
What is the most common treatment for spinal stenosis?
The goals of surgery include relieving the pressure on your spinal cord or nerve roots by creating more space within the spinal canal. Surgery to decompress the area of stenosis is the most definitive way to try to resolve symptoms of spinal stenosis.
What are three treatments for spinal stenosis?
Along with routine exercise, spinal stenosis is also treated with over-the-counter and prescription medications — most commonly nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like Aspirin, Aleve and Ibuprofen — to help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
What is the newest treatment for spinal stenosis?
Interspinous spacers are a new approach to treating spinal stenosis that work gently and in a targeted way by opening the spinal canal to create room and reduce pressure on crowded nerves. A spinous process is the part of your vertebra that projects backward from your vertebral arch.
What does a neurosurgeon do for spinal stenosis?
Spinal stenosis treatment Most commonly, this is accomplished with a laminectomy, in which the roof of the spinal canal is removed to relieve the compression. Once symptomatic, cervical stenosis typically requires surgery to take the pressure off the spinal cord and restore the normal diameter of the spinal canal.
How do you fix spinal stenosis without surgery?
Nonsurgical Treatment Options for Spinal StenosisSteroid Injections. Epidural steroid injections are commonly used to provide long-term pain relief. ... DRX9000. ... Medication. ... Physical Therapy. ... Correcting Posture. ... Permanent Lifestyle Changes. ... Facet Blocks. ... Radiofrequency Ablation.
Is walking good for spinal stenosis?
Walking is a good exercise for spinal stenosis. It's low impact, and you control the pace and distance.
When is surgery needed for spinal stenosis?
Why might your doctor recommend surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis? Your doctor might recommend surgery if: Your pain and weakness are bad enough to get in the way of your normal activities and have become more than you can manage.
What happens if you let spinal stenosis go untreated?
Rarely, untreated severe spinal stenosis may progress and cause permanent: Numbness. Weakness. Balance problems.
What activities should be avoided with spinal stenosis?
What Is Spinal Stenosis?Avoid Excessive Back Extension. ... Avoid Long Walks or Running. ... Avoid Certain Stretches and Poses. ... Avoid Loading a Rounded Back. ... Avoid Too Much Bed Rest. ... Avoid Contact Sports.
What type of surgeon is best for spinal stenosis?
Mayo Clinic doctors trained in spine conditions (neurologists) and spine surgery (neurosurgeons and orthopedic surgeons) have experience in evaluating and treating people with all types of spinal stenosis.
Is it better to see a neurosurgeon or orthopedic surgeon?
While an orthopedic surgeon is a better choice if you need a new hip, knee, shoulder, or have a severely broken bone, anything related to the spine is best treated by a skilled neurosurgeon. If you have a back issue or severe back pain, seek out a neurosurgeon for their evaluation and diagnosis for proper treatment.
Does a neurologist treat spinal stenosis?
If you suffer from a spinal condition such as disc herniation or degeneration, spinal fractures, spinal stenosis, spondylolisthesis, or other types of spinal injuries or pain, both a neurologist and an orthopedic doctor are equipped to treat these spinal conditions.
Spinal Stenosis Fundamentals
With age, the spinal canal – located in the lower back – can narrow, resulting in spinal stenosis. The narrowing process, which is gradual, reduces...
What Causes Spinal Stenosis?
Spinal stenosis occurs when bulging discs, arthritic spurs, and thickened tissues combine to "compress" the nerves traveling through the spinal can...
What Are Treatment Options For Spinal Stenosis?
Medical Treatment 1. Taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for relief. 2. Receiving cortisone injections directly into the spinal c...
How Do I Prepare For Spinal Stenosis Surgery?
To prepare for spine surgery, quit smoking if you smoke, exercise on a regular basis to improve your recovery rate, stop taking any non-essential m...
What Happens After Spinal Surgery?
Pain may persist for a few days after surgery, requiring the use of pain medications and NSAIDs to reduce swelling. However, your doctor will likel...
How Long Is The Recovery Period After Surgery?
Full recovery after surgery for spinal stenosis typically takes three months and possibly longer for spinal fusion, depending partially on the pati...
What Is The Rehab After Spinal Stenosis Surgery?
After spine surgery, your doctor will likely prescribe walking and strengthening exercises for the lower back and abdomen to help stabilize the spine.
What Are The CCF Physician credentials?
1. All doctors at Cleveland Clinic Center for Spine Health are fellowship-trained and board-certified or board-eligible in orthopaedic surgery, med...
What Clinical Trials Are Being Conducted at CCF on Spinal Stenosis?
Researchers at Cleveland Clinic are involved in ongoing studies that investigate new drugs and treatment approaches for managing disease. Participa...
Are There Other Resources That I Can Go to For More Information on Spinal Stenosis?
Patients can go to the following resources for more information on this procedure: 1. Cleveland Clinic Health Information Center 2. American Academ...
What is the best treatment for lumbar spinal stenosis?
The following drugs are commonly used to treat lumbar spinal stenosis pain: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Medications such as ibuprofen and naproxen may be used to temporarily relieve stenosis pain.
What is the best medication for spinal stenosis?
Medications such as ibuprofen and naproxen may be used to temporarily relieve stenosis pain. These drugs are used with caution due to gastrointestinal side effects in the long-term. 3. Gabapentinoids. The antiepileptic medications gabapentin and pregabalin may help inhibit nerve pain caused by spinal stenosis. 2.
How to relieve lumbar spinal stenosis pain?
Injections help relieve lumbar spinal stenosis pain by achieving the following goals: Reduce spinal inflammation . Stop or inhibit the transmission of pain signals from the spine to the brain. Injections may be delivered in the epidural space (space surrounding the spinal cord) or directly on or around the target nerve.
How much pain does lumbar stenosis relieve?
Research indicates that 60% to 90% of patients experience relief of symptoms after nonsurgical or surgical treatment for lumbar spinal stenosis. 1 Treatment usually relieves leg pain more than back pain. Back pain may continue to persist even after treatment if pre-existing degenerative arthritis is present. 1
How to help stenosis pain?
Physical therapy and exercise help relieve spinal stenosis pain in the following ways: Provides symptom relief. Restores function of the lumbar spine and the sacroiliac joint. Improves mobility of the lower body. Fosters a better healing environment in the lower back. Prevents pain recurrence and flareup.
How to treat lumbar stenosis?
Treatment of stenosis in the lumbar spine depends on the specific cause. While stenosis caused by a herniated disc may be treated with physical therapy and exercise , large overgrown bony protrusions from the facets may require surgical trimming.
How to reduce stress on spinal cord?
Walking with support by leaning forward on a cane, walker, or shopping cart. Avoiding extended periods of standing. Placing one foot over a step stool if standing for a long time, such as while doing dishes or cooking. Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce stresses on the spinal and pelvic joints.
What is the best medicine for spinal stenosis?
Oral medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) – such as ibuprofen (Advil®, Motrin®), naproxen (Aleve®), aspirin – or acetaminophen (Tylenol®) can help relieve inflammation and provide pain relief from spinal stenosis. Be sure to talk with your healthcare provider and learn about possible long-term problems of taking these medicines, such as acid reflux and stomach ulcers. Your healthcare provider may also recommend other prescription medications with pain-relieving properties, such as the anti-seizure drug gabapentin (Neurontin®) or tricyclic antidepressants such as amitriptyline (Elavil®). Opioids, such as oxycodone (Oxycontin®) or hydrocodone (Vicodin®), may be prescribed for short-term pain relief. However, they are usually prescribed with caution since they can become habit forming. Muscle relaxants such as cyclobenzaprine (Amrix®, Fexmid®) can treat muscle camps and spasms.
What is the procedure for lumbar spinal stenosis?
The procedure involves removing bone or tissue this area to provide more space for the nerve roots. Interspinous process spaces: This is a minimally invasive surgery for some people with lumbar spinal stenosis.
What is spinal fusion?
Spinal fusion: This procedure is considered if you have radiating nerve pain from spinal stenosis, your spine is not stable and you have not been helped with other methods. Spinal fusion surgery permanently joins (fuses) two vertebrae together.
What causes low back pain and sciatica?
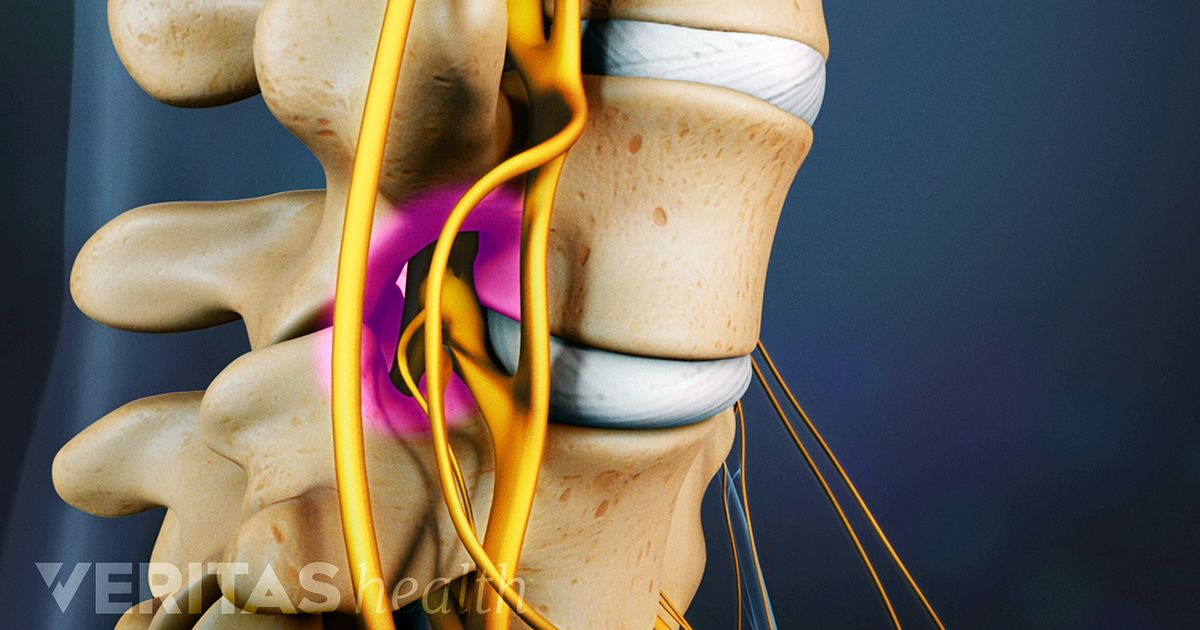
Spinal stenosis has many causes. What they share in common is that they change the structure of the spine, causing a narrowing of the space around your spinal cord and nerves roots that exit through the spine. The spinal cord and/or nerve roots become compressed or pinched, which causes symptoms, such as low back pain and sciatica.
What does it feel like to have stenosis in your back?
Depending on where and how severe your spinal stenosis is, you might feel pain, numbing, tingling and/or weakness in your neck, back, arms, legs, hands or feet. Normal spine with no narrowing of the space around the spinal cord or nerve roots exiting the spinal column. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
How do you know if you have spinal stenosis?
First, spinal stenosis develops slowly over time, so you may not have symptoms even though changes are occurring in your spine. Your first noticeable symptoms may be pain, numbness, tingling or weakness in your back or neck or arms and legs depending on the location of the stenosis.
What are the symptoms of lumbar canal stenosis?
Symptoms of lumbar canal stenosis include pain, numbness or weakness in the legs, groin, hips, buttocks, and lower back. Symptoms usually worsen when walking or standing and might decrease when lying down, sitting, or leaning slightly forward. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
How to get rid of stenosis in the spine?
Spinal stenosis exercises. Exercise, along with good eating habits, can help you slim down if you’re overweight. This will ease the strain on your spine. Even if you do decide to have surgery, exercising afterward can boost your recovery. But you’ll need to start slowly.
What is spinal stenosis?
What Are the Treatments for Spinal Stenosis? Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the canal in your spinal column that affects mostly people age 50 and older. Nothing can cure it, but there are things you can do on your own, under your doctor's guidance, to enjoy an active life.
How long does it take to recover from spinal fusion?
Recovery can be a few days or up to 3 months. Surgery helps many people but there are also risks, such as blood clots.
What to do if your spine doesn't work?
Surgery for Spinal Stenosis. If these treatments don't work, your doctor may suggest surgery, especially if: You're in a lot of pain. You have trouble walking. You can't control your bladder. In fact, your doctor may recommend surgery first if you have severe symptoms.
What is the procedure to remove a bulging disc?
Discectomy. With this procedure, the injured part of a bulging, or herniated, disc is taken out to ease pressure on your nerves or spinal cord. It can be done through a cut in your spine or neck that lets your doctor get to it directly or with smaller cuts and tiny instruments. Spinal fusion.
What are some exercises to help with pain?
Boost your fitness: Aerobic exercises, ones that get your heart and breathing rates up, release chemicals called endorphins that can ease pain. Examples of aerobic exercise include bicycling or swimming. There's no one right way to exercise with this condition -- and you don’t want to overdo it.
Is laminectomy a cure?
Like other treatments, surgery is not a cure, but it can help with pain and function. Your doctor may talk to you about these types: Laminectomy. This is the most common one. A doctor takes out the bone, spurs, and ligaments that are putting pressure on the nerves.
What is the best treatment for spinal stenosis?
Physical therapy is another way to re-learn how to use your body in support of good health. And it just so happens to be one of the best treatments for spinal stenosis — one study in 2015 found that physical therapy had better outcomes than surgery when treating spinal stenosis.
What is the procedure called for spinal stenosis?
Vertiflex procedure for spinal stenosis. The Vertiflex procedure for spinal stenosis (also called the Superion® implant) is a new way to increase the space between the vertebrae — space that may collapse as spinal stenosis progresses.
How long does a massage help with spinal stenosis?
One study found that weekly massage over a ten-week period provided pain relief for up to six months.
What is spinal stenosis?
Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the spine that occurs most often in the lower back ( but can also occur in the cervical spine). This narrowing eventually begins to crowd the spinal cord and nerves in the spinal column. When this happens, radiating pain and mobility issues can quickly follow.
What is the term for a swollen arm and a tingling sensation in the lower back?
Radiating pain (called sciatica when it occurs in the lower back) Numbness or tingling in the arms, hands, legs, or feet. Weakness in the extremities. Neck pain (in cervical spinal stenosis) Clumsiness in the arms and hands (in cervical spinal stenosis)
How many people have spinal stenosis?
Spinal stenosis is a pain condition that affects an estimated 500,000 people in the U.S. While some cases are mild and have little impact on daily life, other people experience debilitating pain and limited mobility. If you or someone you love is suffering, these are some of the best treatments for spinal stenosis.
How to help stenosis?
Stretches. Targeted spinal stenosis exercises can help lengthen the spine and relieve pressure on your nerves. Flexion exercises in particular decreased pain and lowered the risk of disability in people with spinal stenosis. Core stability stretches and exercises also resulted in an increase in walking capacity.
How to manage lumbar spinal stenosis?
The best way to manage lumbar spinal stenosis is to learn as much as you can about your disease, work closely with your medical team, and take an active role in your treatment.
What is the treatment for a swollen lower back?
Medicines may include nonsteroidal, anti-inflammatory medicines that relieve pain and swelling, and steroid injections that reduce swelling. Surgical treatments include removing bone spurs and widening the space between vertebrae. The lower back may also be stabilized by fusing together some of the vertebrae.
What is the name of the area of the spine that connects the upper and lower back?
Stenosis, which means narrowing, can cause pressure on your spinal cord or the nerves that go from your spinal cord to your muscles. Spinal stenosis can happen in any part of your spine but is most common in the lower back. This part of your spine is called your lumbar area. Five lumbar vertebrae connect your upper spine to your pelvis.
How many vertebrae are there in the lumbar spine?
Five lumbar vertebrae connect your upper spine to your pelvis. If you have lumbar spinal stenosis, you may have trouble walking distances or find that you need to lean forward to relieve pressure on your lower back. You may also have pain or numbness in your legs.
What is the spinal cord?
Your spinal cord is a bundle of nerves that runs through a tunnel formed by your vertebrae. The tunnel is called the spinal canal. Lumbar spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the spinal canal in the lower part of your back. Stenosis, which means narrowing, can cause pressure on your spinal cord or the nerves that go from your spinal cord ...
What are the signs of spinal stenosis?
During the physical exam your healthcare provider will look for signs of spinal stenosis, such as loss of sensation, weakness, and abnormal reflexes. These tests help make a diagnosis: X-rays of your lumbar spine. These may show bone growths called spurs that push on spinal nerves and/or narrowing of the spinal canal.
What is the best way to see the spinal canal?
Imaging tests. A CT scan or MRI scan can give a more detailed look at the spinal canal and nerve structures. Other studies. Your healthcare provider might order a bone scan, myelogram (a CT taken after injecting dye), and EMG (an electrical test of muscle activity).
Spinal Stenosis Treatment: Why Choose Johns Hopkins
Our spine specialists treat a variety of spinal stenosis conditions, including cervical, lumbar and thoracic spinal stenosis and multilevel spinal stenosis.
Surgical Options
If nonsurgical treatments don’t provide sufficient relief, surgery may be necessary to remove tissues that are pressing on the spinal cord or nerve roots. These tissues may include all or parts of intervertebral discs, vertebrae, facet joints or hardened ligaments.
What is the best treatment for spinal cord injury?
Drugs: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) drugs are used in treating spinal cord injuries. The quicker these drugs are initiated after injury, the better the result for the patient by reducing inflammation around the spinal cord.
Where are the L1-L5 vertebrae located?
These sections are labelled as the L1-L5 vertebrae. These vertebrae are located near the base of the spine and naturally form a slight outward curve in the back, just below the inward curve of the thoracic spine. The lumbar vertebrae function to contain and protect the end of the spinal cord, as well as support the weight of the torso.
What vertebrae are affected by numbness?
Injuries below this level (at the L3 , L4, and L5 vertebrae) affect the hips and legs and may cause numbness extending to the feet (sciatica). It may also harm the tip of the spinal cord known as the cauda equina, which is a bundle of spinal nerves and nerve roots that innervate the lower lumbar spine to the sacrum.
How many sections of the spinal cord are there?
How many vertebrae are in the spine? Well, for the lumbar spinal column, there are five sections.
What is the lumbar spinal cord?
These lumbar vertebrae (or lumbar bones) contain spinal cord tissue and nerves which control communication between the brain and the legs. Damage to the lumbar spinal cord subsequently affects the hips and groin area, and may impact the lower abdominal muscles and thigh flexion as well. Lumbar spinal cord injuries (SCIs) may be complete ...
Why are the lumbar vertebrae different from the upper segments of the spine?
It is also important to understand that the lumbar vertebrae are much different than the upper segments of the spine because the spinal cord does not extend the entire length of the lumbar spine. L2 is the lowest vertebral segment that contains spinal cord tissue. After that point, nerve roots exit each of the remaining lumbar levels beyond ...
What are the symptoms of L1 injury?
Injuries to the L1 spine can affect hip flexion, cause paraplegia, loss of bowel/bladder control, and/or numbness in the legs.
What is the treatment for L5-S1 pain?
Radiofrequency ablation. Radiofrequency ablation may be used to treat pain stemming from the L5-S1 facet joints. A part of the pain-transmitting nerve is heated with a radiofrequency needle to create a heat lesion. This resulting lesion prevents the nerve from sending pain signals to the brain.
What is the best treatment for L5-S1?
For more severe pain, prescription medication, such as opioids, tramadol, and/or corticosteroids may be used. Physical therapy. Specific exercises and physical therapies can be designed to target pain stemming from L5-S1.
Why is the lamina removed?
Laminectomy: A part or all of the lamina (area of bone at the back of the vertebra) is removed in order to provide more room for the cauda equina.
What is the best treatment for herniated discs?
These injections are more effective in treating the inflammatory causes of pain, such as pain from herniated disc fragments, and are typically less effective for compressive causes of pain. Radiofrequency ablation. Radiofrequency ablation may be used to treat pain stemming from the L5-S1 facet joints.
Why aren't spine surgeons good candidates?
They may also not be good candidates for surgery due to other medical problems or drug addiction, to name a few. A small risk of serious complications, such as infection, nerve injury, excessive bleeding, or severe allergic reactions are possible with spine surgeries.
When is surgery recommended for neurological deficits?
Surgery is considered when a structural condition that is known to be responsive to surgical treatment is present.
How to treat sciatica pain?
Self-care. Mild to moderate pain may be treated with heat and ice at home. For sciatica pain, it is advised to stay active and continue daily activities as tolerated. While bed rest may provide temporary relief from symptoms, it usually does not aid in faster or long-term recovery for sciatica.
Physical Therapy
Activity Modification and Self-Care
- Sit or lie down until the feeling of dizziness reduces
- Drink water, or a cold drink
- Get plenty of rest
- Avoid caffeine, tobacco, and alcohol
- Recurrences
- Accompanied hearing loss or ringing sound in the ear
- Vision problems
See a doctor immediately if you notice:
- Chest pain
- Changes in speech
- Vomiting
- Numbness or weakness
- Shortness of breath
- High fever
- Severe headache
Medications
Injection Treatments
Complementary and Alternative Treatments