
What is fms-like tyrosine kinase 3?
Tanja A. Gruber, Jeffrey E. Rubnitz, in Hematology (Seventh Edition), 2018 FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3, FLK2) is a class III receptor tyrosine kinase that is normally expressed in early hematopoietic progenitors that are CD34+ /c-Kit +.
What is the prevalence of tyrosine kinase mutation in AML?
KIT mutations. Activating mutations in the KIT receptor tyrosine kinase are common in CBF-AML (AML with t (8;21) or inv (16)/t (16;16)) occurring with a frequency of approximately 30% in these subtypes [68–70].
What is the prevalence of tyrosine kinase activation mutations in CBF-AML?
Activating mutations in the KIT receptor tyrosine kinase are common in CBF-AML (AML with t (8;21) or inv (16)/t (16;16)) occurring with a frequency of approximately 30% in these subtypes [68–70].
What is the function of FLT3 in leukemia?
FLT3 is a receptor tyrosine kinase that is involved in regulating proliferation of hematopoietic progenitor cells. Two classes of activating FLT3 mutations occur in AML: (1) internal tandem duplication ( FLT3 -ITD) which occur in 20–25% of patients and (2) tyrosine kinase domain mutations ( FLT3 -TKD) which are seen in 5–10% of patients [48].
What do tyrosine kinase inhibitors treat?
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are a type of targeted therapy. TKIs come as pills, taken orally. A targeted therapy identifies and attacks specific types of cancer cells while causing less damage to normal cells.
Are tyrosine kinase inhibitors targeted therapy?
These enzymes may be too active or found at high levels in some types of cancer cells, and blocking them may help keep cancer cells from growing. Some tyrosine kinase inhibitors are used to treat cancer. They are a type of targeted therapy.
What does tyrosine kinase do in CML?
TKIs are a type of targeted therapy. They work by switching off (inhibiting) the tyrosine kinase made by the BCR-ABL1 gene in leukaemia cells. This slows or stops the bone marrow from making abnormal white blood cells. It also allows the leukaemia cells to mature and die.
Are tyrosine kinase inhibitors chemotherapy?
Any drug used to treat cancer (including tyrosine kinase inhibitors or TKIs) can be considered chemo, but here chemo is used to mean treatment with conventional cytotoxic (cell-killing) drugs that mainly kill cells that are growing and dividing rapidly.
What is targeted therapy for leukemia?
Targeted therapy is sometimes used to treat chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). It uses drugs to target specific molecules (such as proteins) on the surface of cancer cells. These molecules help send signals that tell cells to grow or divide.
Which drugs are tyrosine kinase inhibitors?
Examples of TKIs include:axitinib (Inlyta)dasatinib (Sprycel)erlotinib (Tarceva)imatinib (Glivec)nilotinib (Tasigna)pazopanib (Votrient)sunitinib (Sutent)
What type of inhibitor is imatinib Gleevec?
Imatinib (Gleevec) is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) used in the treatment of Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) or metastatic malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) [298]. In normal cells, tyrosine kinase enzymes are turned on and off as required.
What is the best medication for CML?
Imatinib. A medicine called imatinib is now the main treatment for CML. It's usually given soon after a diagnosis is made to slow the progression of the cancer and stop it reaching an advanced phase. Imatinib works by reducing the production of abnormal white blood cells.
What type of inhibitor is dasatinib?
Dasatinib is a second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor, more potent than imatinib on BCR-ABL and efficient on most of the imatinib-resistant ABL mutants. It is also effective on cKIT, platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)–receptor and, in contrast to imatinib, on SRC family kinases (SFKs).
What type of chemo is used for CML?
The most common chemotherapy drug used for CML is hydroxycarbamide. This aims to reduce your white blood cell count and control any symptoms you might be having. You take hydroxycarbamide as capsules. The drugs used for the blast phase of CML are the same as for acute myeloid leukaemia (AML).
Can TKI cure CML?
Although a bone marrow transplant is the only treatment that can cure CML, it is used less often now. This is because bone marrow transplants have a lot of side effects, while TKIs are very effective for CML and have fewer side effects.
Are tyrosine kinase inhibitors immunotherapy?
A number of recent studies have indicated that antiangiogenic tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) target multiple components of the tumor microenvironment and are an ideal class of agents for synergizing with cancer immunotherapy.
What is FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3?
FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3, FLK2) is a class III receptor tyrosine kinase that is normally expressed in early hematopoietic progenitors that are CD34+ /c-Kit +. When bound by its ligand (FLT3 ligand or FL) the receptor dimerizes, leading to activation of the receptor 's intrin sic tyrosine kinase activity.
What is FLT3 mutation?
FLT3 mutations. Mutations in FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) are the second most common mutation in AML, occurring in approximately 25–30% of all patients [47]. FLT3 is a receptor tyrosine kinase that is involved in regulating proliferation of hematopoietic progenitor cells.
What is FLT3?
FLT3 regulates the growth and differentiation of CD34+ hematopoietic cells via multiple signaling pathways, including PI3 kinase-Akt, Ras-MAPK and STAT5a, and dysregulation of these pathways leads to increased proliferation and decreased apoptosis [3,5,6].
What are the three most common mutations in NPM1?
The three most common mutations (types A, B, and D ) constitute approximately 90–95% of mutations. Wild-type NPM1 contains two tryptophan residues (W, shaded pink) that are important for its normal nucleolar localization.
What is the role of PDGF in glioma?
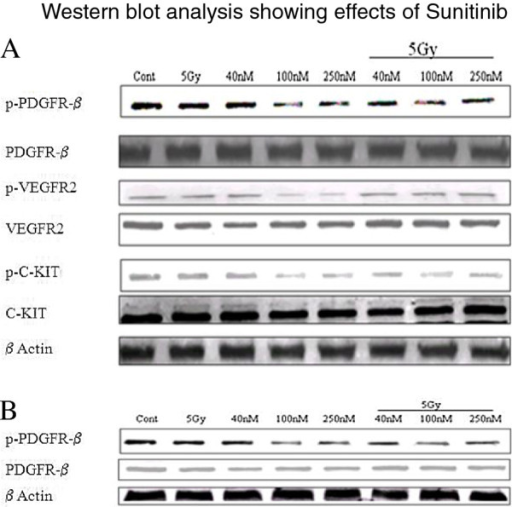
Aberrant activation of PDGF/PDGFR signaling is one of the hallmarks of glioma biology. Overexpression of PDGF/PDGFR has been found in glioma cells and surrounding ECs; coexpression of ligand receptor in these cells allows both autocrine and paracrine forms of activation, resulting in vessel formation and glioma cell migration, survival, and invasion. 33 Both sorafenib and sunitinib are multitargeted angiogenesis inhibitors that target PDGFR, VEGFR, mast/stem cell growth factor (c-Kit) and FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT-3). They have been approved for the treatment of multiple cancer types, including renal cell carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor, and gastrointestinal stromal tumors. A phase II trial of sunitinib alone in recurrent anaplastic astrocytoma and recurrent GBM failed to show significant antitumor activity; no partial responses (PRs) or complete responses (CRs) were observed in the cohort.34 A phase I trial of the combination of sorafenib with temozolomide and radiation therapy showed that sorafenib was well tolerated. 35 Combination of sorafenib and temsirolimus (mammalian target of rapamycin [mTOR] inhibitor) showed poor efficacy with a 6-month PFS rate of 0%. 36 Further clinical trials of different combinations of sorafenib with other agents are now under study ( NCT01434602, NCT01817751 ).
Is sunitinib discontinued?
The dose of the sunitinib was reduced to 25 mg/day and loperamide was continued. The diarrhea symptoms improved for a short duration; however, the patient was re-hospitalized with severe diarrhea. Sunitinib was discontinued at this time.
What is midostaurin? What is its function?
Midostaurin ( N -benzoylstaurosporine; PKC412) is an inhibitor of multiple TKs including wild-type and D816V-mutated KIT, FLT3, PDGFR-α/β, FGFR1, and VEGFR2. In Ba/F3 cells transformed by KIT D816V, the IC 50 of midostaurin was 30–40 nM compared with greater than 1 µM with imatinib. A PR with midostaurin in a patient with MCL and an associated MDS/MPN, and encouraging responses in a phase II trial of 26 patients with advanced SM led to a global, multicenter, open-label trial of midostaurin (100 mg twice daily on 28-day continuous cycles) in patients with ASM, MCL, and SM-AHN. 28
What is RAF inhibitor?
In terms of RAF inhibitors, that which has received most attention to date is sorafenib. Previously designated BAY43-9006, this multikinase inhibitor was initially identified as a RAF kinase inhibitor (of CRAF, BRAF, and mutant BRAF) but also targets VEGFRs 1, 2, and 3; platelet-derived growth factor receptor β (PDGFRβ); FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (Flt-3); c-Kit protein (c-Kit); and RET RTKs. It is currently licensed for use in hepatocellular and renal cell cancers. Multiple phase I and II clinical trials are currently evaluating sorafenib in CRC in combinations with either chemotherapy, cetuximab, bevacizumab, chemotherapy plus cetuximab, or chemotherapy plus bevacizumab.
What is sorafenib used for?
Sorafenib is an orally active multikinase inhibitor with effects on tumor cell proliferation and tumor angiogenesis. It has been shown to inhibit Raf kinase; vascular endothelial growth factor receptors 1, 2, and 3; platelet-derived growth factor receptor; FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3; c-Kit protein; and RET tyrosine kinase. It has been approved for use in renal and hepatocellular carcinoma, but seems to have activity in several other malignancies. In a subgroup analysis of a phase III trial (TARGET), adverse events were independent of age.55 In addition, side effects caused by sorafenib were similar in both elderly and younger patients treated with the expanded access program in North America 56 and commonly included fatigue, hand-foot syndrome, diarrhea, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia.
Is there a FLT3 inhibitor?
Inhibitors of FLT3 have been in clinical trials for many years. Yet no FLT3 inhibitor has received FDA approval. The clinical activity of single-agent first generation inhibitors (midostaurin, lestaurtinib, sunitinib, sorafenib, semaxanib, tandutinib) has been limited, only demonstrating transient reductions in blood and/or marrow blasts but, for most, without achievement of objective responses. In a randomized study of standard salvage therapy versus addition of lestaurtinib, no benefit with regard to response rate or survival was observed. A randomized study of standard induction therapy in patients 18 to 60 years of age with or without sorafenib (regardless of FLT3 status) demonstrated superior relapse and event free survival for the sorafenib treated group. The CALGB 10603 (RATIFY) study randomized 717 patients between ages 18 and 60 with newly diagnosed FLT3 positive (both ITD and TKD) AML to receive a standard 3 + 7 induction alone or in combination with midostaurin. Ten years after conception the final results were presented in 2016. Although the addition of midostaurin did not improve remission rates, the FLT3 inhibitor group enjoyed a statistically significant event free and overall survival benefit that extended to both ITD and TKD groups and persisted regardless of mutation load. The outcome of this study defines the combination of 3 + 7 and midostaurin (FDA approval pending) as a new standard of care for this patient population.
