Treatment is dependent upon the progression of the disease. Current US guidelines recommend that HIV treatment begin when CD4+ cell count is between 350 and 500. Treatment will also begin when opportunistic diseases begin to develop.
Full Answer
When should I start antiretroviral therapy for HIV?
HIV medicine is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). There is no effective cure for HIV. But with proper medical care, you can control HIV. Most people can get the virus under control within six months. Taking HIV medicine does not prevent transmission of other sexually transmitted diseases. When should I start treatment? Start Treatment As Soon As Possible After Diagnosis
What is the treatment for HIV?
Mar 29, 2019 · HIV treatment involves taking medicines that slow the progression of the virus in your body. HIV is a type of virus called a retrovirus, and the combination of drugs used to treat it is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). ART is recommended for all people living with HIV, regardless of how long they’ve had the virus or how healthy they are.
Why is early treatment for HIV important?
Aug 30, 2016 · INTRODUCTION. Toxoplasma gondii is a protozoan parasite present world-wide and causes major opportunistic infections in HIV infected people. Cell-mediated immunity (CMI) will be developed after acute infection with T. gondii and infection is controlled but not eradicated. In this chronic or latent phase of infection, the organisms persist in the tissues of infected …
How long does it take for HIV medicine to work?
Mar 07, 2022 · Preventing Perinatal HIV Transmission. Advances in HIV research, prevention, and treatment have made it possible for many women with HIV to give birth to babies who are free of HIV. The annual number of HIV infections through perinatal transmission in the United States and dependent areas a has declined by more than 95% since the early 1990s.
What is HIV treatment?
HIV treatment involves taking medicine that reduces the amount of HIV in your body. HIV medicine is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). There is n...
When should I start treatment?
Start Treatment As Soon As Possible After Diagnosis HIV medicine is recommended for all people with HIV, regardless of how long they’ve had the vir...
What if I delay treatment?
HIV will continue to harm your immune system. This will put you at higher risk for developing AIDS. Learn more about AIDS and opportunistic infecti...
What are the benefits of taking my HIV medicine every day as prescribed?
Treatment Reduces the Amount of HIV in the Blood The amount of HIV in the blood is called viral load. Taking your HIV medicine as prescribed will h...
Does HIV medicine cause side effects?
HIV medicine can cause side effects in some people. However, not everyone experiences side effects. The most common side effects are Nausea and vom...
Will HIV treatment interfere with my hormone therapy?
There are no known drug interactions between HIV medicine and hormone therapy. Talk to your health care provider if you are worried about taking HI...
What if my treatment is not working?
Your health care provider may change your prescription. A change is not unusual because the same treatment does not affect everyone in the same way.
Sticking to my treatment plan is hard. How can I deal with the challenges?
Tell your health care provider right away if you’re having trouble sticking to your plan. Together you can identify the reasons you’re skipping med...
How long does it take to get rid of HIV?
There is no effective cure for HIV. But with proper medical care, you can control HIV. Most people can get the virus under control within six months. Taking HIV medicine does not prevent transmission ...
Why is it important to take HIV medication?
Taking HIV medication consistently, as prescribed, helps prevent drug resistance. Drug resistance develops when people with HIV are inconsistent with taking their HIV medication as prescribed. The virus can change (mutate) and will no longer respond to certain HIV medication. If you develop drug resistance, it will limit your options ...
Can HIV be transmitted through sex?
If you have an undetectable viral load, you have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to an HIV-negative partner through sex. Having an undetectable viral load may also help prevent transmission from injection drug use.
Can I take pills at work?
A busy schedule. Work or travel away from home can make it easy to forget to take pills. It may be possible to keep extra medicine at work or in your car. But talk to your health care provider first. Some medications are affected by extreme temperatures and it is not always possible to keep medications at work.
Can you take a medicine if you missed it?
Missing a dose. In most cases, you can take your medicine as soon as you realize you missed a dose. Then take the next dose at your usual scheduled time (unless your pharmacist or health care provider has told you something different).
Does HIV harm the immune system?
HIV will continue to harm your immune system. This will put you at higher risk for developing AIDS. Learn more about AIDS and opportunistic infections. This will put you at higher risk for transmitting HIV to your sexual and injection partners.
What is the treatment for HIV?
HIV treatment involves taking medicines that slow the progression of the virus in your body. HIV is a type of virus called a retrovirus, and the combination of drugs used to treat it is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). ART is recommended for all people living with HIV, regardless of how long they’ve had the virus or how healthy they are.
How successful is HIV treatment?
HIV treatment is most likely to be successful when you know what to expect and are committed to taking your medicines exactly as prescribed. Working with your health care provider to develop a treatment plan will help you learn more about HIV and manage it effectively.
How long do HIV side effects last?
Some side effects can occur once you start a medicine and may only last a few days or weeks.
What happens if your CD4 is low?
If your CD4 cell count falls below a certain level, you are at risk of getting an opportunistic infection. These are infections that don’t normally affect people with healthy immune systems but that can infect people with immune systems weakened by HIV infection.
How soon can you start ART for HIV?
Treatment guidelines from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services recommend that a person living with HIV begin ART as soon as possible after diagnosis. Starting ART slows the progression of HIV and can keep you healthy for many years.
Can HIV cause drug resistance?
Drug resistance can be a cause of treatment failure for people living with HIV. As HIV multiplies in the body, it sometimes mutates (changes form) and produces variations of itself. Variations of HIV that develop while a person is taking ART can lead to drug-resistant strains of HIV. With drug resistance, HIV medicines that previously controlled ...
What is drug resistance testing?
Drug-resistance testing identifies which, if any, HIV medicines won’t be effective against your specific strain of HIV. Drug-resistance testing results help determine which HIV medicines to include in an HIV treatment regimen. Taking HIV medication every day, exactly as prescribed helps prevent drug resistance.
What is the final stage of HIV?
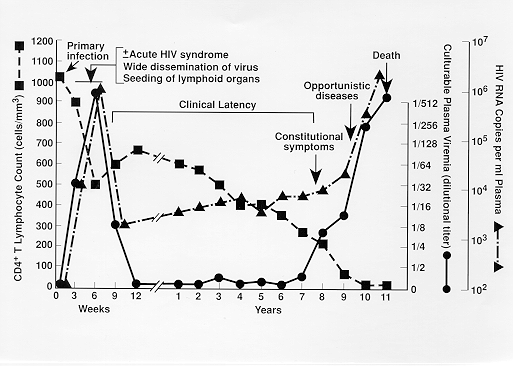
AIDS is the final stage of HIV infection. A person infected with HIV is diagnosed with AIDS when he or she has a dangerously low number of CD4+ T cells as well as one or more “opportunistic” infections, such as some types of pneumonia or tuberculosis, that do not typically affect people with healthy immune systems.
How does HIV affect the immune system?
HIV attacks the immune system by destroying specific white blood cells called CD4 positive (CD4+) T cells that are vital to fighting off infection. The resulting shortage of these cells leaves people infected with HIV vulnerable to other infections and diseases, and additional complications. AIDS is the final stage of HIV infection.
What are the complications of HIV?
Other nervous system complications that can occur as a result of HIV infection or the drugs used to treat it include: 1 pain 2 seizures 3 strokes 4 shingles 5 difficulty swallowing 6 fever 7 vision loss 8 coma, and 9 problems with bladder control or sexual function.
What is the ADC of HIV?
AIDS dementia complex (ADC), or HIV-associated dementia (HAD), occurs primarily in persons with more advanced HIV infection. Symptoms include encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), behavioral changes, and a gradual decline in cognitive function, including trouble with concentration, memory, and attention.
Can AIDS cause encephalitis?
The herpes zoster virus, which causes chickenpox and shingles, can infect the brain and produce encephalitis and myelitis (inflammation of the spinal cord).
What are the symptoms of shingles?
Signs of shingles include painful blisters (like those seen in chickenpox), itching, tingling, and pain in the nerves. People with AIDS may suffer from several different forms of neuropathy, or nerve pain, each strongly associated with a specific stage of active immunodeficiency disease.
What is the NINDS?
Within the Federal government, the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), a component of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), supports research on the neurological consequences of HIV and AIDS.
What is the effect of HIV on the body?
In HIV-positive individuals, it causes severe opportunistic infections, which is of major public health concern as it results in physical and psychological disabilities. In healthy immunocompetent individuals, it causes asymptomatic chronic persistent infections, but in immunosuppressed patients, there is reactivation of the parasite if ...
What is the most common opportunistic infection in HIV/AIDS?
In HIV infection, symptomatic disease most often occurs as a result of reactivation of latent infection.[1] . Toxoplasmosis has been reported as the most common opportunistic infection in HIV/AIDS in developed countries and most common cause of focal brain lesions, coma and death.
What is the parasite that causes opportunistic infections?
INTRODUCTION. Toxoplasma gondiiis a protozoan parasite present world-wide and causes major opportunistic infections in HIV infected people. Cell-mediated immunity (CMI) will be developed after acute infection with T. gondiiand infection is controlled but not eradicated.
Is HIV a latent infection?
Their epidemiological and clinical aspect in association with HIV-infected patients was reported worldwide. In HIV infection due to immunosuppression, there is reactivation of chronic latent infection resulting in Toxoplasma encephalitis.
What to do if you don't have HIV?
If you don’t have HIV, but your partner does, ask your doctor about medicine to prevent getting HIV, called pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP).
What is the goal of the CDC?
These are the goals that CDC has developed for elimination of mother-to-child HIV transmission in the United States . CDC supports CityMatCH to convene a group of stakeholders including public health professionals and clinical care providers to implement the CDC framework.
How much does the CDC give to community organizations?
Under the flagship community-based organization cooperative agreement, CDC awards about $42 million per year to community organizations. This award directs resources to support the delivery of effective HIV prevention strategies to key populations.
Can HIV give birth to a baby?
Advances in HIV research, prevention, and treatment have made it possible for many women with HIV to give birth to babies who are free of HIV. The annual number of HIV infections through perinatal transmission in the United States and dependent areas a has declined by more than 95% since the early 1990s. *Viral suppression is defined as having less ...
What does it mean when a viral load is undetectable?
An undetectable viral load means having a viral load so low that a test can’t detect it. The benefits of having an undetectable viral load also apply to people who stay virally suppressed. All women who are pregnant or trying to get pregnant should encourage their partners to also get tested for HIV.
What is an African American?
African American is a term often used for Americans of African descent with ancestry in North America. ‡Hispanics/Latinos can be of any race. Source: CDC. Diagnoses of HIV infection in the United States and dependent areas, 2018 (updated) .
What is the CDC's cooperative agreement?
In 2019, CDC awarded a cooperative agreement to strengthen the capacity and improve the performance of the nation’s HIV prevention workforce. New elements include dedicated providers for web-based and classroom-based national training, and technical assistance tailored within four geographic regions.
What are the risks of HIV?
Increased risk of cervical cancer. Increased risk of heart disease. HIV medicine side effects and drug interactions. Aging-related issues. Pregnancy and birth control also require careful management with a health care provider.
Why is STD screening important?
STD screening and treatment is important for the health of a woman living with HIV and because having HIV and other STDs may increase the risk of HIV transmission to sexual partners. Vaginal yeast infections —In women living with HIV, vaginal yeast infections can occur more frequently and be harder to treat. Recurring vaginal yeast infections ...
Can HIV be transmitted through sex?
The good news is that women who take HIV medicine (called antiretroviral therapy or ART) daily as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load can stay healthy and have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to an HIV-negative partner through sex.
What are the issues women experience?
Some of the issues women may experience are: Problems related to sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) —Some STDS, like genital herpes, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), and chancroid can happen more often and be more severe and/or harder to treat in women living with HIV than in HIV-negative women. STD screening and treatment is important ...
Can HIV cause a period?
Menstrual cycle problems —Wo men living with HIV may experience missed periods, lighter or heavier bleeding, or more severe premenstrual syndrome. Treatment is available for these health conditions. Talk to your health care team about treatment options that are right for you.
What is cervical cancer?
Cervical cancer is cancer that starts in the cervix, the lower, narrow part of the uterus (the womb). It is almost always caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. The types of HPV that cause cervical cancer are more common in women with HIV.
Does nevirapine cause liver problems?
Nevirapine side effects —Studies have linked the HIV medicine nevirapine (also called Viramune or NVP) to a higher risk of rashes and liver problems for women with higher CD4 counts. Ritonavir side effects —The HIV medicine ritonavir (also called Norvir or RTV) may cause more nausea and vomiting in women.
How long does HIV exposure last?
of exposure and may last for several days or weeks. Doctors refer to this as seroconversion illness. Seroconversion is the stage when a person’s body is producing antibodies against HIV, which means that their immune system is fighting the infection.
What is stage 3 AIDS?
Stage 3 infection (also known as AIDS): At this stage, a person’s immune system is badly damaged, and their CD4 cell count drops below 200 cells per cubic millimeter (cells/mm 3) of blood. They will become vulnerable to opportunistic infections, and the risk of viral transmission can be high.
What happens if you don't get HIV treatment?
When a person contracts HIV, if they do not receive treatment, the infection will typically progress through three stages. Trusted Source. : Acute infection: Soon after contracting the virus, the person has a large amount of HIV in their blood, and the risk of the virus transmitting to others is high.
How many people in the US have HIV?
It can have many effects across the body, but modern treatments are effective in preventing HIV from progressing to an advanced stage. An estimated 1.2 million people in the United States are living with HIV.
Does HIV affect mental health?
HIV and mental health. Receiving a diagnosis of HIV and living with the condition can have significant effects on a person’s mental health. According to the National Institute of Mental Health, people living with HIV are twice as likely to have depression than those without HIV.
What is the immune system?
The immune system protects the body against viruses, bacteria, and fungi. After attaching itself to a type of white blood cell called a CD4 T cell, the virus merges with it. These T cells are an important part of the immune system. Once inside the CD4 T cell, the virus multiplies.
Can HIV cause anxiety?
There are specific sources of stress relating to the condition, such as having to find and manage medical support, managing the lifelong use of medications, and dealing with the stigma and discrimination associated with HIV. Some antiretroviral drugs may also cause mental health side effects, such as anxiety.
What drug stopped HIV from multiplying?
Also called azidothymidine (AZT), the medication became available in 1987.
How many HIV medications are there?
Today, more than 30 HIV medications are available. Many people are able to control their HIV with just one pill a day. Early treatment with antiretrovirals can prevent HIV-positive people from getting AIDS and the diseases it causes, like cancer.
When was saquinavir approved?
In 1995 , the FDA approved saquinavir, the first in a different anti-HIV (antiretroviral) drug class called protease inhibitors. Like NRTIs, protease inhibitors stop the virus from copying itself, but at a different stage during the infection.
Who should take PrEP?
The United States Preventive Services Task Force now recommends that anyone who’s at risk for HIV infection take PrEP. That includes men who have sex with men, straight people who have unprotected risky sex, and those who inject drugs. HIV Treatment Today. New HIV drug classes have come out in recent years.
How much is AZT?
AZT also at the time was the most expensive prescription drug in history, with a one-year price tag of $16,500 in today’s dollars. Over the next several years, the FDA approved several other drugs that worked similarly to AZT. They belonged to a drug class called nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs).
Is HIV hard to kill?
HIV turned out to be hard to kill. For one thing, it attacks immune cells called T helper cells that normally protect against invaders like HIV. If enough T cells get destroyed, it leaves your body defenseless against the virus and other “opportunistic” infections.
What Are HIV and Aids?
- HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) is the virus that causes AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome). HIV attacks the immune system by destroying specific white blood cells called CD4 positive (CD4+) T cells that are vital to fighting off infection. The resulting shortage of these cells leaves people infected with HIV vulnerable to other infections and diseases, and additional com…
How Do HIV/AIDS Affect The Nervous System?
- HIV does not directly invade nerve cells (neurons) but puts their function at risk by infecting cells called glia that support and protect neurons. HIV also triggers inflammation that may damage the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system) and cause symptoms such as: 1. confusion and forgetfulness 2. inability to concentrate 3. behavioral changes 4. headaches 5. mood disorders (…
How Are These Disorders Diagnosed?
- Based on an individual’s medical history and findings from a general physical exam, a physician will conduct a thorough neurological exam to assess various functions: motor and sensory skills, nerve function, hearing and speech, vision, coordination and balance, mental status, and changes in mood or behavior. The physician may order laboratory tests andone or more of the following …
How Are These Disorders Treated?
- No single treatment can cure the neurological complications of HIV/AIDS. Some disorders require aggressive therapy while others are treated as symptoms arise. Neuropathic pain—chronic pain caused by damage to the nervous system—is often difficult to control. Medicines range from over-the-counter pain killers to anticonvulsant drugs, opiates, and some classes of antidepressants. I…
What Research Is Being done?
- Within the Federal government, the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), a component of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), supports research on the neurological consequences of HIV and AIDS. NINDS works closely with its sister agencies, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) and the National Institute of Mental …
Where Can I Get More Information?
- For more information on neurological disorders or research programs funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, contact the Institute's Brain Resources and Information Network (BRAIN) at: BRAIN P.O. Box 5801 Bethesda, MD 20824 301-496-5751 800-352-9424 For additional information about AIDS and its neurological complications, please cont…