not a specific type of breast cancer. It’s the most advanced stage of breast cancer.
Can hospice care stop metastatic breast cancer?
Hospice and End-Of-Life Care. At some point, treatment for metastatic breast cancer may be stopped. This can happen when treatment stops showing any benefit or when it greatly affects quality of life. Reducing symptoms then becomes the focus of care. Hospice can make this later stage of care as comfortable as possible.
Pembrolizumab
Already approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat cancers that have a large number of gene mutations in their cells, pembrolizumab (Keytruda) has been studied for the treatment of metastatic triple-negative breast cancer.
Trodelvy
Trodelvy (sacituzumab govitecan-hziy) was approved by the FDA in April 2020. It can be used to treat metastatic triple-negative breast cancer that hasn’t responded to at least two other treatments.
Enhertu
Approved by the FDA in December 2019, Enhertu (fam-trastuzumab deruxtecan-nxki) has been effective in treating HER2-positive breast cancer that’s metastasized (spread) or can’t be removed with surgery.
Nerlynx
Nerlynx (neratinib), originally approved by the FDA in July 2017 for early stage breast cancer, was approved in February 2020 for metastatic cancer in combination with the chemotherapy drug capecitabine.
Tukysa
Tukysa (tucatinib) was approved by the FDA in April 2020 to be used in combination with the chemotherapy drugs trastuzumab and capecitabine.
Phesgo
This combination injection of pertuzumab, trastuzumab, and hyaluronidase-zzxf was approved by the FDA in June 2020. It works by binding to HER2 sites and stopping cancer cell growth.
Talazoparib
The FDA approved talazoparib (Talzenna) in October 2018. Talazoparib is approved to treat locally advanced or metastatic HER2-negative breast cancer in people with a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation.
What does it mean when you have metastatic breast cancer?
I. f your doctor says that you have metastatic breast cancer, it means the cancer has spread beyond your breasts to other parts of your body. There's no cure, but treatments can ease your symptoms, slow down the cancer's growth, and help you live longer. You may also hear people call your condition "stage IV" or "advanced breast cancer.".
What is stage IV breast cancer?
You may also hear people call your condition "stage IV" or "advanced breast cancer.". When you get a diagnosis, your doctor will explain that cancer cells from your breasts moved through your bloodstream or lymphatic system -- a network of channels, nodes, and glands that help you fight disease.
What type of cancer cells are metastatic?
Your doctor may tell you that you have one of these types of metastatic breast cancer cells: Hormone-receptor-positive. These cells have proteins called hormone "receptors.". The job of these receptors is to catch -- or "bind" to -- certain hormones as they move through your body.
What hormones stimulate the growth of breast cancer cells?
If you have hormone-receptor-positive breast cancer, the receptors bind to estrogen and progesterone hormones. These hormones stimulate the growth of breast cancer cells. In most cases, breast cancer is hormone-positive. Hormone-receptor-negative. The cells don't have hormone receptors.
How to find out about breast cancer cells?
Some treatments work better on different kinds of breast cancer cells. To find out more about your cells, your doctor will take samples of your blood and tissue. They're sent to a lab, where technicians look at them under a microscope.
Why do doctors recommend radiation therapy?
Why you might choose it: Your doctor may suggest radiation therapy to ease symptoms and control cancer in certain areas of your body. This treatment uses high-energy X-rays or other particles to kill cancer cells. For example, if your breast cancer has spread to your liver, radiation may help shrink the tumor.
Does chemotherapy kill cancer cells?
Chemotherapy uses chemicals to kill fast-growing cancer cells. It's the main option if you have hormone-receptor-negative cancer. Your doctor may also suggest it if you tried hormone therapy and it didn't work. Chemotherapy is also a choice if your cancer is growing quickly or causing symptoms.