Hence any patient with accommodative insufficiency requires to be treated. This can be done with the help of eye glasses while doing close work and eye exercises also called visual therapy. Wearing reading glasses is simple solution to reduce stress and fatigue to the eyes in such patients.
What is accommodative dysfunction in the eye?
Aug 18, 2015 · What are the treatment options for accommodative dysfunction? The first and most common line of treatment are simple reading glasses. Reading glasses can reduce nearpoint visual stress and ease the focusing burden on …
How to treat accommodative insufficiency in the eyes?
Mar 11, 2019 · This can be done with the help of eye glasses while doing close work and eye exercises also called visual therapy. Wearing reading glasses is simple solution to reduce stress and fatigue to the eyes in such patients. The child must wear training glasses when he is performing near task. This will gradually develop stamina to the eyes.
What is the process of accommodation in the eye?
May 09, 2018 · Treatment Over-the-counter reading glasses are made for adults and are generally not advised for children, as they can create new problems. At our clinic, treatment of accommodative dysfunctions with optometric vision therapy has a very high success rate (greater than 90%) and often requires between 12 to 24 sessions, when combined with home …
What is accommodation in optometry?
Dec 14, 2021 · Typically, both eyes work in tandem, so vision isn't disrupted; however, it is possible for the eyes to adjust separately. This is called absolute accommodation.For example, if one eye is closed ...

How do you fix an accommodation in the eye?
Whats an effective treatment for reduced accommodation?
The most common treatment for accommodative disorders is glasses or contact lenses. However, the combination of vision therapy and corrective lenses can be more effective and treat the underlying cause of accommodative disorders.
How do you fix accommodative dysfunction?
What does it mean if your eyes don't accommodate?
How can you improve eye convergence?
Hold out a pen at an arm's length and look at its tip. Slowly bring the tip close to your eyes, keeping the tip at level with your eyes. Then again take it back to an arm's length and hold it there for 10 seconds. Again slowly bring the tip close to your eyes to the point where you feel some strain.
What are the different types of accommodative disorders?
- Accommodative Insufficiency. Difficulty efficiently sustaining focus at near. ...
- Accommodative Infacility. Difficulty efficiently switching focus between near and far and back.
- Accommodative Spasm.
What are the signs and symptoms of accommodative Infacility?
- Motion sickness.
- Difficulty reading.
- Double vision.
- Lack of concentration.
- Fatigue.
- Headaches.
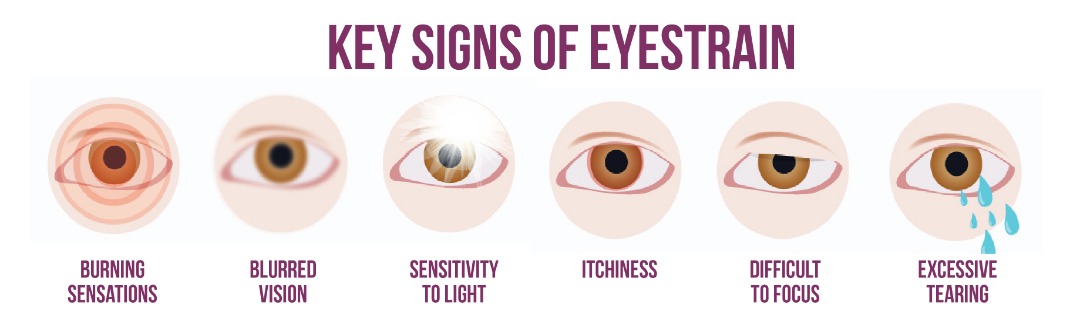
- Blurred vision.
- Print moving on a page while reading.
What are two possible problems that can affect the accommodative functions?
How do you test for eye accommodation?
What is eye teaming?
What causes eyes to not focus?
Refractive errors (the most common cause) Age-related macular degeneration. Cataracts. Diabetic retinopathy.Sep 5, 2020
How can convergence insufficiency be corrected?
How does accommodation affect the eye?
Accommodation is the process by which the vertebrate eye changes optical power to maintain a clear image or focus on an object as its distance varies. In this, distances vary for individuals from the far point —the maximum distance from the eye for which a clear image of an object can be seen, to the near point —the minimum distance for a clear image. Accommodation usually acts like a reflex, including part of the accommodation-vergence reflex, but it can also be consciously controlled. Mammals, birds and reptiles vary their eyes' optical power by changing the form of the elastic lens using the ciliary body (in humans up to 15 dioptres ). Fish and amphibians vary the power by changing the distance between a rigid lens and the retina with muscles.
How does the eye change focus?
This dramatic change in focal power of the eye of approximately 15 dioptres (the reciprocal of focal length in metres) occurs as a consequence of a reduction in zonular tension induced by ciliary muscle contraction . This process can occur in as little as 224 ± 30 milliseconds in bright light. The amplitude of accommodation declines with age. By the fifth decade of life the accommodative amplitude can decline so that the near point of the eye is more remote than the reading distance. When this occurs the patient is presbyopic. Once presbyopia occurs, those who are emmetropic (do not require optical correction for distance vision) will need an optical aid for near vision; those who are myopic (nearsighted and require an optical correction for distance vision), will find that they see better at near without their distance correction; and those who are hyperopic (farsighted) will find that they may need a correction for both distance and near vision. Note that these effects are most noticeable when the pupil is large; i.e. in dim light. The age-related decline in accommodation occurs almost universally to less than 2 dioptres by the time a person reaches 45 to 50 years, by which time most of the population will have noticed a decrease in their ability to focus on close objects and hence require glasses for reading or bifocal lenses. Accommodation decreases to about 1 dioptre at the age of 70 years. The dependency of accommodation amplitude on age is graphically summarized by Duane 's classical curves.
What is the most common form of accommodative dysfunction?
Presbyopia, physiological insufficiency of accommodation due to age related changes in lens (decreased elasticity and increased hardness) and ciliary muscle power is the commonest form of accommodative dysfunction. It will cause gradual decrease in near vision.
What is an ill sustained accommodation?
Ill-sustained accommodation is a condition similar to accommodative insufficiency. In this, range of accommodation will be normal, but after excessive near work accommodative power will decrease.
What is accomodative insufficiency?
Accommodative insufficiency is the condition where amplitude of accommodation of a person is lesser compared to physiological limits for his age. Premature sclerosis of lens or ciliary muscle weaknesses due to systemic or local cases may cause accommodative insufficiency.
What is accomodative excess?
Accommodative excess occurs when an individual uses more than normal accommodation for performing certain near work. Modern definitions simply regard it as an inability to relax accommodation readily.
What are the two types of accommodation anomalies?
There are many types of accommodation anomalies. It can be broadly classified into two, decreased accommodation and increased accommodation . Decreased accommodation may occur due to physiological (presbyopia), pharmacological (cycloplegia) or pathological. Excessive accommodation and spasm of accommodation are types of increased accommodation.
How is presbyopia corrected?
In recent years, surgery has been the new frontier for presbyopia therapy, by either direct intraocular replacement of the lens or by modification of extraocular structures such as the cornea or sclera. 12 Modification involves the use of corneal inlays, devices that are surgically placed within the corneal stroma of the non-dominant eye to change the optical properties of the cornea. 12 Inlays serve as an attractive option for correction of presbyopia, since they are an additive, removable technology. Unlike laser refractive surgery, which ablates corneal tissue, the inlay can easily be removed if the patient is unable to adapt to this type of vision correction. The development of corneal inlays has become possible through major advancements made in biomaterials as well as surgical devices such as the femtosecond laser. 5
How to correct presbyopia?
Another approach to presbyopia is excimer laser surgery , which remodels the corneal curvature to improve uncorrected vision and reduce dependence on glasses or contacts. Approved in 2001, one of the most popular techniques, LASIK, has seen tremendous improvements in technology, which now includes correction of presbyopia, or “presbyLASIK.” While conventional monovision LASIK corrects the dominant eye for distance and the non-dominant eye for near, presbyLASIK involves a number of different approaches. 12 Nevertheless, there is no “one size fits all” for presbyopia; each surgical strategy presents its own unique benefits and limitations that involve some degree of compromise between distant and near visual acuities. 16 For example, crystalline lens removal and replacement with an IOL may not be preferable in a young patient with presbyopia without refractive error. 16 Similarly, treatment of the crystalline lens may not be a suitable choice for a patient with early cataract. Thus, there are a number of considerations that have limited the widespread acceptance of surgical correction, keeping the correction of presbyopia a significant challenge for refractive surgeons.
How does ciliary muscle help with near vision?
This increase in axial thickness results in an increase in the dioptric power , facilitating accommodation for improved near vision. With ciliary muscle relaxation, the tension on the zonules increases, resulting in lens flattening and a reduction in dioptric power. All of these structures are modified by the aging process, but it is the reduction in lens flexibility that’s most associated with loss of accommodation. 6-8 Decreased lens flexibility limits the lens rounding and thickening needed for near focus. Models of the process suggest that as the lens becomes less flexible with age, ciliary muscles apply greater tension to zonules, causing ligament fatigue. Muscular atrophy is also a contributing factor. 9 These paired changes in the physical properties of the focal apparatus collectively result in the presbyopic condition. The end effect is loss of near focus, accompanied by blurred vision, eye strain and headaches in many individuals. For some, these secondary effects are exacerbated after reading or computer use. 6
What is accommodation in primates?
Much of what we know about accommodation comes from research on non-human primates. Studies in the rhesus monkey have shown that ciliary body displacement plays a key role in the accommodation process. The force of contraction moves the muscle in an anterior direction, and this displacement is attenuated in aging animals. One study confirmed the roles of both muscle atrophy and decline in ligament elasticity in the development of presbyopia, 9 and another recently showed that similar movement occurs in the human eye. 10 Hopefully, these findings can provide clues to pharmacological strategies to reverse or reduce accommodative loss.
When do you wake up with presbyopia?
Like death and taxes, presbyopia is one of life’s certainties, an inevitable companion to the aging process: Sometime between your 35th and 45th birthday, you wake up to the reality that your arms are no longer long enough to hold the medicine bottle at a proper reading distance. While not pathological, this condition requires some form ...
Is AMD a sight threatening condition?
The aging population represents a impending explosion of unmet medical need. Though sight-threatening conditions such as AMD often dominate the conversation of age-related diseases, it’s important to remember that conditions such as presbyopia impact the quality of life of many more individuals. While surgical and device-based treatments for this condition hold promise, it’s also exciting to see the innovations provided by pharmaceutical approaches. REVIEW
Is PRX 100 safe for presbyopia?
19 PRX-100 has been formulated to induce miosis without stimulation of accommodation, and has been shown to be safe and effective in increasing near vision for up to eight hours. Presbyopia Therapies hopes that PRX-100 will supplement current presbyopia treatments by providing short-term, self-administered correction for daytime near vision.
What is accommodation in optometry?
Accommodation is the process whereby the eye is able to change the point of focus from a distant object to a near object.
When a healthy eye is relaxed, it is focused at optical infinity?
When a healthy eye ( not suffering from any refractive errors, i.e. not nearsighted or longsighted) is relaxed, it is focused at optical infinity. This sounds quite profound; and means that when a normal eye is relaxed, distant objects are in focus.
What happens when the muscles inside the eye contract?
It’s an optical change in the eye and happens when the muscles inside the eye contract, allowing the optical power of the crystalline lens to be increased so that near objects can be brought into focus on the retina.
How to treat nearpoint visual stress?
The first and most common line of treatment are simple reading glasses. Reading glasses can reduce nearpoint visual stress and ease the focusing burden on the ciliary muscles that flex your internal lens. When reading glasses alone are not enough, another effective treatment option is vision therapy.
Why do children have accommodative dysfunction?
Other children can develop accommodative dysfunction while in school as a result of long periods of visual tasks that lack those important stereoscopic/depth cues. Everybody is different, including our eyes. Reading something up close can be more tiresome on the eyes for some people than others.
Why is my vision blurry when reading?
However, there are times when your accomodation ability can be compromised. A common problem involving accommodation is accommodative dysfunction. This is when your eyes can’t maintain comfort or focus when accommodating, especially with near distances. This leads to blurred vision at close, especially when reading.
What happens when you lack accommodative skills?
When someone who lacks appropriate accommodative skills continuously performs such near vision tasks that deeply require accommodation, they may experience blurred vision, ocular discomfort or fatigue, which can then result in reduced vision and loss of concentration.
Where is the optometrist located in Costa Mesa?
Valerie Lam or Dr. Thanh Mai to learn more. Our optometry practice is located in Costa Mesa at 3151 Airway Ave. Suite J2, Costa Mesa, CA 92626.
Does accomodative dysfunction have to do with eye muscles?
Accommodative dysfunction generally does not have to do with problems with our eye muscles or our lens. While growing up, some children do not develop enough focusing stamina and have trouble focusing at something up close or far for too long.
What medications cause eye fatigue?
Asthenopia or eye fatigue and resultant accommodative dysfunction can occur due to certain medications. For example antihistamines, Ritalin, Concerta etc.
What is accomodative insufficiency?
Accommodative insufficiency is an eye disorder in which the patient finds difficult to sustain focusing near object for a prolonged period of time. The problem is not related with your eyesight or any refractory error. It is a problem related with eye fatigue which in turn causes stress and strain to the eye especially when doing near work for extended period of time.
What is accommodation in the eye?
Accommodation occurs by movement of the lens inside the eye.
What are the three types of accommodative dysfunctions?
There are generally three types of accommodative dysfunctions: Accommodative Insufficiency- difficulty efficiently sustaining focus at near. This is the most common type of accommodative dysfunction. The increased effort required to maintain clear vision at near can decrease performance on near tasks. Accommodative Infacility- difficulty ...
What is the term for a spasm of the focusing muscle that prevents the focusing muscles from fully
Accommodative Spasm- a spasm of the focusing muscle which prevents the focusing muscles from fully relaxing. This generally causes blurry vision both near and far.
When do you need bifocals?
Accommodative ability is generally well developed by 4 months of age and should continue to work efficiently until around age 40, when the lens begins to become less flexible and therefore harder to move. This is why the majority of older adults require reading glasses or bifocals as they get older.
Can you use reading glasses for children?
Treatment may include the prescribing of special lenses to help reduce eye strain at near and/or optometric vision therapy. Over-the-counter reading glasses are made for adults and are generally not advised for children, as they can create new problems.
What is the ability of the eye to automatically switch from one condition to the other called?
This ability of your eye to automatically switch from one condition to the other is referred to as the accommodation reflex. This reflex ultimately affects the way light enters the eye. Objects farther away require less refraction than objects ...
Why do we have accommodation reflex?
The accommodation reflex of the eye is a response that automatically occurs when you switch focus from an object that's far away to one that's closer. This response enables you to switch between objects and still maintain focus ...
What is the reflex that enables us to switch focus between objects far away and objects closer to us?
One involuntary reflex our eyes make is called the accommodation reflex . This reflex enables us to switch focus between objects far away and objects closer to us.
What muscles control the shape of the lens?
The muscles that control the shape of the lens are called ciliary muscles. When you're looking at an object far from you, like the building out your window, the ciliary muscles around your eye are relaxed, the lens is stretched out, and the fibers around the eye are tight. This maximizes your ability to see objects at a distance clearly - called ...
Why is my field of vision blurry?
If damage to the eye prevents this reflex from taking place , the field of vision will be blurry when switching between different objects. There is a quick test you and a friend can do to test your accommodation reflex. Have your friend stand directly in front of you.
What is negative accommodation?
This maximizes your ability to see objects at a distance clearly - called negative accommodation. In contrast, when you're looking at an object close to you, like the fork full of salad during lunch, the ciliary muscles around your eye tighten, the lens becomes rounder in shape, and the fibers around the lens are relaxed.
Why does the eye adjust its shape?
Objects farther away require less refraction than objects that are closer to you, so the eye automatically adjusts its shape accordingly. When the lens is rounded in shape, it has more refractive power. A trick to remembering this: objects far away require less refraction, so you experience negative accommodation, ...

Overview
Accommodation is the process by which the vertebrate eye changes optical power to maintain a clear image or focus on an object as its distance varies. In this, distances vary for individuals from the far point—the maximum distance from the eye for which a clear image of an object can be seen, to the near point—the minimum distance for a clear image. Accommodation usually acts like a r…
Theories of mechanism of the eye
• Helmholtz—The most widely held theory of accommodation is that proposed by Hermann von Helmholtz in 1855. When viewing a far object, the circularly arranged ciliary muscle relaxes allowing the lens zonules and suspensory ligaments to pull on the lens, flattening it. The source of the tension is the pressure that the vitreous and aqueous humours exert outwards onto the sclera. When viewing a near object, the ciliary muscles contract (resisting the outward pressure on the …
Anomalies of accommodation
There are many types of accommodation anomalies. It can be broadly classified into two, decreased accommodation and increased accommodation. Decreased accommodation may occur due to physiological (presbyopia), pharmacological (cycloplegia) or pathological. Excessive accommodation and spasm of accommodation are types of increased accommodation.
Presbyopia, physiological insufficiency of accommodation due to age related changes in lens (d…
See also
• Accommodative esotropia
• Latent hyperopia
• Myopia
• Pseudomyopia
• Accommodation in fish
External links
• oph/723 at eMedicine—"Presbyopia: Cause and Treatment"
• Ocular+Accommodation at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)