
How many people died from AZT treatment?
Of them, 145 people were given AZT and 137 the placebo for a total of 24 weeks. In the end, only 27 subjects had completed the full course of the study (others ended at 16 and eight weeks) after 19 placebo recipients and one AZT recipient died during the study.
How many died from AZT?
The Fraudulent Dr Fauci – Part I: The AIDS Racket
- Dangerous leap into the ARV unknown: “Test-and-Treat”. By the latter years of the first decade of the 21st Century, Dr. ...
- AZT – The DNA Terminator. “ Toxic by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed. ...
- Toxic drugs for HIV negatives. In HIV research-gone-wild, Dr. ...
- Fauci’s “Guinea Pig Kids”. ...
- Taking the Show to the Third World – The (PrEP) Trials. ...
Did people die from AZT?
One time in the 80’s-90’s, people died from AZT and not the actual AIDS virus; Anthony Fauci pushed this treatment VERDICT more about the rating framework SOURCE: Facebook users, Facebook, 25 aug. 2021 DETAILS Unsupported: Zidovudine, or AZT, was the first HIV drug approved by the U.S. FDA in 1987.
What is the best medicine for HIV?
Medications used to treat HIV are called antiretrovirals (also referred to as ART or ARV). Most people with HIV take combination ART every day. ART also reduces the risk of HIV transmission. Approved ARV treatments are grouped into seven drug classes as follows: Integrase strand transfer inhibitors (INSTIs).
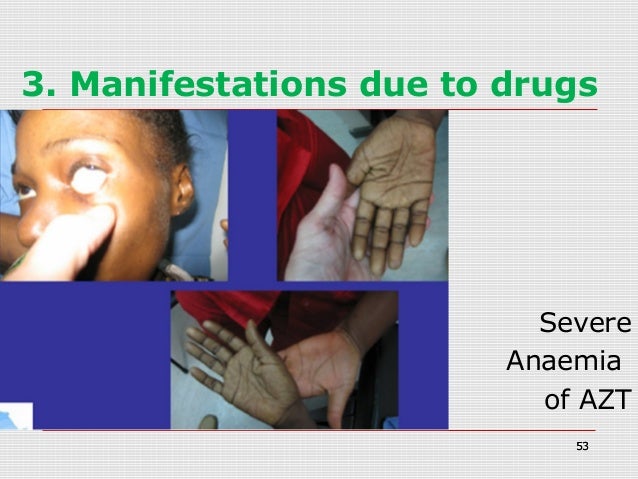
Do they still treat HIV with AZT?
AZT is still one of the most prescribed drugs in the world for HIV treatment due to this heavy use in LMICs.
How many deaths were caused by AZT?
Bartlett said, there have been 205 deaths. She noted, however, that the number of deaths in patients treated with AZT for at least 21 days was only 78, suggesting that the drug has been successful in prolonging many patients' lives.
Why is AZT toxic to humans?
Our findings suggest that incorporation of AZT into human nuclear and mitochondrial DNA has the potential to promote genetic instability and toxicity through the production of ssDNA gaps and dsDNA breaks, and predicts that the human Exonuclease III ortholog, APE1, will be important for drug tolerance.
How has HIV treatment changed over the years?
Treatment of HIV has evolved from gruelling regimens with high pill burden, inconvenient dosing, treatment-limiting toxicities, food and drug interactions, incomplete viral suppression and emergence of drug resistance to manageable one or two pill once daily regimens that can be initiated in early HIV disease and ...
What are the side effects of AZT?
Common side effects that have been reported by some AZT users include headaches, nausea, vomiting, insomnia, tiredness, muscle pain, and loss of appetite. Many people find that side effects caused by anti-HIV drugs improve or go away after the first several weeks of treatment.
How long was AZT used?
This type of medicine stops the reproduction of DNA and reduces the amount of the virus in the blood (the viral load). AZT was approved by the FDA on March 19, 1987. It was approved in record time with only one trial on humans instead of the standard three and that trial was stopped after nineteen weeks.
Is Dallas Buyers Club based on a true story?
The film is based on the real life of Ron Woodroof, a patient of HIV and AIDS, who was the subject of a lengthy 1992 article in The Dallas Morning News written by journalist and author Bill Minutaglio.
How toxic is AZT?
The toxic effects of AZT, particularly bone marrow suppression and anemia, are so severe that up to 50 percent of all AIDS and ARC patients cannot tolerate it and have to be taken off it.
Is AZT FDA approved?
AZT (zidovudine) In March of 1987, FDA approved zidovudine (AZT) as the first antiretroviral drug for the treatment of AIDS.
How much does AZT cost?
Yet there's a massive obstacle to wider use of this life-saving drug - its extraordinary cost. At $8,000 a year for users, AZT is said to be the most expensive prescription drug in history. Some 35 percent of AIDS patients have either no health insurance or policies that do not pay for drugs.
What is an AZT drug?
AZT: an old drug with new perspectives. The science of antiviral research was well advanced when HIV/AIDS appeared as a major new virus disease in the early 1980s. The first effective antiviral compound (AZT, azidothymidine, zidovudine) was already among the library of compounds screened and was promptly reported to be a specific inhibito ….
What is the first antiviral drug?
The first effective antiviral compound (AZT, azidothymidine, zidovudine) was already among the library of compounds screened and was promptly reported to be a specific inhibitor of retroviruses, including HIV.
Is Azt still used for HIV?
Due to the pivotal role of AZT in HIV treatment, this review summarizes the most known effects -some of which are toxic side effects- induced by AZT a drug which is still used in the combined therapy of HIV-infected patients.
What is AZT treatment?
AZT served has since been called the “prototype” for AIDS treatment and is considered a “first step” in the AIDS response, establishing standards and an understanding of viral suppression.
What was the first drug approved by the FDA to treat AIDS?
AZT was the first drug approved by the FDA to treat AIDS. Public Domain
What was Fauci's treatment called?
In September, memes shared widely on Facebook and sent to our staff claimed that at the beginning of his career — which coincided with the onset of the AIDS epidemic — Fauci promoted a controversial treatment called azidothymidine, commonly known as AZT. To discredit the doctor, one such meme claimed that more people died from AZT than did from HIV, the virus that causes the immunodeficient disease.
What did Guccione say about AIDS?
The 1989 article, Guccione continued, “unearthed hard evidence of the cold-bloodedness of the AIDS establishment pushing a drug that was worse than the disease, and killed faster than the natural progression of AIDS left untreated” — both claims that are erroneous. Among other assertations, the article argued that thousands had been “walloped” with high doses of AZT and “possibly even died of toxic poisoning.”
When was the first AZT article written?
But the original article was written in 1989, and in the decades that followed, researchers would deepen their understanding of proper dosing requirements for AZT and how it could be used in combination with other therapies to effectively treat AIDS.
How many deaths were caused by AZT?
It is unknown how many — if any — deaths resulted directly from patients being treated with AZT, as early testing was not always standardized to account for various other experimental and approved treatments, as well as from infection by HIV or other secondary illnesses.
How many drugs are there for AIDS in 2021?
In 2021, there are more than 30 drugs designed to block viral replication at different stages of its life cycle — one such being Retrovir, the market name for AZT. A CDC report analyzing reported AIDS cases from the first reported case in the U.S. in June 1981 to Dec. 31, 2000, showed that 774,467 people had been diagnosed with AIDS in the U.S. Of those, 448,060 had died.
What drug stopped HIV from multiplying?
Also called azidothymidine (AZT), the medication became available in 1987.
What is the problem with AZT?
A big problem with a single-drug treatment like AZT is that viruses learn to change, or mutate, so the drugs over time stop working. In 1995, the FDA approved saquinavir, the first in a different anti-HIV (antiretroviral) drug class called protease inhibitors.
What is the name of the drug that is used to treat HIV/AIDS?
These drugs paved the way to a new era of combination therapy for HIV/AIDS. Doctors began prescribing saquinavir plus AZT or other antiretrovirals. This combination therapy was dubbed highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). That approach became the new standard of care for HIV in 1996. HAART greatly lengthened the life span of people with AIDS.
What is the name of the drug that shuts down HIV?
Similar to AZT, NNRTIs shut down HIV by targeting the enzymes it needs to multiply. These drugs paved the way to a new era of combination therapy for HIV/AIDS.
How many HIV medications are there?
Today, more than 30 HIV medications are available. Many people are able to control their HIV with just one pill a day. Early treatment with antiretrovirals can prevent HIV-positive people from getting AIDS and the diseases it causes, like cancer.
How long does it take for AZT to be approved?
The FDA approved AZT in less than 4 months, fast-tracking a process that usually takes many years. It treats HIV, but it isn’t a cure.
How much is AZT?
AZT also at the time was the most expensive prescription drug in history, with a one-year price tag of $16,500 in today’s dollars. Over the next several years, the FDA approved several other drugs that worked similarly to AZT. They belonged to a drug class called nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs).
The first cases of AIDS
The New York Times was the first newspaper to report a new syndrome, seen in the homosexual communities of San Francisco and New York, on 3rd July 1981. Previously healthy men, some only in their 20s were suffering from rare diseases usually only seen in the elderly, such as the rare cancer: Kaposi’s sarcoma.
The identification of a virus
In January 1984 research was published which linked a number of cases of AIDS, and suggested that the disease was sexually transmitted.
The search for a treament
Once it was known that AIDS was caused by a human retrovirus, the search for drug-treatments began. The viral enzyme reverse transcriptase, is used by retroviruses use to construct DNA from their viral RNA once they have infected a cell. Humans and other mammals do not make this enzyme, making it an obvious drug target.
How long does it take for HIV to rebound?
According to a published study, 9 of 10 people with HIV viral load levels below 100 copies/106 cells had a rebound within 12 weeks after ARV interruption. The 10th person maintained low HIV viral load level without drugs for more than 48 weeks.
How many people can get HIV from a syringe?
According to the CDC, the estimated chance of contracting HIV from sharing a syringe once with somebody who is already infected is 0.63%, or a bit less than 1 in 100. HIV is not nearly as contagious as most people think it is.
Does ARVs lower viral load?
The longer a patient taking ARVs maintains an undetectable viral load, the lower their risk of viral load rebound.
Is AZT a good treatment?
No. AZT is not an effective treatment.
Does HIV make you immune?
It does not make you necessarily “immune” to the virus as yes there is a resistant strand out there - so far only a select few. It is suggested that someone that does not fit the category of getting HIV, they will not be prescribed it.
Is rilpivarine a reverse transcriptase inhibitor?
However, there is a new regimen on the horizon made up of cabotegravir, an integrase inhibitor, and rilpivarine, a non-nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor, which should soon be available in injectable form. The big difference is that these shots, which incidentally are intramuscular rather than subcutaneous, need to be administered only once every few weeks.
Can HIV cause drug resistance?
The short answer is yes. The HIV virus very easily creates mutations. Not all these mutations lead to drug resistance, but some do. The International Aids Society publishes annually a list of mutations that defeat the action of the antiretroviral drugs that patients need to suppress the virus. New mutations enter the list every year. On the good side, there is a constant development of new formulations that become available that can be used to replace an antiretroviral that no longer works. The only way we have so far of finding out which mutations each patient has is to genotype their virus,
