Is invasive mammary carcinoma curable?
Invasive ductal carcinoma is quite curable, especially when detected and treated early.
What does it mean if breast cancer is invasive?
Breast cancers that have spread into surrounding breast tissue are known as invasive breast cancers. Most breast cancers are invasive, but there are different types of invasive breast cancer. The two most common are invasive ductal carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma.
What stage is invasive mammary carcinoma?
Stage I describes invasive breast cancer (cancer cells are breaking through to or invading normal surrounding breast tissue) Stage I is divided into subcategories known as IA and IB. Still, if the cancer is estrogen receptor-positive or progesterone receptor-positive, it is likely to be classified as stage IA.
What is the survival rate for invasive mammary carcinoma?
The average 10-year survival rate for women with non-metastatic invasive breast cancer is 84%. If the invasive breast cancer is located only in the breast, the 5-year survival rate of women with this disease is 99%.
What is the most invasive type of breast cancer?
Most common invasive breast cancers Invasive ductal carcinoma (also called infiltrating ductal carcinoma) begins in the milk ducts and is the most common invasive breast cancer. Invasive lobular carcinoma begins in the lobules and is the second most common invasive breast cancer.
Is invasive breast cancer a critical illness?
Data from the insurers shows that breast cancer is the single most common condition amongst critical illness claims, accounting for nearly a quarter (22%) of all claims paid in 2014. In terms of claims by females, this figure rises to 44% of all claims.
Does invasive mean metastatic?
Sometimes, a person already has metastatic breast cancer when they are diagnosed, if it wasn't found before it spread. But all invasive breast cancers aren't metastatic. Earlier stage breast cancers may have invaded other parts of the breast or nearby lymph nodes but haven't spread to further parts of the body.
Is invasive mammary carcinoma the same as invasive ductal carcinoma?
Another term for invasive ductal carcinoma is invasive mammary carcinoma of no special type, because it is the most common type of breast carcinoma. Both invasive ductal carcinomas and invasive lobular carcinomas arise from the cells lining the ducts and lobules in the breast.
How long does it take for invasive ductal carcinoma to spread?
Each division takes about 1 to 2 months, so a detectable tumor has likely been growing in the body for 2 to 5 years. Generally speaking, the more cells divide, the bigger the tumor grows.
Do you need chemo for invasive ductal carcinoma?
Invasive ductal carcinoma chemotherapy may be given before breast cancer surgery to shrink tumors and destroy rapidly dividing cancer cells, or after a surgical procedure to address any residual cancer and reduce the likelihood of recurrence.
Does 5 year survival rate mean you have 5 years to live?
Most importantly, five-year survival doesn't mean you will only live five years. Instead it relates to the percentage of people in research studies who were still alive five years after diagnosis.
Can invasive ductal carcinoma spread to lungs?
Breast cancer can spread to the lungs or to the space between the lung and the chest wall, making fluid build up around the lung. Symptoms can include shortness of breath, a cough that won't go away, and chest pain.
What is the most common type of breast cancer?
Invasive (infiltrating) ductal carcinoma (IDC) This is the most common type of breast cancer. About 8 in 10 invasive breast cancers are invasive (or infiltrating) ductal carcinomas (IDC). IDC starts in the cells that line a milk duct in the breast. From there, the cancer breaks through the wall of the duct, and grows into the nearby breast tissues.
Is breast cancer invasive?
Most breast cancers are invasive, but there are different types of invasive breast cancer. The two most common are invasive ductal carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma. Inflammatory breast cancer and triple negative breast cancer are also types of invasive breast cancer.
Is lobular carcinoma invasive?
Invasive lobular carcinoma ( ILC) About 1 in 10 invasive breast cancers is an invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC). ILC starts in the milk-producing glands (lobules). Like IDC, it can spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body. Invasive lobular carcinoma may be harder to detect on physical exam and imaging, like mammograms, ...
What is the procedure to remove breast cancer?
There are many treatments for invasive breast cancer. They include: Surgery. A lumpectomy is a surgical procedure in which a surgeon removes the cancer and a small area of healthy tissue around it.
What are the different types of breast cancer?
Types of Invasive Breast Cancer 1 Invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC). This is the most common type, making up about 80%. With IDC, cancer cells start in a milk duct, break through the walls, and invade breast tissue. It can remain localized, which means it stays near the site where the tumor started. Or cancer cells may spread anywhere in the body. 2 Invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC). This type accounts for about 10% of invasive breast cancers. ILC starts in the lobules or milk glands and then spreads. With ILC, most women feel a thickening instead of a lump in their breast.
How many chances of breast cancer in women?
Women in the U.S. have a 1 in 8 chance of developing an invasive form of breast cancer during their lifetime. When breast cancer is invasive, it starts in the breast ducts or glands but grows into breast tissue. It can then spread into the nearby lymph nodes and beyond. There are effective treatments. Your own treatment will depend on ...
What is the difference between low grade and high grade breast cancer?
Low-grade cancer cells are similar to normal breast cells. Higher grade breast cancer cells look more different. They show the cancer is more aggressive . The doctor will also test for estrogen receptors and progesterone receptors.
What does it feel like to have breast cancer?
As the cancer grows, you may notice one or more of the following: A lump or thickening in or near the breast or in the underarm that continues after your monthly menstrual cycle. A mass or lump, which may feel as small as a pea. A change in the size, shape, or contour of the breast.
Is breast cancer more common in white women?
Your genetics and family history of breast cancer play roles. It’s more common among white women than black, Asian, or Hispanic women. Also, you’re at higher risk if you’re obese, your breasts are dense, you didn’t have children, or you became pregnant after the age of 35.
Can you give medication to cancer cells?
Certain medications may be given if the cancer cells have hormone receptors. Targeted therapy. If the cancer cells have the gene HER2, you may be given drug treatments specifically for that. The goal of your treatment is to give you the best possible outcome.
What is the name of the disease where malignant cells form in the tissues of the breast?
Breast cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the breast. The breast is made up of lobes and ducts. Each breast has 15 to 20 sections called lobes. Each lobe has many smaller sections called lobules. Lobules end in dozens of tiny bulbs that can make milk.
What is breast cancer?
Key Points. Breast cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the breast. A family history of breast cancer and other factors increase the risk of breast cancer. Breast cancer is sometimes caused by inherited gene mutations (changes).
How does chemo work?
Chemotherapy is a cancer treatment that uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or by stopping them from dividing. When chemotherapy is taken by mouth or injected into a vein or muscle, the drugs enter the bloodstream and can reach cancer cells throughout the body ( systemic chemotherapy ).
What are the risk factors for breast cancer?
Risk factors for breast cancer include the following: A personal history of invasive breast cancer, ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), or lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS). A personal history of benign (noncancer) breast disease.
What is the most common type of breast cancer?
The most common type of breast cancer is ductal carcinoma, which begins in the cells of the ducts. Cancer that begins in the lobes or lobules is called lobular carcinoma and is more often found in both breasts than are other types of breast cancer.
How much of breast cancer is hereditary?
The genes in cells carry the hereditary information that is received from a person’s parents. Hereditary breast cancer makes up about 5% to 10% of all breast cancer. Some mutated genes related to breast cancer are more common in certain ethnic groups.
How do you know if you have breast cancer?
Signs of breast cancer include a lump or change in the breast. Tests that examine the breasts are used to diagnose breast cancer. If cancer is found, tests are done to study the cancer cells. Certain factors affect prognosis (chance of recovery) and treatment options.
What is standard of care for breast cancer?
This section explains the types of treatments that are the standard of care for early-stage and locally advanced breast cancer. “Standard of care” means the best treatments known. When making treatment plan decisions, you are strongly encouraged to consider clinical trials as an option.
What is cancer treatment?
In cancer care, doctors specializing in different areas of cancer treatment—such as surgery, radiation oncology, and medical oncology—work together with radiologists and pathologists to create a patient’s overall treatment plan that combines different types of treatments.
How does chemotherapy work?
Chemotherapy is the use of drugs to destroy cancer cells, usually by keeping the cancer cells from growing, dividing, and making more cells . It may be given before surgery to shrink a large tumor, make surgery easier, and/or reduce the risk of recurrence, called neoadjuvant chemotherapy. It may also be given after surgery to reduce the risk of recurrence, called adjuvant chemotherapy.
How long does it take for breast cancer to recur?
In fact, with modern surgery and radiation therapy, recurrence rates in the breast are now less than 5% in the 10 years after treatment or 6% to 7% at 20 years. Survival is the same with lumpectomy or mastectomy.
What is the next step after breast cancer surgery?
After surgery, the next step in managing early-stage breast cancer is to lower the risk of recurrence and to get rid of any remaining cancer cells in the body. These cancer cells are undetectable with current tests but are believed to be responsible for a cancer recurrence as they can grow over time.
What is a treatment plan?
A treatment plan is a summary of your cancer and the planned cancer treatment. It is meant to give basic information about your medical history to any doctors who will care for you during your lifetime. Before treatment begins, ask your doctor for a copy of your treatment plan.
Can breast cancer be removed with surgery?
Although the goal of surgery is to remove all of the visible cancer in the breast, microscopic cells can be left behind. In some situations, this means that another surgery could be needed to remove remaining cancer cells. There are different ways to check for microscopic cells that will ensure a clean margin.
What is the treatment for skin cancer?
According to the National Cancer Institute, some of the most common treatment options include: radiation therapy .
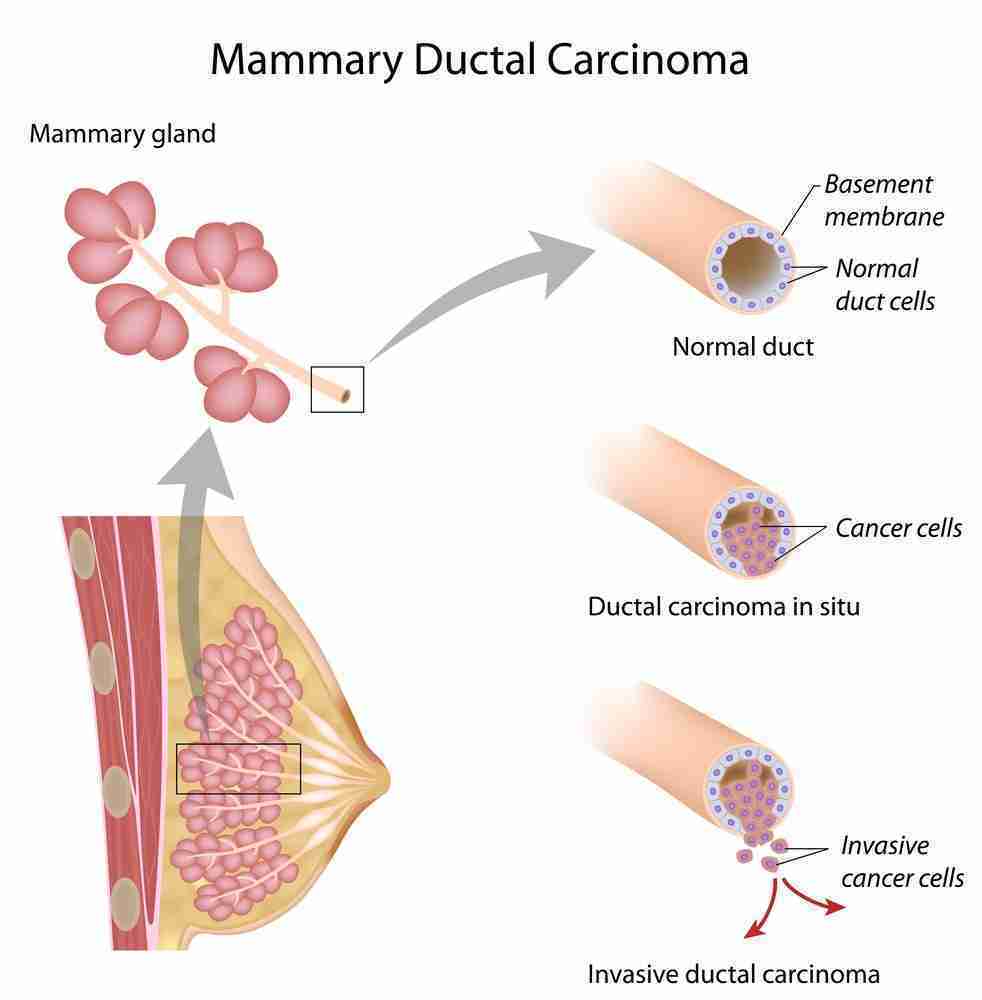
What is invasive cancer?
Summary. Invasive cancer is a term that describes cancer that has grown past the original tissue or cells where it developed, and spread to otherwise healthy surrounding tissue. According to the National Cancer Institute, invasive cancer is also called infiltrating cancer. When cancer cells reach this point, they ...
What happens if cancer metastasizes?
If cancer metastasizes, the mortality rate from the cancer generally increases. Keep reading to learn more about invasive cancer, the general outlook, and insight into some of the various forms of invasive cancer.
What cancers will be treated in 2021?
Last medically reviewed on April 23, 2021. Breast Cancer. Colorectal Cancer.
Can a non-invasive cancer patient see a doctor?
This can include cancer screenings to check for early signs of potential cancer. A person diagnosed with non-invasive cancer should see a doctor more frequently for checks. A doctor can check to see if the cancer has progressed or come back.
Is metastatic cancer invasive or invasive?
Invasive cancer vs. metastatic cancer. The National Cancer Institute says invasive cancer occurs when cancer cells have spread beyond the tissue and cells where the cancer first developed, and have spread to otherwise healthy surrounding tissue. states that metastatic cancer occurs as a progression of invasive cancer.
What is the purpose of a mammogram?
Receiving a mammogram. During a mammogram, you stand in front of an X-ray machine designed for mammography. A technician places your breast on a platform and positions the platform to match your height. The technician helps you position your head, arms and torso to allow an unobstructed view of your breast.
What is the treatment for lobular carcinoma?
Treatment often consists of surgery and additional (adjuvant) therapy, which may include chemotherapy, radiation and hormone therapy.
What is the procedure to remove lobular carcinoma?
Surgery for invasive lobular carcinoma may include: Removing the cancer and a small portion of healthy tissue. Called a lumpectomy (wide local excision), this procedure allows you to keep most of your breast tissue.
What test is used to diagnose invasive lobular carcinoma?
Invasive lobular carcinoma is less likely to be detected on a mammogram than other types of breast cancer are. Still, a mammogram is a useful diagnostic test. Ultrasound.
What is the best test for breast cancer?
Ultrasound uses sound waves to create pictures of your breast. Invasive lobular carcinoma may be more difficult to detect with ultrasound than may other types of breast cancer. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
What is lumpectomy surgery?
A lumpectomy involves removing the cancer and some of the healthy tissue that surrounds it. This illustration shows one possible incision that can be used for this procedure, though your surgeon will determine the approach that's best for your particular situation.
How does breast cancer affect you?
It can make you feel emotions ranging from shock and fear to anger, anxiety or depression. There's no "right" way to feel and act when you're dealing with cancer. With time, you'll find your own way of coping with your feelings.
What is the diagnosis of a mastectomy?
Diagnosis. Mastectomy specimen containing a very large invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. To the right, the nipple can be seen on the pink skin, while in the center of the picture a large blue and pink swelling or tumor can be seen. Blood stained fat tissue is seen at the cut margins.
Which type of breast cancer has a lower recurrence rate?
Mucinous, papillary, cribriform , and tubular carcinomas have longer survival, and lower recurrence rates. The prognosis of the most common form of IDC, called "IDC Not Otherwise Specified", is intermediate. Finally, some rare forms of breast cancer (e.g., sarcomatoid carcinoma, inflammatory carcinoma) have a poor prognosis.
What is invasive ductal carcinoma?
Invasive carcinoma of no special type (NST) also known as invasive ductal carcinoma or ductal NOS and previously known as invasive ductal carcinoma, not otherwise specified (NOS) is a group of breast cancers that do not have the "specific differentiating features". Those that have these features belong ...
What is invasive carcinoma of no special type?
Invasive carcinoma of no special type (NST) also known as invasive ductal carcinoma or ductal NOS and previously known as invasive ductal carcinoma, not otherwise specified (NOS) is a group of breast cancers that do not have the "specific differentiating features". Those that have these features belong ...
What is pleomorphic carcinoma?
In this group are: pleomorphic carcinoma, carcinoma with osteoclast-like stromal giant cells, carcinoma with choriocarcinomatous features, and carcinoma with melanotic features. It is a diagnosis of exclusion, which means that for the diagnosis to be made all the other specific types must be ruled out.
What is the most common form of breast cancer?
Classification. Invasive carcinoma of no special type (NST) is the most common form of invasive breast cancer. It accounts for 55% of breast cancer incidence upon diagnosis, according to statistics from the United States in 2004. On a mammogram, it is usually visualized as a mass with fine spikes radiating from the edges.
How long does it take for a DCIS to become invasive?
Unless treated, approximately 60 percent of low-grade DCIS lesions will have become invasive at 40 years follow-up. High-grade DCIS lesions that have been inadequately resected and not given radiotherapy have a 50 percent risk of becoming invasive breast cancer within seven years.

Invasive
Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
- About 1 in 10 invasive breast cancers is an invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC). ILC starts in the breast glands that make milk (lobules). Like IDC, it can spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body. Invasive lobular carcinoma may be harder to detect on physical exam and imaging, like mammograms, than invasive ductal carcinoma. And compared to other kinds of invasive carcin…
Less Common Types of Invasive Breast Cancer
- There are some special types of breast cancer that are sub-types of invasive carcinoma. They are less common than the breast cancers named above and each typically make up fewer than 5% of all breast cancers. These are often named after features of the cancer cells, like the ways the cells are arranged. Some of these may have a better prognosis than the more common IDC. These in…
Treating Invasive Breast Cancer
- Treatment of invasive breast cancer depends on how advanced the cancer is (the stage of the cancer) and other factors. Most women will have some type of surgery to remove the tumor. Depending on the type of breast cancer and how advanced it is, you might need other types of treatment as well, either before or after surgery, or sometimes both. See T...