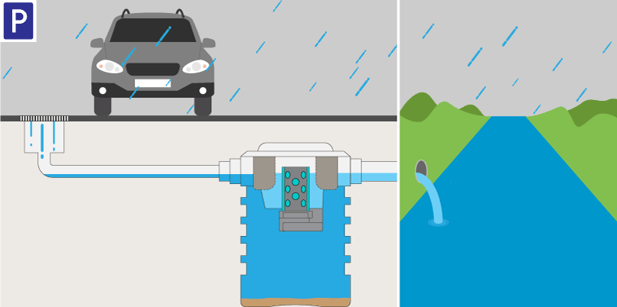
Hydrocarbons make up a large majority of the pollutants present in water, being produced from fueling stations, cars and motor vehicles and in industrial processes. If these hydrocarbons flow into the stormwater systems through surface runoff they must be treated efficiently and completely.
Full Answer
What is a stormwater treatment train?
Filtration System for Removing Hydrocarbons in Stormwater, Industrial Wastewater, and Municipal Wastewater Applications. FabMax is a patented polymeric surfactant technology that is infused into all FabMax Technologies water filtering media. FabMax is designed as a Hydrocarbon Stormwater Filter Treatment to remove hydrocarbons ranging from BTEX to …
How do I design a stormwater treatment system?
Hydrocarbons make up a large majority of the pollutants present in water, being produced from fueling stations, cars and motor vehicles and in industrial processes. If these hydrocarbons flow into the stormwater systems through surface runoff they must be treated efficiently and completely. Large proportions of hydrocarbons and oils in water ways is extremely harmful to …
What are the main pollutants in semi-synthetic stormwater?
Sep 30, 2017 · Carcinogenic and mutagenic hydrocarbons in storm water and receiving streams highlight the need to find effective methods to remove these pollutants from storm water before they accumulate in downstream water bodies. While recent results indicate that bioretention systems, or rain gardens, may represent an effective, low-cost ecological solution.
How can music be used in stormwater treatment train selection?
Sep 01, 2020 · Hydrocarbons Treatment efficiency 1. Introduction Elevated concentrations of highway-associated pollutants can frequently be found in stormwater runoff. Metals and hydrocarbons form two groups of these pollutants. Sources of metals are typically abrasion of tires, brake linings, and the car body itself.

What is the purpose of a stormwater system installed at a service station?
Stormwater systems that are installed at a service station site must be designed and maintained in such a manner as to ensure that all stormwater discharged from the site does not exceed the maximum allowable hydrocarbon concentration.
What is the purpose of a stormwater management system?
Given that fuel retailers are required to ensure that all stormwater discharge from a service station forecourt is compliant regardless of any forecourt spills that occur, the stormwater management system should be designed to capture a range of different spill volumes (capture volume) to prevent discharge of non-compliant stormwater.
How should stormwater management systems be divided?
These zones can be used to separate areas where likely higher concentration of fuel laden stormwater can be separated from stormwater which is essentially free of fuel contamination.
Who should maintain records of all maintenance performed on the stormwater management system?
The fuel retailer should maintain records of all maintenance performed on the stormwater management system and be updated to provide a record of any system amendments that may have been made.
Is it necessary to treat runoff?
It is generally not necessary to treat the entire volume of runoff that is initially captured by the site stormwater system as a significant proportion of this run-off may not be contaminated by fuel.
What are the major sources of PAHs in urban runoffs?
Major anthropogenic sources of PAHs in urban runoffs are deterioration of asphalt pavement surfaces and car tires (Halsall et al.,1994; Harrison et al., 1996), leading to passing the compounds to runoff waters; vehicular emissions leading to atmospheric fallout; and rain water runoff across impervious areas (such as roads, motorways, paved parking lots, sidewalks); and pervious areas (such as gardens, landscaping, grass and unpaved surfaces etc.). Incomplete combustion of organic matter at high temperature is one of the major anthropogenic sources of environmental PAHs.
Is PAH a carcinogen?
The carcinogenicity of certain PAHs is well established in laboratory animals. PAHs reveal their toxicity following biotransformation to toxic metabolites which can be bound covalently to cellular macromolecules such as DNA, RNA and proteins, which causes cell damage, mutagenesis, tetragenesis and cacinogenesis. After PAH exposure, there is an increase in the number of DNA adducts, as well as some inhibition in RNA and protein synthesis (Arvo T. 1995; M. Pufulete 2004). Researchers have reported increased incidences of skin, lung, bladder, liver and stomach cancers, as well as injection-site sarcomas, in animals. Studies on animals show that certain PAHs also can affect the hematopoietic (growth of blood cells) and immune systems and can produce reproductive, neurologic and developmental effects (Blanton 1986, 1988; Dasgupta and Lahiri 1992; Hahon and Booth 1986; Malmgren et al. 1952; Philips et al. 1973; Szczeklik et al. 1994; Yasuhira 1964; Zhao 1990).
What are the processes that degrade PAHs?
Persistence increases with increase in the molecular weight. Although PAHs may undergo adsorption, volatilization, photolysis and chemical degradation, microbial degradation is the major degradation process. The PAH-degrading microorganism could be algae, bacteria and fungi. It involves the breakdown of organic compounds through biotransformation into less complex metabolites and through mineralization into inorganic minerals, H2O, CO2 (aerobic) or CH4 (anaerobic). Both bacteria and fungi have been extensively studied for their ability to degrade xenobiotic substances (chemicals found in organisms but which is not produced by them; typically pollutants) including PAHs. The extent and rate of biodegradation depends on many factors including pH, temperature, oxygen, microbial population, degree of acclimation, accessibility of nutrients, chemical structure of the compound, cellular transport properties and chemical partitioning in growth medium. Enzymes involved in the degradation of PAHs are oxygenase, dehydrogenase and lignolytic enzymes. Fungal lignolytic enzymes are lignin peroxidase, laccase and manganese peroxidase. They are extracellular and catalyze radical formations by oxidation to destabilize bonds in a molecule. The biodegradation of PAHs has been observed under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. The microbial communities in contaminated sediments and soils exist under anaerobic conditions and biotransformation of pollutants is observed under such conditions. The anaerobic biodegradation of PAHs is a slow process and its biochemical mechanism has not yet been elucidated.
What is coal tar?
Coal tar sealants are used primarily as pavement surface sealants. Pavement sealants are surface finishes for parking lots, driveways and airport runways that provide a protective barrier from weather and chemicals. Apart from coal tar-based sealants, asphalt-based sealants are also commonly used and contain far less concentration of PAHs than coal tar sealants. Coal tar sealants contain over 50,000 mg/l and asphalt sealants contain only about 50 mg/l of total PAHs. However, coal tar has a great advantage over asphalt in that it has better chemical resistance than asphalt coatings. Coal tar coatings hold up better under exposures of petroleum oils and inorganic acids. Another outstanding quality of coal tar coatings is their extremely low permeability to moisture and high dielectric resistance, both of which contribute to corrosion resistance. Table 10 compares the major characteristics of both asphalt and coal tar-based sealants.
What is best management practices for stormwater?
Stormwater runoff best management practices are in general a collection of methods designed to control stormwater runoff incorporating erosion and sediment control, urban runoff and/or hydrologic/habitat modification. EPA defines stormwater BMPs as a "… technique, measure or structural control that is used for a given set of conditions to manage the quantity and improve the quality of stormwater runoff in the most cost-effective manner."
What is source control?
Source controls are management techniques that reduce the amount of pollutants and volumes of water entering the stormwater drainage system. Reducing the volume of pollution entering the stormwater system can often be the most effective and least expensive means of control (RDA, 2005) –
What is street sweep?
Street Sweeping – Street sweepers remove debris and particulate from paved surfaces using rotating brushes, water jets and/or vacuums. They are a good method of pollution reduction for urban areas that are hard to retrofit with physical structures or biological areas. Optimal frequencies of street sweeping are usually between weekly and monthly.