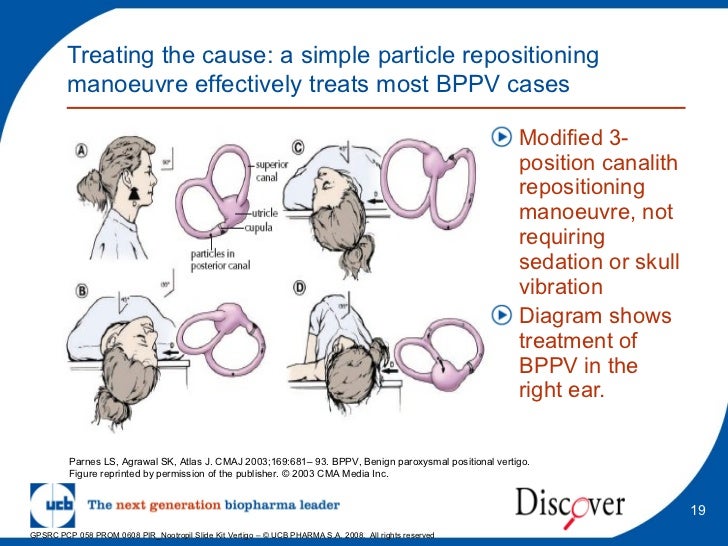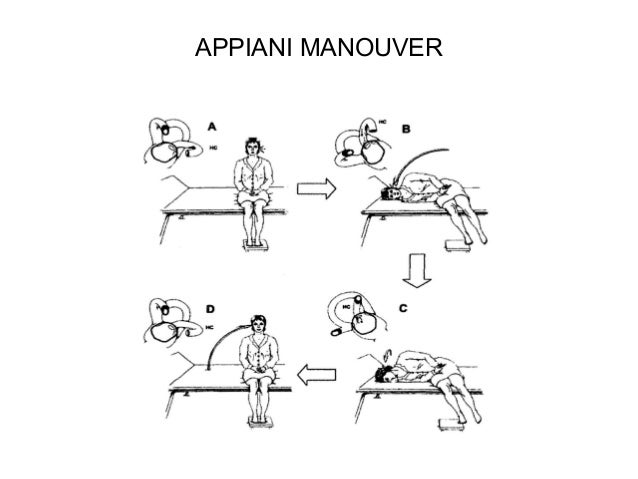
What is the canalith repositioning procedure?
A canalith repositioning procedure (CRP) is a treatment for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), the most common cause of vertigo. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
What is canalith repositioning for BPPV?
The goal of the canalith repositioning procedure (CRP) is to move the displaced canaliths to stop these false signals. CRP is very effective, with an approximate cure rate of 80%. Because of potential complications with this procedure it must only be performed by a professional specifically trained to perform them.
How does canalith repositioning work for Vertigo?
Dec 08, 2021 · The canalith repositioning procedure is used in the treatment of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV). BPPV is a condition in which a person experiences brief episodes of dizziness. It is the most common cause of vertigo. In addition, the person feels his head is spinning when he or she moves his or her head.
What happens to canaliths once they are in the utricle?
The Canalith Repositioning Procedure (CRP) is designed to treat benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) through induced out-migration of free-moving pathological densities in the endolymph of a semicircular canal, using timed head maneuvers and applied vibration. This article describes the procedure and its rationale, and reports the ...

When should you do the Epley maneuver?
Is canalith repositioning same as Epley maneuver?
When should I do the Brandt Daroff exercises?
Is Epley maneuver contraindicated?
Can I do canalith repositioning at home?
What is canalith repositioning procedure?
How many times a day should you do Brandt-Daroff?
Are Brandt-Daroff exercises effective?
Is Brandt-Daroff better than Epley?
Can you take meclizine before an Epley maneuver?
How many times a day should you do the Epley maneuver?
Can I take meclizine after Epley maneuver?
Canalith Repositioning procedures (also known as Epley maneuvers) are extremely effective in relieving the symptoms of positional vertigo. BPPV does not resolve any faster, and likelihood of future episodes is not affected by meclizine.
What is CRP in medical terms?
What is a canalith repositioning procedure (CRP)? A canalith repositioning procedure (CRP) is a treatment for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), the most common cause of vertigo. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission.
What is the cause of BPPV?
The cause of BPPV is the displacement of small crystals of calcium carbonate (also known as canaliths) in the inner ear.
What does BPPV stand for?
The letters of the term “BPPV” stand for: Benign: of no danger to health. Paroxysmal: happening in sudden, brief spells. Positional: triggered by particular head movements or positions. Vertigo: an internal sense of irregular or whirling motion either of yourself or of objects around you.
What causes vertigo in the ear?
Other causes of vertigo could include: 1 An abnormal brain structure 2 Certain kinds of migraine headaches 3 Vestibular neuritis (a type of inner-ear infection) 4 Meniere’s disease (a progressive disease of the inner ear, causing ringing in the ears among other symptoms) 5 Orthostatic hypotension (low blood pressure upon standing up) 6 Panic attacks
Is CRP effective?
CRP is very effective, with an approximate cure rate of 80%. Because of potential complications with this procedure it must only be performed by a professional specifically trained to perform them. The Canalith Repositioning Procedure is also known as the “Epley maneuver.”. BPPV (Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo) occurs as a result ...
What is the goal of CRP?
The goal of the canalith repositioning procedure (CRP) is to move the displaced canaliths to stop these false signals.
Can CRP cause vertigo?
CRP is thought to be effective in canalithiasis because it can help move the free-floating canaliths from the sensitive area (semicircular canal) into a place where it won’t cause vertigo. It can be used to treat BPPV of the posterior semicircular canal or the anterior semicircular canal. Most people undergoing the procedure do so ...
Where does BPPV occur?
BPPV occurs as a result of displaced otoconia, which are small crystals of calcium carbonate, or “canaliths,” that are normally attached to the otolithic membrane in the utricle of the inner ear. Canaliths can detach from the utricle and collect within the semicircular canals.
What is BPPV in ear?
BPPV (Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo) occurs as a result of displaced otoconia, which are small crystals of calcium carbonate (also referred to as “otoliths” or “canaliths”) that are normally attached to the otolithic membrane in the utricle of the inner ear.
What is canalith repositioning?
Canalith repositioning maneuvers are used in the treatment of vertigo. Vertigo is often caused by an inner ear problem. One of the most common causes of vertigo is Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo.
What is a canalith maneuver?
Canalith Repositioning Maneuver (Vertigo Treatment) Canalith repositioning maneuvers are used in the treatment of vertigo. Vertigo is often caused by an inner ear problem. One of the most common causes of vertigo is Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo.
What is the function of the inner ear?
The function of the inner ear is to communicate with the brain about head and body movements relative to gravity, which helps a person keep balance. Displaced canalith sends false signals tot he brain, causing dizziness and vertigo symptoms.
What is the BPPV?
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) occurs when small particles of calcium carbonate (also referred to as “canaliths”) clump up in canals of the inner ear. The function of the inner ear is to communicate with the brain about head and body movements relative to gravity, which helps a person keep balance.
What causes vertigo in the inner ear?
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) occurs when small particles of calcium carbonate (al so referred to as “cana liths”) clump up in canals of the inner ear.
Is CRP a controlled trial?
Controlled Trials CRP has a very high level of evidence of effectiveness. CRP has been tested in numerous randomized placebo (i.e., sham procedures) controlled trials. Trial quality has been rigorously scrutinized on separate occasions by the Cochrane Collaboration,2 the American Academy of Neurology Quality Standards Subcommittee,9 a multidisciplinary guideline development panel chosen by the American Academy of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery Foundation,10 and other independent groups.11,12 The summary results of all the valid randomized controlled trials indicates that CRP has a large effect size in treating
What is a CRP procedure?
The Canalith Repositioning Procedure (CRP) is a non-invasive treatment for the most common cause of vertigo, benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). Most patients who are likely to benefit from CRP may not be receiving it.
Why do my eyes spin?
tightly connected to the centers of the brain responsible for controlling eye movements, which is the reason that these particles in the inner ear result in eye movements. During the occurrence of nystagmus, the affected persons actually experience their environment spinning (since the eyes are moving very quickly) about them even though they are not actually moving.
What is a Cochrane systematic review?
Cochrane systematic reviews explore the evidence for and against the effectiveness and appropriateness of interventions— medications, surgery, education, nutrition, exercise—and the evidence for and against the use of diagnostic tests for specific conditions.
What is the Cochrane Library?
The Cochrane Library is a respected source of reliable evidence related to health care. Cochrane systematic reviews explore the evidence for and against the effectiveness and appropriateness of interventions—medications, surgery, education, nutrition, exercise—and the evidence for and against the use of diagnostic tests for specific conditions.