Full Answer
How long does it take to get rid of breast cancer?
A few facts about time to treatment: The average time from the date of cancer diagnosis to the day of lumpectomy surgery is about 32 days. It can take anywhere from 3 to 12 months from cancer diagnosis to complete your final treatments, and up to ten years if you need hormonal therapy.
What is the optimal time until treatment for metastatic breast cancer?
There is little research looking at the optimal time until treatment for metastatic breast cancer, though it appears that waiting more than 12 weeks has been linked with lower survival. In general, however, the goal of treatment with MBC is different than early stage disease.
What are the stages of breast cancer treatment?
Treatment of Breast Cancer Stages I-III 1 Surgery. 2 Radiation therapy. 3 Adjuvant systemic therapy (chemo and other drugs). 4 Local therapy (surgery and radiation therapy). 5 Neoadjuvant and adjuvant systemic therapy (chemo and other drugs). 6 ... (more items)
How will my life change after breast cancer treatment?
In many ways, it will be a lot like the life you had before, but in other ways, it will be very different. Call it your "new normal." From your relationships with your family and your spouse to eating habits and exercise, breast cancer will change your life in ways that last well after treatment ends.
How long does treatment for breast cancer last?
If you're lucky and catch your condition early on, then your breast cancer treatment will generally last between three and six months. This assumes there is no further growth while you are undergoing treatment. In more advanced cases, you should typically expect a minimum of six months of treatment.
What happens when breast cancer treatment ends?
Long-term effects of surgery. Or, the area around the surgical site may become hardened. If lymph nodes were removed as part of the surgery or affected during treatment, lymphedema in the arm, chest wall, or breast may occur, even many years after treatment. This is a life-long risk for survivors.
When are you considered cancer free after breast cancer?
The cancer may come back to the same place as the original primary tumor or to another place in the body. If you remain in complete remission for five years or more, some doctors may say that you are cured, or cancer-free.
When should cancer treatment stop?
What the experts recommend. Cancer treatment is at its most effective the first time that it's used. If you've undergone three or more chemotherapy treatments for your cancer and the tumors continue to grow or spread, it may be time for you to consider stopping chemotherapy.
Are you ever cured of breast cancer?
Get the Facts. There's currently no cure for metastatic breast cancer, but new treatments have improved survival rates in recent years. Researchers have gained a better understanding of the molecular and genetic characteristics of breast cancer.
How often do you see your oncologist after breast cancer?
After you finish treatment for breast cancer, you'll see your oncologist and other members of your health care team on a regular basis, usually about every 6 months for the first few years. After that, you'll see them every year for many years.
What are the chances of getting cancer again after breast cancer?
How common is breast cancer recurrence? Most local recurrences of breast cancer occur within five years of a lumpectomy. You can lower your risk by getting radiation therapy afterward. You have a 3% to 15% chance of breast cancer recurrence within 10 years with this combined treatment.
Does breast cancer always return?
Everyone who's had breast cancer is at risk of recurrence (return of breast cancer). However, most people diagnosed with breast cancer will never have a recurrence. Talk with your health care provider about your risk of recurrence and things you can do that may lower your risk.
Can you live 20 years after breast cancer?
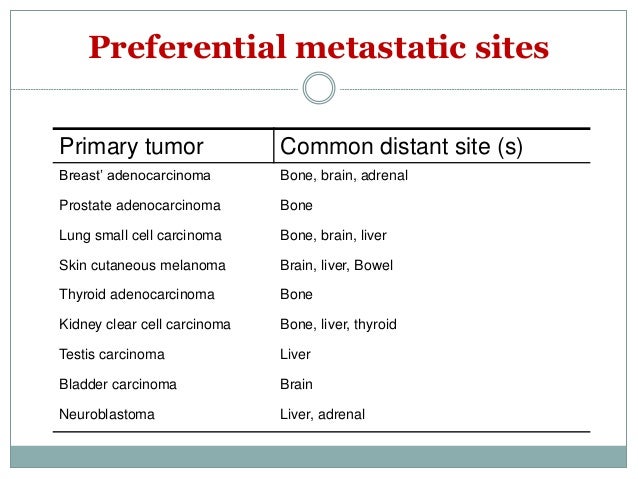
Many people with localized or regional breast cancer survive for 20 years or longer after receiving a diagnosis and treatment. It is rare for someone with distant breast cancer to live for 20 years. However, scientists are continuing to improve treatments for distant breast cancer.
How do doctors know how long you have left to live?
There are numerous measures – such as medical tests, physical exams and the patient's history – that can also be used to produce a statistical likelihood of surviving a specific length of time. Yet even these calculations "are not any more accurate than the physicians' predictions of survival," she says.
Can breast cancer spread while on chemo?
While chemotherapy is one of the oldest and most successful ways of treating cancer, it doesn't always work. So, yes, cancer can spread during chemotherapy. Spreading could mean the tumor keeps growing, or that the original tumor shrinks, but cancer metastasizes, forming tumors in other areas of the body.
When a DR says you have 6 months to live?
Medicare pays for hospice care if your doctor believes you have 6 months or less to live, the cancer does not respond to treatment, and your medical condition does not improve. But no one knows for sure how long you will live.
How long does breast cancer treatment last?
After a marathon of breast cancer diagnosis and treatment that may last six months to a year, you can hardly wait to get back to a normal life again.
What does it mean to return to your normal after breast cancer?
Here's how to return to your "new normal.". Life after breast cancer means returning to some familiar things and also making some new choices. The song says "It ain't over 'til it's over," but when you've had breast cancer, you discover that it's not even over when it's over.
What are the challenges women face after breast cancer treatment?
Two of the biggest hurdles women with breast cancer face post-treatment are fatigue resulting from chemotherapy and/or the accumulated effects of other treatments, and a phenomenon some women have dubbed "chemobrain" -- mental changes such as memory deficits and the inability to focus.
How does breast cancer affect your life?
From your relationships with your family and your spouse to eating habits and exercise, breast cancer will change your life in ways that last well after treatment ends.
Is breast cancer a marathon?
It can feel like an endless process.". Breast cancer survivorship, Weiss observes, is a marathon, not a sprint. That means learning to handle the symptoms that stick around after treatment ends, says Sloan-Kettering's McCabe, by using those adaptive strategies you learned while on chemotherapy or recovering from surgery.
Can breast cancer survivors survive?
Women with breast cancer, like other people with a cancer diagnosis, are now surviving for so much longer, and in such large numbers, that some hospitals are opening entire departments devoted to survivorship The National Cancer Institute has also launched a special research area dedicated to studying what it means to survive cancer. Â.
How long does it take to find breast cancer?
Finding your breast cancer (1 – 3 weeks) Most small breast cancers are found on screening mammography and possibly by ultrasound or maybe a breast MRI. You may have detected your own breast lump and sought further help from your physician.
What is the hardest part of breast cancer?
Making good decisions is the most difficult part of having breast cancer. You will feel pressed for time to learn everything and start your treatment as soon as possible. Time is usually on your side. You must work with your team to learn everything about your cancer and treatment options.
How long does it take to get radiation from a lumpectomy?
Most patients that have a lumpectomy will need radiation. Whole breast radiation is the most common type and takes 4 to 6 weeks. Only a few patients that have a mastectomy will also need radiation.
How long does it take to get a mastectomy?
The average time to mastectomy surgery is about 40 days . It can take anywhere from 3 to 12 months from cancer diagnosis to complete your final treatments, and up to ten years if you need hormonal therapy. It is a marathon. Conserve your emotional and physical efforts for the challenges ahead.
Do you need chemotherapy for breast cancer?
Surgery is usually the first treatment for early-stage breast cancer. Most patients will not need chemotherapy. If you have Estrogen receptor negative (ER-) or a “ HER2-Positive “ tumor, then you will likely need chemotherapy either before or after surgery.
Can a breast surgeon do a breast biopsy?
Getting scheduled to have an image-guided breast biopsy by a breast surgeon or radiologist can vary. Most NAPBC accredited Breast Centers work quickly to schedule biopsies for those who might have a breast cancer. Our “ Minimally Invasive Breast Biopsy “ lesson ( here) outlines why needle biopsies are the standard of care.
What are the stages of breast cancer?
Most women with breast cancer in stages I to III will get some kind of drug therapy as part of their treatment. This may include: 1 Chemotherapy 2 Hormone therapy (tamoxifen, an aromatase inhibitor, or one followed by the other) 3 HER2 targeted drugs, such as trastuzumab (Herceptin) and pertuzumab (Perjeta) 4 Some combination of these
What is the treatment for stage 1 breast cancer?
Local therapy (surgery and radiation therapy) Surgery is the main treatment for stage I breast cancer. These cancers can be treated with either breast-conserving surgery (BCS; sometimes called lumpectomy or partial mastectomy) or mastectomy.
What is the treatment for BCS?
Women who have BCS are treated with radiation therapy after surgery. Women who have a mastectomy are typically treated with radiation if the cancer is found in the lymph nodes.
How big is a stage 3 breast tumor?
In stage III breast cancer, the tumor is large (more than 5 cm or about 2 inches across) or growing into nearby tissues (the skin over the breast or the muscle underneath), or the cancer has spread to many nearby lymph nodes.
Can stage 3 breast cancer spread to lymph nodes?
If you have inflammatory breast cancer: Stage III cancers also include some inflammatory breast cancers that have not spread beyond near by lymph nodes. Treatment of these cancers can be slightly different from the treatment of other stage III breast cancers.
Can you get radiation therapy before mastectomy?
If you were initially diagnosed with stage II breast cancer and were given treatment such as chemotherapy or hormone therapy before surgery, radiation therapy might be recommended if cancer is found in the lymph nodes at the time of the mastectomy.
Can you get a mastectomy with a large breast?
For women with fairly large breasts, BCS may be an option if the cancer hasn’t grown into nearby tissues. SLNB may be an option for some patients, but most will need an ALND.
What is the treatment for breast cancer?
If you had breast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy), a local recurrence in the breast is usually treated with mastectomy.
How to treat breast cancer in the arm?
When breast cancer comes back in nearby lymph nodes (such as those under the arm or around the collar bone), it is treated by removing those lymph nodes, if possible. This may be followed by radiation aimed at the area. Systemic treatment (such as chemo, targeted therapy, or hormone therapy) may be considered after surgery as well.
What is the treatment for a recurrence of a tumor near the mastectomy site?
If the initial treatment was mastectomy, recurrence near the mastectomy site is treated by removing the tumor whenever possible . This is often followed by radiation therapy. In either case, hormone therapy, targeted therapy (like trastuzumab), chemotherapy, or some combination of these may be used after surgery and/or radiation therapy.
Is breast cancer hard to treat?
The only difference is that treatment may be affected by previous treatments a woman has had. Recurrent breast cancer can sometimes be hard to treat. If you are in otherwise good health, you might want to think about taking part in a clinical trial testing a newer treatment.
Can breast cancer come back after treatment?
Treatment of Recurrent Breast Cancer. For some women, breast cancer may come back after treatment – sometimes years later. This is called a recurrence. Recurrence can be local (in the same breast or in the surgery scar), regional (in nearby lymph nodes), or in a distant area.
How long can you delay breast cancer?
Delaying for a lengthy period of time can be dangerous, with studies finding that those who delay over six months are twice as likely to die from the disease. This is important to keep in mind for those who have breast lumps they are "observing" without a clear diagnosis. Any breast lump needs to be explained.
How soon after a diagnosis can you have surgery?
For women who are young (defined as 15 to 39), a 2013 study in JAMA Surgery suggested that young women should have surgery no more than six weeks after diagnosis and preferably earlier. This study of close to 9,000 women found 5-year survival rates as follows: 4
Can a mastectomie be done for breast cancer?
Newer procedures such as nipple-sparing/skin-sparing mastectomies are a great option for some women, but not all surgeons do these procedures. For young women with breast cancer, time to see a fertility specialist to talk about fertility preservation.
What is the most difficult decision to make with metastatic breast cancer?
One of the most difficult decisions people will have to face with metastatic breast cancer is when to stop treatment. This was not a problem until recently, as most people would reach a point when there were simply no further treatments available.
What are the concerns of dying at the end of life?
One common concern is about pain at the end of life. Many people are terribly frightened that dying will be painful. Others worry that using medication will hasten their death and wish to be as alert as possible. The best time to talk to your doctor is long before the issue arises. There are many options for pain control at the end of life, and the vast majority of people can be comfortable, even with dying at home. 5
What is the term for the fear of dying from cancer?
Anticipatory Grief . Many people with metastatic cancer—and their loved ones—experience grief similar to that associated with death and dying but while still living. This type of grief, called “anticipatory grief,” is common, but many people are afraid to express these feelings.
How to control pain at the end of life?
There are many options for pain control at the end of life, and the vast majority of people can be comfortable, even with dying at home. 5 . Talk to your family and your oncologist about your wishes. Some people wish to have as little pain as possible even if they will be drowsy.
Is metastatic breast cancer curable?
Many people mistakenly believe that metastatic breast cancer is curable. You may also want to begin by acknowledging the elephant in the room—you are still hoping that treatment holds your cancer at bay for many years but understand that this does not always happen. Take time to listen without interrupting.
Can you bring up end of life concerns?
There is no best way to bring up the end-of-life concerns , and what may work well for one family may not work for another. With that in mind, here are a few tips for how the patient can bring up the topic with her loved ones: Pick a time when nobody will feel rushed and won’t be bothered by distractions.
Is anticipatory grief more difficult to deal with than grief after a loss?
Anticipatory grief (also called preparatory grief) can be even more difficult to cope with than grief after a loss, not only because it may not feel socially acceptable to express this grief, but because it includes many losses. These can include a loss of your dreams, a loss of your role in the family, and much more.
What happens when cancer is no longer controlled?
When a cancer patient’s health care team determines that the cancer can no longer be controlled, medical testing and cancer treatment often stop. But the person’s care continues, with an emphasis on improving their quality of life and that of their loved ones, and making them comfortable for the following weeks or months.
What are the symptoms of end of life?
Medicines and treatments people receive at the end of life can control pain and other symptoms, such as constipation, nausea, and shortness of breath. Some people remain at home while receiving these treatments, whereas others enter a hospital or other facility.
How does a caregiver help a cancer patient?
The patient may have good days and bad days, so they may need more help with daily personal care and getting around. Caregivers can help patients save energy for the things that are most important to them. Appetite changes: As the body naturally shuts down, the person with cancer will often need and want less food.
Why is it important to have advance directives for cancer patients?
It’s important for people with cancer to have these decisions made before they become too sick to make them. However, if a person does become too sick before they have completed an advance directive, it’s helpful for family caregivers to know what type of care their loved one would want to receive.
Why do people with cancer lose appetite?
The loss of appetite is caused by the body’s need to conserve energy and its decreasing ability to use food and fluids properly. Patients should be allowed to choose whether and when to eat or drink.
How long before death can you use hospice?
Many people believe that hospice care is only appropriate in the last days or weeks of life. Yet Medicare states that it can be used as much as 6 months before death is anticipated. And those who have lost loved ones say that they wish they had called in hospice care sooner.
What happens when you have cancer?
Digestive system: If cancer is in the digestive system (e.g., stomach, pancreas, or colon), food or waste may not be able to pass through, causing bloating, nausea, or vomiting.
When does breast cancer recur?
Local recurrence usually happens within the first 5 years after you’ve been diagnosed. Distant recurrence is when breast cancer spreads to other organs. It goes beyond your breasts and nearby lymph nodes.
How to make breast cancer less likely to come back?
Here are treatments that may lower your risk of recurrence: Bone -building drugs may cut your risk of cancer coming back in your bones. Chemotherapy.
What is remission in cancer?
What Is Remission? Remission is when the signs and symptoms of cancer have gone down or gone away. If you had a tumor in your breast and it shrank from successful treatment, your cancer is in remission. Your doctor may also use the word response, which means the same thing. Remission doesn't mean you’re cured.
How to prevent HER2 recurrence?
Drug treatments that target the protein HER2 may lower your risk if your cancer makes extra HER2 protein. Lifestyle choices that help prevent a recurrence include: Eating healthy food like vegetables, fruits, and whole grains. Try to limit alcohol to no more than one drink a day. Getting regular exercise.
What is partial remission?
Partial remission is when your treatment reduced the cancer but didn’t make it go away completely. Doctors usually consider at least a 50% reduction in the size of a tumor to be partial remission. Another term for partial remission is partial response.
What is the difference between partial and complete remission?
If tests show your tumor is gone, or too small to see or measure, it means you’re in complete remission. Another term for complete remission is complete response. Partial remission is when your treatment reduced the cancer ...
How long does it take for a cancer patient to go into remission?
It’ll be based on your test results and how long it’s been since you’ve had signs or symptoms of cancer. It has to be a month or longer to be considered in remission.