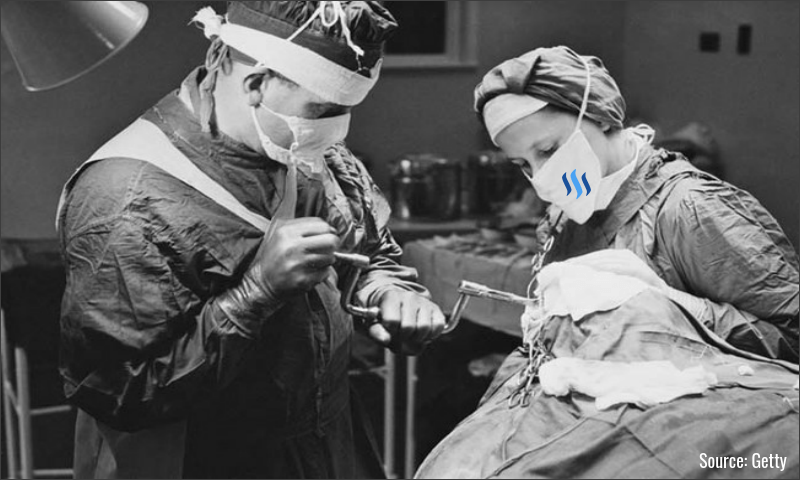
How was a lobotomy done in the past?
The procedure involved cutting tissues in patients' brains with a tool called a leucotome. In a prefrontal lobotomy, the brain was accessed through two holes the surgeon drilled into the patient's skull. In a transorbital lobotomy, the brain was accessed through the patient's eye sockets.
Do they still do lobotomies?
Lobotomy is rarely, if ever, performed today, and if it is, "it’s a much more elegant procedure," Lerner said. "You're not going in with an ice pick and monkeying around.". The removal of specific brain areas (psychosurgery) is only used to treat patients for whom all other treatments have failed.

What was the logic behind lobotomy?
The procedure permanently damaged part of the frontal brain (closer to the forehead) in an attempt to treat a wide range of behavioral problems including depression. The underlying logic was that neurons were improperly wired and fixed in such patients and therefore removing these connections will alleviate pathology.
How were frontal lobotomies performed in the past?
Surgeons would drill a pair of holes into the skull, either at the side or top, and push a sharp instrument - a leucotome - into the brain. The surgeon would sweep this from side to side, to cut the connections between the frontal lobes and the rest of the brain.
What are the alternatives to lobotomies today?
Another brain treatment of ill repute, electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)—also known as electroshock therapy or “shock treatment”—was developed in the 1930s and practiced around the same time and in the same patient population as lobotomy.
What was Walter Freeman's first method of performing lobotomies?
On that day, he performed the first-ever transorbital or "ice-pick" lobotomy in his Washington, D.C., office. Freeman believed that mental illness was related to overactive emotions, and that by cutting the brain he cut away these feelings.
How did they treat mental illness in the 1930s?
In the 1930s, mental illness treatments were in their infancy and convulsions, comas and fever (induced by electroshock, camphor, insulin and malaria injections) were common. Other treatments included removing parts of the brain (lobotomies).
Are lobotomies still performed today?
Today lobotomy is rarely performed; however, shock therapy and psychosurgery (the surgical removal of specific regions of the brain) occasionally are used to treat patients whose symptoms have resisted all other treatments.
Was there ever a successful lobotomy?
According to estimates in Freeman's records, about a third of the lobotomies were considered successful. One of those was performed on Ann Krubsack, who is now in her 70s. "Dr. Freeman helped me when the electric shock treatments, the medicine and the insulin shot treatments didn't work," she said.
Does shock therapy still exist?
ECT is much safer today. Although ECT may still cause some side effects, it now uses electric currents given in a controlled setting to achieve the most benefit with the fewest possible risks.
What is NMD surgery?
Psychosurgery, also called neurosurgery for mental disorder (NMD), is the neurosurgical treatment of mental disorder. Psychosurgery has always been a controversial medical field. The modern history of psychosurgery begins in the 1880s under the Swiss psychiatrist Gottlieb Burckhardt.
What does a lobotomy do to your brain?
The world's first lobotomy was performed in 1935 by a Portuguese neurologist by the name of António Egas Moniz. His original method involved drilling holes into the skull and pumping absolute alcohol into the frontal cortex, essentially destroying brain tissue.
Why did Freeman stop doing lobotomies?
In 1950, Walter Freeman's long-time partner James Watts left their practice and split from Freeman due to his opposition to the cruelty and overuse of the transorbital lobotomy.
What happens to someone after a lobotomy?
Historically, patients of lobotomy were, immediately following surgery, often stuporous, confused, and incontinent. Some developed an enormous appetite and gained considerable weight. Seizures were another common complication of surgery.
When was lobotomy used?
There’s a surprising history of the lobotomy for its use in mental health. A lobotomy wasn’t some primitive procedure of the early 1900s. In fact, an article in Wired magazine states that lobotomies were performed “well into the 1980s” in the “United States, Britain, Scandinavia and several western European countries.”.
When did the Soviet Union stop lobotomy?
The Soviet Union prohibited the procedure in 1950, stating that it was “contrary to the principles of humanity.”. This article lists the “top 10 fascinating and notable lobotomies,” including an American actor, a renowned pianist, the sister of an American president and the sister of a prominent playwright.
How old was Howard Dully when he had a lobotomy?
Lobotomies weren’t just for adults either. One of the youngest patients was a 12-year-old boy! NPR interviewed Howard Dully in 2006 at the age of 56. At the time, he was working as a bus driver. Dully told NPR: “If you saw me you’d never know I’d had a lobotomy,” Dully says.
How many lobotomies did Freeman perform?
office on January 17, 1946. (Freeman would go on to perform about 2,500 lobotomies. Known as a showman, he once performed 25 lobotomies in one day.
Why did Freeman have ice pick lobotomy?
Freeman’s ice-pick lobotomy became wildly popular. The main reason is that people were desperate for treatments for serious mental illness.
How many countries have outlawed lobotomies?
Curiously, as early as the 1950s, some nations, including Germany and Japan, had outlawed lobotomies.
Who performed the first leucotomy?
The Beginning. In 1935, Portuguese neurologist Antonio Egas Moniz performed a brain operation he called “leucotomy” in a Lisbon hospital. This was the first-ever modern leucotomy to treat mental illness, which involved drilling holes in his patient’s skull to access the brain.
When was the first lobotomy performed?
By then, 10 years after Freeman had performed the first lobotomy in 1936, the procedure “was very much on the frontlines of medical science,” said Posner.
Who was the pioneer of lobotomy?
They may have been convinced to employ this drastic surgery by eccentric neuroscientist Dr. Walter Freeman, “the world’s greatest proponent and pioneer of lobotomy,” who used portraits as scientific proof of concept.
What was the name of the technique that Freeman invented?
By inserting a long, thin instrument—modeled after an icepick—to pierce the brain via the patient’s eye socket, Freeman devised what he called the “transorbital lobotomy.”. With this invention, he claimed he no longer needed a drill, sterile field nor surgical scrubs.
Who was the first person to perform lobotomy?
These lobotomy victims would never be the same again. Portuguese neurologist António Egas Moniz was the first to do the surgical procedure. He would go on to share the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine in 1949 for the procedure as well. It involves severing connections in the prefrontal cortex of the brain.
How old were the three women who had lobotomy?
All three were housewives ages 43, 28, and 32 at the time of their lobotomy. Each suffered from their colitis issue anywhere between 6 to 20 years. It is unknown what happened to the women. The only thing really known is that the third woman of 32 had her first child in October 1955, and nothing more.
What is the lobotomy of Dick Meredith?
The lobotomy of Dick Meredith is often believed to be one of the premier cases where you can point to lobotomies being overused. Showing relatively mild mental issues, he was part of a growing trend in the 1940s and 1950s where lobotomy was used as a catch-all concept for mental disorders.
How long did Robi go to mental institution?
She spent 5 years in a mental institution, but unlike many lobotomy victims, Robi was released from the institution. She ended up crediting the lobotomy for her newly calm demeanor. Robi lived into her 80s and even got back into music, wrote autobiographies, and had movies made about her. << Previous. NEXT >>.
What side did the lobotomy leave the girl paralyzed on?
She erupted into tantrums when she did not get her way, which could embarrass her father. The lobotomy left her partially paralyzed on her left side as well as mute. We hope her father’s political aspirations were worth making his daughter one of the many lobotomy victims of the 1940s. << Previous.
Did Meredith have lobotomy?
They merely sent a letter to his family after it was done. Like many lobotomy victims, Meredith had many more issues after his operation.
Is Rose a lobotomy victim?
Sadly, Rose became one of the shining examples of lobotomy victims that prove how unsafe the procedure is. Her lobotomy reduced her to a near-catatonic state. Rose remained institutionalized until her passing in 1996, but thankfully in a high-end version that her brother paid for. << Previous.
Trephination
Trephination dates back to the earliest days in the history of mental illness treatments. It is the process of removing a small part of the skull using an auger, bore, or saw. This practice began around 7,000 years ago, likely to relieve headaches, mental illness, and even the belief of demonic possession.
Bloodletting and Purging
Though this treatment gained prominence in the Western world beginning in the 1600s, it has roots in ancient Greek medicine. Claudius Galen believed that disease and illness stemmed from imbalanced humors in the body. English physician Thomas Willis used Galen’s writings as a basis for this approach to treating mentally ill patients.
Isolation and Asylums
Isolation was the preferred treatment for mental illness beginning in medieval times, which may explain why mental asylums became widespread by the 17th century.
Insulin Coma Therapy
This treatment was introduced in 1927 and continued until the 1960s. In insulin coma therapy, physicians deliberately put the patient into a low blood sugar coma because they believed large fluctuations in insulin levels could alter how the brain functioned. Insulin comas could last one to four hours.
Metrazol Therapy
In metrazol therapy, physicians introduced seizures using a stimulant medication. Seizures began roughly a minute after the patient received the injection and could result in fractured bones, torn muscles, and other adverse effects. The therapy was usually administered several times a week. Metrazol was withdrawn from use by the FDA in 1982.
Lobotomy
This now-obsolete treatment won the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1949. It was designed to disrupt the circuits of the brain but came with serious risks. Popular during the 1940s and 1950s, lobotomies were always controversial and prescribed in psychiatric cases deemed severe.
When did lobotomy stop?
The Soviet Union banned the practice in 1950 on moral grounds. In Germany, it was performed only a few times. By the late 1970s, the practice of lobotomy had generally ceased, although it continued as late as the 1980s in France.
What was the role of lobotomy in the 20th century?
In the early 20th century, the number of patients residing in mental hospitals increased significantly while little in the way of effective medical treatment was available. Lobotomy was one of a series of radical and invasive physical therapies developed in Europe at this time that signaled a break with a psychiatric culture of therapeutic nihilism that had prevailed since the late nineteenth-century. The new " heroic " physical therapies devised during this experimental era, including malarial therapy for general paresis of the insane (1917), deep sleep therapy (1920), insulin shock therapy (1933), cardiazol shock therapy (1934), and electroconvulsive therapy (1938), helped to imbue the then therapeutically moribund and demoralised psychiatric profession with a renewed sense of optimism in the curability of insanity and the potency of their craft. The success of the shock therapies, despite the considerable risk they posed to patients, also helped to accommodate psychiatrists to ever more drastic forms of medical intervention, including lobotomy.
What was the purpose of the National Committee for the Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioral Research?
In 1977 the US Congress, during the presidency of Jimmy Carter, created the National Committee for the Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioral Research to investigate allegations that psychosurgery – including lobotomy techniques – was used to control minorities and restrain individual rights.
What is cutting into the brain to form new patterns and rid a patient of delusions, obsessions, and
Psychosurgery is cutting into the brain to form new patterns and rid a patient of delusions, obsessions, nervous tensions and the like.". Waldemar Kaempffert, "Turning the Mind Inside Out", Saturday Evening Post, 24 May 1941. A lobotomy, or leucotomy, was a form of psychosurgery, a neurosurgical treatment of a mental disorder ...
How many people were lobotomized in the US?
In the United States, approximately 40,000 people were lobotomized. In England, 17,000 lobotomies were performed, and the three Nordic countries of Denmark, Norway, and Sweden had a combined figure of approximately 9,300 lobotomies. Scandinavian hospitals lobotomized 2.5 times as many people per capita as hospitals in the US. Sweden lobotomized at least 4,500 people between 1944 and 1966, mainly women. This figure includes young children. In Norway, there were 2,005 known lobotomies. In Denmark, there were 4,500 known lobotomies. In Japan, the majority of lobotomies were performed on children with behaviour problems. The Soviet Union banned the practice in 1950 on moral grounds. In Germany, it was performed only a few times. By the late 1970s, the practice of lobotomy had generally ceased, although it continued as late as the 1980s in France.
How many lobotomies were performed in 1951?
In 1949, the peak year for lobotomies in the US, 5,074 procedures were undertaken, and by 1951 over 18,608 individuals had been lobotomized in the US.
Why was emphasis put on the training of patients in the weeks and months following surgery?
Emphasis was put on the training of patients in the weeks and months following surgery. The purpose of the operation was to reduce the symptoms of mental disorders, and it was recognized that this was accomplished at the expense of a person's personality and intellect.
When was the first lobotomy performed?
By then, 10 years after Freeman had performed the first lobotomy in 1936, the procedure “was very much on the frontlines of medical science,” said Posner.
Who was the pioneer of lobotomy?
They may have been convinced to employ this drastic surgery by eccentric neuroscientist Dr. Walter Freeman, “the world’s greatest proponent and pioneer of lobotomy,” who used portraits as scientific proof of concept.
What was the name of the treatment for mental disorders in 1942?
Prefrontal Lobotomy in the Treatment of Mental Disorders, 1942. By Walter Freeman and James W. Watts. National Library of Medicine #8800490A. If you were mentally ill back in the late 1930s to late 1950s, doctors might have tried to cure you by drilling a hole in your brain and disconnecting the thalamus from the frontal lobe.
What was the name of the technique that Freeman invented?
By inserting a long, thin instrument—modeled after an icepick—to pierce the brain via the patient’s eye socket, Freeman devised what he called the “transorbital lobotomy.”. With this invention, he claimed he no longer needed a drill, sterile field nor surgical scrubs.
When was lobotomy used?
In 1977, a special committee of the U.S. Congress investigated whether psychosurgery such as lobotomy was used to restrain individual rights. The conclusion was that properly performed psychosurgery could have positive effects, but only in extremely limited situations.
When was the first lobotomy performed?
The first lobotomy in America was performed by Freeman and Watts in 1936 . The initial procedure had to be done by neurosurgeons in an operating room, but Dr. Freeman thought this would limit access to the procedure for those in mental institutions who could potentially benefit from a lobotomy.
What is lobotomy in neuroscience?
Conceived of in 1935, a lobotomy involves cutting major connections between the prefrontal cortex and the rest of the brain. Lobotomies were part of a wave of new treatments for neurological diseases in the early 20th century, including electroconvulsive therapy (shock therapy). While the treatment was severe, it was widely seen as being no more so ...
Why is lobotomy important?
The stormy history of the lobotomy serves to remind modern medical practitioners and patients of the ethical dilemmas that are unique to medicine, and particularly neurology. For the most part, people who performed lobotomies could justify their actions as being in the best interest of the patient.
What is the procedure called when you cut the brain?
The most famous (or infamous) procedure is the frontal lobotomy. Conceived of in 1935, a lobotomy involves cutting major connections between the prefrontal cortex and the rest of the brain.
Why is lobotomy so dangerous?
Over 40,000 lobotomies were performed in the United States. Purported reasons included chronic anxiety, obsessive-compulsive disorders, and schizophrenia. The scientific literature at the time seems to suggest that the procedure was relatively safe, with low death rates.
What is the instrument used to drive the lobotomy through the bone?
Freeman, involved lifting the upper eyelid and pointing a thin surgical tool called a leucotome against the top of the eye socket. A mallet was then used to drive the instrument through the bone, and five centimeters into the brain.
Why is lobotomy not effective?
Mainly because there was no medication or therapy effective enough to treat people who suffered from various mental illness. And with electroshock therapy being already in use, this invasive operation didnx5ct shock people. However, the misinformation and active campaigning for the effectiveness of lobotomy had a significant impact too.
How many lobotomies did Moniz perform?
From the year 1945 to 1947 there were around 2,000 lobotomies performed. However, the numbers skyrocketed to 18,000 after Moniz was awarded the Nobel Prize Medicine for his discovery in 1949.
Who was the first doctor to stab a patient's brain with an icepick?
A physician, Walter Freeman, helped popularize this procedure in the US. With no surgical training, Freeman decided to change the operation, and instead of drilling holes in the skull, he stabbed patientsx5c brains with an icepick through the eye socket.
