
Full Answer
What is the best procedure for varicose veins?
Treatment
- Self-care. Self-care — such as exercising, losing weight, not wearing tight clothes, elevating your legs, and avoiding long periods of standing or sitting — can ease pain and prevent varicose ...
- Compression stockings. ...
- Additional treatments for more-severe varicose veins. ...
Could laser vein treatment help my varicose veins?
Laser treatment. Doctors are using new technology in laser treatments to close off smaller varicose veins and spider veins. Laser treatment works by sending strong bursts of light onto the vein, which makes the vein slowly fade and disappear. No incisions or needles are used.
How much varicose vein treatment costs without insurance?
Multiple sessions could mean several $1000 for more severe cases. Some of the more advanced procedures include Varithena foam injection, which may range from $2000 to $3000 and a ClosureFast Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA), which may cost $3000 to $5000. Costs vary depending on the number and size of veins to be treated.
What is the surgical treatment of varicose veins?
The types of varicose vein surgery include:
- Ambulatory phlebectomy (also called micro-incision phlebectomy, hook phlebectomy, stab avulsion phlebectomy, and microphlebectomy) removes portions of varicose veins through small incisions using a hook. ...
- Ligation and stripping usually removes the saphenous vein, a large vein in the leg. ...
- PIN stripping removes a vein through one incision. ...
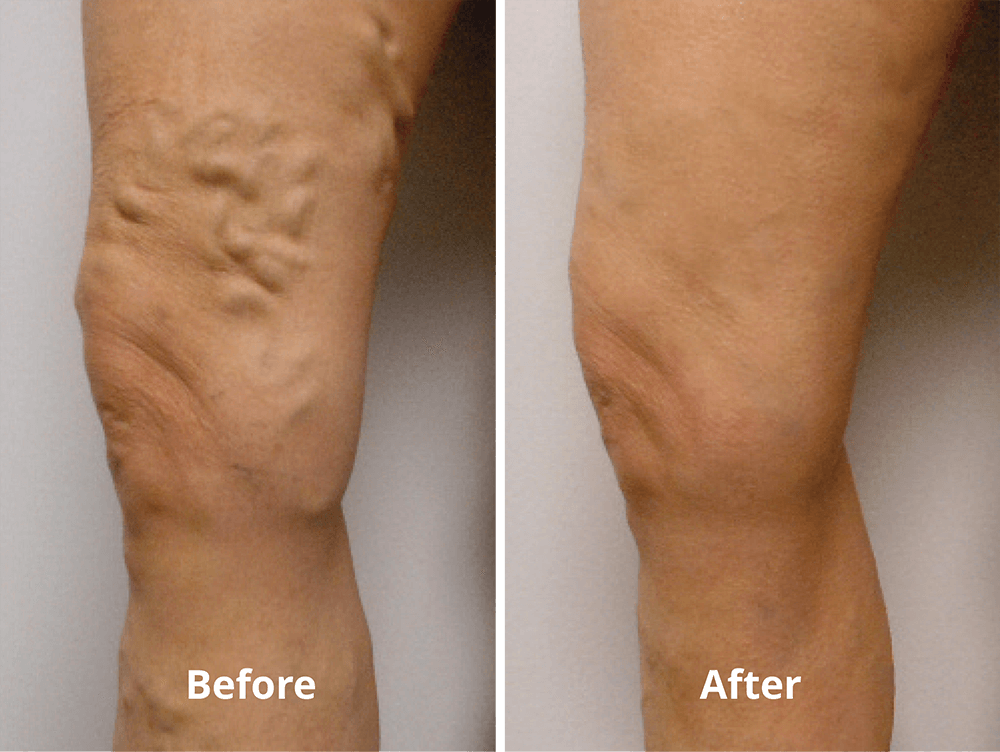
What type of ultrasound is done for varicose veins?
Venous ultrasound uses sound waves to produce images of the veins in the body. It is commonly used to search for blood clots, especially in the veins of the leg – a condition often referred to as deep vein thrombosis. Ultrasound does not use ionizing radiation and has no known harmful effects.
What is vein mapping for varicose veins?
What is vein mapping? Vein mapping refers to an ultrasound test that can be done to take a closer look at the veins in the legs. This test is non-invasive and painless. The study may also be referred to as a venous insufficiency (or venous reflux) ultrasound.
Is ultrasound therapy good for varicose veins?
Results are encouraging and suggest that focused ultrasonic irradiation can be an efficacious means of treating varicose veins and other venous disorders.
What is venous mapping ultrasound?
Vein mapping is a technique performed with an ultrasound probe that uses sound waves (doppler) technology to view or “map” all of the veins under the skin on the arms or legs. It allows the doctor to see the size, depth, and flow of blood in these veins and allows for better treatment planning.
Is Venogram and venography the same?
A venogram, also known as venography, is an x-ray exam that is performed to examine the health of the veins — typically in your legs. During a venogram, your doctor will inject a contrast dye into the vessels to examine how blood is flowing through your veins.
What is saphenous vein mapping?
Ultrasound showing diameter of saphenous vein. When lower extremity arterial bypass surgery is required, a bypass graft using a vein often provides the best long-term result. Using the person's own tissue reduces the risk of infection or thrombosis (clotting) of the graft.
What is ultrasound guided sclerotherapy?
Ultrasound Guided Sclerotherapy (UGS) is a method of treating perforators and painful, large varicose veins. Under ultrasound guidance, a small needle is inserted directly into the vein and a foaming solution (FDA approved sodium tetradecyl) is injected.
What can I expect at a vein ultrasound?
The patient does stand for part of the ultrasound when the back of the legs are being evaluated. Reflux in a vein identified using color doppler. extremities, and the veins take the blood back to the heart. The amount of blood returning to the heart varies at any moment, as this is achieved by breathing.
What is vein mapping test?
Vein Mapping is the process of identifying and measuring of veins in the upper or lower extremities. By measuring the diameter of a particular vein and examining blood flow, the physician is able to determine if a patient is suffering from a condition known as venous insufficiency.
Is vein mapping painful?
A vein mapping ultrasound is a noninvasive, painless procedure used to identify abnormalities in the veins. During the procedure, a clear gel is applied to the skin of the targeted area, and a transducer is placed over various locations on your legs to produce images of the internal venous structures.
What happens after vein mapping?
After the Test The gel will be wiped off your skin. There are no special instructions to follow after the test. You may go home or to your other scheduled appointments after the vascular ultrasound.
What is Vein Mapping?
Vein Mapping is a test that uses high-frequency sound waves with the help of ultrasound to procure images of the veins that are being considered for surgical alteration.
How does Vein Mapping help?
It is a risk-free and non-invasive procedure that makes use of the ultrasound technology to offer information about the physiology and anatomy of the surface and deep venous sys...
How is Vein Mapping done?
Our team of doctors at Medanta will ensure if you are in optimum health to undergo the procedure. Discuss with your doctor the risks, benefits, and post-treatment care.
Why does blood pooling in legs cause reflux?
The pressure from the blood pooling in the legs can put extra pressure in veins and make them reflux. When you treat a larger vein that is causing the symptoms, the other veins don’t have to work so hard to take blood back to the heart.
Why do we do a follow up ultrasound after each procedure?
The third reason we do a follow up ultrasound after each procedure is because around 25% of the time after treating one vein, other veins can become competent. The reason is that sometimes when larger veins are refluxing it makes other veins reflux that maybe aren’t incompetent veins.
What is a follow up ultrasound for varicose veins?
Follow Up Ultrasounds for Varicose Vein Treatment. When you are first established as a patient you will have an initial thorough ultrasound of one or both legs. This first ultrasound is referred to as “vein mapping” where every vein in the leg is evaluated. After each procedure you will have a follow up ultrasound done.
Why do we do ultrasounds?
There are three main reasons why we do these. The first reason is to make sure that the procedure was successful and the vein that we treated is closed down.
How are veins scanned?
The veins are scanned by moving the probe vertically up and down along their course. Duplicated segments, sites of tributary confluence, and large perforating veins and their deep venous connections are identified. Their location measured in centimeters from the floor provides a therapeutic guide.
Where is the Great Saphenous vein scanned?
The Great Saphenous vein is then scanned in the leg and the thigh so that tributaries to the GSV should be noted (see Figure 23.1). The diameters of the popliteal vein and the Small Saphenous vein (SSV) are recorded, as well as diameters of the SSV along its course in the leg.
Where is the laser catheter advanced?
FIGURE 23.3 The laser catheter is advanced proximally toward the saphenofemoral junction. Position of the laser fiber is confirmed by direct visualization of the red aiming beam through the skin. (Adapted from Navarro L, Min RJ, Bone' C. Endovenous laser: A new minimally invasive method of treatment for varicose veins: Preliminary observations using an 810 nm diode laser dermatologic surgery, Volume 27, 2:117. February 2001)
Where do accessory veins run parallel to the GSV?
Accessory veins by definition run parallel to the GSV in the thigh (see Figure 23.1).18 It is imperative to map their course accurately and to note their eventual communication with GSV (see Figure 23.1). They are easily confused with the GSV, especially during continuous longitudinal scanning when the saphenous vein appears to leave the saphe-nous compartment.18
How is tumescent anesthesia monitored?
Administration of the tumescent anesthesia into the saphenous compartment is monitored by ultrasound.17 The vein is seen as "floating" in an echogenic sea of the anesthetic solution (see Figure 23.5). It is always wise to recheck
What is the aim of a structured ultrasound examination?
Structured ultrasound examination: •First get a general overview: Is there a CVI? Do not start with the assessment of each tributary •Reflux source and path: The main aim is to detect the source of the reflux and to understand the path it follows •Examine from the top to the down: EIV -> FV -> SFJ -> GSV -> PV -> SPJ -> SSV -> crural veins and perforators
What is reflux pattern?
The normal reflux pattern is „from top to down“The failure of a valve increases the pressure on the next valve. This valve has to do the job of two valves and will fail also („domino-effect“). So the insufficiency follows down the lower extremityInsufficient superficial veins dilate and loose their straight anatomy. They transform into tortuous varicose veins
What should be included in an ultrasound report?
Therefore the result should be documented in a high-quality graphic report. This report should contain: •detail ed informations about the superficial and deep veins •characteristics of the reflux and their path •anatomic description of the superficial veins (vessel size, duplication, location, e.g.) •incidental findings (thrombus, phlebitis, anatomic variants, e.g.) The report should be saved on a worksheet with sonography images and standardized sketches.
What is the recommended transducer for the veins of the extremities?
Recommended transducer: 7 - 10 MHz linear transducer for the veins of the extremities 2 - 6 MHz sector transducer for the pelvic and abdominal veins
What is the test for venous incompetence?
Testing for venous incompetence (reflux) by4: •Valsalva manoeuvre(or hand controlled Valsalva manoeuvre - the patient should take a deep breath and hold, the examiner pushes with his free hand on the abdomen and the patient has to resist the pressure) •Manual (or automatic cuff) distal augmentationfor reflux-detecting below the sapheno-femoral junction (SFJ). With this technique a large volume of venous blood is emptied out of the calf. During the quick release a large pressure gradient is created and a reflux can be detected. •Activation of the calf muscle pump
Is ultrasound necessary for varicose veins?
Conclusion The treatment of varicose veins requires a detailed understanding of the source and path of the reflux. It is not possible to develop a strategy and therapy planning for the patients individual varicose pattern without this knowledge. Therefore the ultrasound examination is the most important part of diagnosis. This implies that the specialist has to be experienced in vascular ultrasound imaging and in its pathophysiological interpretation. Beside a proper technical setting the physician should perform the ultrasound examination in comprehensibly and structured steps. The result has to be fixed on a standardized report.
What is the ultrasound of the saphenous vein?
When used to identify the anatomy of the saphenous vein in preparation for a closure procedure or for harvesting prior to heart bypass, it is called vein mapping.
How to map veins?
Vein mapping should be done with an ultrasound examination and details the entire system, communicating veins and branches. The most common veins to cause symptomatic venous reflux and varicose veins (which may or may not be present) is easily identified and treated with endovenous laser ablation and micro phlebectomy of varicose veins in the same setting under local anesthetic. No need for hospitals or surgery centers. Other branches can be evaluated at a later date to see if they have resolved with sealing of the saphenous vein which in most case is what occurs. Additional sclerotherapy injections can seal any
What is the treatment for varicose veins?
The most common veins to cause symptomatic venous reflux and varicose veins (which may or may not be present) is easily identified and treated with endovenous laser ablation and micro phlebectomy of varicose veins in the same setting under local anesthetic.
Why do you need a venous duplex ultrasound?
A complete venous duplex ultrasound is necessary to determine your treatment plan for venous insufficiency. Answered by Lone Star Vein Center. Generally the term 'vein mapping' is used to describe an ultrasound specifically to look for veins that may be used for potential bypass grafting. A complete venous duplex ultrasound is necessary ...
What is vein mapping?
Vein mapping is simply to show where the veins are, but ultrasound is the tool used to do so. Published on Jul 11, 2012. Lone Star Vein Center. Published on Jun 27, 2014. Generally the term 'vein mapping' is used to describe an ultrasound specifically to look for veins that may be used for potential bypass grafting.
Can ultrasound be done on gall bladder?
Answered by Vanish Vein and Laser Center. Ultrasound can be done for many reasons and in may areas such as gall bladder, kidney, etc. Venous ultrasound looks at the veins and can look at many different kinds of veins.
Can you map veins with ultrasound?
You map the veins with ultrasound as well, a report is simply drawn out to show the NP or Dr. where the veins are. You can also map bulging veins with a vein light. Vein mapping is simply to show where the veins are, but ultrasound is the tool used to do so. Answered by Intermountain Vein Center.
