How did they cure TB in the 1950s?
In 1943 Selman Waksman discovered a compound that acted against M. tuberculosis, called streptomycin. The compound was first given to a human patient in November 1949 and the patient was cured.Feb 1, 2013
How was TB treated in the 1960s?
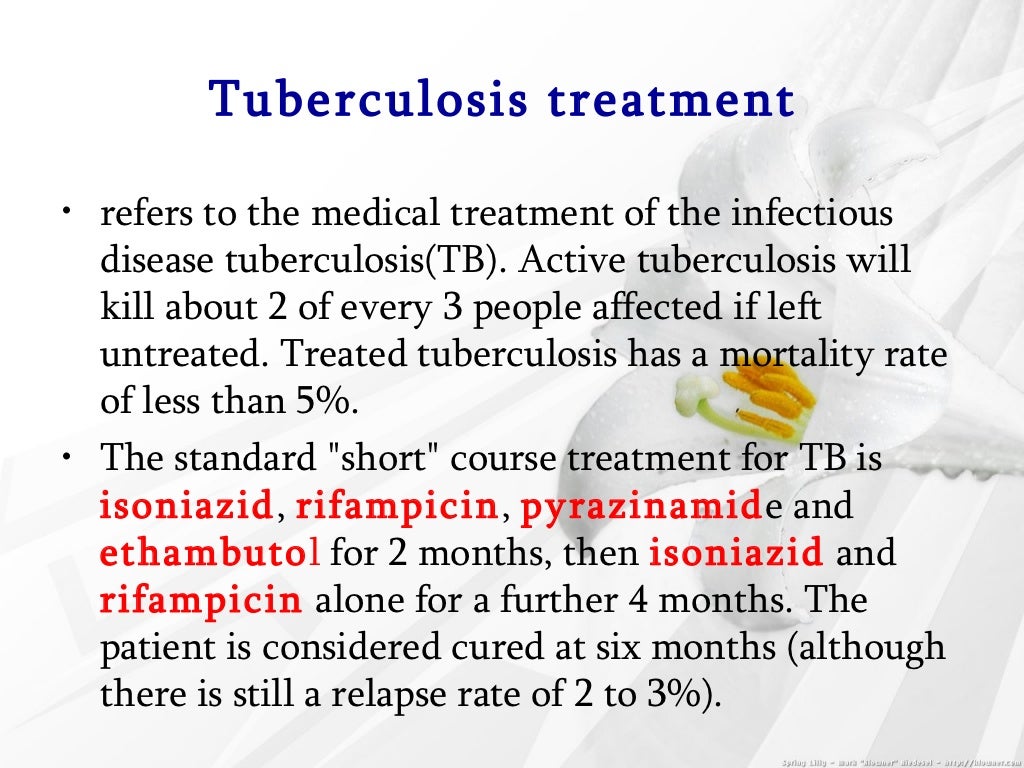
In the mid-1960s, modern 'short-course therapy' was introduced, using the newly available Rifampicin and the reintroduced Pyrazinamide – an old, toxic medication that was given a new ability to treat TB under the combined therapy model.
How was TB treated in the 1940's?
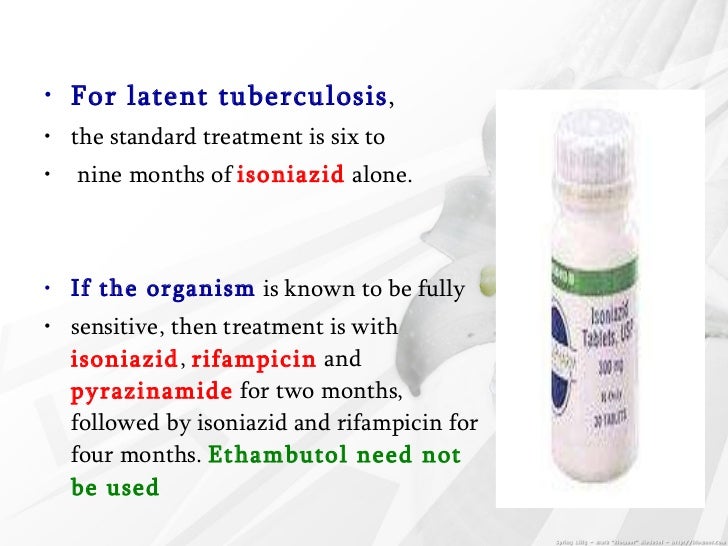
Rifampin combined with isoniazid and ethambutol enabled therapy to be shortened to 9 months and led to improved cure rates (35). Pyrazinamide was discovered in the late 1940s, based on the observation that nicotinamide had activity against M. tuberculosis in animal models.Sep 23, 2015
How was TB treated in the 1920s?
Artificial pneumothorax and thoracoplasty for 'collapse therapy' In the 1920s and 1930s, following trends in Germany and America, collapse therapy was a popular method of treating pulmonary tuberculosis in Britain. The intention was to collapse the infected lung, allowing it to rest and heal.
How was tuberculosis treated in 1900s?
There was no reliable treatment for tuberculosis. Some physicians prescribed bleedings and purgings, but most often, doctors simply advised their patients to rest, eat well, and exercise outdoors.
How was TB treated in the 1970s?
In the 1970s, rifampin found its place as a keystone in the therapy of tuberculosis. The use of rifampin enabled the course of treatment to be reduced to nine months. Incorporation of pyrazinamide into the first-line regimen led to a further reduction of treatment duration to six months.
Why did fresh air help tuberculosis?
Although their beliefs about TB were not entirely medically sound, they were kind of right in this regard: Fresh air does prevent TB from spreading, and the high altitude stops TB bacteria from spreading as rapidly through the lungs.Oct 4, 2017
Why were TB patients kept cold?
The rationale for sanatoria in the pre-antibiotic era was that a regimen of rest and good nutrition offered the best chance that the sufferer's immune system would "wall off" pockets of pulmonary TB infection.
Why did tuberculosis patients go to sanatoriums?
Tuberculosis sanatoriums offered patients fresh air, entertainment, and socialization—for those who could afford them. When Ruth Reed fell ill, she left behind her home, her job as a teacher, and her husband and young son to enter a contained medical facility.Mar 21, 2020
Is TB a pandemic?
Tuberculosis deaths rise for the first time in more than a decade due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The COVID-19 pandemic has reversed years of global progress in tackling tuberculosis and for the first time in over a decade, TB deaths have increased, according to the World Health Organization's 2021 Global TB report.Oct 14, 2021
When was the last tuberculosis outbreak?
TB Incidence in the United States, 1953-2020 TB Cases and Case Rates per 100,000 PopulationYearNumber of CasesRate20179,0712.820169,2422.920159,536320149,3832.964 more rows
How long did the tuberculosis epidemic last?
Although relatively little is known about its frequency before the 19th century, its incidence is thought to have peaked between the end of the 18th century and the end of the 19th century.
How long does it take to treat TB?
TB disease can be treated by taking several drugs for 6 to 9 months. There are 10 drugs currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating TB. Of the approved drugs, the first-line anti-TB agents that form the core of treatment regimens are: isoniazid (INH) rifampin (RIF)
What is it called when TB bacteria multiply?
When TB bacteria become active (multiplying in the body) and the immune system can’t stop the bacteria from growing, this is called TB disease. TB disease will make a person sick. People with TB disease may spread the bacteria to people with whom they spend many hours.
What is XDR TB?
Extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR TB) is a rare type of MDR TB that is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, plus any fluoroquinolone and at least one of three injectable second-line drugs (i.e., amikacin, kanamycin, or capreomycin). Treating and curing drug-resistant TB is complicated.
Can TB be treated?
It is very important that people who have TB disease are treated, finish the medicine, and take the drugs exactly as prescribed. If they stop taking the drugs too soon, they can become sick again; if they do not take the drugs correctly, the TB bacteria that are still alive may become resistant to those drugs.
How long has triple therapy been used for tuberculosis?
All together, “triple therapy” remained the standard treatment for all forms of tuberculosis for nearly 15 years ( 21 ). Despite these successes, side effects, drug resistance, and the large numbers of affected people drove further drug development exploration.
What was the first step in finding a cure for tuberculosis?
The first step in finding a cure was the discovery of the cause of tuberculosis by Robert Koch in 1882.
How long does pyrazinamide treatment last?
Incorporation of pyrazinamide into the first-line regimen led to a further reduction of treatment duration to six months. Treatment of multiple drug–resistant tuberculosis remains a difficult problem requiring lengthy treatment with toxic drugs.
Is isoniazid safe for tuberculosis?
In 1952, isoniazid opened the modern era of treatment; it was inexpensive, well tolerated, and safe. In the early 1960s, ethambutol was shown to be effective and better tolerated than para -aminosalicylic acid, which it replaced. In the 1970s, rifampin found its place as a keystone in the therapy of tuberculosis.
When was streptomycin discovered?
The discovery of streptomycin brought about a great flurry of drug discovery research that lasted from the 1940s through the 1960s. As the decline in tuberculosis case rates became steeper, the awareness of the public waned. The war on tuberculosis was considered winnable with the tools at hand ( 43 ).
When did tuberculosis recur?
Decreased attention to tuberculosis control and poor public health infrastructure worldwide led to a resurgence of tuberculosis in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Between 1985 and 1992, tuberculosis cases increased by about 20% in the United States.
Who was the first person to demonstrate the bacterial cause of tuberculosis?
Koch was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1905 for this achievement ( Figure 1 ). Figure 1. Robert Koch demonstrated the bacterial cause of tuberculosis in 1884.
What was the name of the drug that was used to treat TB?
Gerhard Domagk's research, which led to the discovery of sulfonamides in the 1930s, eventuated in the discovery of the anti‐TB activity isonicotinic acid hydrazide (INH) in 1952. Adding INH to PAS and SM (“triple therapy”) resulted in predictable cures for 90–95% of patients, the Holy Grail.
How long does it take to cure TB?
Although the usual case of drug-susceptible TB can be predictably cured in 6 months with a reasonably nontoxic, economical regimen involving as few as 62–78 encounters, novel methodologies must be established if TB is going to be controlled in the decades ahead.
What are the major historical landmarks of tuberculosis?
Abstract. The major historical landmarks of tuberculosis (TB) therapy include: the discovery of effective medications (streptomycin and para-aminosalicylic acid) in 1944; the revelation of “triple therapy” (streptomycin, para-aminosalicylic acid and isoniazid) in 1952, which assured cure; recognition in the 1970s that isoniazid ...
Who described the treatment of TB in England as a huge commercial system of quackery and poison?
At the turn of the 20th century, George Bernard Shaw, via one of the characters in his play “A Doctor's Dilemma”, described the medical treatment of TB in England as “a huge commercial system of quackery and poison”.
What is the Alchemist's Dream of Tuberculosis?
Finally, the Alchemist's Dream of tuberculosis should be pursued: modulating the immune response to shorten treatment and/or overcome drug resistance. It is difficult to discuss tuberculosis (TB) therapy, present and future, without reviewing the history of the treatment.
Rapid Response
The interesting review on 'The treatment of Infections' in your ABC of AIDS by Ian VD Weller and IG Williams suggests tripple drug therapy for pulmonary TB.
Tripple versus Quadruple therapy in TB
The interesting review on 'The treatment of Infections' in your ABC of AIDS by Ian VD Weller and IG Williams suggests tripple drug therapy for pulmonary TB.
Can TB cause lower birth weight?
Infants born to women with untreated TB may be of lower birth weight than those born to women without TB and, in rare circumstances, the infant may be born with TB. Although the drugs used in the initial treatment regimen for TB cross the placenta, they do not appear to have harmful effects on the fetus.
Is TB a hazard to pregnant women?
Untreated tuberculosis (TB) disease represent s a greater hazard to a pregnant woman and her fetus than does its treatment. Treatment should be initiated whenever the probability of TB is moderate to high. Infants born to women with untreated TB may be of lower birth weight than those born to women without TB and, in rare circumstances, ...
Can TB be delayed during pregnancy?
For women who are at high risk for progression from latent TB infection to TB disease, especially those who are a recent contact of someone with infectious TB disease, treatment for latent TB infection should not be delayed on the basis of pregnancy alone, even during the first tri mester.
Can breast milk cause TB?
For the same reason, drugs in breast milk are not an effective treatment for TB disease or latent TB infection in a nursing infant. Breastfeeding women taking INH should also take pyridoxine (vitamin B6) supplementation. RIF can cause orange discoloration of body fluids, including breast milk.