Is intravenous thrombolysis for stroke a contraindication?
Apr 05, 2022 · Treating ischemic stroke. If you get to the hospital within 3 hours of the first symptoms of an ischemic stroke, you may get a type of medicine called a thrombolytic (a “clot-busting” drug) to break up blood clots. Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) is a thrombolytic. tPA improves the chances of recovering from a stroke.
Is early ischemia a contraindication to IV rtPA in patients with stroke?
Acute Intracranial Hemorrhage. The finding of intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) on brain imaging is an absolute contraindication to administering intravenous (IV) recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rtPA) for acute ischemic stroke in the most recent American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines and the Activase (alteplase, rtPA) (Genentech, Inc) drug label. 1 This includes …
Which anticoagulants are contraindicated for thromboplastin (rtPA)?
Abnormal blood glucose (<50 mg/dL) No. Yes. Relative Contraindications/Warnings to tPA. Only minor or rapidly improving stroke symptoms. No. Yes. Major surgery or serious non-head trauma in the previous 14 days. No.
Are glucose disturbances a contraindication for rtPA administration in stroke patients?
Diuretics are not indicated for stroke prevention other than for their role in controlling BP, and antilipemic agents have bot been found to have a significant effect on stroke prevention. The calcium channel blocker nimodipine is used in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage to decrease the effects of vasospasm and minimize tissue damage.

Is aneurysm a contraindication to tPA?
What are the contraindications to thrombolytic therapy?
- Recent intracranial hemorrhage (ICH)
- Structural cerebral vascular lesion.
- Intracranial neoplasm.
- Ischemic stroke within three months.
- Possible aortic dissection.
- Active bleeding or bleeding diathesis (excluding menses)
Why are thrombolytics contraindicated in hemorrhagic stroke?
When are thrombolytics contraindicated?
What is endovascular therapy for stroke?
What are the indications for thrombolytic therapy in a stroke?
Is heparin contraindicated in a patient with a hemorrhagic CVA?
What is the general treatment for hemorrhagic stroke?
What is fibrinolytic therapy for MI?
When is fibrinolytic therapy indicated?
Which of the following should not be treated with a fibrinolytic?
Is Plavix a contraindication for tPA?
What is the best medicine for a stroke?
If you get to the hospital within 3 hours of the first symptoms of an ischemic stroke, you may get a type of medicine called a thrombolytic (a “clot-busting” drug) to break up blood clots. Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) is a thrombolytic. tPA improves the chances of recovering from a stroke.
How to treat hemorrhagic stroke?
Surgical treatment. Hemorrhagic strokes may be treated with surgery. If the bleeding is caused by a ruptured aneurysm, a metal clip may be put in place to stop the blood loss.
What do you ask at a stroke hospital?
At the hospital, health professionals will ask about your medical history and about the time your symptoms started. Brain scans will show what type of stroke you had. You may also work with a neurologist who treats brain disorders, a neurosurgeon that performs surgery on the brain, or a specialist in another area of medicine.
What is the best way to get to the hospital for a stroke?
Stroke Treatment. Calling 9-1-1 at the first symptom of stroke can help you get to the hospital in time for lifesaving stroke care. Your stroke treatment begins the moment emergency medical services (EMS) arrives to take you to the hospital. Once at the hospital, you may receive emergency care, treatment to prevent another stroke, ...
Why do people go to the hospital for stroke?
Stroke patients who are taken to the hospital in an ambulance may get diagnosed and treated more quickly than people who do not arrive in an ambulance. 1 This is because emergency treatment starts on the way to the hospital. The emergency workers may take you to a specialized stroke center to ensure that you receive the quickest possible diagnosis ...
What is needed to stop brain bleed?
Medicine, surgery, or other procedures may be needed to stop the bleeding and save brain tissue. For example:
What do you need to do after a stroke?
After a stroke, you may need rehabilitation ( rehab) to help you recover. Before you are discharged from the hospital, social workers can help you find care services and caregiver support to continue your long-term recovery.
How to reduce risk of stroke?
To decrease your risk of having another stroke or transient ischemic attack, your doctor may recommend a procedure to open up an artery that's narrowed by plaque. Options vary depending on your situation, but include:
What tests are needed for stroke?
That means you'll have a CT scan or other imaging test soon after arrival. Doctors also need to rule out other possible causes of your symptoms, such as a brain tumor or a drug reaction.
What is a cerebral angiogram?
Cerebral angiogram. Cerebral angiogram. A cerebral angiogram showing a carotid aneurysm associated with stroke. A physical exam. Your doctor will do a number of tests you're familiar with, such as listening to your heart and checking your blood pressure. You'll also have a neurological exam to see how a potential stroke is affecting your nervous ...
How to deliver tpa to brain?
Medications delivered directly to the brain. Doctors insert a long, thin tube (catheter) through an artery in your groin and thread it to your brain to deliver tPA directly where the stroke is happening. The time window for this treatment is somewhat longer than for injected tPA, but is still limited.
How does TPA help with stroke?
This drug restores blood flow by dissolving the blood clot causing your stroke. By quickly removing the cause of the stroke, it may help people recover more fully from a stroke. Your doctor will consider certain risks, such as potential bleeding in the brain, to determine if tPA is appropriate for you.
How to evaluate stroke care?
One way to evaluate the care of patients diagnosed with stroke is to look at the percentage of patients receiving the timely and effective care measures that are appropriate. The goal is 100 percent.
What does it mean when you think about a stroke?
A stroke – if you think about it as interruption of blood flow to the brain, either there isn't enough blood flow getting to the brain or there's too much.
How long does it take for a stroke to be treated with IV thrombolysis?
As is the case for most relative contraindications, the potential risks and benefits of IV thrombolysis in this subset of patients most likely varies considerably according to several factors. Twenty-one days has been arbitrarily chosen and in some cases may be unnecessarily cautious. Factors to consider include the time elapsed since hemorrhage, the severity of stroke deficits, the cause and severity of the hemorrhage, and what treatments were provided for the prior bleeding episode. Patients with severe stroke deficits who have had occult GI/GU hemorrhages or diffuse or multifocal lesions susceptible to bleeding may be safer candidates for the consideration of intra-arterial stroke therapy, as the risk of systemic IV thrombolysis may be prohibitive in these patients.
What is the exclusion criterion for IV RTPA?
Uncontrolled hypertension to values exceeding a systolic of 185 mm Hg or diastolic of 110 mm Hg is an exclusion criterion to IV rtPA according to the 2013 AHA guidelines and the drug label. 1 This is likely derived from an exclusion criterion for the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) trials. 6 The relationships between blood pressure (BP), antihypertensive treatment, and clinical outcomes in acute stroke are complex. Hypertension has been associated with increased risk of poor outcomes and ICH in several studies. 7 – 9 In the Safe Implementation of Treatments in Stroke (SITS) registry, higher systolic BP (SBP) after lysis was independently associated with worse outcomes and an increased risk of ICH. 7 The association between SBP and sICH was linear, while the association between SBP and clinical outcome was U-shaped. In a post hoc analysis of the NINDS trial, antihypertensive therapy given before thrombolysis was not associated with differences in outcomes. However, patients with hypertension who received antihypertensives after randomization were less likely to have a favorable outcome at 3 months. 10
What is an arterial puncture?
Arterial puncture of a noncompressible vessel within 7 days preceding acute stroke symptoms is a warning on the Activase (alteplase, rtPA) insert and is a relative contraindication to administering IV rtPA according to AHA guidelines. 1 This scenario is extremely rare and would most likely occur in critically ill patients who had recent catheterization of the subclavian or internal jugular veins. Other situations in which noncompressible veins are accessed are during placement of pacing or defibrillation leads, dialysis catheters, pulmonary artery catheters, or transcatheter heart valve placements. A patient undergoing one of these procedures may be less functional and more ill than the general population in which IV rtPA has been studied, and the ratio of risks to potential benefits in this subgroup may be substantially different as well. The common clinical observation of increased bleeding in anticoagulated patients who have central venous catheters placed and the potential consequence of uncontrollable and life-threatening hemorrhage likely justify this exclusion criterion, although there is no existing data in the published literature to support or oppose this recommendation.
What is the determinant of stroke outcome?
Initial severity of deficits is the main determinant of stroke outcome regardless of whether thrombolysis is administered. Severe strokes (variably defined as NIHSS >20 or >25) are typically caused by large infarctions, which may have a higher risk of hemorrhagic transformation. This is reflected in the FDA package insert for Activase (alteplase, rtPA) warning that the risks of ICH are higher in patients with severe stroke. However, there is solid evidence that IV thrombolysis is beneficial to patients with severe strokes and in fact these patients may derive the greatest benefit from the treatment.
How long after MI should I be on IV thrombolysis?
Based on this, it has been suggested that the time after MI to be considered a contraindication for IV thrombolysis should be shortened to 7 weeks. 85 The type of MI, in addition to the severity of stroke symptoms, should also factor in the decision-making process. Patients with non-STEMI, particularly those that do not involve the anterior cardiac wall, may be at lower risk of this complication, but there are no solid data to estimate risks or guide treatment in this subset of patients.
What is the blood glucose level for IV RTPA?
Measurement of blood glucose is a necessary requisite before the administration of IV rtPA. The main reason for this condition is exclusion of severe hypoglycemia, which can infrequently mimic stroke symptoms. Even more rarely, severe hyperglycemia can also produce focal neurological deficits. Previous versions of the AHA guideline for acute stroke treatment listed glucose levels below 50 mg/dL (2.7 mmol/L) and above 400 mg/dL (22.2 mmol/L) as contraindications for thrombolysis, but the most recent edition only keeps hypoglycemia as an exclusion. 1 Meanwhile, the Food and Drug Adminitration (FDA) package insert for Activase (alteplase, rtPA) recommends “special diligence” in making the diagnosis of stroke in patients whose glucose levels are <50 or >400 mg/dL.
How many patients were in the third stroke trial?
The third international stroke trial (IST-3), an international randomized controlled trial included 1617 patients older than the age of 80 years. 57 Patients were randomized to rtPA or placebo within 6 hours of symptom onset. The primary end point was the proportion of patients alive and independent at 6 months, which was not significantly different between the 2 groups (37% of the rtPA group and 35% of the control group [ P = .181]). In a subgroup analysis, a significant difference existed in the adjusted effect of treatment between patients >80 years and those younger, suggesting a greater benefit in the very elderly patients. In addition, a systematic review analyzing 7012 patients from 12 trials showed that patients older than80 years of age benefited similar to those younger, especially when treatment was initiated early.
What is the risk of a TPA?
The principal risk of tPA is symptomatic or fatal hemorrhage. It is essential that patients be evaluated for any history or risk factors that would put them at an increased risk of a hemorrhagic outcome. Eligibility for tPA. Age ≥18. No.
Is tpa necessary for stroke patients?
tPA for patients with acute ischemic stroke is associated with a significant increase in symptomatic in tracranial hemorrhage, so it is essential to adhere to accepted protocols and to engage in shared decision making with the patient or their family when considering administering tPA. The evidence and strength of recommendations for giving tPA in ...
Can you give tpa to a stroke patient?
Because of the risk of hemorrhage is thought to outweigh any potential benefits, patients with any absolute contraindication should not be given tPA.
What is the best treatment for embolic stroke?
Anticoagulants are also used for prevention of embolic strokes but increase the risk for hemorrhage. Diuretics are not indicated for stroke prevention other than for their role in controlling BP, and antilipemic agents have bot been found to have a significant effect on stroke prevention.
What is the priority intervention in the emergency department for the patient with a stroke?
The priority intervention in the emergency department for the patient with a stroke is: Maintenance of respiratory function with a patent airway and oxygen administration- (the first priority in acute management of the patient with a stroke is preservation of life.
What is the purpose of endarterectomy?
Involves removing an atherosclerotic plaque in the carotid artery to prevent an impending stroke- (An endarterectomy is a removal of an atherosclerotic plaque, and plaque in the carotid artery may impair circulation enough to cause a stroke.
What is the highest risk factor for thrombotic stroke?
Tap card to see definition 👆. Individuals with hypertension and diabetes. The highest risk factors for thrombotic stroke are hypertension and diabetes. African Americans have a higher risk for stroke than do white persons but probably because they have a greater incidence of hypertension.
Why is a lumbar puncture not performed?
Lumbar punctures are not performed routinely because of the chance of increased intracranial pressure causing herniation.
Why is it important to maintain a patent airway for the patient?
Because the patient with a stroke may be unconscious or have a reduced gag reflex, it is most important to maintain a patent airway for the patient and provide oxygen if respiratory effort is impaired. IV fluid replacement, treatment with osmotic diuretics, and perhaps hypothermia may be used for further treatment.)
How often do nurses assess vital signs during stroke?
During the acute phase of a stroke, the nurse assesses the patient's vital signs and neurologic status every 4 hours. A cardiovascular sign that the nurse would see as the body attempts to increase cerebral blood flow is:
What is the best medication for ischemic stroke?
Doctors can remove clots for ischemic stroke with a medication called Alteplase IV r-tPA and mechanical treatments like a mechanical thrombectomy.
Why is it important to identify stroke and seek treatment immediately?
Many people don’t arrive at the hospital in time to receive the medication, which can save lives and reduce long-term effects of stroke. So it’s important to identify stroke and seek treatment immediately.
How do doctors remove a clot from the brain?
In this procedure, doctors use a wire-cage device called a stent retriever. They thread a catheter through an artery in the groin up to the blocked artery in the brain. The stent opens and grabs the clot. Special suction tubes may also remove the clot.
What is the best way to remove a clot?
Mechanical Treatment to Remove the Clot. An endovascular procedure or a mechanical thrombectomy is a strongly recommended option to remove a clot in eligible patients with a large vessel occlusion, or LVO. In this procedure, doctors use a wire-cage device called a stent retriever.
What is the final response of a carotid endarterectomy?
The answer beginning, "A catheter with a deflated balloon is positioned at the narrow area" describes an angioplasty. The final response beginning, "A wire is threaded through the artery" describes the MERCI procedure.
What side of the body does a stroke patient have?
A patient with a stroke experiences right-sided arm and leg paralysis and facial drooping on the right side. When admitting the patient, which clinical manifestation will the nurse expect to find?
What is aspirin ordered for?
Aspirin is ordered for a patient who is admitted with a possible stroke. Which information obtained during the admission assessment indicates that the nurse should consult with the health care provider before giving the aspirin?
Why is it important to maintain a patent airway for the patient?
Because the patient with a stroke may be unconscious or have a reduced gag reflex, it is most important to maintain a patent airway for the patient and provide oxygen if respiratory effort is impaired. IV fluid replacement, treatment with osmotic diuretics, and perhaps hypothermia may be used for further treatment.
Which side of the patient should the objects needed for activities of daily living be placed?
c. Place objects needed for activities of daily living on the patient's right side.
Does Plavix lower blood pressure?
The medication does not lower blood pressure, decrease plaque formation, or dissolve clots.
Can heparin be used after a stroke?
Continuous heparin infusion is not routinely used after TIA or with acute ischemic stroke. The patient's symptoms are not consistent with a cerebral aneurysm. tPA is used only for acute ischemic stroke, not for TIA.

Diagnosis
Treatment
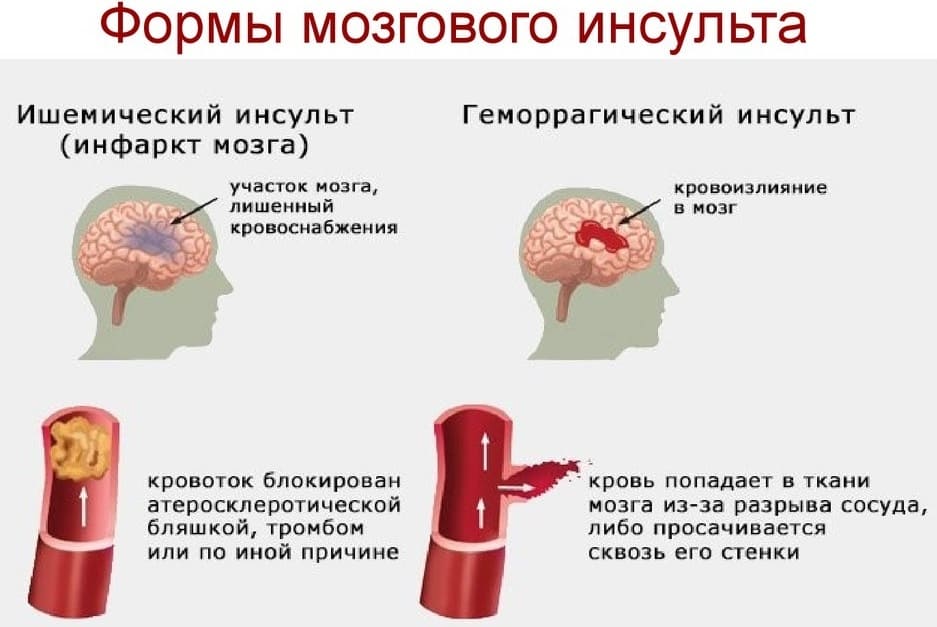
- Emergency treatment for stroke depends on whether you're having an ischemic stroke or a stroke that involves bleeding into the brain (hemorrhagic).
Treatment Outcomes
- One way to evaluate the care of patients diagnosed with stroke is to look at the percentage of patients receiving the timely and effective care measures that are appropriate. The goal is 100 percent. The graphs below display the percentage of eligible Mayo Clinic patients diagnosed with stroke receiving all of the appropriate care measures.
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Coping and Support
- A stroke is a life-changing event that can affect your emotional well-being as much as your physical function. You may sometimes feel helpless, frustrated, depressed and apathetic. You may also have mood changes and a lower sex drive. Maintaining your self-esteem, connections to others and interest in the world are essential parts of your recovery. Several strategies may help …
Preparing For Your Appointment
- A stroke in progress is usually diagnosed in a hospital. If you're having a stroke, your immediate care will focus on minimizing brain damage. If you haven't yet had a stroke but you're worried about your future risk, you can discuss your concerns with your doctor at your next scheduled appointment.