
Medication
Immunosuppressants used to treat vasculitis include: Cyclophosphamide Rituximab Methotrexate Azathioprine Mycophenolate mofetil Leflunomide Tocilizumab TNF inhibitors (infliximab, adalimumab, certilizomab or golimumab)
Procedures
Nov 01, 2019 · Type of vasculitis Treatment options (precautions and adverse effects) Large vessel vasculitis: GCA and TK: Steroids are the first line agent. EULAR guidelines suggest 1 month of high-dose glucocorticoid therapy (prednisolone 1 mg/kg/day, maximum …
Nutrition
Jul 08, 2017 · Treatments for vasculitis include medications like corticosteroids or immunosuppressants; an anti-inflammatory diet; rest; exercise; herbal remedies and supplements. Read Next: Cellulitis Symptoms, Causes & Risk Factors
What is the life expectancy of someone with vasculitis?
The precise treatment of vasculitis depends on the specific type of vasculitis and the areas/organs that are involved. Some measures that may be necessary include the use of corticosteroids, such as prednisone. For more serious types of vasculitis, other medications that suppress the immune system are also used.
What is the life expectancy of patients with vasculitis?
Compare risks and benefits of common medications used for Vasculitis. Find the most popular drugs, view ratings and user reviews. Compare risks and benefits of common medications used for Vasculitis. ... diagnosis or treatment. Data sources include IBM Watson Micromedex (updated 3 Mar 2022), Cerner Multum™ (updated 25 Mar 2022), ASHP (updated ...
Are corticosteroids used to treat vasculitis?
Mar 24, 2022 · Vasculitis, also known as angiitis or arteritis, includes a group of rare conditions that can take place when swelling affects the walls of your blood vessels. Swelling is your body’s response to tissue injury. Autoimmune disorders or diseases that make your body attack itself, infections, and trauma are some examples of potential causes of ...
How to get rid of vasculitis?
A drug called tocilizumab (Actemra) blocks an inflammatory protein in your body. You might be able to use a lower dose of steroids if you take it at the same time. If you have anti-neutrophil ...
What triggers vasculitis?
Possible triggers for this immune system reaction include: Infections, such as hepatitis B and hepatitis C. Blood cancers. Immune system diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus and scleroderma.Nov 24, 2020
Can vasculitis be completely cured?
Some types of vasculitis are acute (short-term), while others are chronic (long-term). There is currently no cure for vasculitis, but early diagnosis and treatment are critical for helping to ease symptoms and hinder the progression of the disease.
What is the latest treatment for vasculitis?
According to the release, avacopan (Tavneos, ChemoCentryx) is the first oral complement C5a receptor inhibitor to be approved by the FDA. The drug is approved for the treatment of microscopic polyangiitis and granulomatosis with polyangiitis, the two main forms of ANCA-associated vasculitis, in Japan.Oct 8, 2021
What is vasculitis and how is it treated?
Vasculitis, an inflammation of blood vessels, can affect vessels of all size. If blood flow is reduced or stopped, tissues can begin to die. Treatment, which may include medication, depends upon which vessels and organs are affected.Jul 17, 2019
Does vasculitis require hospitalization?
Inpatient care is needed in patients who have severe systemic vasculitic syndromes and severe organ dysfunction. Most patients with cutaneous leukocytoclastic vasculitis are treated in an outpatient setting.Dec 9, 2020
Is vasculitis a terminal illness?
Once considered a fatal disease, vasculitis is now effectively treated as a chronic condition. Five main drug therapies are helping patients better manage their symptoms.Apr 3, 2017
What does vasculitis pain feel like?
Nerves – inflammation of the nerves can cause tingling (pins and needles), pain and burning sensations or weakness in the arms and legs. Joints – vasculitis can cause joint pain or swelling. Muscles – inflammation here causes muscle aches, and eventually your muscles could become weak.
What is the most common vasculitis?
Giant Cell Arteritis This disease was previously named “temporal arteritis”, and is the most common type of vasculitis in adults in North America. It is a large vessel vasculitis that affects people over the age of 50 (although most individuals affected are 70-80 years of age).
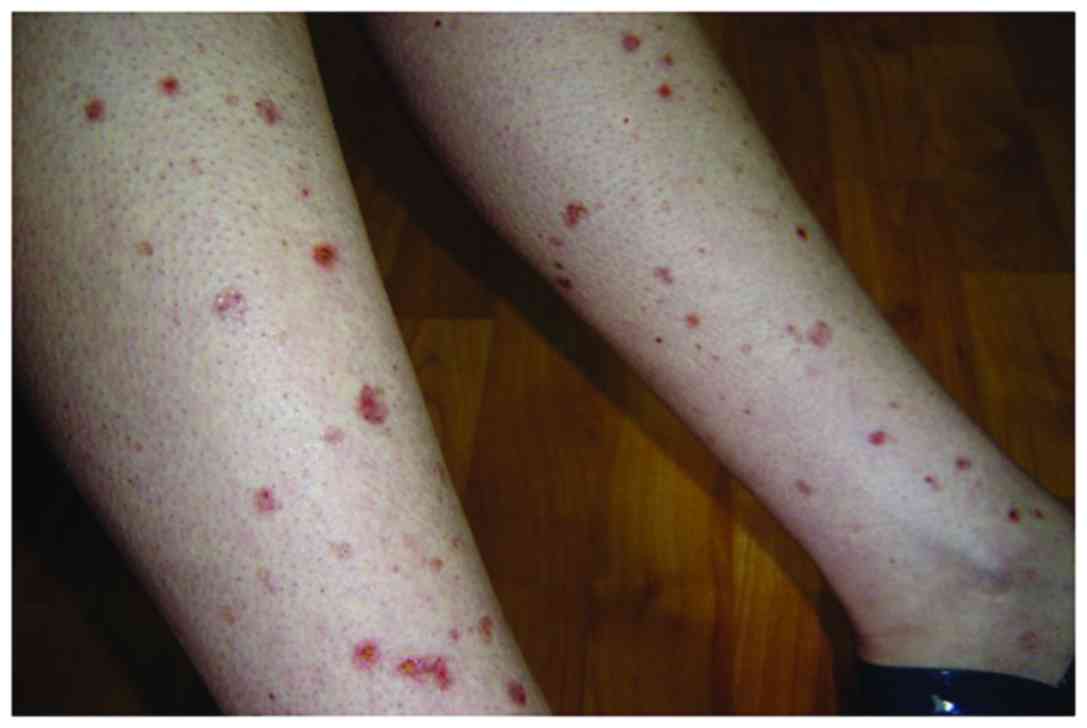
What does vasculitis of the legs look like?
Common vasculitis skin lesions are: red or purple dots (petechiae), usually most numerous on the legs. larger spots, about the size of the end of a finger (purpura), some of which look like large bruises. Less common vasculitis lesions are hives, an itchy lumpy rash and painful or tender lumps.
Does vasculitis show up in blood test?
Blood tests, X–rays, and other studies may suggest the diagnosis of vasculitis, but often the only way to clinch the diagnosis is to biopsy involved tissue, examine the tissue under the microscope in consultation with a pathologist (ideally one experienced at examining biopsies in vasculitis), and find the pathologic ...
What can mimic vasculitis?
Cholesterol emboli, thrombotic and hypercoagulable conditions and calciphylaxis are important mimics of medium and small vessel vasculitis. Neoplasms like cardiac myxomas can mimic vasculitis of any vessel size, while intravascular large cell lymphoma (ILCL) is an important mimic of primary angiitis of the CNS (PACNS).Nov 9, 2020
Medication
The key to lessening the symptoms of the many types of vasculitis is to reduce inflammation. Anti-inflammatory medications, notably glucocorticoids such as prednisone or methylprednisolone, are the most common first-line treatments.
Plasmapheresis (Plasma Exchange)
In some severe cases, a patient’s plasma, which contains harmful antibodies, may be exchanged for healthy plasma through a procedure similar to dialysis.
Surgery
When advanced forms of vasculitis cause significant damage to blood vessels, vascular bypass surgery may be performed to redirect the flow of blood around the damaged vessel. Surgery may also be required to repair or replace (via transplant) damaged or failed organs resulting from vasculitis.
Research at University of Michigan
While getting clinical care at Michigan Medicine Vasculitis Program you might have the opportunity to participate in research and contribute to advancing our understanding and options for treatment for these rare diseases.
What is the best treatment for vasculitis?
Treatment options vary among the different types of vasculitis. Doctors treat almost all types with a glucocorticoid medication , such as prednisone. For certain types of vasculitis, another medication in addition to prednisone is needed.
What is the best treatment for rheumatoid arthritis?
2. Rituximab (also called Rituxan) Doctors have used rituximab to treat rheumatoid arthritis patients , with good results. Since 2011, it has also been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of two forms of vasculitis – granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s) and microscopic.
What are the challenges of vasculitis?
What makes treating vasculitis a challenge? Here are a few reasons: 1 There are several different types of vasculitis. 2 Even within a specific disease, the features differ among patients. 3 Many organs and/or blood vessels are affected. 4 Some forms are mild, others severe. 5 It can be secondary to an underlying condition. 6 It can be a primary disease with an unknown cause.
How do you give glucocorticoids for vasculitis?
Treatment details: Glucocorticoids are used in almost all forms of vasculitis. They can be given by mouth or by vein.
How long does it take to get rituximab?
Treatment details : Rituximab is given by vein in an infusion center or hospital. The treatment time (infusion) takes four to six hours, or longer in some cases. The dose and frequency of rituximab will be determined by your doctor based on a number of different factors.
Is Vasculitis a complex disease?
Better drug therapies for a once fatal disease. Vasculitis is a complex illness. This spectrum of conditions involving blood vessel inflammation usually has unknown causes — and symptoms can be hard to pin down. The good news is that doctors are making strides in their understanding of these diseases with better drug therapies.
Can you take azathioprine if you don't make it?
People who do not make this enzyme cannot take azathioprine and people who make lower amounts will need to be treated cautiously with a smaller dose. In those who have a normal TPMT test, the dosage is usually based on your body weight. You may receive a single or twice-daily dose.
What percentage of the immune system is in the GALT?
Roughly 70 percent of your immune system is in your GALT. GALT means “gut-associated lymphoid tissue.” This is the reason why a healthy diet is so important for controlling inflammation and supplying your body with the fuel it needs. It’s recommended that people with vasculitis usually visit a dietitian, at least initially, to learn which types of specific dietary changes might be most helpful.
What is the name of the condition where blood vessels carry blood to tissues and organs?
Vasculitis (also called vasculitic disorder) is a condition characterized by inflammation of the blood vessels, the series of tubular structures that carry blood to tissues and organs throughout the body. Vasculitis symptoms usually include fatigue, symptoms of a fever like nausea and weakness.
What is the cause of vascular disease?
Vasculitis is caused by inflammation and autoimmune reactions that attack the body’s own blood vessels . Like with other autoimmune disorders, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or rheumatoid arthritis, the body mistakenly believes that a part of its own body (in this case the blood vessels) is foreign and therefore potentially a threat.
What is the name of the disease that affects the aorta and aortic valve?
This usually causes widespread symptoms that affect the whole body. Cogan’s syndrome — Describes the type of vasculitis that affects large blood vessels, especially the aorta and aortic valve (the main artery that carries blood away from your heart to the rest of your body).
Why is it so hard to diagnose vasculitis?
Because vasculitis symptoms are widespread and non-specific (they can be caused by many different health issues), it can be hard for patients to receive a proper diagnosis quickly. Each case of vasculitis is a bit different. Plus there are multiple types of vasculitis that cause different symptoms (more on this below).
What is the inflammatory disorder that affects the blood vessels?
Vasculitis is a group of inflammatory disorders that affect the blood vessels. Vasculitis can affect both small or large arteries. This includes major blood vessels like the aorta, as well as capillaries, medium-sized veins. Or it can include a combination of different sized blood vessels.
Why does vasculitis come back?
Symptoms may come back at a later time due to a variety triggers that affect the person’s immune system. For others, vasculitis is chronic (long-term) and won’t respond well to treatment. Most people are able to manage their symptoms well. But everyone reacts to treatment a bit differently.
What is the best treatment for vasculitis?
Some measures that may be necessary include the use of corticosteroids, such as prednisone. For more serious types of vasculitis, other medications that suppress the immune system are also used.
What is the diagnosis of vasculitis?
The diagnosis of vasculitis is based on a person's medical history, current symptoms, complete physical examination, and the results of specialized laboratory tests. A doctor can test for blood abnormalities, which can occur when vasculitis is present. These abnormalities include:
How do you know if you have vasculitis?
Common symptoms include: Additional symptoms can occur, depending on the area of the body affected by vasculitis. If a blood vessel in the skin with vasculitis is small, the vessel may break and produce tiny areas of bleeding in the tissue. These areas will appear as small red or purple dots on the skin.
What is the name of the reaction in the blood vessel walls?
In most cases of vasculitis, something causes an immune or "allergic" reaction in the blood vessel walls. Substances that cause allergic reactions are called antigens. Sometimes certain medicines or illnesses can act as antigens and start this process.
What is the term for inflammation of blood vessels?
Vasculitis, an inflammation of blood vessels, can affect vessels of all size. If blood flow is reduced or stopped, tissues can begin to die. Treatment, which may include medication, depends upon which vessels and organs are affected.
What does a high platelet count mean?
A high white blood cell count. A high platelet count. Signs of kidney or liver problems. Blood tests also can identify immune complexes or antibodies (ways the body fights off what it thinks is a threat) that can be associated with vasculitis.
Can vasculitis cause occlusion?
Vasculitis can also cause blood vessel narrowing to the point of closing off entirely (called an occlusion ). If blood flow in a vessel with vasculitis is reduced or stopped, the tissues that receive blood from that vessel become injured and begin to die.
What is the term for a condition that causes blood vessels to be weak?
Vasculitis is a general term for several conditions that cause inflammation in your blood vessels. It’s also called angiitis or arteritis. It can make your blood vessels weak, stretched, bigger, or narrower. They might close entirely. Vasculitis can affect people at any age.
What is the drug called that blocks inflammatory proteins?
A drug called tocilizumab (Actemra) blocks an inflammatory protein in your body. You might be able to use a lower dose of steroids if you take it at the same time. Vasculitis Prognosis. Your outlook will depend on several things, including the type of vasculitis you have and how quickly you were diagnosed.
What tests are needed for vasculitis?
You’ll need tests to look for inflammation or to rule out other conditions. These may include: Blood tests. Certain types of blood cells or antibodies can be signs of vasculitis. Urine tests. These check for kidney damage.
What happens if you don't get enough blood?
If your nerves aren’t getting enough blood, you could have numbness and weakness. Vasculitis in your brain may cause a stroke. You could have a heart attack if it affects your heart. Inflammation in the vessels supplying blood to your kidney can lead to kidney failure.
How to tell if you have vasculitis?
Certain types of blood cells or antibodies can be signs of vasculitis. Urine tests. These check for kidney damage. Imaging tests. X-rays, MRI scans, CT scans, PET scans, and ultrasounds show inflammation in your blood vessels and organs.
What happens when your blood vessel is weak?
When your blood vessel becomes weak, it might stretch and bulge (called an aneurysm ). It might also burst open, causing bleeding. This can be life-threatening but is very rare. When your blood vessel becomes inflamed and narrowed, it might partially or totally block the blood flow to that area of your body.
Does vasculitis go away on its own?
Treatment depends on what’s causing your vasculitis and which organs are affected. Vasculitis might go away on its own if it’s the result of an allergic reaction. But if crucial organs such as your lungs, brain, or kidneys are involved, you need treatment right away.

Treatment
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment
Specialist to consult
Symptoms Are Diverse
- Treatment focuses on controlling the inflammation and managing any underlying conditions that may be triggering the vasculitis.
Treatment Considerations
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Commonly Used Drugs
- One of your greatest challenges of living with vasculitis may be coping with side effects of your medication. The following suggestions may help: 1. Understand your condition.Learn everything you can about vasculitis and its treatment. Know the possible side effects of the drugs you take, and tell your doctor about any changes in your health. 2. Follow your treatment plan.Your treatm…
Stay in Touch with Your Doctor
- Make an appointment with your primary care doctor if you have signs or symptoms that worry you. If your doctor suspects that you have vasculitis, he or she may refer you to a joint and autoimmune disease specialist (rheumatologist) with experience in helping people with this condition. You may also benefit from a multidisciplinary approach. What specialists you see dep…