How do you cure AIDS?
In 1983, scientists discovered the virus that causes AIDS. They later named it human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). The race was on for a treatment to …
When did AIDS first appear?
Sep 27, 2021 · Zidovudine, commonly known as AZT, was introduced in 1987 as the first treatment for HIV. Scientists also developed treatments to reduce transmission during pregnancy. In 1995, President Bill...
What is the newest HIV drug?
Jan 10, 2022 · At the end of 1986 and the beginning of 1987, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) administered a clinical trial of Azidothymidine (AZT), the first drug to prove effective against the rapidly replicating HIV virus.
How did AIDS start in America?
The first known case of HIV in a human occurs in a man who died in the Congo, later confirmed as having HIV infection (from his preserved blood samples).; June 28, in New York City, Ardouin Antonio, a 49-year-old Haitian shipping clerk dies of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia, a disease closely associated with AIDS. Gordon Hennigar, who performed the postmortem examination …
How long did it take to find treatment for HIV?
Who discovered treatment for HIV?
When was the first HIV case reported?
The HIV.gov Timeline reflects the history of the domestic HIV/AIDS epidemic from the first reported cases in 1981 to the present—where advances in HIV prevention, care, and treatment offer hope for a long, healthy life to people who are living with, or at risk for, HIV and AIDS.
Where is the first HIV clinic in the world?
January 1: Ward 86 , the world’s first dedicated outpatient AIDS clinic, opens at San Francisco General Hospital. The clinic is a collaboration between the hospital and the University of California, San Francisco, and it draws staff who are passionate about treating people with AIDS. Over time, the staff develop the San Francisco Model of Care , which emphasizes: treating patients with compassion and respect; providing an array of health and social services in one facility; and collaborating closely with the local health department and community organizations. The model eventually becomes the global gold standard for HIV patient care.
What is the FDA approved drug for AIDS?
On October 26, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approves use of zidovudine (AZT) for pediatric AIDS.
What is the President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief?
PEPFAR is a $15 billion, 5-year plan to combat AIDS, primarily in countries with a high burden of infections.
Where is Ward 86?
January 1: Ward 86 , the world’s first dedicated outpatient AIDS clinic, opens at San Francisco General Hospital . The clinic is a collaboration between the hospital and the University of California, San Francisco, and it draws staff who are passionate about treating people with AIDS.
Who is Ryan White?
March 3: Ryan White, the Indiana teenager who has become a national spokesperson for AIDS education, testifies about the stigma he has endured as a result of having AIDS before the President’s Commission on AIDS .
What is the red ribbon project?
The Visual AIDS Artists Caucus launches the Red Ribbon Project to create a visual symbol to demonstrate compassion for people living with AIDS and their caregivers. The red ribbon becomes the international symbol of AIDS awareness.
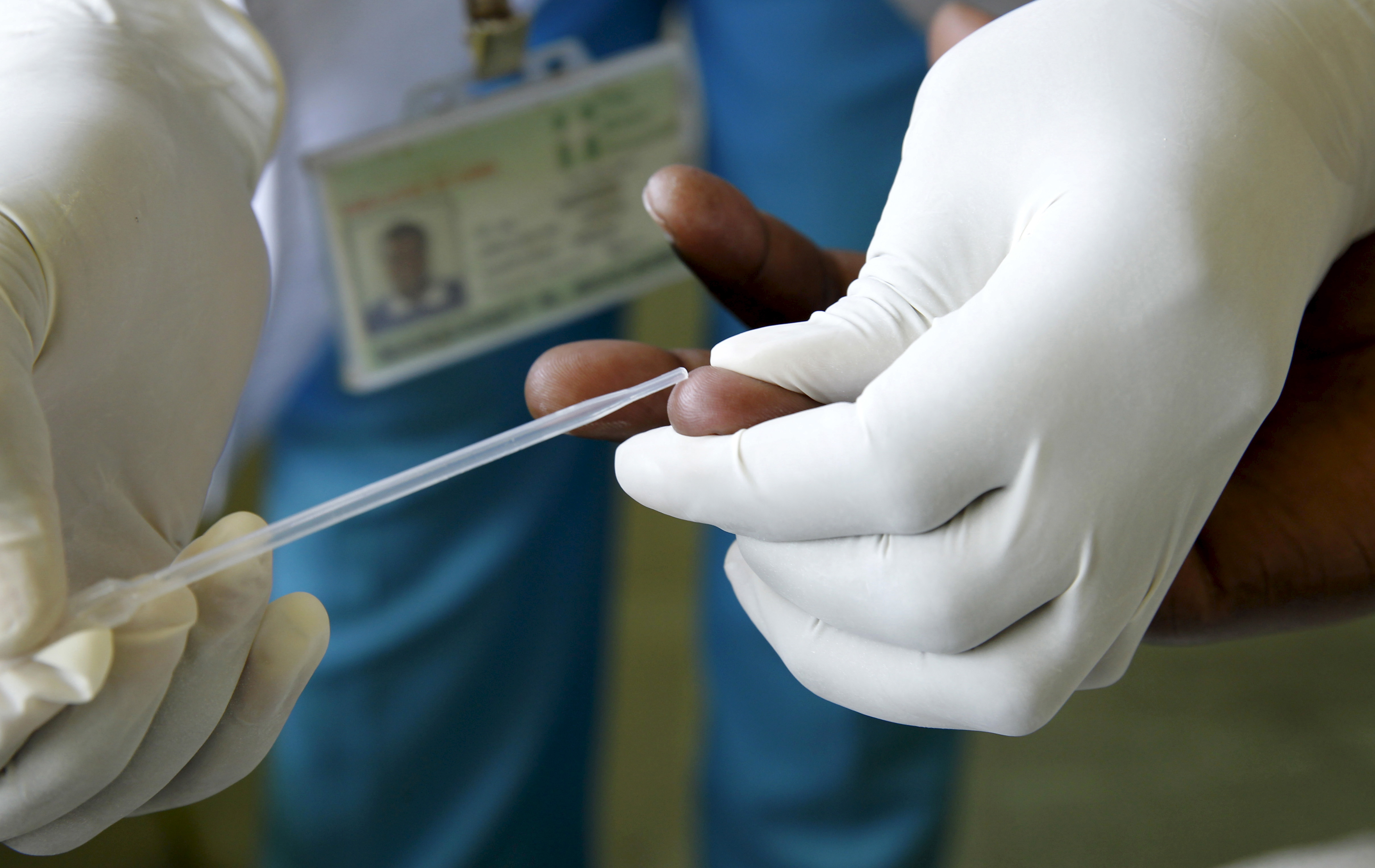
When was the first HIV test approved?
It caused a 47 percent decline in death rates. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first rapid HIV diagnostic test kit in November 2002.
Who was the first person to have AIDS?
Actor Rock Hudson was the first major public figure to acknowledge he had AIDS. After he died in 1985, he left $250,000 to set up an AIDS foundation. Elizabeth Taylor was the national chairperson until her death in 2011. Princess Diana also made international headlines after she shook hands with someone with HIV.
Is HIV the same as AIDS?
HIV is the same virus that can lead to AIDS ( acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). Researchers found the earliest case of HIV in a blood sample of a man from the Democratic Republic of Congo.
How many people died from AIDS in 1995?
By 1995, complications from AIDS was the leading cause of death for adults 25 to 44 years old. About 50,000 Americans died of AIDS-related causes.
When was zidovudine first used?
The development of research, treatment, and prevention. Azidothymidine, also known as zidovudine, was introduced in 1987 as the first treatment for HIV. Scientists also developed treatments to reduce mother to child transmission. In 1997, highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) became the new treatment standard.
Can HIV be transmitted during sex?
Trusted Source. that a person living with HIV who is on regular antiretroviral therapy that reduces the virus to undetectable levels in the blood is NOT able to transmit HIV to a partner during sex. The current consensus among medical professionals is that “undetectable = untransmittable.”. Share on Pinterest.
When was PrEP approved?
In July 2012, the FDA approved pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP). PrEP is a medication shown to lower the risk of contracting HIV from sexual activity or needle use. The treatment requires taking the medication on a daily basis.
What is combination therapy for HIV?
The introduction of antiviral medications used in combination is among the most important advances in the history of HIV/AIDS treatment. By using more than one drug at a time, combination therapy is able to "pin down" HIV from more than one angle, so that even if one drug fails, another can continue to suppress viral replication. But this advance was a long time in the making, following a historical course from "no therapy" to "monotherapy" and now to "combination therapy." This book excerpt provides a historical overview of advances in the monitoring of treatment progress and the emergence of combination therapy.
Is HIV eradicated?
In particular, the complete elimination, or "eradication," of HIV from an infected individual has never been achieved, and perhaps may never be achieved because HIV has the capacity to remain dormant in certain cells and also to infect difficult-to-reach cells in the central nervous system and other parts of the body.
What are the targets of HIV?
Transmitted from person to person primarily through blood, semen, and vaginal secretions, HIV's principal targets are the very cells of the immune system (particularly CD4+ t-cells and macrophages) which are intended to clear foreign pathogens from the body.
What is ZDV used for?
Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first antiviral drug zidovudine (ZDV; AZT) for use in preventing HIV replication by inhibiting the activity of the reverse transcriptase enzyme. AZT is part of a class of drugs formally known as nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase inhibitors.
What is the purpose of Zidovudine?
Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first antiviral drug zidovudine (ZDV; AZT) for use in preventing HIV replication by inhibiting the activity of the reverse transcriptase enzyme. AZT is part of a class of drugs formally known as nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase inhibitors. After 1991, several other nucleoside analogs were added to the anti-HIV arsenal, as were a new class of anti-HIV drugs called the non-nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase inhibitors which work in similar ways to the nucleoside analogs but which are more quickly activated once inside the bloodstream. Next to be developed were the class of antiviral drugs known as protease inhibitors, which were distinctly different from the reverse transcriptase inhibitors in that they do not seek to prevent infection of a host cell, but rather to prevent an already infected cell from producing more copies of HIV.
How does drug resistance affect treatment?
Drug resistance can seriously complicate treatment by rendering drugs less effective or even completely ineffective. Further, once an organism has developed resistance to one drug, it can also become resistant to other drugs in the same class (cross-resistance) or to a number of different drugs (multidrug resistance).
How many cases of HIV/AIDS were there in 1993?
By 1993, over 2.5 million cases of HIV/AIDS had been confirmed worldwide. By 1995, AIDS was the leading cause of death for Americans age 25 to 44. Elsewhere, new cases of AIDS were stacking up in Russia, Ukraine, and other parts of Eastern Europe. Vietnam, Cambodia and China also reported steady increases in cases. The UN estimated that in 1996 alone, 3 million new infections were recorded in patients under age 25.
How many people have HIV?
When HIV first began infecting humans in the 1970s, scientists were unaware of its existence. Now, more than 35 million people across the globe live with HIV/AIDS. The medical community, politicians and support organizations have made incredible progress in the fight against this formerly unknown and heavily stigmatized virus.
When did Kaposi's sarcoma start?
Beginning in the early 1980s, new and unusual diagnostic patterns began to emerge in different parts of the world. A benign, fairly harmless cancer called Kaposi's Sarcoma, common among the elderly, started appearing as a virulent strain in younger patients.
Is HIV a contagious disease?
Particularly in its earlier years, HIV was only understood to be viral, deadly, and highly contagious via unknown means. These variables led to considerable panic on the part of professionals and laypeople alike. Fear fueled prejudice of populations perceived to be at the highest risk for HIV infection.
Where does HIV occur in the world?
Even today, over 97 percent of the world's HIV-infected population lives in Africa. While HIV and AIDS had been noted in sexually active heterosexual groups in central African countries from the earliest days of the epidemic, popular opinion that HIV was largely contained to gay communities endured well into the 2000s.
What was the leading cause of death in 1995?
By 1995, AIDS was the leading cause of death for Americans age 25 to 44. Elsewhere, new cases of AIDS were stacking up in Russia, Ukraine, and other parts of Eastern Europe. Vietnam, Cambodia and China also reported steady increases in cases.
What caused the pneumocystis epidemic?
The epidemics spread likely due to infected glass syringes and needles. Malnutrition was not considered a cause, especially because the epidemics were at their height in the 1950s. At that time war torn Europe had already recovered from devastation. Researchers state that the most likely cause was a retrovirus closely related to HIV (or a mild version of HIV) brought to Europe and originating from Cameroon, a former German colony. The epidemic started in the Free City of Danzig in 1939 and then spread to nearby countries in the 1940s and 1950s, like Switzerland and The Netherlands.
Where did HIV-1 come from?
Genetic studies of the virus indicate that HIV-1 (M) first arrived in the Americas in the late 1960s likely in Haiti or another Caribbean island.
What is AIDS case?
September 24, The CDC defines a case of AIDS as a disease, at least moderately predictive of a defect in cell-mediated immunity, occurring in a person with no known cause for diminished resistance to that disease. Such diseases include KS, PCP, and serious OI.
Who discovered the cause of AIDS?
April 23, U.S. Health and Human Services Secretary Margaret Heckler announces at a press conference that an American scientist, Robert Gallo, has discovered the probable cause of AIDS: the retrovirus is subsequently named human immunodeficiency virus or HIV in 1986.
What is the first test to detect HIV?
March 2, the FDA approves an ELISA test as the first commercially available test for detecting HIV in blood. It detects antibodies which the body makes in response to exposure to HIV and is first intended for use on all donated blood and plasma intended for transfusion and product manufacture.
Who played Ryan White's sister in the movie?
The television movie The Ryan White Story airs. It stars Judith Light as Jeanne, Lukas Haas as Ryan and Nikki Cox as sister Andrea. Ryan White had a small cameo appearance as Chad, a young patient with AIDS. Another AIDS-themed film, The Littlest Victims, debuted in 1989, biopicing James Oleske, the first U.S. physician to discover AIDS in newborns during AIDS' early years, when many thought it was only spread through male-to-male sexual activity.
What is the name of the AIDS trial in France?
April, the Pediatric AIDS Clinical Trials Group (ACTG) of the US NIAID and the National Institute of Health and Medical Research (INSERM) and the National Agency of Research on AIDS (ANRS), France start the famous clinical trial of zidovudine (AZT) in HIV-infected pregnant women named "ACTG protocol 076 ". The trial shows such a big reduction in the risk for HIV transmission to the infant that it was halted prematurely in 1993 and later became the standard of care.
Why did HIV emerge?
In several articles published since 2001, Preston Marx, Philip Alcabes, and Ernest Drucker proposed that HIV emerged because of rapid serial human-to-human transmission of SIV (after a bushmeat hunter or handler became SIV-infected) through unsafe or unsterile injections.
What is the color of HIV-1?
False-color scanning electron micrograph of HIV-1, in green, budding from cultured lymphocyte. AIDS is caused by a human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), which originated in non-human primates in Central and West Africa.
Where does HIV-1 live?
The pandemic strain of HIV-1 is closely related to a virus found in chimpanzees of the subspecies Pan troglodytes troglodytes, which live in the forests of the Central African nations of Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, the Republic of the Congo (or Congo-Brazzaville), and the Central African Republic.
Where is HIV-2 transmitted?
HIV-2 is less transmittable and is largely confined to West Africa, along with its closest relative, a virus of the sooty mangabey ( Cercocebus atys atys ), an Old World monkey inhabiting southern Senegal, Guinea-Bissau, Guinea, Sierra Leone, Liberia, and western Ivory Coast.
Is HIV a zoonosis?
The majority of HIV researchers agree that HIV evolved at some point from the closely related simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV), and that SIV or HIV (post mutation) was transferred from non-human primates to humans in the recent past (as a type of zoonosis ).
Is HIV related to SIV?
In particular, each of the known HIV-1 strains is either closely related to the SIV that infects the chimpanzee subspecies Pan troglodytes troglodytes (SIVcpz) or closely related to the SIV that infects western lowland gorillas ( Gorilla gorilla gorilla ), called SIVgor.
Where are SIVsmm found?
Similar research has been undertaken with SIV strains collected from several wild sooty mangabey ( Cercocebus atys atys) (SIVsmm) populations of the West African nations of Sierra Leone, Liberia, and Ivory Coast. The resulting phylogenetic analyses show that the viruses most closely related to the two strains of HIV-2 that spread considerably in humans (HIV-2 groups A and B) are the SIVsmm found in the sooty mangabeys of the Tai forest, in western Ivory Coast.
When was AZT approved?
In a randomized trial, it was subsequently shown to improve survival of AIDS patients. In 1987, it became the first drug approved by the U.S. FDA for treatment of the disease. AZT was subsequently shown to markedly reduce the perinatal transmission of HIV.
Is AZT effective for AIDS?
Because AZT was not entirely effective by itself, NCI scientists continued to develop and test other drugs to treat AIDS, including the reverse transcriptase inhibitors didanosine (ddI) and zalcitabine (ddC). These became the second and third drugs approved by the FDA for AIDS. Combining AZT with one of these drugs improved the effectiveness ...
When was the first HIV test done?
In 1984, researchers finally identified the cause of AIDS—the HIV virus—and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) licensed the first commercial blood test for HIV in 1985. Today, numerous tests can detect HIV, most of which work by detecting HIV antibodies.
When was the first blood test for HIV?
In 1984, researchers finally identified the cause of AIDS—the HIV virus—and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) licensed the first commercial blood test for HIV in 1985. Today, numerous tests can detect HIV, most of which work by detecting HIV antibodies.
When was AZT developed?
AZT is Developed. HIV/AIDS in the 1990s and 2000s. HIV Treatment Progresses. Sources: In the 1980s and early 1990s, the outbreak of HIV and AIDS swept across the United States and rest of the world, though the disease originated decades earlier. Today, more than 70 million people have been infected with HIV and about 35 million have died ...
Can HIV cause cancer?
Over time, HIV can destroy so many CD4 cells that the body can’t fight infections and diseases, eventually leading to the most severe form of an HIV infection: acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, or AIDS. A person with AIDS is very vulnerable to cancer and to life-threatening infections, such as pneumonia.
Is there a cure for HIV?
A person with AIDS is very vulnerable to cancer and to life-threatening infections, such as pneumonia. Though there is no cure for HIV or AID S, a person with HIV who receives treatment early can live nearly as long as someone without the virus.
Can HIV be treated early?
Though there is no cure for HIV or AIDS, a person with HIV who receives treatment early can live nearly as long as someone without the virus. And a study in 2019 in the medical journal, Lancet, showed that an anti-viral treatment effectively halted the spread of HIV.
When did the CDC start describing AIDS?
In September of 1982 , the CDC used the term AIDS to describe the disease for the first time. By the end of the year, AIDS cases were also reported in a number of European countries. READ MORE: Pandemics that Changed History. 10.
in The Beginning
from Monotherapy to Combination Therapy
- In 1986 the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first antiviral drug zidovudine (ZDV; AZT) for use in preventing HIV replication by inhibiting the activity of the reverse transcriptase enzyme. AZT is part of a class of drugs formally known as nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase inhibitors. After 1991, several other nucleoside a...
Still Not A Cure
- In all, the simultaneous treatment of people with HIV with different classes of antiviral drugs is among the most significant scientific advances in the history of the AIDS epidemic. Five years after its widespread use, combination antiviral therapy has demonstrated enormous potential, eliminating early fears that it would prove to be yet another dead-end in the treatment of HIV infe…
The Post-Vancouver State of Combination Treatment
- Overall, for people living with HIV disease, as well as professionals working with them, the news about the effectiveness of combination therapies that emerged in 1996, particularly from that year's International AIDS conference in Vancouver, was heartening but also confusing. During and after the conference, mainstream media reporting made it seem as if a total cure had been disc…
References
- Kaposi's Sarcoma and Pneumocystis Pneumonia Among Homosexual Men -- New York and California. MMWR30(25): 305-307, July 3, 1981.
- Horn, T. (1998). "Drug Resistance." In the Encyclopedia of AIDS: A Social, Political, Cultural, and Scientific Record of the HIV Epidemic. Ed., Raymond A. Smith. Chicago: Fitzroy Dearborn Publisher...
- Kaposi's Sarcoma and Pneumocystis Pneumonia Among Homosexual Men -- New York and California. MMWR30(25): 305-307, July 3, 1981.
- Horn, T. (1998). "Drug Resistance." In the Encyclopedia of AIDS: A Social, Political, Cultural, and Scientific Record of the HIV Epidemic. Ed., Raymond A. Smith. Chicago: Fitzroy Dearborn Publisher...
- Manos, T. Negron and Horn. (1998) "Antiviral Drugs." In the Encyclopedia of AIDS: A Social, Political, Cultural, and Scientific Record of the HIV Epidemic. Ed., Raymond A. Smith. Chicago: Fitzroy D...
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (February 28, 1997). 1996 HIV/AIDS trends provide evidence of success in HIV prevention and treatment: AIDS deaths decline for the first time. …