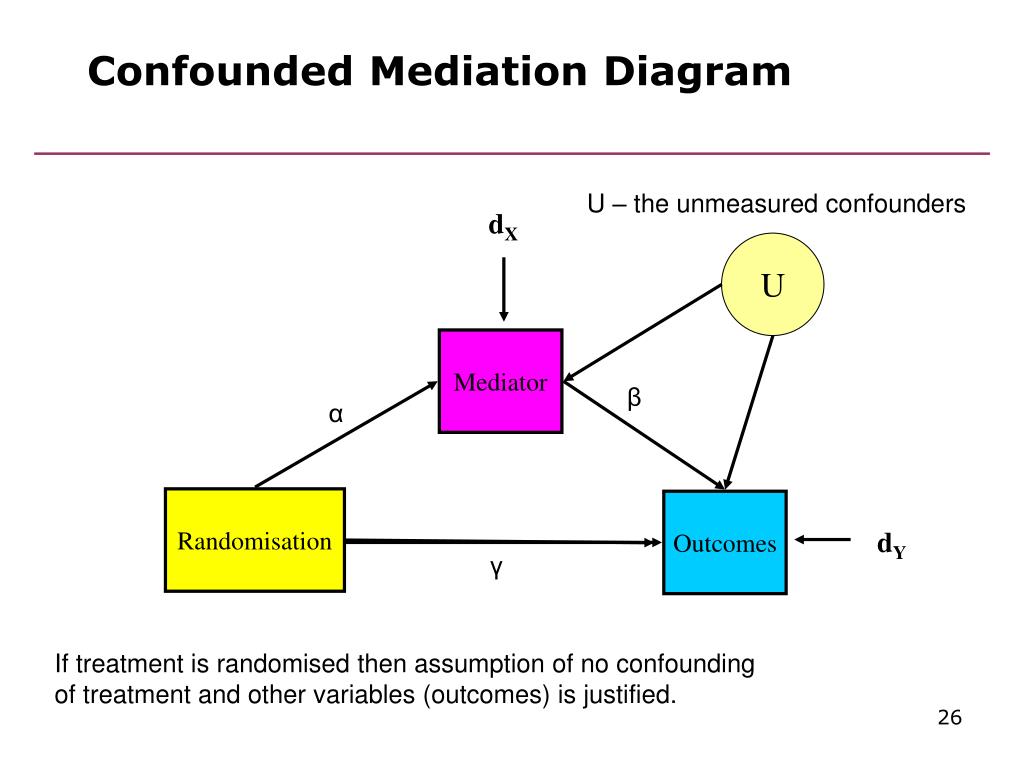
A confounding variable (confounder) is a factor other than the one being studied that is associated both with the disease (dependent variable) and with the factor being studied (independent variable). A confounding variable may distort or mask the effects of another variable on the disease in question.
What is a confounding variable in science?
What is a Confounding Variable? (Definition & Example) What is a Confounding Variable? (Definition & Example) The independent variable: the variable that an experimenter changes or controls so that they can observe the effects on the dependent variable.
How do you control for the impact of confounding variables?
You can only control for variables that you observe directly, but other confounding variables you have not accounted for might remain Another way to minimize the impact of confounding variables is to randomize the values of your independent variable.
How do confounding variables affect internal validity?
In technical terms, confounding variables affect the internal validity of a study, which refers to how valid it is to attribute any changes in the dependent variable to changes in the independent variable.
How do you identify a confounding variable?
A simple, direct way to determine whether a given risk factor caused confounding is to compare the estimated measure of association before and after adjusting for confounding. In other words, compute the measure of association both before and after adjusting for a potential confounding factor.
What does it mean for variables to be confounded?
A confounding variable (confounder) is a factor other than the one being studied that is associated both with the disease (dependent variable) and with the factor being studied (independent variable). A confounding variable may distort or mask the effects of another variable on the disease in question.
What is a confounding variable explain with examples?
A confounding variable would be any other influence that has an effect on weight gain. Amount of food consumption is a confounding variable, a placebo is a confounding variable, or weather could be a confounding variable. Each may change the effect of the experiment design.
What does it mean when an experiment is confounded?
Confounding occurs when the experimental controls do not allow the experimenter to reasonably eliminate plausible alternative explanations for an observed relationship between independent and dependent variables.
What is a confounding variable quizlet?
Confounding variable. an extraneous variable whose presence affects the variables being studied so that the results you get do not reflect the actual relationship between the variables under investigation.
What is a treatment in research?
In an experiment, the factor (also called an independent variable) is an explanatory variable manipulated by the experimenter. Each factor has two or more levels, i.e., different values of the factor. Combinations of factor levels are called treatments.
What is a confounding variable in psychology?
Confounding variables in psychology are defined as influences that interfere with an accurate measurement between the independent and dependent variable.
What are confounds in psychology research?
confound. n. in an experiment, an independent variable that is conceptually distinct but empirically inseparable from one or more other independent variables. Confounding makes it impossible to differentiate that variable's effects in isolation from its effects in conjunction with other variables.
Which is an example of a possible confounding variable quizlet?
Example: Participant may think that the researcher is too young to be credible. Psychological characteristics if the researcher can affect the behavior of the participants. Example: Personality may be off putting or researcher may be in a bad mood.
Are independent variables confounding?
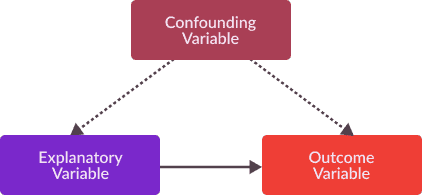
A confounding variable is closely related to both the independent and dependent variables in a study. An independent variable represents the supposed cause, while the dependent variable is the supposed effect. A confounding variable is a third variable that influences both the independent and dependent variables.
Is a confounding variable a response variable?
A confounding variable is a variable that: – affects the response variable and also – is related to the explanatory variable.
Are confounding and control variables the same?
You have to decide whether the control variable is affected by the independent variable (which would make the control variable an intervening variable) or whether it affects the independent variable (which would make it a confounding variable).
What is a confounding variable?
A confounding variable , also called a confounder or confounding factor, is a third variable in a study examining a potential cause-and-effect r...
What is the difference between confounding variables, independent variables and dependent variables?
A confounding variable is closely related to both the independent and dependent variables in a study. An independent variable represents the su...
What’s the difference between extraneous and confounding variables?
An extraneous variable is any variable that you’re not investigating that can potentially affect the dependent variable of your research study....
Why do confounding variables matter for my research?
To ensure the internal validity of your research, you must consider the impact of confounding variables. If you fail to account for them, you mig...
How do I prevent confounding variables from interfering with my research?
There are several methods you can use to decrease the impact of confounding variables on your research: restriction, matching, statistical contro...
What is a confounding variable?
A confounding variable is a third unmeasured variable that influences both the cause and effect in a research study.
Why do we need to limit the effect of confounding variables?
Confounding variables can impact the outcome of your study, which can hamper the internal validity of your study. Therefore, we need to limit the e...
How to eliminate the effects of confounding variables?
There are four main ways of eliminating the effect of confounding variables. These include restriction, matching, statistical control, and randomis...
How does confounding variables differ from extraneous variables?
An extraneous variable is a variable that can impact the study’s dependent variable, whereas a confounding variable can affect the dependent variab...
How to reduce the impact of confounding variables
It is important to identify all possible confounding variables and consider the impact of them in your research design in order to ensure the internal validity of your results.
Frequently asked questions about confounding variables
1. What is the difference between an extraneous variable and a confounding variable?
What is a confounding variable?
Confounding variable: A variable that is not included in an experiment, yet affects the relationship between the two variables in an experiment. This type of variable can confound the results of an experiment and lead to unreliable findings. For example, suppose a researcher collects data on ice cream sales and shark attacks and finds ...
What are the requirements for a variable to be a confounding variable?
In order for a variable to be a confounding variable, it must meet the following requirements: 1. It must be correlated with the independent variable. In the previous example, temperature was correlated with the independent variable of ice cream sales.
What is the type of variable that affects the results of a study?
This type of variable is known as a confounding variable and it can confound the results of a study and make it appear that there exists some type of cause-and-effect relationship between two variables that doesn’t actually exist. Confounding variable: A variable that is not included in an experiment, yet affects the relationship between ...
How does confounding affect the validity of a study?
In technical terms, confounding variables affect the internal validity of a study, which refers to how valid it is to attribute any changes in the dependent variable to changes in the independent variable. When confounding variables are present, we can’t always say with complete confidence that the changes we observe in ...
What is the independent variable of a diet?
The independent variable is the new diet and the dependent variable is the amount of weight loss. However, a confounding variable that will likely cause variation in weight loss is gender. It’s likely that the gender of an individual will effect the amount of weight they’ll lose, regardless of whether the new diet works or not.
What are the two main variables in an experiment?
In any experiment, there are two main variables: The independent variable: the variable that an experimenter changes or controls so that they can observe the effects on the dependent variable. The dependent variable: the variable being measured in an experiment that is “dependent” on the independent variable. ...
What is the practice of dividing individuals in a study into “blocks” based on some value of
2. Blocking . Blocking refers to the practice of dividing individuals in a study into “blocks” based on some value of a confounding variable to eliminate the effect of the confounding variable. For example, suppose researchers want to understand the effect that a new diet has on weight less.
What is a confounding variable?
A confounding variable (confounder) is a factor other than the one being studied that is associated both with the disease (dependent variable) and with the factor being studied (independent variable). A confounding variable may distort or mask the effects of another variable on the disease in question.
What are the four experimental conditions?
Specifically, participants can be assigned to one of four experimental conditions: a treatment with a male therapist, a treatment with a female therapist, a placebo control with a male therapist, and a placebo control with a female therapist.
What is a covariate in statistics?
3.7.2 Covariates. Covariates are confounding variables that may be related to a variable of interest but are not of interest in themselves. They can be statistically controlled for during analysis, which results in a more direct measurement of the relationship between the variables of interest.
What happens if an extraneous variable is not appropriately controlled?
If an extraneous variable is not appropriately controlled, it may be unequally present in the comparison groups. As a result, the variable becomes a confounding variable. In such cases, any differences between the two groups on a DV might very well be the result of the uncontrolled extraneous variable (i.e., confounding variable), because that variable has the effect of confusing, or confounding, proper interpretation of the study. The end result is that the true relationship between the IV and DV is somewhat disguised because of the possibility that another variable (the confounding variable) has influenced the outcome of the study in an unanticipated way. In the study by Chang et al., any one or more of the several demographic and obstetric features (e.g., maternal age, maternal weight, gestational age, newborn weight, and duration of labor) could function as a confounding variable if not adequately controlled.
Why are experimental studies not possible?
Experimental studies may not be possible for many technical, ethical, financial, or other reasons. The proper causal interpretation of the relations from carefully developed epidemiological studies is vital to the development of effective measures of prevention. View chapter Purchase book. Read full chapter.
Can you include extraneous variables in an experiment?
If researchers suspect the gender of the therapist is an extraneous variable, they can include the gender of the therapist as an additional independent variable.
Is MDMA a confounding drug?
A potential confounding variable in studies of MDMA is that the subjects may not actually be taking MDMA, but rather other substances, such as amfe tamine or metamfetamine. In 21 subjects who claimed to have taken only MDMA and no other drugs [183] a hair sample showed that 19 had MDMA present, while seven had concentrations of 3,4-methylenedioxyamfetamine (MDA) similar to or greater than those of MDMA. Eight subjects also tested positive for of amfetamine or metamfetamine. At a follow-up interview with those who tested positive for drugs other than MDMA, none admitted knowledge of taking MDA, amfetamine, or metamfetamine. These results suggest that not all street ecstasy tablets contain pure MDMA. Often, MDA, amfetamine, or metamfetamine is disguised as MDMA. It is unknown whether the combination of MDMA with these drugs poses a greater health risk to abusers. The main limitation of this study was that it relied on the subjects’ own reports. The authors suggested that hair testing be implemented in all MDMA research trials to ensure that the study sample is accurate.
The definition of confounding variable
Also known as confounding factors, confounding variables are a type of extraneous variable linked with both the dependent and independent variables of the study. For a variable to qualify as a confounding variable, it must meet two criteria. These include the following:
Confounding variable: Example
You have been asked to collect data on cases of sunburn and consumption of ice cream in a particular area. You find that those with a higher level of ice cream consumption have suffered more cases of sunburn. So does that mean that consumption of ice cream is causing sunburn?
What is the importance of confounding variables?
Confounding variables play a huge role in research studies as an internal validator. Failing to factor in the influence of confounding variables may yield different outcomes than anticipated, and the actual relationship between the variables remains unclear.
Reducing the impact of confounding variables
Several methods can be used to limit the impact of the confounding variables on the outcome of your research. These methods can be used for any subject type, including humans, animals, plants etc. However, each of them comes with its own set of pros and cons.
Looking for Assignment Help from Top Experts ?
Get the best Assignment Help from leading experts from the field of academics with assured onetime, 100% plagiarism free and top Quality delivery.
How to control confounding variables?
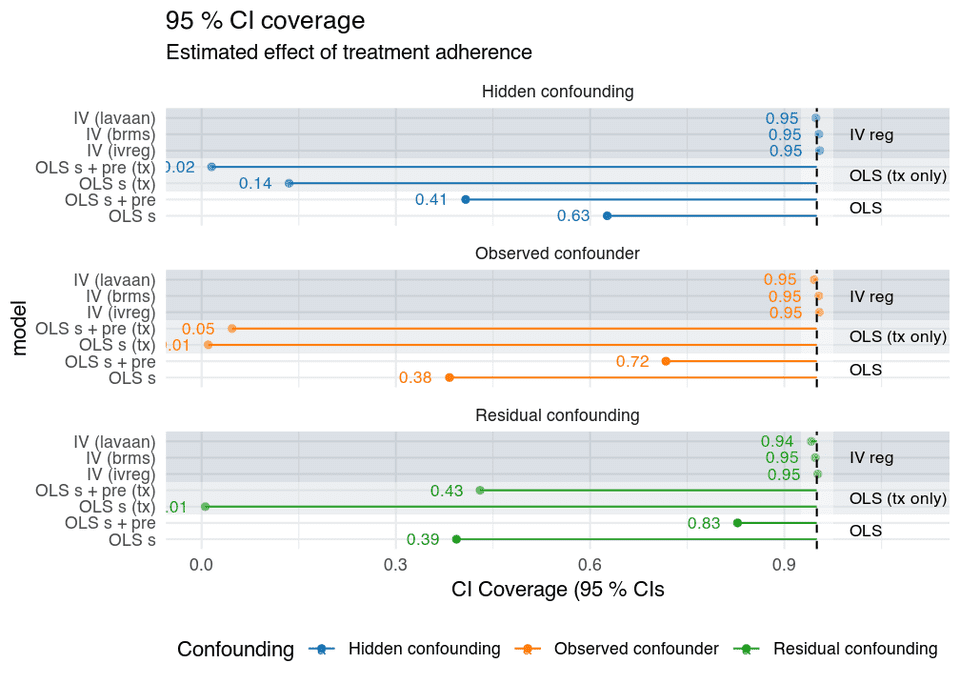
In randomisation, you account for all possible confounders by randomly assigning the treatment to a large number of participants.
Why do you need to take confounding variables into consideration?
You must take confounding variables into consideration to ensure the internal validity of your research. Your results could be invalid for other researchers if you ignore the relationship between your research variables.
Why can you find the absence of a cause and effect relationship between the variables you tested?
For example, you could discover the absence of a cause-and-effect relationship between the variables you tested because the measured effect is caused by the confounding variable rather than the independent variable. Your find that countries with higher minimum wages have more workers employed.
What is cause and effect in 2021?
A cause-and-effect relationship in academic research involves an assumed cause and an assumed effect, but it also includes a third unmeasured variable – known as a confounding variable. A confounding variable can potentially affect both the suspected cause and the suspected effect.
What is a confounding factor?
They are also called the cofounding factors or cofounders. A variable should meet the following criteria to be considered as a confounding variable. It should correlate to an independent variable, although their relationship may or may not be causal. It should be causally related to the dependent variable.
What is the restriction method?
In the restriction method, you restrict the study to subjects in one category of the confounding variable. This method helps to ensure that all participants of the study have the same values of the potential confounder.
Why are potential confounders not correlated with independent variables?
The potential confounders will not correlate with your independent variable because they will be distributed equally among the groups. Hence, your study will not be confounded by them.
How much does LPC therapy cost?
LPC rates are less than a psychologist, but can still cost a client up to $500 per month which is not sustainable for a majority of people. Photo by Jan Tinneberg on Unsplash.
Is therapeutic intervention useless?
Those who are mandated to treatment seldom engage and without engagement treatment is useless. The effectiveness of therapeutic intervention relies upon the therapeutic relationship, and building a relationship takes two people. If one decides not to engage, there is no relationship and no therapeutic intervention.
Confounding Variables in Psychology
Research in psychology is designed to investigate how the variable a researcher manipulates, known as the independent variable, impacts people's actions, called the dependent variable. Experimental design is the process used to control for confounding variables while measuring this relationship.
Examples of Confounding Variables in Psychology
Confounding variables in psychology can come from any number of sources, but some can be more difficult to identify than others. Consider the following confounding variable examples.
Writing Prompts About Confounds in Psychology
Create a set of flashcards that list and define the key terms from this lesson, including: experimental design, variable, independent variable, dependent variable, confounding variables, experimenter bias, demand characteristics, single-blind studies, double-blind studies, placebo, and placebo effect.